Head injury causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention methods
The clinical picture is divided into 3 types:
- cerebral, implies the brain’s response to damage;
- local, depends on the area of damage, the greatest danger is from injuries that affect the medulla oblongata;
- meningeal, characterized by irritation of the membranes of the affected organ.
General cerebral symptoms occur with any type of injury:
- feeling of nausea, possible vomiting;
- painful sensations in the brain area;
- attacks of dizziness;
- poor concentration;
- weakened memory.
Meningeal symptoms indicate a brain contusion and involve intense pain, muscle tension in the neck and back, and vomiting, which is not accompanied by relief.
Local symptoms allow you to determine the area where the blow fell. If the occipital part is damaged, the functioning of the visual apparatus is disrupted. This is explained by the location of the nerve pathway from the eyeballs. Patients complain of blindness and double vision.
Symptoms of brain contusion
The bruise is classified into degrees, depending on the severity of the injury. The lung is characterized by the following symptoms:
- fainting for no more than 10 minutes;
- rapid recovery of the body without medical intervention;
- involuntary movements of the eyeballs;
- decreased sensitivity on the opposite side of the body;
- gradual disappearance of symptoms, absence of complications. In mild cases, the clinical picture completely disappears within 3 weeks.
A moderate bruise is accompanied by the following disorders:
- fainting lasting up to 4 hours;
- dullness of consciousness throughout the day;
- pronounced cerebral symptoms;
- meningeal syndrome;
- disruption of the speech apparatus;
- inability to control the movements of the right or left limbs;
- rapid breathing.
Severe degrees are fatal and are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- dullness of consciousness for several days;
- disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- loss of memories of events that preceded the injury;
- disruption of the visual apparatus;
- constant feeling of anxiety;
- mental excitability.
Symptoms of soft tissue contusion of the head
Injury to soft tissues without brain damage is not very dangerous. This is a common injury. The main symptom is the presence of swelling on the head after a blow. When you palpate it, painful sensations appear. Severe soft tissue bruise is accompanied by redness of the skin, clouding of consciousness, bleeding from the nasal cavity, vomiting, constant fatigue, and increased local temperature.
First aid for head injury
Human life is in the brain, and the brain is in the head. Therefore, head injuries are especially life-threatening. And therefore, any suspicion of a serious head injury is a reason to call an ambulance. As you know, the brain is firmly protected by the bones of the skull. But it is the skull that most often causes brain damage during trauma. When hitting the head (or the head), the brain continues to move by inertia, sharply colliding with the bones of the skull. A concussion occurs.
In this case, the head hurts, dizziness begins, vomiting, the skin turns pale, cold sweat appears, and a short-term loss of consciousness may occur. In especially severe cases, respiratory and cardiac problems occur. Therefore, artificial respiration and cardiac massage may be necessary.
If a skull fracture occurs, bone fragments can damage the brain (traumatic brain injury). A sign of a traumatic brain injury is the leakage of blood or light fluid (CSF) from the nose or ear, and bruising around the eyes. It is very important to know that with skull fractures, symptoms may not appear immediately, but several hours after the injury! Therefore, calling an ambulance if you are hit on the head is mandatory.
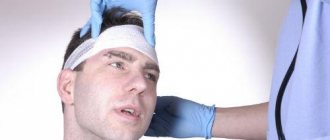
First aid for head injuries must be provided with particular care: avoid unnecessary movements and pressure, use a sterile bandage and antiseptics so as not to introduce infection into the tissues surrounding the brain.
An infection that gets into the wound can penetrate inside the skull and infect the brain and its membranes. As a result, serious diseases such as encephalitis or meningitis can develop.
First aid procedure for head injury
If the victim is unconscious, then it is necessary to check the breathing/pulse and, if they are absent, perform artificial respiration and cardiac massage.
If there is breathing/pulse, then it is necessary to lay the person on his side (to avoid blockage of the airways with the tongue and vomit) and call an ambulance.
If there is consciousness, then simply lay the victim down so that he does not move until the ambulance arrives. A person with a head injury should not be sat down, much less tried to be lifted to his feet - this can dramatically worsen his condition.
If there is no obvious damage to the bones of the skull, cold should be applied to the site of impact (a cloth moistened with cold water or ice in a cloth). This will reduce pain and stop tissue swelling, which leads to increased intracranial pressure.
If there is a bleeding wound on the head, it is necessary to lubricate the skin around the wound with iodine or brilliant green (to prevent infection). Then put a gauze pad on the wound and bandage the head. But this should be done very carefully, especially if there is a suspicion of a skull fracture.
If pieces of bone, metal or other foreign bodies stick out in the wound, touching or removing them is strictly prohibited. This is fraught with serious consequences, as heavy bleeding and tissue damage may begin. In such cases, a bandage using a roller rolled up like a donut is recommended. To do this, roll the cotton wool into a “sausage”, wrap it with gauze or a bandage and place it around the protruding object. The wound is covered with a sterile napkin (in two or three layers) and bandaged.
The victim can also only be transported in a supine position.
Next: Neck injury
First aid
Immediately after the impact, carefully place the child on the bed and carefully examine his head. At the same time, there is no need to rush and fuss so that the baby does not become even more frightened. After all, hysteria can increase intracranial pressure or increase bleeding from a wound.
When a lump forms, apply ice wrapped in a piece of cloth to it. A cold water bottle or a bag of frozen food wrapped in a towel will do. A cooling compress will help relieve swelling and prevent the development of a hematoma. But you need to hold it for no more than five minutes.
If you find a wound, treat its edges with hydrogen peroxide and apply a gauze or cloth swab to absorb the blood. If bleeding does not stop within 10 minutes, call a doctor.
If there is no damage at the site of impact, the child's condition should be closely monitored for at least a week. Moreover, in the first few hours it is better not to put the baby to bed, since the main symptoms of a concussion appear precisely at this time.
Children of the first year of life cannot talk about their health. Consult a doctor if you notice prolonged crying, refusal to eat, restless sleep, or vomiting.
An older child needs to be asked in detail how he fell and where the pain is felt. If the impact is muffled by the carpet, and the fall itself was not dangerous, medical attention is not required. But it doesn’t hurt to watch the baby for a few days to make sure there are no dangerous consequences.
Treatment of wounds and abrasions
First of all, it is necessary to disinfect the resulting wound. This must be done before treatment. Otherwise, an infection may enter the wound and tissue, causing inflammation.
For cuts, wounds and abrasions, proceed according to the following algorithm:
- Washing - the wound is washed under running water, preferably with laundry soap. You can dissolve soap in a bottle of water and wash the wound with the solution. This way, dirt and sand are washed away, and bleeding, if it is small, also stops.
DON'T : Do not use water from open bodies of water (river, lake, pond), as microorganisms live in them that can cause contamination and infection.
If you get a wound in nature and there is no clean water at hand, then you need to wash the wound with any water-based antiseptic - hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine, miramistin, a solution of potassium permanganate or furatsilin. All or any of these products should always be kept in your first aid kit.
- Removing foreign matter and objects. At this stage, foreign bodies are removed from the wound. This is done using tweezers, very carefully.
DO NOT: widen the wound, dig into it, etc. It is better to seek help from specialists.
- Stopping bleeding - if the bleeding does not stop after washing the wound, then it is necessary to press the wound with a napkin or cotton swab, which must first be moistened in hydrogen peroxide. In cases where the wound is deep, accompanied by severe bleeding, peroxide will not help. In such cases, you need to put a clean napkin on the wound and go to the emergency room.
- Treatment of the wound - any antiseptic can be used for treatment. It is desirable that it be water-based.
DO NOT : pour alcohol solutions on wounds and abrasions (iodine, brilliant green, vodka, etc.), as they can lead to burns rather than treatment. Such solutions can only lubricate the tissues surrounding the wound.
- Healing ointments - these compositions must be used to help wounds heal faster. These can be sprays, gels, ointments, jellies. For example, solcoseryl, panthenol, argosulfan, eplan, etc. After the wound is treated, wipe it with a dry, clean cloth and apply ointment.
DO NOT: use bactericidal powders on fresh wounds because they interfere with the process of tightening the edges.
- Applying a bandage - if the injury is small, then a bandage is not required. If small injuries are left open, they heal much faster. In addition, napkins and bandages stick to the scabs, and when the bandage is removed, the scabs come off along with the bandages, and this is not only accompanied by pain, but also interferes with the healing of the wound. For large wounds, bandages are indispensable. This is necessary for protection and application of healing agents, but bandages are applied after the crust has formed and dried. For deep wounds, a bandage is applied so that the edges of the wound are tightened as much as possible.
Types of abrasions and wounds
We encounter cuts and all kinds of abrasions in everyday life. An abrasion is damage caused by mechanical friction against a rough and rough surface, often hard. This may be the result of a fall on asphalt or gravel.
The abrasion may be superficial, in which case only the epidermis is affected. The area turns red and swells a little. If the injury is deeper, then not only the epidermis is damaged, but also the capillaries, which leads to pinpoint bleeding, droplets of blood are released, but most importantly, the person experiences severe pain.
A cut is a shallow cut wound. With such an injury, either only the skin is damaged, or the layer of fatty tissue is affected. In such cases, bleeding occurs, the intensity of which will be determined by the depth of the cut and the number of damaged vessels.
Wounds can be superficial or deep, and large vessels can even be damaged. In this case, severe bleeding occurs. Wounds may be accompanied by bruises and bruises. In addition, dirt, various objects, earth, etc. often get into the wound.
Consequences of injury
If a child hits his head, in addition to bleeding, he may also experience the following symptoms:
- nausea;
- drowsiness;
- loss of appetite;
- headache.
The appearance of such symptoms should alert adults; they indicate the occurrence of neurological problems (concussion, hemorrhage). The child must be taken to see a specialist within 24 to 48 hours after he hits his head. The child must undergo a full examination, which includes:
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Ultrasonography.
- Computed tomography.
These diagnostic methods will help the doctor determine the degree of damage, create an appropriate course of treatment and rehabilitation.
Types of head injury
Head injuries are usually divided into 2 types:
- open. They are characterized by the presence of damage to soft tissues and skull bones. With open injuries, an inflammatory process may occur inside the membranes and brain tissue. First aid for an open head injury involves calling an ambulance. If a child breaks his head, he needs hospitalization;
- closed. This type of injury is characterized by the formation of swelling; bone and soft tissue remain unharmed. First aid for such damage is to relieve swelling by applying cold to the injured area. Cold (wet towel, ice pack) should be maintained for 5 - 10 minutes.