Various sleep disorders can be associated with neurological diseases, mental disorders and psychological characteristics of a person. The most common phenomenon is talking while sleeping. These can be meaningful words, mumbles, short phrases and even dialogue. At the same time, children talk in their sleep more often than adults.
The exact reasons for this phenomenon are unknown. It is assumed that this may be a variant of the normal condition or a sign of pathology.
Basic information
In the medical and psychological literature, talking during sleep is called sleep-talking. This is a common parasomnic disorder associated with various conditions. Its various manifestations are possible: short screams, muttering, monologues and dialogues. This can be an independent phenomenon or a manifestation of somnambulism, in which motor activity occurs. Doctors consider this condition to be a variant of the norm, but in some cases, a child talking in his sleep indicates the presence of certain problems. To clarify the causes of the disease, it is necessary to conduct an examination.
If your child talks in his sleep, there is no need to panic. This condition occurs in every person at least once in their life and is considered safe. Pronunciation of sounds, screams and muttering occur due to nightmares, sleep paralysis and other parasomnic phenomena. You need to pay attention to other suspicious manifestations, such as increased anxiety, decreased mood, or signs of neurological disorders. Very rarely, sleep talking indicates brain damage.
Oral speech is regulated by the brain. In the area of the vocal cords there are muscle structures on which voice production depends. A person consciously sets muscle fibers in motion and performs articulation with the help of his tongue and lips. During childhood, articulation gradually develops, so conscious functions are not always present. A 2-3 year old child has poor control over the pronunciation of sounds. At 4-5 years of age, vocabulary increases and early features of oral speech are consolidated. As a rule, by the time children enter school, at 6-7 years of age, the nervous regulation of speech function has fully matured. However, some disorders may persist in school-age children.
Is there any meaning in the words of the sleeping man?
Many people think that what a person says in a dream is his secret thoughts and desires, as if it works, like with that proverb about a drunk who has everything on his tongue. Now, this is not true. According to the International Classification of Sleep Disorders, talking does not reflect previous behavior or memories.
Not only is up to 60% of what is said incomprehensible, but the rest simply doesn’t make any sense. It’s as if a neural network randomly formulated phrases according to the syntactic norms of the language.
In any case, dream speaking has so far been studied very poorly; there are real fears that scientists will soon refute everything that they have claimed before.
Sleep and speech function
The state of sleep is natural. This is a kind of rest mode for the body, when the reaction to external and internal stimuli is reduced. A sleeping person has poor auditory, visual and tactile sensitivity. At this time, a change in activity patterns occurs in the brain, allowing nerve cells to accumulate energy and structure information.
Sleep is also characterized by other physiological changes, including relaxation of skeletal muscles, changes in respiratory rate and heart rate.
Sleep structure:
- Orthodox sleep
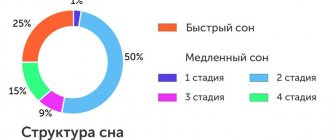
Continues for 60-80 minutes. Traditionally divided into four phases. The first phase is characterized by a change in the electrical activity of the brain. Physiological changes occur, such as slower breathing and heart rate. In the second phase, consciousness turns off, but the person is still easy to wake up. During the fourth phase, a deep state of sleep occurs, when it is very difficult to wake a person. At this time dreams appear. It is the fourth phase of slow-wave sleep that is characterized by various parasomnic disorders, including sleep talking.
- Fast wave sleep
This period lasts for 15-20 minutes. Electrical activity in the brain resembles wakefulness, but the person cannot move or think clearly. Vivid dreams arise that can be easily recalled immediately after waking up. Spontaneous motor activity of the eyeballs is characteristic. Hormonal and autonomic changes occur. It is believed that during fast-wave sleep there is an active redistribution of information in consciousness.
Normally, a sleeping child does not move or speak, since motor activity is blocked. The release of a special hormone during sleep helps reduce muscle tone, including the muscles of the oral cavity. This is necessary to ensure that a person does not accidentally injure himself in an unconscious state. At the same time, it is sometimes possible to spontaneously “turn on” certain muscle groups, including muscle fibers responsible for articulation. The exact causes of this phenomenon are unknown, but it is believed that the mechanism of development of sleep-speaking is similar to somnambulism and night paralysis. Muscle tone increases faster than a person returns to clear consciousness.
Baths
For a sound sleep you need a warm bath. Its temperature should be no more than 38 degrees. You can add a few drops of oil to the water - chamomile, mint, lavender. You should not use only citrus fruits, as they have a tonic effect. The procedure is performed in no more than 20 minutes. After this you can go to bed.
Why does a child talk in his sleep?
The mechanism for the formation of sleep-speaking may be associated with mental activity and physiological disorders. It should be borne in mind that such an “illness” is typical for most people, so it is important to distinguish the natural pronunciation of sounds in a sleeping state from signs of somnambulism and other disorders. Numerous studies have made it possible to clarify the possible mechanisms of this phenomenon.
Known Causes:
- Violation of the mechanism of muscle atony. As already mentioned, the body blocks muscle activity during the night. This protective mechanism is associated with the activity of parts of the midbrain. It is assumed that muscle atonia can spontaneously “turn off” during sleep. For example, during REM sleep, movement of the eyeballs occurs. It is possible that it is during this period that sleep talking is possible.
- Organic brain damage. This is a rare cause of this phenomenon. Damage to the pons and medulla oblongata nuclei is possible. In this case, other signs of pathology will certainly appear that are not related to night rest. These may include movement disorders, decreased intelligence and emotional disorders.
- Taking medications. If your child suddenly starts talking in his sleep, you need to pay attention to the medications he is taking. For example, psychotropic drugs that affect the exchange of neurotransmitters in the brain often cause sleepiness. First of all, these are selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (antidepressants). Taking antidepressants is accompanied by other problems, including a decrease in the duration of night rest and frequent awakenings at night.
- Other neurological diseases, such as intracerebral hemorrhage, damage to the auditory nerve and multiple sclerosis, in which the myelin sheath of nerve structures is destroyed. As with organic brain damage, the child will have other obvious symptoms.
- Insomnia or hypersomnia. The patient sleeps too little or too much. The recommended amount of sleep depends on age. At the age of 10-11 years, a child may need the “adult norm” of 8-9 hours. Lack of night rest has a greater effect on the state of the nervous system. Symptoms such as irritability, anxiety, weakness and decreased mood appear.
- Hormonal changes. This reason is most common for patients aged 12-13 years, when, on average, boys and girls begin the main stages of puberty.
- Psychological reasons. In this case, sleep talking is not associated with physiological disorders.
Psychological factors
If your child often talks in his sleep, you need to pay attention to his psychological well-being. Many adverse factors increase the risk of developing this disorder. First of all, these are violations in the emotional sphere. Main triggers:
- Chronic stress
The mechanism of adaptation of the nervous system to adverse influences is called stress. If stress factors affect a child for too long and too often, complications develop.
- Constant worry
One of the consequences of chronic stress is anxiety. The patient begins to experience fear for no reason. Anxiety in the evening and at night makes it difficult to fall asleep and provokes frequent awakenings.
- Family troubles
These are constant conflicts with parents, violence from parents, etc.
- Increased psychological excitability
A common condition that most often occurs in children during preschool age. Signs of increased excitability include disobedience, restlessness, hyperactivity and decreased concentration.
Honey mixtures
Honey is an excellent sleeping pill; various mixtures are created with it that have a positive effect on the condition. The classic is milk with a spoon of honey before bed. But other recipes are also suitable:
Regular use of such mixtures restores sleep and calms you down. The person will sleep peacefully and therefore there will be less risk of nightmares and conversations at night.
Additional signs
If the patient begins to talk while sleeping, you need to pay attention to the behavior. Symptoms indicating pathology can appear both during night rest and while awake. Often these are subtle signs that are not associated with any disorders:
- the patient grinds his teeth at night;
- during wakefulness, absent-mindedness and impaired concentration are observed;
- there is a lack of coordination in space;
- decreased cognitive functions, including memory and intelligence;
- the child walks and talks in his sleep;
- signs of restlessness and anxiety appear during the daytime;
- there is a decrease in mood, frequent tearfulness;
- lack of motivation and decreased performance (apathy);
- lack of appetite and weight loss.
If these symptoms appear, it is recommended to consult a neurologist for examination. It is important to exclude diseases of the nervous system and parasomnic disorders. For example, if the patient sleeps with his eyes open and moves around in a sleeping state, somnambulism must be excluded.
Herbal infusions
The best recipes are:
Associated states
There are comorbid diseases that may be associated with the pronunciation of sounds at night. First of all, these are other parasomnic disorders and mental disorders. There is also a possible relationship with pathologies of the endocrine system. Let's consider the pathologies in which sleep talking often occurs.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
A disorder of mental and neurological activity in children, manifested by increased excitability, impulsivity, decreased concentration, impaired cognitive functions and deterioration in the assimilation of new information. The patient often talks during the night's rest due to insufficient inhibition of the nervous system and increased reaction to external stimuli.
Somnambulism
Motor activity of a sleeping person. A child in a sleeping state talks, screams, gets out of bed, moves around the apartment and even performs meaningful actions. However, after waking up, he cannot remember anything.
Somnambulism (sleepwalking) is a type of mental disorder in which people perform certain actions while in a state of sleep.
Hyperthyroidism
Excessive production of thyroid hormones. These substances are responsible for the general regulation of the body. Due to the excessive release of hormones into the bloodstream, symptoms such as irritability, insomnia, aggressiveness, decreased concentration and increased physical activity occur.
Epilepsy
A neurological disease in which convulsive attacks occur periodically. This is a chronic pathology that cannot be completely eliminated. As the disease progresses, a variety of mental and neurological complications develop. Talking while sleeping can be a manifestation of nocturnal epilepsy.
At the same time, talking while asleep is often an isolated symptom. If nothing else bothers the patient, no special diagnosis is required.
Ways to get rid of the problem
Exacerbations in most cases are observed as a result of emotional and mental stress, stressful situations. When sleep talking is a real problem and causes inconvenience to a person, it is recommended to independently reduce the number of unpleasant attacks using simple measures:
- getting enough regular sleep;
- a constant and correct regime of rest with wakefulness;
- proper and specialist-recommended sleep hygiene.
However, these measures are not enough. You should refrain from:
- constant worries and stress;
- drinking alcohol, smoking tobacco at night;
- watching programs and films that stimulate the emotional background;
- taking tonic and caffeinated drinks in the evening, for example, tea, coffee, cola, alcohol;
- learning or processing new information just before bed.
In case of exacerbation of stressful periods, it is necessary to take sedatives, but after prior consultation with a doctor.
Survey
First, you need to contact a psychotherapist who will conduct tests to identify signs of anxiety, decreased mood and hyperactivity. Particular attention is paid to the child’s relationships with parents and peers. Key risk factors are identified. If necessary, the patient is referred to another specialist. Consultation with a neurologist, child psychiatrist, endocrinologist, epileptologist and therapist may be required.
Special examinations:
- Long-term psychological observation. Regular consultations help to identify the prerequisites for the occurrence of sleep talking.
- Study of the functioning of the brain during wakefulness and sleep: electroencephalography, somnography. If necessary, visual examinations are performed to exclude organic brain damage.
- Examination of internal organs, including the study of hormonal levels.
It is important to inform the specialist about the medications you are taking, diagnosed diseases and other symptoms.
When should you worry?
The following signs are reasons to contact a neuropsychiatrist:
- multiple attacks;
- exacerbation of existing neurological and mental diseases;
- sleepwalking;
- aggression;
- the chatterbox complains of lack of sleep and feeling tired in the morning.
Treatment is prescribed in case of illness. There are no specific drugs for sleep talking. Complex therapy is carried out, for example, for epilepsy or concussion.
To make a diagnosis, you will need to find out the details. It is recommended to clarify the picture of what is happening before contacting doctors.
The specialist will ask a number of questions:
- Frequency of attacks: per night, week.
- Degree of clarity of speech: nonsense, screams, mooing, moaning/full sentences and phrases, speaking in an unknown language.
- Daily routine of a chatterbox.
Keeping a diary will be a plus when contacting a psychoneurologist. It reflects when the chatterbox goes to bed, falls asleep (presumably), and wakes up. The duration and nature of the conversation are noted. Night conversations are recorded on a voice recorder. The doctor will prescribe an EEG (electroencephalography), study the records, and find out the cause of the disorder.
What to do
Psychological assistance is the main aspect of treatment if the child does not have pathologies of the brain and internal organs. It is necessary to eliminate all possible factors for the development of chronic stress.
Methods for improving psychological well-being include restoring calm family relationships, reducing academic workload, and eliminating conflict situations in relationships with peers. Family and individual counseling may be required. If pathologies of the central nervous system and internal organs are detected, doctors provide treatment.
What are the causes of somniloquy?
Dream speaking has been little studied. The main reasons are the manifestation of emotions and heredity.
It is known that late-night conversation is encouraged by:
We recommend reading! Click on the link:
For what reasons does a child sleep poorly and what can be done?
- stress, depression, apathy;
- physical fatigue;
- sleep/wake disorder;
- drugs, including caffeine, alcohol, tobacco;
- heavy food at night;
- medical supplies;
- diseases - somatic, mental, neurological;
- concomitant sleep disorders - enuresis, sleepwalking, apnea, nightmares;
- stuffiness in the bedroom.
Negative and positive events can drive the body into a depressive state. External stimuli depend on many factors. A person, due to his psychology, often cannot change his perception of what is happening: he gets nervous, angry, overexerted. Illness also contributes to conversations. A high temperature associated with a common cold causes bouts of sleep-speaking.
But there are circumstances that the speaker has the power to change. The cause of parasomnia should be sought in lifestyle.