What is asthenic syndrome, asthenia?
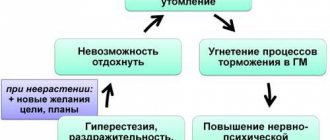
Asthenic syndrome is a syndrome characterized by a state of mental irritable weakness, rapid depletion of nervous processes, unstable mood, impatience, decreased performance for prolonged physical activity and mental stress, intolerance to bright light, loud sound, strong smell, emotional lability, and sleep disturbances. The term " asthenic syndrome " comes from the Greek word "astheneia", which means "weakness, impotence". Asthenic syndrome has synonyms - chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS, CFS), asthenia , asthenic reaction , asthenic condition , asthenia of the nervous system .
Asthenic syndrome in children: symptoms
What is the clinic for asthenia in children? Asthenic syndrome in children has characteristic symptoms : tearfulness, moodiness, increased drowsiness, fatigue, fatigue, excitability, overexcitability, poor sleep, motor disinhibition, dizziness. At school, gymnasium, and lyceum, children remain productive only in the first lessons and in the first half of the school hour. Children with asthenia or asthenic syndrome have poor attention, they are often distracted in class, attention is depleted, immunity decreases, and childhood diseases occur. Children often make mistakes, miss letters, underwrite letters, swap letters, double letters, underwrite words, forget to put commas or periods, and make incorrect indentations. With asthenia, with asthenic syndrome, autonomic reactions and autonomic disorders are often observed: acrocyanosis, hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating), poor appetite, discomfort, pain, unpleasant sensations in the heart (in the heart area).
Asthenic syndrome in adults: symptoms, signs, manifestations of asthenia
What is the clinic for asthenic syndrome in adults, men and women? Asthenic syndrome in adults (men, women), in adolescents (boys, girls) has typical symptoms : irritability, restlessness, sleep disturbance, intolerance to loud sound, fatigue, mood swings, bad mood (low, depressed mood), poor mental tolerance and physical activity, fatigue, decreased self-control, intolerance to bright light, impatience, inappropriate behavior, intolerance to strong odors, poor willpower, irritability, excitability, melancholy, apathy. The person feels tired, but often continues to do something. Lethargy can occur without exercise and does not go away even after rest. Sometimes in old age there is a decrease in memory, headache, fatigue from life, mentism (involuntary flow of thoughts), tearfulness, increased tearfulness, hyperesthesia, tearfulness (unreasonable crying for any minor reason), whims (moody). They are also characterized by “harassing”, “harassing” relatives, dissatisfaction with work, life, financial condition, and people around them.
Signs of other psychogenic neurotic disorders
Obsessive-compulsive neurosis actually includes obsessions (obsessions) and phobias (obsessive fears).
Obsessive disorders are represented by obsessive thoughts that are stereotypically repeated and extremely painful for the patient. Compulsions are repeated behaviors that purport to prevent harmful or dangerous events that are extremely unlikely to occur. The patient is formally critical of ritual actions, but cannot overcome them on his own. Phobic disorders include fear of certain situations. The patient is critical of his own phobic experiences, understands their alienness, strives to overcome them, but cannot free himself from them. The following obsessive fears are encountered:
- Agoraphobia is a persistent fear of being in crowds of people, fear of public places (workplaces, shops, streets, open squares, theaters, concert halls), and independent long trips on various types of transport;
- Claustrophobia – fear of closed spaces;
- Thanatophobia – fear of death;
- Cancerophobia – fear of cancer;
- Cardiophobia is the fear of severe heart disease.
Hysterical neurosis includes conditions that arise in patients with an obvious or objectively proven conflict situation (violation of interpersonal relationships, insoluble problems), even if the patient denies it.
More often, such conditions arise and stop suddenly. Some of them (anaesthesia and paralysis) gradually develop and persist for a long time. There is no connection between the mental disorder and neurological or physical disorders. The “benefits” for the patient and the clearly psychogenic nature of the disorders raise suspicions about attitudinal behavior. These specific psychopathological manifestations are disease states with specific pathogenetic mechanisms. Hysterical amnesia is manifested by impaired memory for recent stressful events, accompanied by depressive feelings. Memory loss is often partial. It is not caused by intoxication or organic brain damage.
Hysterical movement disorders reflect the patient’s subjective ideas about an alleged neurological disease, but the nature of the complaints does not correspond to real organic disorders. The presence of movement disorders allows the patient to avoid a difficult psychotraumatic situation. The intensity of the manifestation of disorders is closely related to the number of people who are present near the patient. Patients use the violations themselves to attract the attention of others.
Hysterical neurosis can be manifested by the following motor disorders:
- convulsive seizures;
- paralysis (complete and partial);
- hyperkinesis (excessive violent motor acts that occur against the patient’s will);
- contractures (stiffness of joints);
- mutism (a condition when the patient does not answer questions and does not even make it clear that he hears them);
- hysterical stupor (depressed mental state, manifested in silence, inhibition, inactivity).
The patient may experience convulsions similar to epileptic seizures.
All these disorders are not caused by organic damage to the organ or other disease. There are no signs such as tongue biting, involuntary urination, consequences of sudden falls, or loss of consciousness. Sensory disturbances during hysteria are manifested by a variety of sensitivity disorders:
- anesthesia (loss of sensitivity to pain);
- hyposthesia (decreased pain sensitivity);
- hyperesthesia (increased pain sensitivity);
- paresthesia (sensation of itching, burning, crawling).
Sensory disturbances often correspond to areas of innervation.
Patients experience bright, unusual hysterical pains. There is loss of hearing and vision. Depressive neurosis is a condition that is determined by the depressive triad: decreased mood, mental and motor retardation. Symptoms of the disease are moderately expressed, affect the patient’s behavior, but allow the individual to maintain social adaptation. Patients' ability to concentrate and self-esteem decreases. Night sleep disturbances and anxiety are typical.
Make an appointment
Asthenic syndrome, causes of asthenia
Asthenia and asthenic syndrome have certain causes of development. What are the main reasons for the development of asthenia and asthenic syndrome?
- Adynamia, physical inactivity.
- Great physical or mental stress, overload.
- Exposure to an electromagnetic field (EMF) is electromagnetic radiation.
- Excitement, stress, worry, conflicts.
- Hypertension, hypertension, hypertension, high, high blood pressure.
- Depression, depressive state.
- Working on a computer for a long time, watching TV, talking on a cell phone, using devices such as microwave ovens (microwave ovens), tablets, tablets, smartphones.
- Alcohol abuse, alcoholism.
- Intoxication.
- Infectious diseases, STIs.
- Coronary heart disease (CHD), angina pectoris, myocardial infarction.
- Constitutional characteristics of a person.
- Weather sensitivity, intolerance to changes in atmospheric pressure, intolerance to magnetic drills, increased solar activity (solar flares).
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Neurosis, neuroses.
- Improper organization of work, overtime at work, irregular work schedule.
- Nervous diseases, diseases of the nervous system.
- Organic diseases of the brain, central nervous system, central nervous system.
- Obesity.
- Human psychotype (psychological type of the nervous system).
- Overload of the nervous system in educational institutions (institute, university, academy, school, gymnasium, lyceum, technical school, college, kindergarten, courses).
- Poor emotional atmosphere at work.
- Poor nutrition, anorexia.
- Post-traumatic arachnoiditis.
- Mental illnesses.
- Psychosis, psychoses, psychopathy.
- Somatic diseases.
- Chronic diseases.
- Traumatic brain injury, traumatic brain injury, concussion, brain contusion, brain compression.
- Schizophrenia, initial stage.
Treatment
When treating asthenic depression, the following principles are observed:
- Stopping an exacerbation (episode).
- Stabilization of the condition.
- Long-term (individual) anti-relapse (preventive) therapy.
The extent of therapeutic intervention depends on the severity of the episode, the patient's age, and his general health (comorbidities). First of all, it is necessary to exclude the presence of a high suicidal risk.
At home
In the absence of psychotic complications (hallucinatory phenomena, delusions, catatonia), treatment can be carried out on an outpatient basis. Indications for hospitalization are determined by the doctor in a personal conversation. Treatment at home is effective only if the recommendations are strictly followed, with which loved ones can help.
Questionable methods, herbal infusions and folk remedies reduce the quality of the events. They won’t do anything better, but they can delay the onset of remission and lead to aggravation of the clinical picture. In addition, some components of dietary supplements or herbal preparations often cause side effects.
Asthenia, asthenic syndrome, types of asthenia in men and women
Neurologist, neuropathologist, reflexologist, reflexologist distinguish types of asthenia , types of asthenic syndrome : morning (morning), daytime (day), evening (evening), nocturnal (at night) asthenia (neurotics), neurocirculatory asthenia, functional or organic asthenia, mental asthenia ( psychological), psychogenic and physiogenic, cerebral asthenia, infectious (post-infectious), post-viral (post-viral, post-viral asthenia syndrome), alcoholic (post-alcoholic), sexual (post-sexual), tonic, hypersthenic, hyposthenic, somatogenic (somatic), neurocirculatory, agastric, skin , traumatic (post-traumatic), neurasthenia . Reflexotherapists, neurologists, neuropathologists distinguish various variants of asthenic syndrome: astheno-vegetative syndrome, astheno-subdepressive syndrome, astheno-hypochondriacal syndrome.
Astheno-vegetative syndrome is characterized by both manifestations of asthenia and severe autonomic disorders.
Astheno-subdepressive syndrome is a non-psychotic pathological condition characterized by mild melancholy with a feeling of loss of vitality and activity. Physical and mental fatigue, weakness, exhaustion, mental and emotional hyperesthesia, emotional lability, absent-mindedness and distractibility of attention are observed.
Astheno-hypochondriacal syndrome is characterized by a combination of asthenia with exaggerated concern for one’s health.
VSD (vegetative vascular, vegetative vascular dystonia) of mixed, hypotonic, hypertonic type.
ICD 10 code
Stress-related and somatoform neurotic disorders in ICD 10 are classified in categories F40-F48. Neurosis is a disease with reversible mental disorders. The disease is caused by exposure to traumatic factors. Neurotic disorder is characterized by the presence of the following symptoms:
- disturbances of well-being, somato-vegetative, emotional functions;
- mental exhaustion;
- the patient’s awareness of the fact of his illness;
- absence of disruption of the reflection of the real world.
Psychiatrists distinguish the following clinical forms of neurotic conditions: asthenic neurosis (astheno-neurotic disorder or neurasthenia), obsessive-compulsive neurosis, hysterical neurosis, neurotic depression (depressive neurosis).
Prevention of asthenia
Sarklinik has developed an effective program “ Prevention of asthenia ”, which allows you to avoid future exhaustion of the nervous system. A healthy nervous system is a reality today. The peculiarity of the disease is that the symptoms slowly, gradually, but clearly increase, and the condition worsens sharply. Do not expect dangerous complications of asthenia, asthenic syndrome; contact Sarclinic for timely treatment.
Sign up for a consultation. They have contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo: (©) Bds | Dreamstime.com \ Dreamstock.ru The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Logoneurosis: treatment of logoneurosis in children, adults, how to treat
Phobia, fear, how to get rid of fear, how to overcome, treat and overcome fear, treatment in Saratov
Transient ischemic attack: symptoms, treatment of the brain
Vegetative vascular dystonia: treatment of VSD, how to treat VSD, symptoms, signs
Neuroses, neurosis, treatment of neurosis, neurasthenia, how to treat
Comments ()
Diagnostics
Only a highly qualified specialist can diagnose neurosis, since the symptoms are very nonspecific. This may require consultation with doctors of various specialties:
- therapist;
- endocrinologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- cardiologist;
- neurologist.
Before scheduling a consultation with a psychiatrist, the patient is prescribed an examination. Taking into account the complaints, the doctor selects the necessary studies:
- MRI, CT;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland, genital organs;
- ECG;
- Echocardiography;
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
Early diagnosis makes it possible to treat neurotic disorders in the early stages.
The Yusupov Hospital has its own diagnostic center with modern equipment of European quality. Doctors at our clinic regularly attend conferences, receive scientific titles and master new treatment methods. When diagnosing neurosis, differential diagnosis is carried out with other diseases:
- enteritis, gastritis;
- psychopathy;
- angina pectoris;
- hypothyroidism;
- adrenal tumor.
The main difference between neurotic disorders and somatic pathology is that as a result of examinations of internal organs, no deviations from the norm are observed. To confirm neurosis, special psychological tests are carried out: anxiety, the Zung and Beck depression test, the K. Leonhard questionnaire.