Stroke is a clinical syndrome represented by general cerebral and focal neurological disorders. It develops suddenly as a result of an acute cerebrovascular accident, persists for at least 24 hours or ends in death at this or earlier time. There are ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes. Ischemic strokes occur 5 times more often than hemorrhagic strokes. In addition, so-called complex strokes (mixed strokes, hemorrhagic infarctions) are possible.
Coma during stroke mainly develops in the case of hemorrhagic stroke. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital provide emergency care to patients admitted in a coma, using individual treatment regimens with modern drugs.
For the effective treatment of patients with stroke, the neurology clinic has all the conditions:
- modern diagnostic equipment with high resolution;
- the high scientific potential of the clinic, which employs professors and doctors of the highest category;
- effective high-class life-support equipment;
- comfortable conditions for patients’ stay and European service;
- psychological assistance to relatives and patients after recovery from a coma;
- innovative rehabilitation techniques.
All cases of patients with stroke entering a coma are discussed at the Expert Council. The decision on treatment methods is made collectively. All this together increases the chances of recovery for patients with stroke admitted in a coma to the Yusupov Hospital. Thanks to the early start of rehabilitation measures, many patients completely restore lost functions and return to normal life.
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital diagnose stroke in 3 stages:
- initially distinguish stroke from other conditions associated with brain damage;
- at the second stage, the nature of the stroke itself is determined - hemorrhagic or ischemic;
- in conclusion, the area of vascular damage and the pathogenesis of cerebral infarction in ischemic stroke or the localization of hemorrhage and possible mechanisms of its development in hemorrhagic stroke are clarified.
Difficulties in diagnosing a stroke arise in cases where the patient has a pronounced disorder of consciousness - coma, which does not allow conducting a survey and finding out how the disease developed. In this case, the diagnosis at the first stage is based solely on the data of the neurological examination. Of the focal neurological symptoms in a patient in a comatose state caused by a stroke, the following symptoms are often found:
- paresis of gaze or floating movements of the eyeballs;
- anisocoria (different pupil sizes in the right and left eyes)
- strabismus (squint);
- “flabby” upper eyelid;
- suppression of the corneal reflex;
- facial asymmetry;
- sail sign (“bloating” of the cheek when breathing);
- hemiparesis or hemiplegia (complete or partial impairment of the motor function of the limbs on one side of the body according to the central type).
There is no contact with a patient in a coma; the detection of a rotated foot in a patient lying on his back, decreased tone or muscle spasm in the extremities is of certain importance in the diagnosis of hemiparesis. Neurologists determine the following symptom: in a patient lying on his back, passive flexion of the head is accompanied by flexion of the lower limb in the hip and knee joints on the side of the pathological focus, and on the side of hemiplegia the leg remains in the same position.
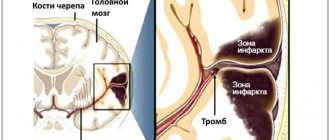
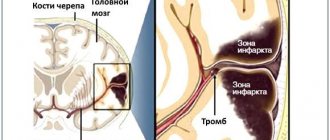
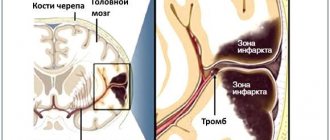
The most difficult and responsible task of the second stage is the accurate and rapid diagnosis of the nature of the stroke, since in the acute period of the disease, further treatment tactics and the prognosis for the patient largely depend on this. After ensuring the functioning of vital organs, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital perform magnetic resonance imaging on a patient with a stroke. It is especially informative in case of hemorrhagic stroke, as it allows you to quickly determine the nature of the stroke, the location of the hemorrhage and the size of the affected area.
Symptoms of coma during stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by a predominance of cerebral symptoms in the initial period of the disease. Next, focal neurological symptoms rapidly develop, often leading within a few minutes to a state of coma. This is especially common with hemorrhage in the cerebellum and brain stem. The following symptoms are characteristic of a hemorrhagic stroke of the subarachnoid hemorrhage type:
- relatively young age of the patient;
- sudden onset of the disease during vigorous physical activity;
- severe headache with loss of consciousness;
- emotional arousal;
- rise in blood pressure, and subsequently body temperature;
- often absence of focal neurological symptoms.
In 100% of cases, blood is found in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients.
Coma after a stroke is characterized by the following symptoms:
- lack of consciousness;
- spontaneous urination and defecation.
- lack of response to external stimuli - light, touch, sounds, pain.
In a coma as a result of a hemorrhagic stroke, the patient suddenly loses consciousness, the face becomes cyanotic, breathing is noisy, the pupils are of different sizes, and they react sluggishly to light. In the case of coma that develops in the presence of an ischemic stroke, loss of consciousness, a sharp decrease in blood pressure, slowing of the pulse, and cardiac arrhythmias are observed. The patient is pale, covered in cold, sticky sweat, and has shallow breathing.
Doctors distinguish 4 degrees of coma after a stroke:
- Grade I is characterized by minor brain damage. The patient experiences lethargy or complete loss of consciousness. Reflex functions are preserved. The prognosis is encouraging;
- II degree: noisy intermittent breathing, deep sleep in the absence of the slightest reaction to pain, loss of skin reflexes, convulsions;
- III degree: loss of consciousness, drop in blood pressure and decrease in body temperature;
- IY degree is considered incompatible with life due to the death of a significant part of the brain.
Prevention
The main preventive measure in this case is the prevention of extensive cerebral stroke. You need to remember 5 simple rules:
Blood pressure should be under control. If possible, purchase a tonometer for home use. This is especially true for older people. Semi-automatic or automatic devices are more suitable for them. Blood pressure should be measured three times a day. Record the results.
Doctors recommend reducing the amount of cholesterol. To do this, you need to change your diet and add exercise.
- Why does coma occur during a stroke and are there any chances?
As prescribed by your doctor, you can take medications to prevent the formation of blood clots. They are especially needed for those who have undergone surgery or suffer from vascular pathologies, such as varicose veins.
Also, timely consultation with a doctor will protect you from stroke and, as a result, from coma. None of the alarming symptoms should be ignored.
Stages of medical care for patients in a coma after a stroke
Patients in a state of coma that has developed as a result of a stroke are provided with medical care at the prehospital stage by emergency physicians:
- restore airway patency;
- provide oxygen through an air duct or transfer the patient to artificial ventilation;
- prevent aspiration (foreign bodies entering the respiratory tract).
When there is a sharp decrease in blood pressure, drugs are used that have a vasopressor effect (alpha-adrenergic agonists) and improve myocardial contractility (cardiac glycosides), drugs that replenish the volume of circulating fluid (crystalloid solutions and low molecular weight dextrans). If the patient develops seizures, tranquilizers and antipsychotics are used. If necessary, barbiturates and inhalation anesthesia are used.
When a patient is admitted to the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, doctors take emergency measures:
- maintaining an optimal level of oxygen supply;
- monitoring of blood pressure and correction of cardiac activity;
- administration of pressor amines (1 ml of 1% mesotone solution intramuscularly or subcutaneously, caffeine, corticosteroids;
- constant monitoring and correction of acid-base balance in the body;
- control of swallowing (in the presence of dysphagia, a nasogastric tube is inserted to prevent aspiration bronchopneumonia and ensure adequate nutrition for the patient);
- control of the condition of the bladder and intestines.
There are currently no specific drug treatments for hemorrhagic stroke. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital are taking measures aimed at reducing the usually high intracranial pressure. At the same time, they normalize blood pressure, the state of the blood coagulation system and the permeability of the vascular wall, and support the activity of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. In the absence of contraindications, surgical interventions are performed at partner clinics. In the case of an ischemic stroke, patients are brought out of a coma and the restoration of lost functions is immediately begun using methods of drug therapy and physical rehabilitation.
If signs of coma appear, the patient should be placed on a horizontal surface, turn his head to the side and call an ambulance. Call and alert the clinic staff about the current situation. The Yusupov Hospital employs professors and doctors of the highest category who use modern equipment and medications that allow them to do everything possible to bring a patient out of a coma after a stroke.
Treatment prices:
| Service | Price, rub) |
| Types of therapies | |
| Standard detoxification therapy | 3 500 ₽ |
| Double Detox Therapy | 6 000 ₽ |
| Enhanced Detoxification Therapy | 7 500 ₽ |
| Maximum detoxification therapy | 9 500 ₽ |
| Quick sobering up at home | 7 500 ₽ |
| Hospital at home 1 day | 22 000 ₽ |
| Advanced hospitalization | 15 000 ₽ |
| Treatment in hospital | |
| Accommodation | |
| Economy chamber (6 beds) | 2 000 ₽ |
| Standard room (4 beds) | 3 000 ₽ |
| Increased comfort (2 seater) | 5 500 ₽ |
| VIP chamber (1 person) | 12 500 ₽ |
| Individual post 24/7 | 5 000 ₽ |
| Medical and social rehabilitation 21 days | 140 000 ₽ |
| Service | Price, rub) |
| Initial consultation with a narcologist | for free |
| Consultation with a psychologist | 3 000 ₽ |
| Psychiatrist consultation | 5 000 ₽ |
| Coding at home Torpedo | 7 500 ₽ |
| Express output and encoding (doublet) | 13 500 ₽ |
| Coding using the Dovzhenko method | 12 000 ₽ |
| Hypnosis classic session | 13 000 ₽ |
| Ericksonian hypnosis session (NLP) | 8 000 ₽ |
| Coding method Torpedo | 5 500 ₽ |
| Double block | 8 000 ₽ |
| Esperal injection for 1 year | 9 900 ₽ |
| Tetlong for 3 months | 10 500 ₽ |
| Esperal gel for 1 year | 15 000 ₽ |
| Selincro course of therapy | 12 500 ₽ |
| Implantation of Disulfiram for 1 year | 18 000 ₽ |
| Vivitrol injection for 1 month | 26 000 ₽ |
| Naltrexone stitching for 3 months | 35 000 ₽ |
| Neuroimplantation Prodetoxon for 6 months | 47 500 ₽ |
| Narcopsychotherapy session | 50 000 ₽ |
| Neutralization of encoding | specify |
| Psychodiagnostics / pathological diagnostics | 7 500 ₽ |
| Psychotherapy session | 5 000 ₽ |
| Family psychotherapy | 6 000 ₽ |
| Outpatient rehabilitation in Moscow | 33 000 ₽ |
Expand
ANONYMOUS TREATMENT OF DRUG ADDICTION
How to get to us
A team of doctors will quickly arrive at your address, carry out the first resuscitation measures and urgently deliver the victim to the intensive care unit of a drug treatment clinic.
Article verified by an expert
Terekhova Anna Vladimirovna
psychologist-consultant on socio-psychological work with addicted clients and their families. More than 10 years of experience.
Similar articles:
How safe is IQOS?
Is it possible to restore the nervous system after spice?
Manipulation of drug addicts and alcoholics. How to resist manipulation
Methadone: composition, effect and consequences
Phenibut addiction
One comment on ““Drug coma””
- Alexandra:
June 29, 2021 at 10:57 pm
Drug coma is a condition characterized by depression of the central nervous system caused by drug use. Coma is often a consequence of taking opiates, barbiturates, salts and spice. Due to the powerful effects such psychoactive substances have on the body, even in microscopic doses, an overdose is more than likely.
Answer
How is it determined that coma has turned into death?
Modern medicine is able to maintain breathing, cardiac activity and provide nutrition for a long time to a person in a deep coma. Death is declared when blood flow to the brain stops and irreversible pathological changes occur.
These changes are diagnosed using computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. The absence of any brain activity is determined by electroencephalography methods, and cessation of cerebral circulation is recorded angiographically.
Based on the totality of the obtained indicators, death is diagnosed and, in agreement with relatives, life support equipment is turned off.
Question and answer
Does it happen that a patient comes to his senses after he has been declared brain dead?
Such cases do happen. For example, on December 23, 2011, doctors definitely and objectively confirmed the brain death of 21-year-old American student Sam Schmidt, who fell into a deep coma after an accident. Sam's parents were advised to think about consenting to the removal of their son's organs for transplantation, and an hour later a consultation was to be held on the issue of turning off the equipment that supports life in his body. Suddenly Sam moved his fingers, began to respond to calls and woke up.
How to get to the rehabilitation center in Aksakovshchina?
From the metro station "Pushkinskaya", "Kamennaya Gorka" by minibus 1203 TK, from the railway station, metro station "Kamennaya Gorka" - by minibus 1500 TK.
Do the Belarusian media publish information about those who came out of a coma, about what they felt?
The most recent publication with such interviews was on the TUT.BY website in the “Health” section on May 20, 2021.
Danger of condition
Coma is dangerous because the brain suffers from hypoxia. At the same time, its cells die. The primary task is to resume its blood circulation and restore functions. The patient undergoes detoxification measures. In case of uremic type, hemodialysis may be prescribed. When hypoglycemic - glucose.
If intoxication begins, shock develops, and brain tissue experiences energy deficiency. The consequences may be as follows:
- The condition is getting worse.
- Lethality sets in.
- Energy deficiency increases, oxygen starvation of the central nervous system increases, and neurons die. Even if such a patient survives, the risk of disability is high.
Bottom line
We have given the most common classification. Coma is an extremely serious condition. Cerebral circulation is seriously impaired. Extensive swelling may develop. This is a direct threat to life. Nobody knows how long it will last. Doctors can only eliminate the cause and stabilize the condition. Unfortunately, there are frequent cases of death due to the development of coma of the 3rd and 4th degrees. The risk group is the elderly. They are more likely to develop coma. At the same time, their body reacts worse to treatment. In infants, coma can develop with prolonged umbilical cord entanglement.
Movies lie
In May 2006, the journal Neurology published an article by the American doctor E. Wijdix entitled “Depiction of coma in modern feature films.”
A very unexpected topic for a serious medical journal that publishes the results of scientific research in the field of human brain activity and its diseases. It is clear that viewers do not expect complete life truth from a film, even a realistic one; film critics do not evaluate a work of art by how accurately a medical episode corresponds to the description of the disease in a textbook; what is more important is the symbolic level of the image, a certain global statement of the author. For example, in the film “Talk to Her,” the outstanding Spanish director Pedro Almodovar tells the story of a young talented ballerina who not only awakens after a many-year coma, but also almost completely recovers. At the end of the film, a girl comes to the theater to watch her favorite ballet, leaning only lightly on a cane. Dr. Wijdix harshly criticizes the film for the implausibility of such an outcome, but in fact this is the director’s deeply labored message about the great transformative power of love.
Meanwhile, Dr. Wijdix's concerns are not unfounded. Having analyzed 30 films produced between 1970 and 2004, he came to the conclusion that only in two patients in a coma are shown realistically, in the rest they are beautiful in appearance, like the heroine of the fairy tale “Sleeping Beauty,” and immediately after emerging from a coma they become cheerful and active, and even perform feats, defeating superior enemy forces (as in the American TV series “24 Hours”). Doctors in such films are depicted as caricatures and do not inspire any credibility.
But the most important thing was something else: out of 72 non-medical respondents, 28 viewers, that is, 39%, reported that when making decisions regarding loved ones who find themselves in a coma, they would rely on knowledge gleaned from watching movies. And this is a worrying sign.
It is difficult to say how representative this result is, but it can be assumed with a high probability that the “sleep of reason” is mythologized for most of us, and when we find ourselves in a severe stressful situation, if a misfortune has happened to a person close to us, we do not really know what to expect, but what to hope for and how to act.