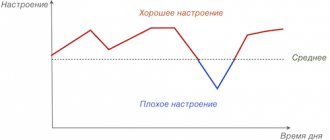
Frequent emotional overload and repeated stress can often lead to the fact that the nervous system ceases to work stably. As a result, nervous disorders of varying severity occur. Often people try to wait until all the symptoms go away on their own, but often the wait-and-see tactic leads to a worsening of the situation and the development of the disease. The difficulty of contacting a specialist for such disorders is that several highly specialized doctors deal with the nervous system. To figure out which of them treats in each specific case, you need to find out what is within its competence.
Which specialists will help?
Dysfunctions of the nervous system can be caused by a variety of reasons and have completely different manifestations. Specialists dealing with such diseases are divided into 3 main categories: neurologist, psychotherapist and psychiatrist. All of them must have a diploma of higher medical education, after which they must complete an internship within 2 or 3 years and begin independent practice.
Neurologist
A neurologist is a specialist whose field of activity covers all areas of neurology: prevention, examination and influence on the central and peripheral parts of the nervous system. Neurology studies in detail the anatomy, functioning and treatment of the nervous system.
The term “neuropathologist,” which was actively used in Soviet medicine, also belongs to this category. Now it is considered outdated and incorrect, but sometimes out of habit it is used by individual doctors.
Psychotherapist
Psychotherapist - a doctor who deals with patients with mild or moderate mental disorders is called a psychotherapist. A prerequisite for his practice is a detailed study of psychotherapy.
The psychotherapist's field of activity is mental disorders caused by childhood traumas, severe stress, or due to genetic predisposition. As a rule, patients treated by this doctor do not have organic or anatomical brain injuries, but exhibit only psychological disorders.
The question often arises as to whether there are differences between a psychologist and a psychotherapist. There is a difference, and it lies in the fact that a psychologist does not have a higher medical education, and therefore can only advise patients, while a psychotherapist has the right to make a diagnosis and prescribe a course of treatment.
Psychiatrist
The scope of his activity is almost the same as that of a psychotherapist, but the psychiatrist also works with cases of the highest severity. A doctor who has studied for 6 years at a medical university and spent 2 years in an internship or is engaged in the activities of a graduate student has the right to work as a psychiatrist.
If a psychotherapist’s treatment methods are predominantly based on speech, and medications are used only as an aid, then the psychiatrist primarily carries out drug treatment and active non-drug therapy. Such methods cause stimulation of brain activity.
What diseases does a neurologist treat?
- cardiovascular - hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke;
- infectious - damage to the central nervous system due to syphilitic and AIDS infections, herpetic encephalitis;
- degenerative - Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases;
- traumatic - bruises of varying severity, concussions, diffuse damage to axons in traumatic brain injuries;
- pathologies of the cerebrospinal fluid system - persistent increase in intracranial pressure, hydrocephalus;
- demyelinating - Guillain-Barré syndrome, multiple sclerosis;
- helminthiasis - opistrochiasis, echinococcosis;
- oncological - gliomas, meningiomas;
- mycotic - candidiasis, cryptococcosis of the central nervous system;
- epileptic - primary (without involvement of the brain matter in the pathological process) and symptomatic epilepsy caused by traumatic brain injury, tumors;
- congenital - cerebral palsy.
Reasons for contacting
Depending on the health of a particular person, his temperament and the type of personal reactions, the symptoms of nervous disorders can be very individual. But there are a number of signs that are inherent in most cases:
- long-term sleep disturbance;
- increased irritability and neuroses;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- severe unreasonable anxiety;
- constant desire to sleep;
- a sharp decrease in ability to work and activity;
- absentmindedness;
- difficulty concentrating on a specific action or object;
- noticeable deterioration of short-term memory;
- obsessive thoughts;
- panic attacks.
Often all these signs do not add up to the overall picture and are ignored for a long time by a person who needs the help of a doctor. All of the above signs can be perceived as a change in mood, emotional exhaustion, moral fatigue, etc. But for a specialist, a combination of these signs will indicate a certain disease.
Over time, physical manifestations of the disease are added to the above conditions:
- dizziness;
- severe shortness of breath;
- neuralgia;
- feeling of strong heartbeat;
- difficulty swallowing and enlarged thyroid gland;
- digestive disorders (constipation or diarrhea, stomach pain, flatulence);
- lack of appetite;
- increased body temperature after stress;
- surges in blood pressure.
The most common symptom that accompanies most mental disorders is a severe headache that occurs periodically. In severe cases, it is combined with fainting.
How does an appointment with a neurologist proceed?
The initial consultation includes a survey and neurological examination of the patient. During the conversation, the doctor listens to complaints and asks additional questions. During the examination, reflexes and the presence of external signs are checked - symmetry of the shoulders and limbs, disorders of posture and motor ability. For a professional neurological examination, special instruments are used, the set of which depends on the nature of the disease. It could be:
- hammer (reflexes);
- needle, brush/cotton wool (deep and superficial pain sensitivity, respectively);
- tuning fork (susceptibility to vibration);
- compass (sensitivity at different points of the body);
- pens, pencils, keys (object sensitivity);
- dynamometer (muscle strength measurement).
Causes of nervous disorders
Most people believe that mental and neurological disorders are caused solely by nervous breakdowns and difficult emotional conditions. This is not true at all, the reasons may be:
- injuries resulting in damaged nerves (most often head injuries);
- acute or chronic hypoxia, leading to oxygen starvation of the brain and other tissues of the nervous system;
- osteochondrosis;
- prolonged overheating or hypothermia of the body (in this case, the degree of damage directly depends on the time of exposure to high or low temperatures);
- poisoning with neurotropic substances that selectively affect cells of the nervous system;
- factors that have an aggressive effect on the body - electric current, prolonged vibration, electromagnetic field;
- metabolic disorders with damage to the central or peripheral parts of the brain;
- suffered serious illnesses (most often of the endocrine system);
- hereditary factors - depression, bulimia or anorexia, schizophrenia, alcoholism, severe neuroses or Alzheimer's disease in one of the blood relatives;
- the presence of tumors in the body;
- inflammatory or parasitic diseases of the brain.
Why you shouldn’t bother yourself with such questions
When we organized our clinic, we proceeded from the fact that our body is one system where everything is connected. The nervous system controls the entire body, it gives us movement, sensitivity, emotions, thinking and consciousness. And in diseases of the nervous system, manifestations will be in all areas: motor, sensitive, mental.
We gathered a team of psychiatrists, psychotherapists, neurologists and organized a hospital where we can fully provide assistance for mental disorders and neurological diseases, as well as for conditions where both of these areas have been affected by the disease. We help both children and elderly patients.
With us, in one place, you can undergo an examination and, if necessary, receive treatment for diseases of the mental, psychosomatic and neurological spheres. Our specialists: psychiatrists, psychotherapists, neurologists, psychologists, therapists, rehabilitation specialists.
The modern system of medical care has divided diseases of the nervous system into different areas. Psychiatry separately, psychotherapy separately, narcology separately, neurology separately, rehabilitation separately, hospitals separately, dispensaries and clinics separately, psychological assistance - in itself.
Our clinic successfully combines all these areas, so it can safely be called:
- neurological,
- psychotherapeutic,
- neurological, psychoneurological dispensary,
- hospital for crisis and borderline conditions,
- center for the treatment of mental illness, a place of psychological support,
- a children's psychiatric hospital, a clinic for the treatment of age-related changes in the nervous system,
- family clinic...
... and other and other names.
How to get an appointment
If the patient understands which doctor to contact, then this must be done as soon as possible. If the patient has doubts, then it is advisable to go to a therapist, who will identify a specialist.
In order to choose a qualified doctor, you need to pay attention to the following features:
- sufficient practical experience in the treatment of nervous disorders;
- an integrated approach to determining the patient’s condition;
- It is desirable to have scientific articles or works in the area that the patient is faced with;
- sufficient initial consultation time (at least 30 minutes).
At the appointment, the doctor will determine the further direction of the examination, if necessary. Having all the necessary data, he will be able to make a diagnosis and prescribe drug or non-drug treatment. If necessary, the patient will be recommended a course of treatment in a hospital.
Consultations with a doctor online Taking care of your health is a life priority for everyone.
Communicate with doctors online and receive qualified assistance without leaving your home. Try it Please note! The information on this page is provided for informational purposes only. To prescribe treatment, you must consult a doctor.
Development of a treatment regimen
When selecting a therapeutic course, the psychoneurologist takes into account the patient’s anamnestic data. Usually the specialist prescribes:
- Medications:
- neuroleptics (Azaleptin, Ariprizole, Quentiax);
- tranquilizers (Phenazepam, Diazepam, Hydroxyzine);
- antidepressants (Fevarin, Humoril, Amitriptyline);
- sedatives (Persen, Afobazol);
- vitamins (Cyanocobalamin, Thiamine, Pyridoxine).
- Physiotherapeutic measures aimed at reducing the negative impact of irritating factors (electric sleep, circular shower, darsonvalization, electrophoresis).
- Massage (manual segment or acupressure, mechanical).
In addition, the doctor recommends that the patient follow a diet and sleep schedule, spend frequent time in the fresh air, and perform therapeutic exercises.
Signs of neurological diseases
Diseases of the nervous system do not appear immediately, but develop slowly and gradually. They lead to dangerous, severe and irreversible consequences - paralysis, disability, loss of intelligence. As a person ages, this risk only increases.
With peripheral paralysis, muscle contractility is lost, a person cannot move independently, he does not control his own. Paresis is a partial loss of motor activity in the muscles. In both conditions, muscle atrophy develops, muscle volume decreases, tendon reflexes are absent, and muscle tone is lost.
Central paralysis is manifested by increased muscle tone and increased speed of tendon reflexes. When the basal ganglia, which are located in the white matter of the brain, are damaged, the regulation of motor and autonomic function occurs, which affects the motor skills of movements. They slow down, become involuntary, trembling (tremor) appears, and muscle tone changes. If the cerebellum is damaged, coordination of movements is impaired, speech becomes unclear and slow, and the limbs weaken.
Make an appointment
When to contact a neurologist
One of the most common symptoms in which you should consult a neurologist is headache. It can be a consequence of overwork, constant stress, increased anxiety, atherosclerosis, micro-stroke, etc. Almost always, this condition is tolerated “on your feet” and is eliminated with painkillers. Such an approach can lead to negative consequences, since a headache is a signal from the body about the development of pathology. There are many diseases, a symptom of which is headache. Only a qualified neurologist will be able to determine the root cause of the ailment and select adequate treatment.
You should also make an appointment with a neurologist if you have the following symptoms:
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- periodic darkening or blurriness before the eyes;
- sleep disturbance (insomnia, nightmares, sleepwalking);
- muscle pain;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- unsteadiness of gait;
- speech disorder;
- visual impairment;
- loss of consciousness;
- single or repeated convulsive seizure;
- osteochondrosis;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system.
It will be useful to visit a neurologist for prevention for those who are exposed to factors that provoke neurological pathologies:
- frequent stress;
- work that requires increased attention;
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse);
- old age (after 60 years the risk of developing dementia increases);
- hereditary predisposition to neurological diseases.
The patient should consult a neurologist if his motor reaction has slowed down, a feeling of stiffness in the body, trembling in the arms and legs, or convulsive muscle contractions has appeared. Pain in the back, shoulders, arms and legs, decreased sensitivity in some areas of the skin, numbness and tingling also require examination by a neurologist. If memory deteriorates, changes in sense of smell, or taste disturbances, a consultation with a good neurologist is necessary. This doctor will also help patients suffering from unreasonable attacks of fear, panic, rapid heartbeat, chills or a feeling of heat throughout the body.
Characteristic symptoms
Nervous system disorders are distinguished by a large number of ailments, each of which has its own symptoms. However, there are also general signs that can help diagnose a neurological problem:
- headaches and migraine attacks;
- speech disorders;
- urinary incontinence;
- problems with swallowing;
- pain in the muscles of the legs, lower back, thoracic region;
- imbalance, fainting;
- depressed state, sleep disturbances;
- convulsions;
- numbness in various parts of the body;
- fast fatiguability;
- noise in ears;
- loss of orientation in space;
- memory losses.
Diagnostic methods
Examination using instrumental and (less often) laboratory methods is an integral part of the diagnosis of neurological diseases and their complications. The choice of a specific technique is carried out taking into account the nature of the violations. In modern diagnostics, one or more studies from the following list may be used:
- magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI. The procedure is performed with or without contrast; a contrast tomogram has more accurate results;
- computed tomography, or CT scan, of the brain;
- echoencephalography (ECHO-EG), positron emission tomography (PET/CT);
- angiography of cerebral vessels;
- X-ray, ultrasound of the spinal column;
- myelography;
- ultrasound with Doppler (Doppler scanning);
- electroneuromyography (EEG);
- gamma encephalography (EEG).
For radiculitis and intervertebral hernias, a lumbar puncture may be prescribed. A number of diseases require blood and urine tests.