Many people are familiar with the feeling of pulsation in the head. This condition does not necessarily indicate pathology; it is possible and normal under certain conditions. Most often, the feeling of pulsation in healthy people is provoked by stress, strong emotions, physical overload or a sudden change in weather. In these cases, the unpleasant sensations are short-term and go away on their own.
At the same time, pulsation accompanies migraines, atherosclerosis, autonomic dysfunction and many other diseases, bringing the patient a lot of discomfort and anxiety. It can be considered an alarming symptom, since without examination it is impossible to say what exactly caused it and whether it really does not indicate pathology. The cause can be relatively harmless - autonomic dysfunction (VSD), for example, or very serious - a tumor, an aneurysm.
Pulsation in the head can occur with noise, ringing in the ears, dizziness, panic attacks, it occurs in various areas of the head - the temples, the back of the head, in one half. Pathological pulsation can be long-lasting, repeated many times, and this is exactly the case when you should go to a doctor - a neurologist or therapist.
Pulsation of the cervical vessels is also possible, which can be physiological or associated with atherosclerotic lesions, heart defects, arrhythmia, and arterial hypertension. In this case, an examination is also necessary to exclude the pathological nature of the pulsation.
Clinical picture of the condition
It is worth distinguishing a simple headache from sensations when pain occurs when pressure is applied. These symptoms signal different diseases; they are not equivalent to each other. If the cause of a migraine most often lies in impaired blood circulation in the brain and organic causes, then if the temple hurts when pressed, it is most likely due to problems with blood vessels, osteochondrosis, and heart pathologies.
Often pressure on the temple, accompanied by pain, is typical for older people and neurotic individuals. At the same time, symptoms such as increased anxiety, insomnia, sleep problems, irritability, unmotivated aggression, fixation on certain events, and difficulties in communication develop.
With such symptoms, it is highly recommended not to self-medicate. These may be manifestations of early dementia or neuropathy, encephalopathy. Drug treatment and competent selection of pharmacological agents will help stop the inevitable progression of the disease. And if the patient tries to self-medicate at home, the symptoms will increase, and after a few years the person may become incapacitated.
Possible causes of this symptom
Why do my temples hurt when pressed? This is not a separate disease, but often signals serious health problems: cerebral vessels, blood pressure, vestibular system, cervical spine.
The most common diseases in which the temple hurts when pressed:
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- hypertension;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- arrhythmia and cardiomyopathy;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- withdrawal syndrome;
- magnetic storms and increased atmospheric pressure;
- chronic stress and overwork;
- excessive physical activity (leads to overload of blood vessels and thinning of their walls).
Migraine, which every person has experienced at least once in their life, is also manifested by pain when pressing on the temple. Chronic migraine and vegetative-vascular dystonia have a lot in common, and only an experienced neurologist can distinguish one diagnosis from another based on the combination of a number of symptoms.
Causes of pulsation of blood vessels in the head
The causes of pulsation in the head are extremely varied. Among them are those diseases that older people are more susceptible to, and those that occur in young people, being asymptomatic for the time being. Based on the nature of vascular pulsation, it is impossible to determine the exact cause of this symptom. After a conversation with the patient and a simple examination, a specialist can only suggest the pathology that provokes vascular disorders, and additional instrumental examinations will help clarify it.
Pulsation in the head accompanies diseases such as:
- Autonomic dysfunction (vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD);
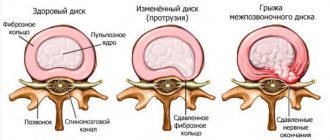
- Degenerative changes in the cervical spine - hernias, osteochondrosis, instability, congenital developmental features;
- Damages of the vascular wall - atherosclerosis, vasculitis;
- Aneurysm, vascular malformation;
- Neoplasms of the head and neck;
- ENT pathology;
- Glaucoma, incorrectly selected glasses;
- Suffered traumatic brain injuries;
- Neuroses, neurasthenia and other psychiatric problems.
Arterial hypertension is one of the most common causes of pulsation in the head.
This disease is also very common among mature and elderly people, for whom pulsation in the head is a well-known symptom.
Hypertension primarily affects the arteries and arterioles, which become spasmed due to constant high pressure, resulting in impaired blood flow in the brain. Against the background of a sharp rise in pressure - a crisis - the patient feels pulsation in the temples, pain in the back of the head, possibly dizziness and tinnitus. The higher the pressure number, the more obvious and painful the pulsating feeling, but as the pressure readings drop to normal, the symptoms gradually disappear.
Autonomic dysfunction is common among young adults, children and adolescents.
More often, females suffer from the disorder, and the regulation of vascular tone by the autonomic nervous system is disrupted, resulting in fluctuations in systolic pressure, pulse, and it is quite possible that a pulsating feeling may occur even in the throat.
Pulsation against the background of autonomic dysfunction is provoked by stress, emotional experiences, physical overload and fatigue. Smoking and alcohol abuse have a negative impact.
Ripple with VSD occurs without pain, but is often accompanied by other signs of autonomic disorder - sweating, redness of the face, discomfort and rumbling in the abdomen, cardialgia, a feeling of shortness of breath with increased breathing, weakness and decreased performance, low-grade fever. Mood swings and panic attacks are also characteristic, which often help diagnose the cause of the pulsation.
Degenerative changes in the spine can be detected in almost every second adult inhabitant of the planet.
Such a wide spread of pathology is facilitated by a sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work, and excess weight. Disc herniations, developmental abnormalities of the bony processes of the vertebrae, and osteochondrosis cause compression of blood vessels and nerves, resulting in pain and pulsation in the back of the head and parietal regions. The pulsations are accompanied by numbness in the limbs, neck pain, and fluctuations in blood pressure.
cerebral atherosclerosis
Structural changes in vascular walls
in the form of atherosclerosis, inflammation (vasculitis) can cause narrowing of their lumen and hemodynamic disturbances. When an artery is half stenotic by an atherosclerotic plaque, the brain begins to experience hypoxia even with the active functioning of collateral blood flow pathways. Patients with atherosclerosis of the arteries of the head complain not only of a feeling of pulsation, but also of noise, ringing in the ears and head, decreased memory and mental performance, they are prone to depression and apathy.
Inflammation of the vascular wall is called arteritis. It can be a consequence of an autoimmune disease, injury, surgery, or infectious disease. In the acute period of vasculitis, pulsation occurs with intense headache, general weakness, and possibly anxiety.
An extremely dangerous cause of pulsation of the vessels of the head is considered to be an aneurysm or arteriovenous malformation. An aneurysm is a tangle of pathologically developed vessels that can be located in any part of the brain. Arteriovenous malformation is an interweaving of arterial and venous dysplastic vessels. These formations are almost always congenital in nature, are asymptomatic for a long time and can manifest as periodic throbbing pain in a certain part of the head - in the temples, back of the head, crown of the head.
Since vascular anomalies are accompanied by a violation of the structure of the walls of the vessels that form them, under certain conditions their rupture can occur - during a pressure surge, injury, or severe stress. Rupture of blood vessels results in hemorrhage into the substance of the brain or under its membranes, which is often fatal.
The feeling of pulsation depends on the size of the aneurysm - the larger it is, the more clearly the patient feels the pulsation. Small aneurysms may not cause pain, but the pulsating symptoms are usually bothersome. In addition to pulsation, other signs of malformation are possible: noise in the head, memory loss, anxiety, and with large aneurysms - seizures.
New growths in the head and neck can also contribute to unpleasant, palpable throbbing.
They occur much less frequently than hypertension, atherosclerosis or osteochondrosis, but often affect children and young people. In addition to pulsation, tumors cause pain, dizziness, with an increase in intracranial pressure, nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief are added, convulsions and other neurological symptoms are possible - decreased vision, paralysis of the limbs, coma, etc.
Ripple without other symptoms can accompany small neoplasias, which put pressure on the vessels from outside and impede the flow of blood through them. More often it appears in the morning and increases as the tumor grows. Pulsation in the head may be one of the first symptoms of tumor growth.
Inflammatory processes of the ENT organs,
accompanied by the accumulation of exudate there, can manifest themselves as pulsating sensations in the head, a feeling of fluid transfusion from the side of the affected ear. In addition, patients are bothered by headaches, noise, whistling in the head, and progressive hearing loss.
Glaucoma
, incorrectly selected glasses or refusal of them due to insufficient visual acuity create not only negative sensations in the eyes, provoke even greater vision problems, dizziness and a feeling of lightheadedness, but can also cause pulsation in the temples and frontal area.
This pulsation becomes more noticeable with an increase in intraocular pressure, eye strain when working with a computer, reading, and is accompanied by a headache.
Pulsation in the head in some cases accompanies traumatic brain injuries.
In the acute phase, it is combined with severe headache, vomiting, convulsions, and in severe cases, consciousness is also impaired. The consequence of the injury can be periodically recurring attacks of pain and throbbing in the head.
Various neurotic disorders, schizophrenia and other psychiatric diseases
often occur with pulsation in the head, which the patient can describe very colorfully, clearly defining the location of its localization, which can complicate diagnosis, because it is quite difficult to check whether the patient is telling the truth.
Neurasthenia is a borderline disorder that is provoked by stress, overwork, improper work and rest patterns, and individual characteristics of emotional response. Chronic tension of the nervous system sooner or later leads to its exhaustion, and a person turns into a neurasthenic patient who complains of constant fatigue, insomnia or drowsiness, irritability, decreased appetite and bad mood. In addition to these complaints, pulsation in the head, pain, noise, which intensifies against the background of emotional experiences, are also characteristic.
In the case of schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders, the situation is more complicated: unclear pulsations and noise may be part of the hallucinations that the patient experiences, and in addition to a vivid description of symptoms, the doctor is often faced with their exaggeration, which significantly complicates an objective assessment of symptoms.
Intracranial pressure
If intracranial pressure readings are significantly higher than normal, the patient feels a dull, prolonged pain in the back of the head and temples, which intensifies with strong pressure. People with increased intracranial pressure describe this condition as “as if water has accumulated in the skull and the head is about to burst.” This condition sometimes occurs immediately after waking up. In some patients, on the contrary, symptoms worsen in the late evening.
In some cases, changes in atmospheric pressure can provoke surges in intracranial pressure. This can cause the patient to wake up at night from a severe migraine, while pressure on the temples and back of the head will cause acute pain. Chronic stress and overwork can also cause increased intracranial pressure.
In the absence of drug treatment and lifestyle changes, intracranial pressure can lead to organic changes that cause permanent chronic ailments. In the future, this may threaten the patient with the possible development of encephalopathy, various neuropathies, and a decrease in cognitive functions.
Why did pain appear in the right temple of the head?
Pain in the area of the right temple in various pathologies differs in character and degree of intensity, often radiating to the ear, eyeballs, neck, bridge of the nose.
The main causes of pain in the temple on the right:
- disturbance of cerebral vascular tone;
- influenza, ARVI, sore throat – pain in the head rarely occurs in the morning, intensifies in the evening;
- smoking, alcohol abuse;
- severe intoxication;
- migraine;
- increased or decreased intracranial pressure;
- in older people, the temple often begins to ache when the weather changes, which may indicate hypertension, atherosclerosis;
- injuries to the brain and skull bones;
- dysfunction of the jaw joints;
- bad tooth, otitis media, sinusitis, conjunctivitis;
- VSD, oxygen starvation;
- stress, mental and physical fatigue - these factors most often provoke the appearance of cephalalgia in a child.
Blockage of blood vessels in the brain causes temporal pain
Regular discomfort in the temple and neck in the morning indicates an incorrect position of the body during sleep, which can be caused by an excessively flat or high pillow or soft mattress.
In women, a dull pain in the right temple occurs due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, PMS, menopause, discomfort after sleep or rest almost completely disappears.
The nature of pain in the temple on the right side and possible causes of its occurrence
How exactly the pain syndrome manifests itself in the temporal region, where it radiates, can preliminarily determine the cause of the pathological condition.
Characteristics of pain:
- Pulsating, squeezing - the body’s reaction to stress, overwork; such a symptom may indicate sudden changes in intracranial pressure, vascular spasms, migraines. Discomfort, which increases when bending over, may be a sign of an abscess of brain tissue, accompanied by nausea and fever. Sometimes knocking in the temporal region with right-sided pulpitis, otitis media.
- Shooting, stabbing – severe and sharp pain is often a sign of trigeminal neuralgia, an inflammatory process in the temporal arteries. Unpleasant sensations intensify when pressing, talking, and can spread to the occipital and frontal areas; additional symptoms are increased sensitivity of the facial skin, insomnia, and a feeling of numbness in the temporal region.
- Aching – unpleasant sensations are of psychogenic origin, characterized by irritability, panic attacks, and chronic fatigue. Sometimes there is colitis and aching in the right temporal zone when intracranial pressure increases.
- Dull - a consequence of traumatic brain injury, accompanied by dizziness, nausea, loss or confusion. If such sensations bother you immediately after waking up and intensify when you change body position, this may indicate a brain tumor.
- Expanding pain radiating into the eyes occurs with vascular pathologies - atherosclerosis, hypertension, migraines, and is accompanied by stuffy ears, attacks of dizziness, flickering spots before the eyes, and nausea.
- Pressure - indicates problems with the cervical spine, osteochondrosis, osteoarthrosis, in which the blood supply to brain tissue is disrupted. Severe pulsation and acute pressing pain combined with nausea, epileptic attacks, star-shaped rash, intolerance to light and loud sounds are a sign of meningitis.
Read also: What to do if your tooth hurts badly?
Pressing pain indicates the development of cervical osteochondrosis
Important! Foods high in tyramine - cheese, chocolate, legumes, red wine, beer, kvass, yeast baked goods - can trigger a nagging pain in the head. The cause of cephalalgia is often monosodium glutamate and nitrites - these dangerous substances are present in many sauces, canned food, smoked meats, and fast food.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
Unstable functioning of the heart and blood vessels is a common cause of headache when pressed. These are serious conditions in which self-medication is unacceptable and consultation with a cardiologist is necessary. Does your temple on the right side hurt when pressed and do you feel pulsation of the veins? Most likely the cause is arrhythmia. This condition also often causes dizziness, darkening of the eyes, and short-term fainting. The patient feels weak and nauseated. Does your temple on the left side hurt when you press? Perhaps the reason is surges in blood pressure. It must be measured regularly to rule out hypertension.
With the combination of all these symptoms, we can talk not only about arrhythmia, but also about angina pectoris and cardiomyopathy. When blood pressure rises, the nature of the pain in the temples is stabbing or throbbing. If the indicators are lowered, then nagging discomfort, dizziness appears, and a short-term loss of consciousness may occur.
In some cases, problems with the functioning of the cardiovascular system are caused by changes in atmospheric pressure, weather changes, and chronic stress. This condition cannot be left to chance. It can lead to chronic diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
Hormonal disorders
If a woman has pain near her temple when pressed, then perhaps it is due to diseases of the hormonal system. With thyrotoxicosis, the symptoms are varied - migraines and pain in the back of the head and temples when pressed can occur. If there is a deviation in TSH levels, hair loss (alopecia), asthenia, dysphoria, irritability, and anxiety are also possible.
Another reason why temples hurt when pressed is premenstrual syndrome. This condition is not a disease and occurs in approximately 30% of women aged 16 to 43 years. To avoid it, before the onset of menstruation, you should rest more, avoid physical activity, hypothermia, and stress. In some cases, a course of vasodilator drugs will help. A prescription for such medications can be obtained from a neurologist.
Local diseases
If it hurts just below the temple when pressed (the sensation is not located in the temple itself, but next to it), then most likely the cause is local diseases. These are meningitis, sinusitis, inflammation of the nasopharynx and sinuses, ARVI, and other infectious diseases. This is due to an increase in temperature and the accumulation of mucus in certain parts, which with its volume puts pressure on the tissues of the skull.
To treat such conditions, antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs should be used. These are “Kagocel”, “Sinupret”, “Arbidol” and others. An immunologist can prescribe a medicine that would be ideal for a particular patient and does not cause side effects.
If the temple on the right side hurts when pressed (at the same time there is nasal congestion, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes and other symptoms of ARVI and influenza), then the inflammatory process occurs on the right side of the nasopharynx, tonsils and sinuses. It is necessary to more actively use medicinal aerosols and sprays specifically for the treatment of the right nostril and the side of the throat. Does your temple on the left side hurt when you press? Accordingly, the inflammatory process is more active on the left.
Vegetovascular dystonia
This disease is a complex of functional disorders, which is based on dysregulation of vascular tone of the autonomic nervous system. This is a common reason why the right temple hurts when pressed. Vegetative-vascular dystonia is characterized by pain in the temples and without pressure. In the early stages, it is simply an unpleasant squeezing sensation, as if the head is in a vice. In parallel with this, the patient often experiences anxiety, unmotivated fear, phobias, and depressive disorders appear.
There is an opinion among patients that a neurologist makes a diagnosis of “vegetative-vascular dystonia” if he cannot correctly diagnose it. Allegedly, the symptoms of VSD are so extensive that they can be attributed to every second resident of our country. A competent neurologist will only laugh at such a statement: the diagnosis of “vegetative-vascular dystonia” has clear symptoms and really exists, although it is difficult to treat with medication. The patient's condition with this disease can be significantly alleviated not by pills and injections, but by changing lifestyle and giving up bad habits (in particular, smoking cigarettes).
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Has several stages. At the initial stage of development, this disease makes itself felt only by mild dizziness. In some cases, vision decreases (because the optic nerve is pinched). At the second stage, the patient begins to experience headaches, and short-term loss of consciousness is possible. The main difference between osteochondrosis and increased intracranial pressure is that the neck and shoulders hurt, and the cartilage crunches when you rotate your head.
If, in parallel with these symptoms, the patient’s temple hurts when pressed, then we can confidently say that the problem is precisely osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. The treatment of this pathology is carried out by an orthopedist and a neurologist. The following medications are prescribed:
- Intramuscular injections of drugs that include cyanocobalamin, pyridoxine, thiamine, riboflavin, nicotinic acid.
- Over-the-counter mild nootropics.
- Vasodilators.
- Medicines designed to compensate for the deficiency of collagen and elastin in the body.
What should you do if you have a throbbing sensation in your head or neck?
The pulsation in the head and neck cannot but disturb. When it occurs for the first time and unexpectedly, it can lead to panic and severe fear, because this symptom can indicate a number of serious diseases. Patients with migraine or VSD may well get used to repeated pulsation without perceiving it as a symptom of a dangerous pathology, but this does not relieve them of the need to visit a doctor.
Regardless of the cause, which the patient may even suspect, pulsation in the head or neck should be a reason for consultation with a specialist and examination. With such symptoms, you should go to a therapist, neurologist, phlebologist (for venous pulsation in the neck). The therapist can refer you for consultation to a cardiologist, endocrinologist, psychiatrist, ophthalmologist, or oncologist, depending on other complaints and the result of the initial examination.
When talking with a doctor, it is important to clarify at what time of day the pulsation appears, whether it is associated with nervous or physical stress, weather changes, or the phase of the woman’s menstrual cycle. In addition to pulsation, other symptoms should be described, if any (pain, dizziness, etc.).
If there is pulsation in the head, MRI, angiography, ultrasound with Doppler scanning of the vascular trunks of the head and neck, radiography of the cervical spine, and encephalography are indicated. Venous pulsation often requires phlebography, echocardiography, and ECG. An exact list of examinations is compiled by a therapist or neurologist, suspecting specific causes of pulsation.
Treatment for pulsation in the head and neck may consist of prescribing analgesics, antihypertensive drugs, vascular drugs and nootropics, and in some cases surgery is necessary - removal of a tumor, aneurysm, implantation of an artificial heart valve. All patients with this symptom are recommended to normalize their regimen, eliminate stress and physical overload, and maintain a balanced diet and physical activity.
Arteritis of the temporal region
Arteritis is an inflammatory disease of the arteries.
A rather rare disease in which a small lump forms on the temple, hurts when pressed and pulsates. It occurs most often in people over fifty years of age. The appearance of arteritis in young people is possible in isolated cases only in the presence of a genetic predisposition.
Arteritis is treated by a neurologist, surgeon, and therapist. At the same time, the patient may suffer from migraines, a feeling of fluid accumulation in the brain, and surges in blood pressure.
Prevention of pain in the temporal region
To prevent headaches from bothering you and interfering with your usual lifestyle, you should follow some simple rules, the main ones of which are:
- When working at a computer or driving for a long time, take short breaks and give your eyes a rest.
- Sleep at least 6 hours a day.
- Include foods containing vitamin C (such as orange or cherry juice) in your daily diet.
- Regularly ventilate the room you are in during the day.
- Every day, set aside half an hour for walking.
You need to understand that pain in the temporal region is the first “bell” that certain changes are occurring in the body (in particular in the brain). If headache attacks are regular, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Hangover and withdrawal symptoms
The morning after a stormy party brings not only headaches and nausea, but also serious stress on the arteries and blood vessels. The body struggles with the consequences of severe ethanol intoxication. Due to the suppression of the tone of the vascular walls, people often complain that it hurts near the temple when pressed. Depending on the individual characteristics of the sick person, the pain may be located in the back of the head or forehead. In some cases, the left temple hurts when pressed, but the right one does not.
In this case, there is only one treatment - try to remove toxic products from the body as quickly as possible. To do this, you can use Enterosgel, preparations with activated carbon in the composition. After severe intoxication, it is necessary to take a course of vitamins with magnesium, selenium, and iodine.
Often such patients complain: “I press on my temple and it hurts.” They often exaggerate the scale of the problem. If pain in the back of the head and temple occurs after alcohol abuse, you should not run to the doctor and look for serious pathologies. It’s enough to simply eliminate ethanol-containing drinks from your diet once and for all.
What to do for pain in the right temple?
If the pain in the right temporal zone is not accompanied by additional unpleasant symptoms, as first aid you can take an anesthetic or antispasmodic - Ketorol, Ibuprofen, Citramon, Spazmalgon, Nimesil, all medications should be taken after meals, with a sufficient amount of water. Folk remedies help with minor discomfort.
Medicines
Treatment of cephalgia in the right temporal zone is aimed at eliminating pain and pathologies that caused its appearance.
Main groups of medicines:
- Clonazepam, Phenobarbital - anticonvulsants help eliminate severe pain that occurs with trigeminal neuralgia;
- Sumatriptan, Rapimig are effective drugs against migraines; they should be taken simultaneously with anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Solpadeine, Askofen, Pentalgin are combined painkillers that quickly relieve pain of any intensity;
- Arbidol, Tamiflu - antiviral agents;
- Lisinopril, Felodipine - new generation drugs for the treatment of hypertension;
- Phenotropil, Piracetam - nootropics, help normalize intracranial pressure;
- Torvazin, Klivas - statins, prescribed for atherosclerosis;
- Actovegin, Ascorutin - improve vascular tone;
- Mexidol, Tenoten - help eliminate the manifestations of VSD;
- Persen, Novo-Passit – fight psychogenic pain;
- Diclofenac, Finalgel - ointments to reduce pain in pathologies of the cervical spine.
Read also: “Stone boner” or 5 ways to improve your erection
Arbidol antiviral drug
Additional methods include massage, exercise therapy, acupuncture, psychotherapy, physiotherapy, and health resort treatment.
For pain in the right temple of various origins, nutritionists recommend consuming 150 g of sauerkraut, 15 ml of honey, olive or flaxseed oil daily.
Treatment with folk remedies
If there is pain in the area of the right temple, you need to brew weak green or mint tea, add a slice of lemon and a little honey, sometimes resting for 15–20 minutes in silence helps to quickly cope with the unpleasant sensations.
Simple recipes to combat headaches:
- Brew 220 ml boiling water 1 tbsp. l. chopped lemon balm, leave in a sealed container for half an hour, strain. Drink in small sips throughout the day.
- Pour 400 ml of boiling water over 2 tbsp. l. oregano, strain after 30 minutes, drink 100 ml three times a day.
- Dissolve 15 ml of apple cider vinegar in 1 liter of water, drink a piece of thin cloth in the solution, make a compress on the forehead, hold for 20–40 minutes.
- If there is a shooting in the temple, you need to lightly beat off a fresh cabbage leaf, grease it with liquid honey, and apply it to the sore area.
Oregano decoction will help relieve temple pain
A light massage of the cervical spine and shoulders with rosemary or menthol oil helps to eliminate cephalgia. You can comb your hair slowly with a comb made from natural materials.
Which doctor should I consult if my temple hurts when pressed?
First you need to get a voucher to see a therapist. He will prescribe the standard necessary tests - a biochemical blood test, a general urine test. After receiving the results, the overall clinical picture will become clearer. If leukocytes are elevated, then the cause of pain in the temple is most likely caused by inflammatory processes in the sinuses, lymph nodes, and nasopharynx. This condition is easily treatable.
If the tests are normal, the therapist will give you a coupon for a consultation with an endocrinologist and a neurologist. For patients who find it unpleasant to be in a public clinic and do not have time to wait their turn, there are paid diagnostic centers. There you can make an appointment directly with an endocrinologist, surgeon and neurologist. In this case, tests and procedures will also be paid.
Diagnostics
Since pain in the right temple occurs for various reasons, only a thorough examination will help establish the true cause of the pathology.
Diagnostic methods:
- general, lipid, and biochemical blood tests;
- analysis for determination of thyroid hormones;
- tumor marker test;
- ECG;
- Doppler examination of blood vessels;
- MRI, CT scan of the brain, spine, electroencephalography;
- X-ray of neck, jaw.
During the initial examination, the doctor necessarily measures arterial parameters, listens to the sounds and rhythm of the heart, and invites an ophthalmologist to assess the condition of the fundus.
An MRI of the head can help identify the cause of pain.
How is diagnosis carried out and possible treatment options?
To find out the exact reason why it hurts above the temple when pressed, you will have to undergo a series of studies. If a patient goes to a clinic at his place of residence, he is required to provide all procedures free of charge (everything will be paid for by the insurance company with which the sick person is registered under the medical policy). As mentioned above, if the patient does not have time to wait for an appointment with a coupon in public medical institutions, he can go to private diagnostic centers and undergo diagnostics for a fee.
To diagnose the severity of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, MRI and CT are prescribed. After determining the stage, the neurologist prescribes treatment. These can be either ordinary vitamin-mineral complexes, physiotherapy and exercise therapy, or serious prescription anesthetic drugs. It all depends on how far the pathological condition has gone.
To diagnose vegetative-vascular dystonia, it is enough for a neurologist to compare a number of symptoms. There is no research that could help accurately identify this disease. In some cases, it makes sense to undergo an MRI of the brain vessels. The cost of such a study is about seven thousand rubles in paid diagnostic centers. MRI of cerebral vessels is informative and will help establish an accurate diagnosis not only for VSD, but also for organic brain disorders, intracranial pressure, and encephalopathy.
Diagnosis and treatment
To accurately determine the factors that cause pain in the temples in each individual case, the patient is prescribed a comprehensive examination. Laboratory and instrumental research methods are used, which include:
- Blood test (ESR level and general analysis);
- Scintigraphy;
- Lumbar puncture;
- CT scan;
- X-ray of the appendage of the sinuses and skull;
- MRI of the temporal bone.
After identifying the causes of pain in the temporal region, the specialist prescribes a course of treatment aimed not only at relieving the pain syndrome, but also at eliminating the source. The course of treatment may include anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs and analgesics.
Additionally, the doctor may recommend changing your daily diet, leading an active lifestyle and spending more time outdoors.