Dandy-Walker syndrome is a severe malformation of the brain. This congenital anomaly in children is characterized by underdevelopment or hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis, cystic lesions of the fourth ventricle and widening of the posterior cranial fossa.
Dandy-Walker syndrome is a complex symptom complex caused by a congenital brain defect formed during embryogenesis and characterized by a severe course. The pathology is based on simultaneous damage to the most important brain structures: the cerebellum, ventricles, medulla oblongata, cranial nerves and large vascular trunks. Cerebellar hypoplasia is characterized by a decrease in its size and decreased function. Perhaps its complete absence. Enlargement of the ventricles of the brain is caused by congenital cysts or tumors. These signs of pathology are always combined with hydrocephalic changes, which are not manifestations, but complications of the syndrome.
Inadequacy of the cerebrospinal fluid pathways leads to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles, which should normally be removed from the brain. Its pathological accumulation contributes to the development of cerebral hydrops, manifested by signs of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome. Thanks to the constant pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid, the expansion of the skull bones begins. Dandy-Walker syndrome is accompanied by multiple defects of internal organs: heart, blood vessels, kidneys, bones.
The syndrome was discovered by American surgeons - Dandy in 1921 and Walker in 1944. The disease is registered in girls somewhat more often than in boys. In newborns, the cranium rapidly expands, psychomotor development slows down, and signs of hydrocephalic syndrome, intracranial hypertension, and damage to the cerebellum and cranial nerves appear. Almost every patient has associated anomalies: hypoplasia of the corpus callosum, congenital heart defects, atypical structure of the facial skeleton.
The pathology can be diagnosed during pregnancy. Experts usually detect echographic signs of the disease in the second trimester during a routine ultrasound. As the fetus develops, ultrasound indicators become more pronounced. The following signs indicate Dandy-Walker syndrome: brain cysts, cerebellar hypotrophy, ventriculomegaly. Abnormal fetal development detected by ultrasound is a reason for artificial termination of pregnancy.
Forecast
In cases where a child is born with a severe form of development of syndromes, he lives for a maximum of a month and a half.
If the disease is of moderate severity, then he usually remains alive, but great difficulties arise with his mental development. As a rule, the child has a low level of intelligence that cannot be increased. The prognosis for the development of a sick child is very unfavorable and frightening for many.
In most cases, children die in the first year of their life. If the child survives, he needs to be constantly under the supervision of his attending physician.
The prognosis for treatment is favorable if the disease is detected in a timely manner and treatment is carried out. In this situation, residual effects are possible: a slightly increased size of the skull, retardation of movements and speech. In other respects the child is practically healthy.
Causes
To date, there is no confirmed data on what provokes the development of such a disease. Scientists suggest that the causes of the anomaly may be infectious diseases that the woman suffered during pregnancy (measles, rubella, etc.), ingestion of toxic substances (alcohol, nicotine, drugs, etc.), intrauterine trauma or genetic disorders in fetal development.
Very often, this pathology is accompanied by disturbances in the development of the organs of the genitourinary system.
The first trimester of pregnancy is considered the most dangerous period, so a woman needs to pay special attention to her health at this time. Often this pathology develops in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Diagnostic measures
The main task of the doctor is to carry out prenatal diagnosis of pathology. Ultrasound examination of the fetus allows one to suspect the disease and make a differential diagnosis with other congenital anomalies (Edwards syndrome, etc.). A confirmed diagnosis is an indication for termination of pregnancy with the woman’s consent. After the birth of a child, diagnostic measures are carried out according to a certain algorithm:
- Collection of existing complaints and external examination of the child. The specialist identifies abnormalities in the structure of the skull bones, an increase in the size of the fontanelles and head, as well as neurological symptoms. The latter is represented by muscle hypertonicity and impaired fine motor skills.
- When talking with parents, risk factors for the development of pathology are identified - infectious diseases suffered during pregnancy, alcoholism, drug addiction, etc.
- An ultrasound scan of the structures of the central nervous system and internal organs is performed. The examination allows us to identify developmental abnormalities and determine the tactics for their treatment.
- Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is used to examine the condition of internal organs. The methods replace ultrasound, as they have greater diagnostic value for doctors.
- Consultations with a pediatrician, neurologist, cardiologist, ophthalmologist and other specialists if indicated.
Only a doctor should interpret the results of the studies. Incorrect diagnosis is the cause of progression of disorders of the brain and internal organs, leading to serious complications.
Prevention and prognosis
Congenital syndromes that progress at the genetic level cannot be prevented. There is no point in taking preventive measures. Experts recommend that all pregnant women regularly visit a gynecologist, undergo an ultrasound scan every trimester, and strictly follow the recommendations of the attending physician.
The risk of developing pathology in the fetus increases if the expectant mother smokes, drinks alcohol, or leads an unhealthy lifestyle. The consequence of such behavior is the formation of internal organ defects in the fetus.
The prognosis of the syndrome is generally unfavorable. Most sick children with pronounced signs of pathology die in the first year of life. The rest of the kids will not be able to live a full life. Due to existing motor and mental disorders, they cannot sit or stand independently and grow up mentally retarded. Working with psychologists, speech pathologists and other specialists does not help such patients. It is completely impossible to get rid of deviations in psychophysical development and cure neurological defects. Sick children need careful care and require special attention. Congenital defects of the central nervous system make a person disabled. Brain dysfunction and progressive hypertension are the causes of death of the patient.
Dandy-Walker syndrome is an incurable congenital disease characterized by brain abnormalities, cerebellar dysfunction, and cerebrospinal fluid dynamics disorders. Such pathological changes are accompanied by pronounced clinical symptoms.
general information
Dandy-Walker syndrome was described by American neurosurgeons Walter Dandy and Earl Walker. The disease occurs in one person in 25,000. Women are more susceptible to it than men.
Dandy-Walker syndrome is accompanied by a combination of three congenital anomalies: cerebellar deformation, underdevelopment of the cerebrospinal fluid tract and neoplasms in the posterior cranial fossa.
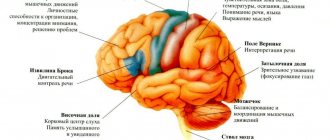
The cerebellum is a part of the brain that is located under the occipital zones of the hemispheres. It is responsible for regulating muscle tension, maintaining balance and coordinating movements. With Dandy-Walker syndrome, hypotrophy (shrinkage) of the hemispheres and the vermis, the middle part located between the hemispheres, occurs. In some cases, the worm is completely absent.
CSF tracts (foramina of Magendie and Luschka) are openings through which CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) flows from the ventricles of the brain. The foramen of Magendie connects the third and fourth ventricles with the cisterna magna. The foramen of Luschka provides communication between the fourth ventricle and the subarachnoid space of the membranes.
Normally, cerebrospinal fluid constantly circulates and ensures metabolism in the brain tissue. Dandy-Walker syndrome is accompanied by overgrowth or absence of liquor ducts. As a result, cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the ventricles, causing:
- hydrocephalus (water on the brain) of varying degrees;
- cystic dilatation (sustained enlargement) of the fourth ventricle;
- intracranial hypertension;
- enlargement of the posterior fossa of the skull and the formation of a cerebrospinal fluid cyst in it.
Child with Dandy–Walker syndrome
Characteristic symptoms
The syndrome is recognized around the 5th month of pregnancy thanks to ultrasound. The study shows the presence of cysts in the cranial fossa, underdevelopment of the cerebellum, and an excessive increase in the volume of the fourth ventricle. As the fetus develops, these signs become more distinct.
Later, abnormal development of the kidneys, fusion of the fingers of the upper and lower extremities (sometimes complete), and clefts formed on the palate and lip are observed. If an ultrasound was not performed during pregnancy, then immediately after the birth of the child, all of these symptoms can be easily detected.
Muscle spasms and nystagmus make themselves felt due to increased intracranial pressure (ICP). Because of this, the newborn behaves extremely restlessly. In practice, there have been cases where pronounced signs of hydrocephalus were not observed.
Manifestation of the disease
When performing a routine ultrasound, a pregnant woman reveals characteristic signs of defective fetal development. The Dandy-Walker anomaly announces itself:
- closure or complete absence of the Magendie and Luschka holes;
- inadequate parameters of the cranial fossa;
- atrophy of the cerebellar hemispheres;
- cysts;
- hydrocephalus.
The disease is considered congenital, although there are rare cases where signs appear after the age of four. In medical practice, there are isolated cases when Dandy-Walker syndrome manifests itself for the first time in an adult. The patient experiences severe muscle spasms, poor coordination, protrusion of the back of the head, and develops mental disability.
Treatment of Dandy-Walker malformation
Each form of anomaly is characterized by a certain degree of severity. Newborns with a severe form of the disorder have virtually no chance of survival. In the case where the defect turns out to be compatible with the life of the infant, its mental development is associated with great problems. Every parent, having heard such a diagnosis, should be prepared for the fact that their child will forever remain with a low level of intelligence. No amount of remedial training can help in this case. It is almost impossible to give an accurate forecast, but the likelihood of death is extremely high.
In addition, it is almost pointless to treat the anomaly and hope for a complete recovery. If the swelling of the brain gets worse, the doctor will plan surgical treatment. Reducing the pressure inside the skull is achieved by shunting the fourth cerebral ventricle.
All therapy carried out after diagnosis is aimed at combating symptoms. Motor disorders and mental retardation make the child’s basic independent actions impossible—the patient cannot sit, stand, much less walk.
Since the anomaly is accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of other organs, therapeutic measures should be focused on possible problems with the heart and kidneys. Pathological changes in the face also require close attention. In this case, it is impossible to do without qualified medical care.
When an anomaly is detected in a child in the womb, parents are faced with a difficult question: to terminate the pregnancy or agree to give birth
It is important to remember that the child will be doomed to suffer from an incurable disease all his life.
Surgery is fraught with risks of complications, but this is the only way to relieve the patient from increasing symptoms, reduce the level of fluid accumulated in the ventricles, and normalize its outflow. Bypass surgery creates an artificial channel through which excess cerebrospinal fluid flows into the abdominal or chest cavity.
Prices
| Disease | Approximate price, $ |
| Prices for diagnosing migraine | 7 060 — 8 260 |
| Prices for diagnosing childhood epilepsy | 3 100 — 4 900 |
| Prices for brain shunting for hydrocephalus | 33 180 |
| Prices for treatment of Parkinson's disease | 58 600 |
| Prices for migraine treatment | 9 680 |
| Prices for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | 6 550 |
| Prices for diagnosing epilepsy | 3 520 |
| Prices for rehabilitation after a stroke | 78 300 — 82 170 |
| Prices for treatment of childhood epilepsy | 3 750 — 5 450 |
| Prices for treatment of multiple sclerosis | 4 990 — 17 300 |
Causes
The causes of Dandy–Walker syndrome have not been established. The main factor predisposing to the development of the disease is heredity. If one of the parents was diagnosed with a pathology, then the child is highly likely to inherit it. However, statistics show that Dandy-Walker syndrome often occurs sporadically (randomly) in children.
Other factors that provoke abnormal brain development:
- infections suffered by a woman during pregnancy, especially rubella and cytomegalovirus;
- diabetes mellitus in the expectant mother;
- alcohol abuse, drug addiction.
These preconditions have the greatest negative impact during the first trimester of pregnancy, when the fetal brain is formed.
Scientists do not provide an accurate description of the mechanism of development of Dandy-Walker syndrome. Some of them believe that the root cause is underdevelopment of brain elements. Others suggest that increased production of cerebrospinal fluid during fetal development leads to structural deformations.
Is it possible to improve the child's condition?
In most cases, treatment of the disease is completely pointless. All therapeutic procedures are used to relieve symptoms. The pathology varies in severity for each child and will sooner or later lead to the death of the patient.
In severe cases of the disease, children die in the first months after birth. If the violations are compatible with life, then serious difficulties arise with the physiological and psychological development of the baby. With the help of treatment, mental retardation and motor disorders cannot be eliminated; the child will not be able to sit or stand on his own. The level of intelligence is at a low level, and this cannot be corrected in any way.
If cerebral hydrocele progresses, surgical treatment is performed in the form of fourth ventricle bypass. During the operation, the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is normalized, and the pressure inside the skull is reduced.
If the child still has kidney pathologies, heart defects and other diseases, then appropriate therapy should be prescribed.
If the pathology was discovered during pregnancy, the woman is recommended to undergo an artificial termination of pregnancy.
Advantages of treatment in Israel
- World-renowned doctors with enormous clinical experience.
- Equipping clinics with high-precision equipment.
- Endoscopic neurosurgical operations.
- Medicines of the latest generation.
- Reasonable prices.
Timely, accurate diagnosis and an adequate therapeutic course will improve well-being and ensure the possibility of normal further development of the child. Don’t waste time, contact an Israeli clinic and trust the health of your baby to world-renowned doctors.
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(0 votes, average: 5 out of 5)
Manifestations of the disease
The symptoms of Dandy-Walker syndrome are varied. Both practically normal development of the child after birth and severe neurological changes leading to severe disability and even death are possible. According to some data, normal development of intelligence occurs in half of the cases of isolated defect; it is even possible that the syndrome is accidentally discovered during examination of adults.
children with Dandy-Walker syndrome
The intrauterine course of the pathology is determined by the degree of brain damage, the increase in hydrocephalus, and the presence of other developmental defects. The prognosis is significantly worse when the syndrome is diagnosed before birth. With deep disturbances in the formation of the brain, hydrocephalic syndrome comes to the fore among other manifestations:
- Increase in head diameter;
- Bulging of the fontanel.
The increase in the diameter of the skull occurs mainly due to the occipital region, in which a cyst forms, causing thinning and stretching of the bone base. With severe hydrocephalus, the baby's head actively grows during the first two months, and at the same time, the sutures between the bones in the front or back part separate. In addition, it is characteristic:
- Increased nervous excitability (reflexes);
- Oculomotor disorders - nystagmus, strabismus;
- Attacks of respiratory arrest;
- Facial nerve paresis.
Symptoms of cerebellar disorders in newborns cannot be identified, and even a severe defect in the formation of cerebellar structures does not always cause significant signs of ataxia (motor disorders), which is recorded in only a third of patients.
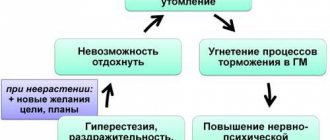
Much more often than motor disorders, disorders of mental activity and intelligence occur, which manifest themselves against the background of general motor “awkwardness.” 25% of patients with a hypoplastic cerebellum have signs of autism, and therefore experts are trying to find a relationship between changes in the cerebellum and autism in children.
Children with hydrocephalus at an early age are restless, sleep poorly, are characterized by a monotonous cry, increased reflexes, floating eye movements and their rolling, pronounced vessels of the cornea, a noticeable subcutaneous venous network as the size of the head grows. Spontaneous motor activity of newborns may be weakened, convulsions and tetraparesis are possible due to muscle hypertonicity.
At an older age, a lag in mental and intellectual development becomes noticeable; children cannot learn, get tired quickly, and do not assimilate new information well, which makes the adaptation process extremely difficult. In severe cases, learning is completely impossible, and therefore the child needs constant outside help, care and consideration of the issue of disability.
Motor development is noticeably delayed. In severe forms of the anomaly, children cannot learn to roll over, crawl, sit up and walk in a timely manner, do not keep their eyes on toys, get tired quickly and often cry. Possible nutritional disorders with malnutrition, a general decrease in immunity, and frequent infectious diseases.
The combination of a defect of the nervous system with other anomalies of organ development predisposes to serious complications, including not only brain dysfunction, dementia, convulsive syndrome, but also heart failure, a tendency to pneumonia with heart defects, chronic renal failure and uremia with congenital polycystic disease, which aggravates phenomena of cerebral edema and can cause the death of the patient.
With severe occlusive hydrocephalus, death can occur in early infancy from cerebral edema, fatal arrhythmias, respiratory arrest due to compression of brainstem structures, severe pneumonia and other infectious complications.
In adults, a gradual increase in hydrocephalus with cranialgia, decreased memory and attention, irritability, a tendency to depression, morning sickness and vomiting at the height of headaches is possible. In severe cases, convulsive syndrome occurs. There may be problems with coordination and performing small movements, uncertainty when walking, and visual disturbances.
Main features
The disease is classified according to the degree of insufficiency in the development of cerebellar structures. Based on this, complete and incomplete forms of the disease are distinguished.
Manifestations of the disease in newborns and in adult children differ. A specialist can see the first signs on an ultrasound in the prenatal period, these include:
- The size of the fourth ventricle does not correspond to the norm for the duration of pregnancy - it is significantly enlarged.
- Underdevelopment of the cerebellum.
- The presence in the cranial fossa of a cavity filled with fluid - a cyst.
These signs give the doctor reason to make an assumption about the presence of the described disease. The diagnosis is confirmed by a combination of internal and external manifestations:
- Disproportion of the child's skull. The head seems disproportionately large.
- Craniotabes, in which the flat cranial bones in the area of the fontanelles become thinner, softening of the bone tissue occurs.
- The occipital bone loses its correct outline.
- Enlarged fontanels.
- Weakness of cry.
- Hydrocephalus is an accumulation of fluid caused by a violation of its outflow from the ventricles of the brain.
- Irregularly formed jaws, nasal turbinates.
- Nystagmus is involuntary oscillatory movements of the eyeballs.
- Uncontrolled convulsive contractions of the muscles of the arms and legs.
- Syndactyly is the fusion of the digital phalanges of the upper or lower extremities.
- Constantly bent position of the limbs, caused by tension in the muscle tissue (spastic tetraparesis).
- Motility disorders.
- Restless behavior.
In children over the age of one year, the pathology is manifested by attacks of headache, nausea and vomiting, irritability, impaired coordination of movements, vision problems, and mental and intellectual development delays.
Often the disease is accompanied by heart defects, kidney disease, and deviations in the development of facial bones.
Symptoms of the disease
A similar disease in the development of the baby is determined when an ultrasound is performed at the beginning of pregnancy. Namely, all the symptoms of this disease are visible already by the 20th week. The main evidence of the appearance of pathology is all kinds of indicators indicating a lesion in the brain: a cystic formation in the fossa of the skull is clearly visible, the cerebellum is poorly developed, and the 4th ventricle is excessively dilated. Moreover, ultrasound indicators are more clearly expressed as the fetus develops.
In the future, you can notice the formation of clefts in the area of the hard palate and lips, improper formation of the renal system and defects. In the case where an ultrasound examination was not performed on a pregnant woman for some reason, signs of the syndrome can be seen with the naked eye after the birth of the newborn. Due to high intracranial pressure, such a child is often very restless. He develops hydrocephalus with muscle spasm and nystagmus. Sometimes there may be no symptoms of hydrocephalus.
Initially, you may notice the formation of the following symptoms:
- Atresia (overgrowth or natural defect) of the foramen of Magendie and Luschka,
- Expansion in the volumes of the posterior fossa of the skull,
- Death of the cerebellar hemispheres,
- The appearance of cystic formation and fistula,
- Hydrocephalus at different stages.
This symptomatology is clearly visible during an ultrasound scan of the unborn child. For this reason, it is important for the expectant mother to regularly conduct research and undergo tests.
In children
This disease is considered a childhood disease. This disease manifests itself quite rarely; its symptoms are noticeable when the fetus is formed, during an ultrasound scan. If for some reason the examination is not done, this is fraught with quite serious complications for the child.
Subsequently, noticeable cerebellar symptoms appear. Older children experience a disorder of motor coordination, for this reason they have difficulty moving and walking (in some situations they are not even able to walk at all). The main symptom is almost incurable retardation in intellectual development. You can also notice the development of related problems: diseases of the renal and cardiac systems, improper formation of fingers, face and hands, as well as impaired visual function.
In adults
This disease is a clinical and anatomical variant of irregular dropsy. The pathology is characterized by such signs as atresia of the foramina in the brain and an increase in the volume of the 3rd and 4th ventricles.
Although this anomaly is considered natural, sometimes it begins to appear in a four-year-old child or later. For a long time, any signs of this disease do not appear. In some situations, decompensation is noticeable already in school or adolescence. In the rarest situations, the initial indicators of the disease may appear in an adult.
The main symptoms of this disease in adulthood are as follows:
- Gradual increase in head volume,
- Severe motor coordination disorder, the appearance of imprecise and wide movements,
- The formation of nystagmus, manifested in a flickering movement from one side to the other,
- Formation of frequent convulsive seizures,
- Severely increased muscle tone (sometimes spasticity appears). The muscles are constantly tense.
- Intellectual inferiority develops, manifested in the inability to recognize relatives, difficulty reading and distinguishing letters, and the inability to write anything.
Consequences
Often the prognosis for such an anomaly is unfavorable. The life expectancy of a child is determined by the presence of a concomitant illness. According to statistical data, the death of a baby can often occur if the syndrome develops after childbirth. Serious complications of the disease include:
- Intellectual and psychological defects that cannot be corrected throughout life;
- Slow psychomotor skills;
- Neurotic diseases, namely, increased muscle tone, impaired motor function.
Since the disease is congenital and progresses at the genetic level, it cannot be prevented. Therefore, preventive measures will be meaningless. However, while a woman is carrying a baby, she should be periodically examined using ultrasound to timely detect the development of an anomaly. If a pregnant woman is suspected of developing Dandy-Walker syndrome in her baby, an ultrasound examination is prescribed at intervals of several weeks. If a pathology is detected, the level of the child’s impairment is examined and a decision is made on whether it is advisable to continue the pregnancy in the future.
It should be noted that the risk of the formation of such an anomaly increases significantly if a woman continues to smoke and drink alcohol during pregnancy. For this reason, pregnant women are advised to maintain a healthy lifestyle, since the consequences that may arise from such an attitude are often not compatible with life.
Treatment of Dandy-Walker syndrome
Dandy-Walker syndrome is an incurable congenital disease. It cannot be treated. Palliative care is provided to patients and their parents. Treatment includes medication and surgery. The volume of therapy is selected depending on the severity of pathological symptoms. The child should be regularly examined by a pediatrician, neurologist and neurosurgeon. Among the drugs prescribed for Dandy-Walker syndrome are:
- Sedatives. They help normalize the child’s emotional background, eliminate irritability and moodiness.
- Painkillers. They reduce the severity of pain and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Vitamin complexes. Improves the process of transmission of nerve impulses.
- Diuretics. Helps lower blood pressure. Drugs in this group remove excess fluid from blood vessels.
- Corticosteroids. Prescribed to reduce the amount of cerebrospinal fluid produced in the ventricles of the brain.
- Vasodilators. They stabilize blood microcirculation in the vessels and expand their lumen. Thanks to vasodilators, it is possible to facilitate the outflow of liquor fluid.
- Plasma substitutes. Reduce the progression of pathological symptoms of Dandy-Walker syndrome. Helps maintain brain function.
- Beta blockers. Prescribed to reduce edema syndrome.
In addition to drug treatment, patients with Dandy-Walker syndrome are prescribed physical therapy. It includes:
- mud therapy;
- salt baths;
- massage.
Physiotherapeutic treatment is used to reduce muscle hypertonicity and normalize the patient’s emotional background.
Surgical treatment of Dandy-Walker syndrome
The indication for surgical intervention is the need to create a new pathway for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. The operation is performed using the following methods:
- Ventriculo-peritoneal shunt. The operation involves inserting a soft tube into the cavity of the ventricle. Next, the catheter is directed into the abdominal cavity. It is performed subcutaneously behind the ear and in the collarbone area. The manipulation is performed to drain and absorb brain fluid in the abdominal cavity.
- Endoscopic ventriculostomy. It involves making a hole in the skull bone. The neuroendoscope is advanced into the ventricle. Using the tool, excess liquid is removed. Endoscopic ventriculostomy is considered a minimally invasive procedure. The operation does not cause late complications.
Doctors warn that surgery is carried out to eliminate hydrocephalus. Restoring mental and neurological functions in this way is impossible. At the Yusupov Hospital, operations are performed by experienced surgeons.
Treatment options
Treatment is symptomatic, aimed at correcting the manifestations of pathology. To eliminate muscle hypertonicity and movement disorders, drug therapy is carried out. Additionally, physiotherapeutic methods are used - massage, therapeutic exercises. Mental development disorder is practically untreatable.
With progressive hydrocephalic syndrome, surgical intervention is indicated - shunting of the fourth ventricle to create a normal outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. Typically, cerebrospinal fluid is drained into the abdominal cavity. After surgery, intracranial pressure is regularly monitored.
Forms of manifestation of the disorder and complications
If we talk about the varieties of the disease, then there are two of its forms - complete and incomplete. In the complete form, the cerebellar vermis is completely absent; the incomplete form is characterized by partial underdevelopment of the cerebellar parts.
Among congenital pathologies of the development of the nervous system, many diseases belong to the class of dangerous. Dandy-Walker malformation turns out to be one of the most difficult diseases in terms of the course, treatment and subsequent prognosis. The mental development defect in this disorder is irreversible. The neurological status may also remain for life - muscle hypertonicity and improper coordination of movements will be observed.
Symptoms
Signs of fetal malformation detected by ultrasound:
- Cysts and tumors in the brain,
- Reduction in the size of the cerebellum and decrease in its functions,
- Ventriculomegaly,
- External deformities - cleft palate and upper lip,
- Occlusion of foramina and absence of channels in the brain,
- Kidney abnormalities
- Inferiority of the structures of the liquor drainage system,
- Death of the cerebellar hemispheres,
- Fistulas in the brain.
Most scientists recognize Dandy-Walker syndrome as a congenital anomaly. But despite this, clinical signs of pathology may first appear in a small child, schoolchild, teenager and even an adult.
Symptoms of pathology in newborns:
- Disproportionately large head compared to the body,
- Protrusion of the back of the head
- Osteomalacia of the skull bones,
- Bulging of the fontanelle,
- Limitation or decrease in motor activity of the arms and legs,
- Involuntary movements of the limbs,
- Reduced resistance and elasticity when squeezing the skin and soft tissues,
- Arrhythmia,
- Constant crying, moodiness, restlessness of the child,
- A faint cry
- Facial deformation
- Hyperreflexia,
- Increased excitability
- Eyeball twitching,
- Strabismus,
- Convulsive contraction of the muscles of the limbs,
- Constant bending of arms and legs due to muscle tension
- Brief cessation of breathing during sleep
- Damage to the facial nerve.
The clinical picture of Dandy-Walker syndrome in adults consists of the following symptoms:
- Cerebellar symptoms - nystagmus, imprecise and wide movements, dizziness, changes in gait, dysarthria, scanned speech, tremor, incoordination of movements, inability to perform rapid alternating actions;
- Signs of high intracranial pressure and hydrocephalus - anxiety, nausea, vomiting, dull, aching headache in the morning, dizziness, pale skin, weakness, lethargy, reaction to bright light and loud sound, walking “on tiptoe” with hypertonicity of the leg muscles, lethargy, mnestic disorders, inattention, convulsive syndrome, coma;
- Impaired motor coordination - difficulty walking, muscle hypertonicity, spasms and muscle tension, frequent seizures;
- Incurable retardation in intellectual development - patients do not recognize their relatives, cannot read, distinguish letters, write, become irritable, forgetful;
- Symptoms of kidney abnormalities are periodic lower back pain, increased blood pressure, swelling on the face around the eyes, on the body and legs, difficulty urinating, burning and itching during this process, cloudy urine with bloody discharge;
- Signs of congenital heart disease are shortness of breath that occurs during minor physical exertion, increased heart rate, general weakness and pale skin, cyanosis, heart pain, fainting, swelling of the extremities;
- Syndactyly, deformation of the face and the entire skull, increased volume of the head;
- Impaired visual function – decreased visual acuity, diplopia.
Diagnostics
Dandy-Walker syndrome is diagnosed in the prenatal period by ultrasound scanning. After the birth of the child, the diagnosis is made based on:
- collecting anamnesis - symptoms are refined and cases of the disease in the family are identified;
- neurological examination - nystagmus, pathological enlargement of the head and muscle hypertonicity are determined;
- neurosonography - ultrasound of the brain, which can be performed before the fontanelles close;
- tomography - allows you to identify abnormalities in the structure of the brain and hydrocephalus after the closure of the fontanelles.
Additionally, an ultrasound of the heart and genitourinary system is performed to identify congenital defects.
Tomogram of the brain is normal (left) and with Dandy-Walker syndrome (right)
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of the syndrome can be prenatal and postnatal. In the first case, an anomaly is detected in the fetus during an ultrasound scan of a pregnant woman. Parents must decide to terminate the pregnancy or save the life of the baby, who will only suffer and suffer.
Dandy-Walker syndrome on a diagnostic image
After the birth of a sick child, he is examined and characteristic symptoms that are visible to the naked eye are identified: muscle hypertonicity, range of movements, increased head volume. Then specialists collect family history, asking parents about the presence of similar diseases in the family. Determination of neurological status - the presence of nystagmus, incoordination of movements and other signs of anomaly.
To detect defects of internal organs, it is necessary to undergo additional instrumental diagnostics: ultrasound of the heart, angiography, CT and MRI of the brain and kidneys. Patients are shown an ophthalmological examination, echocardiography and other necessary methods for studying the vital functions of the body. Medical genetic counseling with karyotype study is carried out for persons with hereditary diseases in their family.