Risk factors for stroke in older people
This disease affects people of all ages, but the most common stroke is in an old person. Doctors believe that the likelihood of pathology increases in those who have reached 60 years of age and doubles with each passing decade. According to statistics, 75% of all recorded strokes occur in people 65 years of age and older. The diagnosis causes serious complications in old age; the body recovers extremely rarely and not completely. The causes of stroke in an old person are most often associated with concomitant diseases that provoke problems with blood vessels. Typically this is:
- Severe hypertension (persistent high blood pressure), complicated by frequent hypertensive crises (3-4 times a year) is one of the most serious risk factors after 80 years.
- Atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation), when the heart beats at irregular intervals and provokes the formation of blood clots. During blood circulation, a clot can enter the brain vessels and cause a stroke.
- Increased blood cholesterol levels. With age, lipid metabolism is disrupted in the human body, the amount of cholesterol deposits on the inner walls of blood vessels increases, and blood clots form, complicating normal blood flow and causing stroke.
- Sedentary lifestyle, poor metabolism and obesity. Brittle bones and all kinds of joint diseases cause people over 80 to move less and build up excess fat mass, which, together with other factors, can lead to a stroke.
- Kidney diseases. Disorders of the urinary system have a detrimental effect on blood circulation, thereby increasing the risk of stroke.
- Endocrine diseases, in which an excess of any hormones leads to high blood pressure.
- Diabetes mellitus is an extremely dangerous cause of stroke. With this disease, the patient experiences dehydration of the body; against this background, the walls of blood vessels are deformed, plugs and growths form on their walls, and the blood thickens.
- Acute rheumatic fever is an inflammation of connective tissues, including the lining of blood vessels and the heart.
- A history of myocardial infarction (necrosis of a portion of the heart muscle), present in a patient after 80 years of age, gives a correct prognosis of stroke in an old person.
- Any acute viral infection against the background of a chronic disease can also cause a stroke.
- The most common cause of stroke in an old person is vascular atherosclerosis, in which the resulting plaques block the blood passage and, when they enter the brain, provoke an attack. It happens that a patient can suffer several micro-strokes in succession, but due to their mild symptoms, he does not attach importance to his condition.
Medical scientists have established a pattern that before the age of 80, stroke more often affects women, but after 82–85 years, it affects men.
We recommend
“Hallucinations in old people: causes and solutions” Read more
What is a major stroke
A major stroke is an acute disruption of the blood supply to a large area of the brain. This type of stroke differs from a regular one in that a large number of parts of the brain are affected. And if the disease is not stopped in time, the cells will begin to die throughout the affected area. In most cases, a major stroke occurs as a result of damage to the branches of the carotid artery (one of the largest vessels in the human body). As a consequence of this, a large area of the brain is affected, which can lead to either death, or the person remains disabled for the rest of his life.
Features of a major stroke
- the functioning of the branches of the carotid artery is disrupted;
- Most of the brain is affected;
- in most cases, the person remains disabled or dies due to complications;
- full recovery after a major stroke occurs only in exceptional cases;
- this type of disease in most cases occurs as a secondary disease (a person already has some disease that provokes a major stroke).
Features of a stroke in an old person
Stroke is a disease that requires emergency medical intervention. At different ages, the consequences of pathology will differ markedly. Patients over 70–80 years of age have a very severe clinical picture of the disease and minimal chances of survival, especially if a major stroke occurs.
It is in old age that 45% of patients who have had an attack are susceptible to subsequent coma in the first few days. After a stroke, an old person's prognosis for restoring the body's functional capabilities will be much worse than that of people under 50 years of age. Even if the patient manages to survive, there is a high chance of remaining disabled, most often bedridden.
Elderly people, fearing to upset their loved ones, often ignore the symptoms of the disease themselves, thereby aggravating their situation during a stroke. When working with such patients, some characteristic features of the course of the disease should be taken into account:
- Stroke increases rapidly and is more severe, since the body of an old person is subject to age-related changes and is burdened by other chronic diseases.
- Elderly people put off visiting a medical facility, citing the fact that this is a common ailment at their age. Unfortunately, age plays a negative role, since at the time of a stroke, brain tissue is affected much faster in an older person.
- In older patients, major ischemic stroke is diagnosed more often than in 30–40 year olds.
- The most common cause of attacks after 60 years is the presence of atherosclerotic plaques.
We recommend
“High blood pressure in older people: treatment, prevention and traditional methods of combating the disease” Read more
Its symptoms
Symptoms of hemorrhagic major stroke:
- unexpected blow to the head;
- redness of the facial skin;
- high pressure;
- rare, barely palpable pulse;
- one of the pupils is abnormally dilated;
- speech disorder;
- possible loss of consciousness;
- hoarse, less often bubbling, breathing;
- paralysis of the arm and/or leg on the opposite side from the one where the extensive stroke occurred (for example, the disease damaged the right hemisphere, which means there will be paralysis of the left arm and/or leg);
- tongue retraction;
- the person cannot swallow;
- stiffness (tension) of the neck muscles;
- leg muscle stiffness.
Symptoms of ischemic extensive cerebral stroke:
- loss of consciousness for a short period of time;
- rapid pulse, in most cases irregular;
- the patient has chills;
- low-grade fever (temperature gradually increases over time);
- pale skin all over the body.
It is immediately worth noting that when a stroke occurs, there is first an asymptomatic stage. Then the signs begin to manifest themselves, but the person either cannot talk about them or they do not believe him. And only at a critical moment do most symptoms appear, when it may already be too late. Therefore, if a person already has 2-4 signs of a major stroke, it is necessary to immediately call an ambulance, especially if the person is at risk.
How not to miss a stroke in an old person
We have already said that a stroke in patients over 80 years of age has irreversible consequences. Therefore, as soon as you notice the above signs of illness in your loved ones or acquaintances who have crossed the eighty-year mark, immediately seek help from specialists.
If in young people, during a stroke, only a couple of symptoms appear, then in an old person, a stroke manifests itself in all its diversity, is bright and difficult.
You should be alert to general symptoms: dizziness, headache, poor coordination of movements, numbness on one side of the body.
Hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by the following symptoms:
- sudden and severe headache;
- rapid breathing accompanied by wheezing;
- redness of the skin, especially the face;
- a sharp increase in pressure;
- intermittent heartbeat;
- possible vomiting;
- numbness of the limbs and facial muscles.
In the first minutes of a hemorrhagic attack, immediately after a vessel ruptures, a person may lose consciousness. Depending on how the intracranial hemorrhage is localized, loss of vision and hearing can occur. Vomiting during a stroke can lead to aspiration in an old person, and therefore to respiratory arrest. In the most severe forms, patients experience seizures or even coma.
Signs of ischemic stroke:
- nausea and vomiting due to headache;
- sluggish, impaired movements, inability to lift or even move limbs;
- double vision when looking at objects, a blurry picture before the eyes;
- dizziness and disorientation;
- sensory disturbance;
- numbness of the mouth, inability to speak.
In the ischemic form, symptoms appear gradually. The acute phase is considered to be the first 6 hours after the attack.
If you suspect that an old person has had a stroke, then even before the team of doctors arrives, you can independently determine the primary diagnosis by performing simple tests:
- Ask the patient to smile. If a stroke occurs, one part of the face will remain motionless.
- Have the person try to simultaneously raise or at least stretch their arms forward. In case of a stroke, this can be done with only one hand.
- Try to talk to the victim, pay attention to his articulation. If cerebral circulation is impaired, it is almost impossible to pronounce words.
- Invite a person to stick out his tongue; the tip of the patient will certainly deviate to the side, in the direction of the lesion in the brain tissue.
Even if only one of the tests failed, the patient most likely had a stroke. In this case, there is no time to waste, but it is necessary to provide him with first aid.
Temperature during a stroke in an old person is an important indicator for determining the severity of the attack. The later a person’s temperature rises from the onset of a stroke, the more unfavorable the prognosis for the patient, and the greater the risk of death. High temperature is also a critical indicator that will subsequently prevent the body from recovering. This is due to the fact that hyperthermia worsens the hemorrhage and the hematoma begins to put pressure on the brain.
We recommend
“Recovery of older people after a stroke: tips and practical recommendations” Read more
Classification
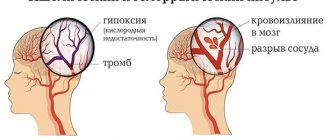
Extensive or severe stroke of the brain is of two types: ischemic and hemorrhagic. These varieties are further divided into several subspecies: in the first case there are five more, in the second case there are two more. Above, these two types have already appeared more than once in the text, so it’s time to find out what a hemorrhagic extensive stroke is and what an ischemic extensive cerebral stroke is in more detail.
Ischemic
Ischemic major stroke of the brain can be of 5 types:
- atherothrombotic – due to atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries (develops slowly);
- cardioembolic – partial or complete blockage of blood vessels in the brain (develops quickly);
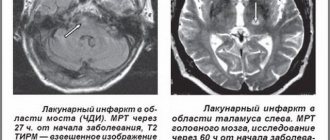
- lacunar – damage to perforating arteries (develops over several hours);
- hemodynamic – a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- microocclusive – a violation of the coagulation and anticoagulation system of the human body.
In fact, ischemic stroke occurs slightly more often than hemorrhagic stroke, but the consequences of this stroke are milder. And this type of disease can be treated more easily if medical assistance is provided in a timely manner.
Mechanism of ischemic stroke
Ischemic stroke occurs due to blockage of a blood vessel in the brain. As a consequence of this, a certain area of the main organ does not receive blood with oxygen and nutrients. This means that the cells begin to “starve” and then gradually die. Most often, ischemic stroke occurs due to blockage of a vessel by an embolus or thrombus.
Hemorrhagic
There are only two types of hemorrhagic major stroke: intracerebral and subarachnoid. If in the first case a person can more or less recover and return to his usual way of life, then in the second case the disease more often ends in death. Indeed, with a subarachnoid extensive stroke, a large amount of blood enters the subarachnoid membrane, where it damages vital centers.
Mechanism of hemorrhagic stroke
If an ischemic stroke is accompanied by blockage of a vessel, then a hemorrhagic stroke occurs as a result of a rupture of a cerebral artery and the release of blood outside the vessel. Of course, the nutrition of a certain area of the main organ stops, which means that after some time necrosis will begin (if help is not provided in time). And if blood gets into the subarachnoid membrane, then minutes will count.
First aid for stroke
A quick reaction from relatives who can provide first aid to an old person after a stroke will help prevent serious consequences and provide the necessary treatment in the future.
So what needs to be done:
- position the patient so that the legs are 25–30 degrees below the head;
- try to determine blood pressure and pulse indicators, record them;
- if the patient has lost consciousness, do not try to move him to the bed, just lay him down correctly and leave him alone;
- After the ambulance doctors arrive, talk clearly and intelligently about the person’s previous condition, the medications he is taking, and the visible symptoms of the attack.
There are actions that doctors strictly prohibit taking. Under no circumstances should you:
- use ammonia when recovering from a fainting state;
- hold limbs during convulsions;
- try to offer the patient medications that may get stuck when swallowing (it is better to completely stop taking medications until specialists arrive).
We recommend
“Low blood pressure in an elderly person: treatment and prevention” Read more
Symptoms
A stroke at 80 years old, the prognosis of which will be positive, is a quick response to the symptoms of the disease and timely treatment. If a grandparent has a hemorrhagic attack, the symptoms will be as follows:
- severe headache accompanied by rapid breathing and wheezing;
- strong, intermittent heartbeat, leading to fainting or near-fainting;
- blood pressure rises sharply, while the face becomes very red;
- limbs and facial muscles go numb;
- the patient feels sick and vomits.
Important! Signs of this type of stroke develop rapidly, so the patient usually loses consciousness at the beginning of the attack.
Depending on the area of the brain where the hemorrhage occurred, the patient may lose hearing or vision, and if it is a major stroke, seizures may begin and a coma may occur.
If, for example, an ischemic stroke occurs on the right side, the symptoms will be as follows:
- severe headache with vomiting and nausea;
- it is difficult for the patient to make any movement due to almost absolute weakness;
- visual function decreases, often the picture bifurcates;
- vertigo with impaired spatial orientation;
- memory lapses, disturbances of touch and speech.
Important! Time in the case of ischemic stroke is extremely important, because the symptoms develop gradually and become acute in 5-6 hours.
Treatment of stroke in an old person
If there are signs of a stroke, you should consult a cardiologist. After collecting the necessary information from relatives and the patient himself, the attending physician prescribes blood tests and conducts:
- echocardiography;
- electrocardiogram;
- magnetic resonance (computer) tomography;
- ultrasonography.
All this will allow us to identify the pathology, the location of the lesion, and determine the type of stroke.
The patient also needs examinations by a neurosurgeon and an ophthalmologist, which can identify other affected areas in the body.
It is quite difficult to determine the pathology of hemorrhagic stroke in patients over 75 years of age. Typically, such patients have mild changes in the blood test or they may also indicate other diseases. In such cases, doctors conduct additional examinations, such as electroencephalography and angiography.
Treatment should only take place in a hospital setting under the supervision of a physician. A specialist can prohibit transporting a patient to a hospital only in the case of a severe coma with severe impairment of vital functions.
In order for treatment to benefit an elderly patient, he must follow the sequence of procedures, complete their full course and subsequent rehabilitation measures. Only under such conditions will an old person be able to quickly recover from an attack.
The main goal of treatment after a stroke is to restore the functioning of the cardiovascular system and protect the remaining brain cells. After the patient is recovered from a serious condition, he is prescribed medication and physical therapy.
Medicines for the treatment of stroke in an elderly person are available only by prescription. Among them:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Medicines aimed at reducing blood pressure by reducing vascular tone. A very large group of medications does not affect the presence of cholesterol and does not affect atherosclerosis.
- Class 2 receptor blockers. They have a long period of action, consistently reduce blood pressure, and have virtually no side effects. In conventional therapy, they are often prescribed for chronic hypertension.
- Diuretics. They are used if the first groups of drugs are contraindicated for the patient due to various, most often age-related, reasons.
- Beta blockers. Designed to dilate peripheral blood vessels, lower blood pressure, and help fight arrhythmia.
- Calcium antagonists. As a rule, they are used to treat stroke in old age in the presence of concomitant angina and other heart rhythm disorders. Often prescribed together with ACE inhibitors.
- Adrenergic receptor blockers. Used to reduce blood pressure. Can be used for renal failure and diabetes.
- Centrally acting drugs. With a pronounced effect, contractions of arrhythmias can also lower blood pressure. Used for comprehensive healing of the heart muscle.
- Vascular drugs. In case of a stroke in an old person, they are administered as injections to restore nerve cells and blood vessels in the brain.
- Nootropics. Indispensable during the rehabilitation period of elderly patients for the restoration of brain cells.
- Antihypoxants. Preventative drugs. Prescribed if there is a risk of developing oxygen deficiency.
- Thrombolytics thin the blood, prevent the formation of blood clots and plaques, and are used to restore blood composition.
During the rehabilitation period, various natural supplements and vitamins are included in the patient’s diet.
What treatment does the doctor prescribe depending on the type of stroke?
1. In case of hemorrhagic form, the patient is given intramuscular injections of calcium gluconate, and intravenous injections of calcium chloride. For treatment, Rutin, Vikasop, Dicynon, ascorbic acid with gelatin, Rutamin, and aminocaproic acid are used. If necessary, the lateral hematoma is removed by surgery. In emergency cases, other surgical procedures may be used.
2. For ischemic stroke, vasodilators and nicotinic acid are used. The patient is recommended to use “Trental”, “Stugeron”, “Heparin”, “Phenilin”, “Aspirin”, “Prodectin”, “Complamin”, solutions of diethyphene and cocarboxylase.
We recommend
“Vitamins for elderly people over 70: which ones are needed first” Read more
Main reasons
A major stroke does not occur out of nowhere; this disease is always provoked by some reason. Depending on this, an ischemic or hemorrhagic major stroke occurs. For example, in the first case, the cause may be a spasm of the carotid and vertebral arteries, blockage of a large vessel with a blood clot. In the case of hemorrhagic stroke, the disease can occur due to high blood pressure (blood pressure), physical or mental stress, and so on. The types of stroke will be discussed in more detail below.
0
Causes of hemorrhage
But there are several common precipitating factors that can cause both ischemic and hemorrhagic major stroke of the brain:
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- inactive lifestyle;
- cardiac dysfunction;
- atherosclerosis;
- hypertension;
- high blood cholesterol levels;
- smoking, drug and alcohol use.
In most cases, the prevention of any stroke is based on compliance with the principles of a healthy lifestyle (healthy lifestyle). Therefore, if a person cares about his health, then he should lead an active lifestyle, give up bad habits, and as he gets older, see a doctor.
What does a stroke mean for older people?
Almost all older people over the age of 80 suffer from one or another chronic disease. Accordingly, when stroke occurs in such patients, treatment and recovery measures are complicated. At this age, surgery is usually prohibited if an aneurysm is detected in a patient, which also negatively affects the course of the pathology. What other reasons complicate the treatment of stroke in an old person?
- Due to the fact that elderly patients do not tolerate anesthesia well, and operations due to concomitant pathologies are often accompanied by hemorrhages and other side effects, surgical intervention is rarely used for people over 70–75 years of age.
- Extensive atherosclerosis in elderly patients becomes permanent, pronounced and difficult to treat. You can only slightly lower the level of cholesterol in the blood, but it is very difficult to rid the blood vessels of fatty plaques.
- Treatment of stroke is complicated by the presence of concomitant chronic diseases.
- Susceptibility to infectious diseases that weaken the body of an old person, impair blood clotting, lead to oxygen starvation and other adverse consequences.
- The need to take a variety of medications to keep the body normal. Forced reduction in drug dosages.
- The risk of recurrent stroke if the course of rehabilitation is not completed, the required diet and other medical recommendations are not followed.
- The impossibility of restoring the brain of an elderly person after a coma resulting from a hemorrhagic stroke.
An old person who has had a stroke has neurological impairment. Almost 100% of patients over 80 years of age become disabled after an attack. Relatives need to be prepared for the need for constant care for the patient, as well as for the following consequences of the illness:
- complete or partial lack of movement (paralysis) of the body;
- paresis (impaired motor functions) of the limbs;
- loss of orientation in space;
- impaired speech;
- loss of swallowing function;
- complete or partial deafness;
- lack of urinary and bowel control;
- changes in mental and emotional state.
We recommend
“The main problems of older people and ways to solve them” Read more
Consequences of a stroke
Unfortunately, as a result of brain damage, important functions are impaired, which are not always amenable to recovery. Let's look at the main ones.
Paralysis
It involves damage to the nerve endings that control muscle function, resulting in loss of motor function. Paralysis can be of the whole body or part of it. The most common form is one-sided. May affect facial muscles.
Speech dysfunction
A common consequence of a stroke that occurs due to damage to the areas of the brain responsible for speech. Expressed in complete/partial loss of the ability to speak and perceive the words of others. With a partial form, the conversation is unclear; with a complete form, there is an inability to utter at least a word.
Deterioration of the visual organs
A stroke can damage the parts of the brain responsible for visual function. As a result, there is deterioration in vision, loss of individual parts from the field of view (up to ½), and strabismus (difficult to treat).
Impaired motor coordination
Most often occurs with a brainstem stroke. Manifests itself in the form of dizziness and staggering when moving. Depending on the form of the pathology and severity, it may manifest itself during the first days after the attack or over a longer period.
Swallowing dysfunction
It occurs due to a disruption of the reflex process or paralysis of facial muscles. It is also a consequence of brainstem infarction.
May manifest:
- Difficulty chewing food.
- Difficulty swallowing food.
- Pain while eating.
- The entry of food particles from the oral cavity into the respiratory organs, in particular the nose.
Formation of bedsores
It is observed in paralyzed patients due to prolonged stay in one position. In this case, less nutrients reach the tissues. The result is their starvation and further death. The areas most affected are areas closely pressed to the bed.
Pneumonia
As a result of paralysis, the patient cannot cough up the mucus that accumulates in the bronchi and enters the lungs. Next, inflammation begins.
Depressive state
The most common consequence that minimizes the effectiveness of treatment and rehabilitation. You need the help of a qualified psychologist and a course of antidepressants.
Coma
One of the dangerous consequences, considered a transitional state to death. During this period it is noted:
- slowing down metabolism;
- decrease in body temperature;
- change in breathing pattern;
- falling into unconsciousness;
- lack of response to external stimuli.
The prognosis for coma is predominantly unfavorable.
How to recover and prevent another stroke for an old person
For older people after a stroke, even in a hospital setting, they offer classes on special simulators and select individual exercises that need to be continued at home. The basis of the rehabilitation period, along with taking medications and physiotherapeutic procedures, is a properly selected diet:
- minimum amount of sugar and salt in the diet;
- reducing the consumption of animal fats (pork, lamb, butter, some dairy products);
- The basis of the diet is lean vegetable soups, vegetable oils, cereals, fruits and vegetables.
It is recommended to steam dishes and eat boiled or baked foods. To avoid difficulty chewing, it is better to eat fairly well-chopped food.
In the post-stroke period, many patients have a deteriorating emotional state, feel morally depressed, and have their usual sleep patterns disrupted. What sedatives does a doctor usually prescribe for an old person after a stroke? As a rule, these are sleeping pills and antidepressants: Doxepin, Mirtazapine, Trazodone. Nicergoline is used as an additional medicine, which not only reduces the symptoms of insomnia and mental disorders, but also helps reduce the tone of the cerebral arteries and improves blood flow. It is worth warning that long-term use of these drugs can be addictive. Beware of this and listen to medical advice.
In recent years, PNF therapy (proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation) has been actively recommended for older people who have suffered a stroke, a technique that allows them to regain the ability to move. Simple physical exercises improve motor functions and prevent the development of complications - paralysis and muscle dystrophy.
Other methods are also effective in treating stroke in older people:
- soft tissue manual therapy - working out all muscles allows you to restore their tone;
- Vojta therapy - through targeted pressure on certain areas of the body, the activity of motor muscles and reflexes is triggered. In some cases, completely paralyzed patients after a course of procedures were able to roll over and crawl on their own;
- The Castillo Morales method is a set of exercises that allows you to restore the breathing and swallowing functions, as well as the speech of the victim. Usually carried out in conjunction with psychological therapy;
- kinesio taping - special elastic patches glued to the patient’s skin not only improve microcirculation and lymph outflow, but provide additional support and strengthening to the joints;
- The Mulligan concept is a type of manual therapy method that has proven itself in the treatment of stroke in an old person. Special manipulations by the doctor alleviate the excessive pain of the actions, and the patient, overcoming the pain, can improve the exercises day by day;
- bobat therapy (neurodynamic rehabilitation) is a practice that helps to correct movement patterns and overcome lack of movement.
All these techniques are usually used to treat stroke in an old person in a rehabilitation center under the guidance of experienced doctors. Additionally, patients are prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures, magnetic brain stimulation to restore speech, and transcranial stimulation to improve vascular function.
You can also achieve good results after acupuncture, which helps normalize muscle activity and restore motor functions, improve tissue condition, and form reflexes.
Treatment of a stroke in an old person and the subsequent rehabilitation period is a rather lengthy set of measures that falls on the shoulders of the patient’s relatives and friends. The choice of good doctors, strict adherence to all recommendations, the desire and efforts of the patient himself, the patience and responsibility of relatives help many who have suffered an attack to return to a comfortable standard of living.
Forecast
In fact, it is impossible to give a rehabilitation prognosis without knowing the patient’s medical history and the nature of the disease. Since it depends on a huge number of factors: how long the stroke lasted, what type of disease, whether the person has chronic diseases, age, qualifications of medical personnel, availability of modern medical supplies, the patient’s desire to follow the doctor’s recommendations, how quickly first aid was provided, etc. Further.
In most cases, people after an extensive stroke remain disabled to one degree or another, since it is not always possible to completely restore lost function after extensive necrosis. However, modern treatment methods make it possible to compensate for the consequences and complications of a stroke, bringing the patient closer to his usual lifestyle. But for this it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations and set yourself up for the best outcome.
Chances of surviving past 80
Unfortunately, a large number of elderly people are not able to survive a major cerebral stroke. In most cases, the body cannot cope with the shock, and the person falls into a coma from which he never recovers. Therefore, it is important, at least from the age of 40-50, to prevent stroke: follow a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits, and see a doctor at least once every six months to a year.
How long do they live after severe brain damage?
It is impossible to answer the question of how long people live after a major stroke. Since a person can live either a few days after an impact or several decades. This again depends on a variety of factors, including the patient’s lifestyle and the characteristics of his body. To increase your chances of a long and good life after a stroke, you should follow a healthy lifestyle and follow the recommendations of your doctor.
Rehabilitation activities
How to avoid a stroke at this age? There is no consensus, because each organism is individual, as is its wear and tear at this moment. Even if the family or the patient himself accurately and painstakingly follows the recommendations of doctors, the prognosis may not improve or not be fully realized, but a relapse can be avoided if:
- The patient will switch to proper nutrition. It is very important to follow a dietary regime so that the body has the strength to fight the disease. Skipping meals can have bad consequences.
- With partial or complete paralysis, the patient needs a special mattress against bedsores, as well as special exercises to prevent them.
- Diuretics prescribed by your doctor will help prevent the gradual development of swelling.
- Measures are being taken to treat other diseases. If they are launched, they will provoke a second attack, which always ends in death for patients of this age group.
In addition, doctors have confirmed that regular use of drugs responsible for reducing the rate of ischemic attacks leads to an expansion of the therapeutic window, which immediately follows hemorrhage. Therefore, people caring for such a patient must constantly monitor that all pills are taken on time. If such an elderly person managed to avoid death after a stroke, then, unfortunately, partial or complete paralysis cannot be ruled out.
Such a patient will not be able to care for himself independently, and this requires constant care for the old man. This situation also affects the psyche of an elderly person. He becomes capricious and vulnerable, like a child, which will require patience and courage from the person caring for him, because this is difficult for both him and his patient.
To summarize the above, we can be sure that the absence of consequences for a patient at the age of 80 years after a stroke is more the exception than the rule. Usually the prognosis is sad, as are the consequences, and relatives and friends should be prepared for this.