When the bone behind the ear really hurts , most of us are in no hurry to go to the doctor, but try to help ourselves at home. But a timely visit to a specialist and competently prescribed treatment could significantly improve the situation and hasten the onset of recovery.
The danger of pain in the bone behind the ear is that it can be caused by a number of unfavorable factors. And the treatment of all these diseases may differ significantly. Therefore, it is so important to promptly seek help from a professional and find out the cause of the disease.
Attempts at self-treatment may be unsuccessful. A person may begin to treat one disease, while in fact the cause of ear pain lies in something completely different. As a result, this leads to the loss of precious time and the development of all kinds of complications.
Why does it shoot behind the ear?
A lumbago behind the ear may mean inflammation of the mastoid process.
A lumbago in the head behind the ear on the right, on the left is a sharp impulse in the head, an unreasonable pain. Shooting cranialgia is not an independent disease, but a symptom of various pathological conditions.
If there is a shooting behind the ear in the head, additional symptoms rarely occur. During severe attacks, patients may complain of nausea and vomiting, and dizziness. Body temperature often rises, numbness in the extremities bothers you, and your vision becomes dark.
With lumbago, the pain affects one side of the head and radiates to the ear, jaw, and neck. Attacks last several seconds or minutes, less often – 1-2 hours, and can occur 5-10 times a day.
Causes of lumbago in the head:
- Diseases of the ENT organs. With otitis media, sinusitis, and sinusitis, a twitching pain occurs near the inflamed organ and radiates to the head.
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Unpleasant sensations in the head and ear area occur due to compression of nerve fibers. Twitching in the head with intervertebral hernia, osteochondrosis, arthritis of the joints of the lower jaw, osteomyelitis.
- Trigeminal neuralgia. Severe lumbago occurs on one side of the face. With neuritis of the facial nerve, pain behind the ear is one of the first signs of the disease. After 2 days, paralysis of the facial muscles on one side occurs.
- Dysfunction of the autonomic ganglia in diseases of the brain, nervous system, bone structures of the head and jaw. Shoots in the head behind the ear with inflammation of the jaw joints, vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Often discomfort occurs due to lack of sleep, overwork, and during PMS. Shooting sensations occur with alcohol and toxic intoxication.
- Pain may indicate the presence of tumors and cysts, cerebral aneurysms.
- Ophthalmological diseases. In case of eye diseases, pulsation occurs in the frontal region, which gradually moves to other parts of the head.
- Traumatic brain injuries. Such pathologies require emergency medical care.
Sometimes headaches are a consequence of damage to peripheral nerve endings. Shooting occurs with fractures, gangrene, concussion, and inflammatory processes in internal organs.
Causes of headaches behind the ears
A headache in the ear area is a symptom of various pathologies that can cause significant harm to health. Doctors advise paying attention to the first symptoms, as diseases can progress. Painful sensations behind the ears can be accompanied by fever, hearing loss and other complaints - they must be taken into account during diagnosis.
Diseases of the hearing organ
The main reason why a headache behind the ear on the left or right is due to diseases of the hearing organ. Discomfort can be caused by inflammatory processes or damage in any of its parts. The hearing organ is divided into the outer, middle and inner ear. The outer part is represented by the auricle, ear canal and eardrum. The main function of the middle ear is to equalize pressure in the outer and inner sections. The inner ear has the most complex structure and is called the labyrinth. It is he who recognizes sound vibrations and transmits them to the cerebral cortex.
Chronic or throbbing pain in the head behind the ear may be the first sign of the following diseases:
- Otitis is an inflammation of the outer, middle or inner ear. The disease is accompanied by acute pain and discomfort. An advanced process can be complicated by purulent inflammation, in which case discharge from the ear canal appears.
- Labyrinthitis is a dangerous disease, inflammation of the labyrinth of the inner ear. The process is often one-sided, manifesting itself on the left or right side. Complaints include not only headaches, but also nausea and loss of coordination. The labyrinth is responsible not only for the perception of sounds, but also for balance.
- Meniere's disease is a pathology of non-infectious origin. Its main symptom is an increase in the volume of endolymph, the fluid in the inner ear. It is manifested by chronic unilateral pain behind the ear, nausea, and decreased hearing acuity.
- Mastoiditis is an inflammatory process that affects the process of the temporal bone. It can be caused by injury, viral or bacterial infection. It is accompanied by elevated temperature, a sharp deterioration in health, and purulent discharge from the auditory canals. The disease is more often diagnosed in children than in adults.
- Fungal diseases (otomycosis) - cause inflammatory reactions, itching and irritation. The infection most often affects the external parts of the hearing organ. In the initial stages, the fungus is not dangerous, but without treatment it can become complicated by purulent processes.
Head pain in the ear area is a dangerous phenomenon, since it may indicate various diseases of the hearing organ. Pathological processes without timely treatment spread to the internal parts. Air deficiency and the presence of endolymph provide a favorable environment for the development of bacterial infection. Its development is dangerous due to purulent inflammation, which can cause damage to the membranes of the brain and deterioration of hearing until it is completely lost.
Infectious diseases
Seasonal colds, acute respiratory viral infections and influenza are common diseases that affect adults and children. They are caused by a viral infection and are transmitted through airborne droplets and household routes. They can be recognized by their characteristic features:
- headaches behind the ears, as well as in the forehead and back of the head;
- increase in body temperature to 37 degrees or more;
- nasal congestion, swelling of the mucous membranes;
- cough, sore throat, redness and soreness;
- general weakness, drowsiness, decreased performance.
With viral diseases, the temperature rises already in the first days after the infection becomes active. This sign, combined with pain in the head near the ear, indicates the need to stay in bed, drink plenty of fluids and take supportive medications. However, if your health suddenly deteriorates, self-medication will be harmful. Even a common cold can be complicated by pneumonia or spread to the membranes of the brain if the immune system is weakened and cannot cope with the infection.
Other reasons
If your head hurts behind your ears, this may indicate various disorders. This symptom accompanies various infectious and non-communicable diseases that occur in acute or chronic forms. As a result of the diagnosis, pathologies may be detected that require urgent treatment.
- Migraine is a chronic disease that manifests itself as a one-sided headache, but can affect the entire surface of the head. Its exacerbation can be caused by hormonal changes, changes in atmospheric pressure, stress and other reasons. Migraine is often diagnosed in middle-aged women.
- Lymphadenitis is inflammation of the lymph nodes. In the ear area there are auricular, occipital and cervical lymph nodes. They can become inflamed due to previous infectious diseases, as well as with pathologies of the immune system. Superficial nodes are felt under the skin in the form of round, painful, dense formations. In an acute process, redness of the skin over the affected area and an increase in general body temperature may be observed.
- Shingles is a fungal disease that is transmitted by contact. Its pathogen can also be found on towels, bedding and other household items that come into contact with the skin. It causes pain, inflammation, severe itching, redness and peeling of the skin in the neck, back of the head and ears. The disease causes acute headaches, lumbago in the muscles and a general deterioration in well-being.
- Neuralgia is pain associated with inflammation or damage to the nerves. Headaches behind the ear are associated with the trigeminal nerve, which carries branches to the skin of the face and scalp. The causes of neuritis are hypothermia, previous viral diseases, injuries to the cervical spine and other factors.
- Arthritis or arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint is a pathology that causes unilateral acute pain behind the ear. It intensifies during chewing, talking and any jaw movements. Diseases can be caused by injuries, dental problems, and infectious agents.
- Neoplasms inside the auricle are a surgical pathology. During diagnosis, boils, tumors and other formations may be detected that cause pain and itching and cause hearing impairment. Their timely removal will restore normal health and prevent complications.
- Dental diseases are one of the common causes of ear pain. Caries, incorrect position of teeth and other pathologies can cause destruction of surrounding tissues and acute pain.
A headache that affects the area behind the ears can occur even in the absence of serious problems. It occurs when you are very tired, after intense physical activity, or due to stress. In some cases, symptoms disappear after proper rest, restoration of sleep patterns, and also as a result of proper nutrition. However, if the headache occurs frequently, it is important to seek medical help.
What does the localization of lumbago in the head indicate?
Pain can occur due to inflammation in the muscles of the neck and back of the head.
If it shoots on one side, this indicates problems in the organs on the left or right side. Discomfort occurs when the ear, eye socket, or limbs become inflamed. Unpleasant sensations are disturbing if there is a tumor or an aneurysm, if the neck is blown.
Jerking pain in the occipital region indicates diseases of the cervical spine. With osteochondrosis and hernia, dizziness, tinnitus, weakness, and fatigue are additional concerns.
Shooting pain that radiates to the ear area occurs due to problems with the cervical spine, inflammation of the oropharynx, and hearing organs. Pain in the frontal area is a consequence of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, runny nose, and sinusitis.
If it shoots in the crown area, this indicates problems with the spine. Jerking pain in the temples occurs when the temporal artery is damaged, inflammation of the temporomandibular joint, or trigeminal neuralgia.
What are the possible reasons
The anatomical location of the hearing organ and the adjacent lymph nodes, as well as its proximity to the brain, contributes to the rapid spread of the inflammatory process and increases the risk of complications.
Pain in the area of the bone behind the ear can be of various types. Unpleasant sensations can appear on one side or on both sides at the same time.
The most common causes of pain in the bone behind the ear are:
- Inflammation in the ear - otitis media. It can be external, middle and internal.
- The inflammatory process of the parotid lymph nodes is lymphadenitis.
- Mumps is a type of airborne infection.
- Development of cerumen plug in the ear canal.
- Inflammation of the paranasal sinus located in the temporal bone - acute or chronic mastoiditis.
In addition to inflammatory diseases, pain in the bone behind the ear may be caused by exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis or trigeminal neuralgia.
What to do with shooting cranialgia
Using an ultrasound sensor, it is possible to find the problem of pain behind the ear.
Shooting pain cannot be ignored, since cranialgia appears in serious illnesses. First you need to see a therapist, the doctor will determine the frequency, location and duration of the attacks. After examination and initial diagnosis, he will write out a referral to an ophthalmologist, ENT specialist, neurologist, surgeon or vertebrologist.
Diagnostic methods:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- CT, MRI of the head, cervical spine;
- X-ray;
- dopplerography;
- electroneuromyography;
- ECG.
Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor will draw up a treatment regimen.
Diagnostics
Consultation with an otolaryngologist is necessary first of all to exclude ear, nose and throat diseases. If necessary, the doctor will refer the patient to specialists.
At your appointment, the ENT doctor will conduct a survey and examine the lump. To collect anamnesis, the doctor will check whether there is pain when pressing, whether there have been infectious diseases. In addition, he will take into account whether the bump behind the ear is soft or hard, whether it is pedunculated or tightly adjacent.
Next, the doctor will order a blood test to diagnose inflammation. To determine the cause of the tumor, an ultrasound or x-ray is performed.
Effective treatments
Mastoiditis is treated with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
If you have a shooting pain in the head, self-medication is dangerous. Painkillers only relieve discomfort, but do not eliminate the cause of its occurrence. Only a doctor can prescribe medications and select a safe dosage.
To treat lumbago in the head, the following drugs are used:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics;
- muscle relaxants, antispasmodics;
- corticosteroids;
- broad-spectrum antibiotics;
- chondroprotectors, pain-relieving ointments;
- nootropics, neuroprotectors, means for normalizing cerebral circulation;
- B vitamins;
- antiepileptic drugs;
- tranquilizers.
For severe diseases, drugs are prescribed by injection. Mild forms can be treated at home.
After the acute attack has stopped, physiotherapy is prescribed. For shooting headaches, applications with ozokerite or paraffin, UHF, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, and galvanic current help.
Treatment for headaches behind the ear
The course of treatment includes various techniques that will eliminate the cause of the headache and all manifestations of the disease. A regimen can only be selected after examination and a final diagnosis; taking medications at home is not recommended. The following treatments may be needed:
- symptomatic drug therapy - includes painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins, remedies against cold and flu symptoms;
- antibacterial therapy - antibiotics are prescribed for bacterial diseases, as well as to prevent complications of viral infections;
- dental treatment – necessary for caries, diseases of teeth and gums;
- surgical intervention is prescribed to remove tumors in the ear canals, as well as when conservative treatment of mastoiditis is insufficiently effective.
At the Clinical Brain Institute, doctors will select the most effective treatment regimen. In most cases, taking medications as scheduled is sufficient, but additional procedures or surgery may also be required. The patient should listen to the opinion of specialists with many years of experience and strictly follow all recommendations.
How effective are folk remedies?
A warming compress can be used if there is no purulent inflammation.
For cranialgia, non-traditional methods should be used only in combination with medications. Folk remedies relieve pain, inflammation, and speed up the healing process.
You can get rid of shooting pain in the head at home in the following ways:
- Massage the crown, occipital region, and cervical region. You can use Zvezdochka balm, pain-relieving ointments, essential oils of mint, lavender, eucalyptus or juniper.
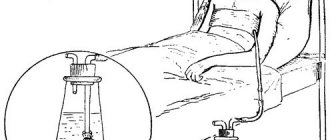
- Dry heat - make compresses with heated salt. Warming procedures are contraindicated at elevated temperatures and purulent processes.
- Prepare a solution of 3 parts Novocaine and 1 part Dimexide. Use for compresses.
Before using folk remedies, you should consult your doctor.
Prevention methods
Doctors have a number of recommendations that will help prevent headaches behind the ears. They are easy to follow at home:
- observe a regime of rest and physical activity, regularly carry out moderate exercise;
- pay attention to proper brushing of teeth and oral hygiene;
- observe bed rest in case of viral diseases, avoid contact with other people;
- carry out ear hygiene, while cleaning the ears carefully so as not to damage the eardrum;
- avoid hypothermia in the neck and head;
- Seek medical help promptly if headaches occur regularly or occur with high intensity.
The Clinical Brain Institute specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases that manifest themselves as headaches in the ear area. Here you can undergo a full examination and get advice from specialists of a narrow and broad profile. For long-term treatment, a course of procedures and round-the-clock supervision by doctors, it is possible to stay in a hospital. During outpatient treatment, it is important to follow all recommendations and promptly contact for re-examination.
How to avoid shooting pain in the head
The basis of a healthy immune system is proper nutrition.
To prevent the development of cranialgia, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system and lead a healthy and active lifestyle.
Prevention methods:
- follow a daily routine, get enough sleep;
- exercise regularly;
- when working sedentarily, do gymnastics for the eyes and neck every 2 hours;
- take vitamin complexes twice a year;
- avoid hypothermia, stress, overwork;
- follow safety rules when engaging in extreme sports.
Shooting pain in the head or behind the ear is a reason to visit a therapist or neurologist. Timely diagnosis and proper treatment will help avoid the development of complications and dangerous consequences of diseases.
Inflammatory process in the ear
Most often, the bone behind the ear hurts when an inflammatory process such as otitis media develops. Children are most often affected by the disease. In addition to pain, general body temperature may increase and tinnitus may occur. A characteristic sign of such a disease may be a sharp increase in pain in response to pressure on the tragus of the ear. Often this complication is observed in a child after suffering from a runny nose or sore throat.
If the disease is severely advanced, serous or purulent discharge may flow from the ear.
If the inflammation is not acute - the pain in the ear is moderate and the body temperature does not rise - you can try to help yourself at home. For this purpose, a dry warming compress is applied to the ear area; the affected area must be kept warm at all times.
In the event that inflammation is at the very initial stage, usually such simple home measures are enough to stop the developing pathological process.
However, if the pain does not go away for more than two days and the body temperature rises, the neck and head begin to hurt, and liquid discharge appears from the ear canal, you should immediately consult a specialist. Under no circumstances should you try to take antibacterial drugs on your own. If purulent discharge flows from the ear, this is a direct contraindication to any thermal procedures. In addition to treating the ear, it is also necessary to treat the cause of otitis media - a sore throat or a viral infection.
Other inflammatory processes
Pain in the bone behind the ear can be caused by inflammation of the mastoid process of the temporal bone and the paranasal sinus, which is localized in the same bone - mastoiditis. This inflammation may be the result of previous otitis media.
A characteristic symptom of mastoiditis is severe pain in the bone located behind the ear. The patient may feel discomfort on one side or both. The pain is accompanied by high body temperature and signs of general intoxication - headache, malaise, aching joints. Purulent contents may leak from the ear canal. On palpation, the bone is perceived as softened.
An equally common inflammatory process that causes such pain is damage to the salivary gland - sialadenitis. The disease can occur as a result of non-compliance with the rules of oral hygiene or in the presence of a chronic source of infection - sore throat or caries. The process can also be one- or two-way. As a rule, symptoms of general intoxication do not develop with sialadenitis. Pain and slight swelling appear behind the ear. In the future, pain in the jaws may occur when talking or chewing.
Neurological diseases
Quite often, pain behind the ear can be caused by inflammatory-dystrophic changes in the cervical spine - cervical osteochondrosis. In this case, thinning of the intervertebral disc and pinching of soft tissues between the vertebral bodies are observed.
Pain behind the ear with osteochondrosis may be accompanied by a feeling of muscle stiffness and a strong crunch in the neck. Clinical signs of cervical osteochondrosis are very often mistaken for symptoms of a number of other diseases.
For diagnostic purposes, X-rays and computed tomography of the cervical spine are performed. Treatment is prescribed by a neurologist.
The bone behind the ear can also become sore with trigeminal neuralgia. In this case, severe excruciating pain affects only one side of the face and neck. In this case, the patient is prescribed anticonvulsants, as well as B vitamins.