Risk factors for stroke and heart attack
Planning a preventative treatment regimen is based on addressing risk factors that are largely similar for heart attack and stroke.
Metabolic risk factors include:
- dyslipidemia (impaired lipid metabolism - organic compounds, including fats and fat-like substances);
- arterial hypertension;
- obesity;
- metabolic syndrome;
- diabetes mellitus and other endocrinopathies;
- coagulopathies (diseases that develop as a result of disorders of the blood coagulation and anticoagulation systems).
Common markers of heart attack and stroke are:
- previous cardiovascular diseases;
- peripheral vascular pathology;
- calcium index;
- stress test results;
- hypertrophy (thickening of the wall) of the left ventricle.
Atherosclerotic stenosis of the carotid arteries and brain tumors increase the risk of stroke. The provoking factors of a heart attack are:
- atrial fibrillation;
- dysplasia (developmental disorder) of connective tissue;
- arteritis;
- diabetes.
Although the incidence of stroke is higher in men, it is more severe in women, and about half of deaths from stroke occur in women.
Make an appointment
Returning to work
A stroke will be a real challenge for you if you have previously worked. It can leave a big imprint on your life and change your role in the family and society. Many people do not look at the situation realistically and try to do many things in a short period of time. Fatigue, cognitive complications such as memory loss, and difficulty concentrating may mean you will not be able to return to work. It is important to have an honest conversation with your employer so that you can consider on-the-job adaptation. Part-time work and a reduced workload may be a viable option. Don't be too hard on yourself if things don't work out or aren't going as well as they did before you had your stroke. A lot of people are returning to work. Many see this as an opportunity to try something new, such as working from home or taking on new responsibilities.
Signs of a stroke
To diagnose cerebral blood supply disorders, it is necessary to use stroke recognition techniques:
- When trying to smile, you need to pay attention to the corners of the mouth - in case of a stroke, it can be directed downwards, the smile looks crooked and asymmetrical;
- When trying to speak, it may be difficult to pronounce even the simplest words and sentences;
- When trying to raise both arms, asymmetry is observed;
- The protruding tongue falls to the side.
If at least one of the symptoms is positive, you must immediately call an ambulance. Under no circumstances should you give him water, feed him, lift him, or take him by handy transport to the nearest hospital, as this can cause harm.
Daily routine
A daily home routine can be helpful. Your day will be less monotonous and this will allow you to learn to listen to yourself and determine when you feel active and do some housework accordingly. The daily routine is based on your needs and the needs of your loved ones. Think about what chores you need to do every day, what you can do on your own, what you need help with, and what you will need to learn to do again. Think about how much time you will need to complete all this work. If you feel yourself getting tired, try to perform the most difficult and tiring tasks that require more energy during the day or week when you feel more energized, making sure to take time to rest. It is very important to be as active as possible. Try to continue your hobbies, social activities and other activities as much as possible. And if you can, try to breathe fresh air every day!
Help in the acute period
Which doctors are needed in the treatment of stroke depends on the period of the disease, but in any case, they must be experienced, highly qualified specialists who know how to properly provide assistance in this situation.
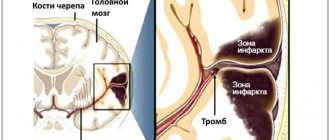
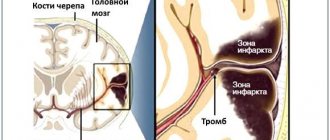
When diagnosing an ischemic stroke in a patient, the doctor’s goal is to restore blood supply with subsequent rehabilitation. This may require blood thinning medications or mechanical removal of the clot using a catheter. To remove atherosclerotic plaques, endarterectomy is performed, and to increase the diameter of blood vessels, plastic surgery with stenting is performed.
Sick leave
Inpatient treatment only stabilizes the health condition, and then the person receives further treatment at home. A sick leave certificate after a stroke is opened in the hospital, and after discharge the stroke patient renews the document by visiting a doctor.
The duration of disability depends on the nature of the brain lesion:
- mild ischemic stroke is treated for about 3 months;
- a patient after surgery for removal of an intracranial term requires a minimum of four months of rehabilitation.
Sick leave after a stroke can be extended to 7-8 months. After this time has expired or if the doctor sees that full rehabilitation is impossible, the patient is sent to MSEC to receive disability.
Resuscitation in the early post-stroke period is one of the important stages of rehabilitation treatment. Intensive therapy helps prevent brain swelling and reduce the lesion. If a person has been taken away with a diagnosis of stroke, then there is no need to look for which department to treat stroke - patients after an acute attack are hospitalized in the ARC.
How long to stay in hospital if you have a stroke
Poor blood circulation in the brain, in other words, stroke, treatment involves three stages:
- prehospital;
- stay in the intensive care unit;
- treatment in a general ward.
The length of stay of a patient in a hospital, according to treatment standards, is 21 days, provided the patient has no violations of vital functions, and 30 days in case of serious violations. When the length of a patient’s stay in a hospital is insufficient, a medical examination is carried out followed by the development of an individual course of rehabilitation.
All patients diagnosed with stroke are subject to hospitalization. The length of stay in intensive care depends on a number of factors, including:
- depression of vital functions;
- degree of damage to brain tissue. With a major stroke, patients stay in intensive care longer;
- the need for constant monitoring if there is a high risk of recurrent stroke;
- severity of the clinical picture;
- level of depression of consciousness and others.
Basic and differentiated therapy
Treatment of a patient in the intensive care unit involves basic and differentiated therapy.
Basic treatment is aimed at:
- fight against cerebral edema;
- restoration of normal functioning of the respiratory system;
- patient nutrition;
- maintaining hemodynamics at an acceptable level.
Differentiated therapy involves:
- normalization of arterial and intracranial pressure, elimination of cerebral edema after hemorrhagic stroke. In the first two days, a decision is made regarding the need for surgery. Neurosurgeons at the Yusupov Hospital daily perform surgical interventions to eliminate the consequences of stroke and save the lives of hundreds of patients. All manipulations are carried out using modern medical equipment using effective proven techniques;
- accelerating metabolic processes, improving blood circulation and increasing the resistance of brain tissue to hypoxia when diagnosed with ischemic stroke. The length of stay in intensive care directly depends on the timely and adequate course of treatment.
In most cases, young people recover much faster than older patients.
It is possible to transfer a victim from the intensive care unit to a general ward after meeting a number of criteria:
- the patient can breathe independently, without the support of devices;
- the patient is able to call a nurse or doctor for help;
- there is a stable level of heart rate and blood pressure;
- the possibility of bleeding is excluded.
Only after the patient's condition has stabilized can the doctor transfer the patient to the ward. In a hospital setting, various rehabilitation procedures are prescribed to quickly restore lost functions.
In the neurology department of the Yusupov Hospital, patients are not only developed an individual course of rehabilitation therapy, but also given psychological support.
If necessary, psychologists work with loved ones and relatives of the patient to teach them the basics of caring for a person who has suffered a stroke.
Average duration of treatment
Below we present the average statistical time of treatment in a psychiatric and psychotherapeutic clinic for various mental illnesses and behavioral disorders, as well as the duration of therapy after discharge from the hospital.
Data taken from real clinical practice . We remind you that these deadlines are not standards!
| Disease | Degree of severity, severity of the condition | Wed. length of hospitalization | Wed. terms of treatment after discharge from hospital |
| Psychosis | heavy | 60 days | 2 years |
| moderate severity, first-time acute psychosis | 30 days | 12 months | |
| mild psychotic symptoms, exacerbation of chronic psychoses | 10 days | 6 months, with chronic psychoses many years | |
| Borderline mental disorders (neuroses, personality disorders, reactive states) | severe symptoms | 30 days | 12 months |
| average severity of symptoms | 10 days | 6 months | |
| mild symptoms | several days (1-5) | 30 days | |
| Panic attacks, anxiety disorders | long-term anxiety disorders, phobias, generalized anxiety disorder | 30 days | 1.5 years |
| mixed anxiety and depressive disorder, neurasthenia | 15 days | 12 months | |
| panic attacks newly diagnosed | 10 days | 6 months | |
| Depression | severe depression, depression with psychosis, suicidal behavior | 45 days | 12 months |
| moderate severity of depressive symptoms, first-time depressive attack | 30 days | 9 months | |
| mild depressive symptoms | 10 days | 4 months | |
| Organic mental disorders (consequences of traumatic brain injuries, neuroinfections and intoxications, vascular disorders of the brain, etc.) | severe psychoses with delusions and deceptions of perception | 45 days | 2 years |
| “organic” psychoses of moderate severity, acute psychoses due to dementia, delirium | 30 days | 12 months, for dementia - constant monitoring throughout life | |
| organic personality disorder, borderline “organic” disorders (sleep disorders, mood disorders, movement disorders) | 21 day | 12 months | |
| asthenic condition | 10 days | 6 months | |
| Schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder | 30 days | constantly | |
| Alcohol addiction | alcohol dependence in combination with mental disorders, 3rd stage of alcohol dependence | 30-45 days | 2 years, at stage 3 – for life |
| 2nd stage of alcohol dependence | 21 day | 12 months | |
| Stage 1 and beginning of stage 2 of alcohol dependence | 10 days | 12 months | |
| Withdrawal from binge drinking, relieving poisoning, eliminating a hangover, sobering up (these measures are not treatment for alcohol addiction) | 1-2 days | No | |
| Drug addiction | 2nd and 3rd stages of addiction, concomitant mental disorders | 45 days | 3 years |
| 2nd stage of addiction with preserved criticism of the disease, rehabilitation potential | 30 days | 3 years | |
| 1st stage of addiction | 10 days | 12 months |
As can be seen from the table, for mental disorders and behavioral disorders, the average treatment time after discharge from hospital is long: calculated in months and even years.
Different treatment methods have their own duration of use.
Recovery period
The rehabilitation period is aimed at restoring lost functions and improving the quality of life of patients who have suffered a stroke. The doctor develops a rehabilitation program individually for each patient, taking into account the scale of the vascular accident, age, comorbid pathology, etc.
In case of strokes, doctors assign a special role to the prevention of recurrent strokes, which includes proper nutrition, giving up bad habits, eliminating excess weight, and regular monitoring by a doctor.
Is full recovery possible after a stroke?
The patient’s relatives play a significant role in the rehabilitation of a patient after a stroke. It depends on their attention, care, patience and correct actions whether the patient’s lost functions can return.
The recovery process after a stroke is a difficult period, both for the patient himself and for his loved ones. The rehabilitation time depends, first of all, on the degree of damage to brain tissue. Patients may have impaired coordination of movements, mobility of limbs, speech, memory, hearing, and vision.
The patient’s persistence and positive attitude can speed up the recovery time of lost functions.
An experienced team of doctors will speed up the rehabilitation process thanks to a well-designed individual treatment program.
Levels of recovery after stroke
After hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes, there are three levels of recovery:
- the first is the highest. We are talking about the complete restoration of lost functions to their original state. This option is possible in the absence of complete death of nerve cells in a region of the brain;
- the second level is compensation. The early stage of recovery, usually in the first six months after a stroke. Lost functions are compensated by the involvement of new structures and functional restructuring.
- The third level involves readaptation, that is, adaptation to the emerging defect. The patient’s relatives and friends play a significant role in this process. They are the ones who help the patient learn to live with the emerging defect.
Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital, if necessary, work with the patient’s relatives, teaching them the specifics of care, as well as providing them with psychological support.
Fatigue
Fatigue is one of the most common symptoms of stroke. This symptom affects most people who have had a stroke, regardless of its severity, and is usually most noticeable when they return home from the hospital.
This type of fatigue is different from the usual and usual fatigue for us, and it does not depend on your activity or activity. Each of us sometimes feels tired, but this feeling often goes away after rest. However, after a stroke, the fatigue you feel may make you feel like you don't have the energy to do anything. Often you may feel that the feeling of fatigue comes completely unexpectedly and at this moment the only thing you can do is rest until this feeling passes.
Sometimes it takes months or even years for this symptom to go away. Many people after a stroke say they have good days and bad days - days when they feel they can do more things and days when they need to rest more because they feel tired. During the recovery process, good days tend to increase and bad days decrease. Often this fatigue is invisible to other people, so it can be difficult for them to understand what you are feeling. Despite this, you can help yourself in various ways. The key to success is to realize that it is not your fault and it is not your fault. You need to accept the fact that it takes a long time to overcome this symptom of fatigue.
Prognosis for recovery after stroke
Favorable factors for recovery after a stroke include:
- timely early start of rehabilitation therapy;
- spontaneous early recovery of lost functions.
Among the unfavorable factors of recovery after a stroke are:
- advanced age of the patient;
- large area of brain tissue damage;
- poor blood circulation around the affected brain tissue;
- damage to cells in functionally important areas of the brain.
Basics of Stroke Recovery
In the process of rehabilitation, the positive attitude of the patient himself and his desire to return to independent life are important. Psychological support and assistance from the patient’s relatives plays a huge role. You can make an appointment with a neurologist by phone.
Memory recovery after stroke
Treatment of patients after a stroke takes place in the neurological department. Memory restoration depends on many factors: the size of the area of brain damage, the location of the damage, and the timeliness of medical care. The faster blood circulation in the brain is restored, the greater the chance of memory recovery after a stroke.
Memory restoration after a stroke is possible with the participation of several specialists - a neurophysiologist, psychologist, neuropsychologist, neuropsychiatrist. Help for a patient after a stroke is provided at the rehabilitation clinic of the Yusupov Hospital. In the hospital, the patient is treated according to an individual recovery program; many specialists take part in the development of such a program. When developing the program, the patient’s health condition, the severity of brain damage, and memory impairment are taken into account.
In some cases, it takes several years to restore memory and speech; during recovery, the doctor prescribes medication, a special diet, various trainings - color therapy, rhythm therapy, music therapy and others. Memory restoration at home is not always successful due to the lack of a training program and knowledge in the field of rehabilitation of patients after a stroke.
You can make an appointment with a neurologist at the Yusupov Hospital by phone. Consultation with a specialist, full patient care, rehabilitation using innovative equipment, massages and exercises will help the patient regain full memory.
Restoring a hand after a stroke
A positive attitude and support from family have an impact on rapid recovery from illness. Partial paralysis of the arm is a common occurrence after a stroke and is characterized by stiffness of movement and limited motor ability of the arm. Functional paresis (partial paralysis) refers to neurological syndromes, caused by disruption of the nervous system, damage to the nervous system pathway due to damage to the cerebral cortex after a stroke. Paralysis of the arm is the complete absence of voluntary movements of the limb.
Recovery from a stroke may involve the hand or the entire limb. With partial paralysis, the ability to move the arm or hand freely is impaired; the person cannot fully care for himself or perform basic actions. To restore motor ability, the patient must perform daily exercises for finger motor skills and limb motor skills.
The rehabilitation process of restoring motor activity of the limbs requires patience from the patient and a lot of work - this will allow you to return to a full life after a stroke. You can make an appointment with a neurologist by phone. The rehabilitation doctor will develop individual exercises for the patient, the patient will be under constant medical supervision and receive qualified assistance from specialists.
Consequences after a stroke are an integral part of the disease, so you need to be prepared for them. Often, negative consequences that inhibit the restoration of body functions are caused by real estate, a person remaining in a supine position for a long time. The most common of them are bedsores, thrombosis, intestinal paresis and pneumonia.
PREVENTION OF BEDSORES
Bedsores are the death of soft tissues due to impaired blood circulation in them. Locations of bedsores: shoulder blades (shoulders), thoracic spine, sacrum, greater trochanter of the femur, buttocks, tailbone, heels, other places (ears, back of the head, elbows, ankles, fingers).
Bedsores can occur on any part of the body that experiences prolonged pressure. The most dangerous areas are the areas of bone protrusions, that is, those places where the bones are located close to the surface of the skin and the layer of muscle tissue is poorly developed. If the patient lies on his back, then the most vulnerable parts are the heels, buttocks, shoulder blades and the back of the head. In the side position - outer ankle, upper outer thigh (where the top of the thighbone is near the surface of the skin). Rubbing your knees is dangerous (so it is recommended to always place a pillow between them). When sitting for a long time, the entire weight of the body falls on the sit bones (there are two of them, one on each side of the anus), and in these areas there is also a high risk of bedsores.
To prevent bedsores, a number of measures are necessary:
- mandatory daily toileting of the entire surface of the skin (“bathing in bed” - alternately wiping all parts of the body with a sponge). It should be borne in mind that rubbing the skin with camphor alcohol is not recommended, as this leads to overdrying of the skin and disruption of its integrity. To cleanse the skin, it is better to use liquid soaps, shampoos, foams, tonics, and wet wipes specially designed for bedridden patients. You can also use low-allergenic special skin care products.
- daily change of linen;
- in accordance with the degree of risk of developing bedsores, the frequency of changing patient positions is established: for people with a high risk of developing bedsores - every 2 hours during the day and 3.5 hours at night; for persons with very high risk - every 1-1.5 hours during the day and 2.5-3 hours at night;
- only persons with a high and very high risk of developing bedsores and urinary disorders such as incontinence should resort to placing a Foley catheter, since the use of diapers will lead to the development of bedsores;
- use anti-bedsore mattresses (for people at very high risk of developing bedsores). The mattress is continuously deflated at one point and inflated at others, is in continuous movement, constantly exerting a massaging effect on all the soft tissues of the bedridden patient that are in contact with the surface of the mattress;
- elements of massage (stroking and light vibration) should be carried out on areas of the skin exposed to the greatest pressure to improve blood circulation in these areas;
- You should not sit too close to the heaters if pain sensitivity is reduced, and in cold weather it is necessary to carefully wrap weakened limbs, wearing extra socks and gloves.
In order to prevent the formation of bedsores and ulcers, it is important to prevent the patient from lying on a hard, uneven mattress or sitting on a hard seat. Place soft pillows or foam rubber under those areas of the body where there are bony protrusions.
For a patient lying on his back, who cannot be turned on his side, it is convenient to use a rubber pad under the sacrum. The backing circle should be inflated quite weakly so that it changes its shape as the patient moves. Cotton-gauze circles (two small rings made of soft fabric) are placed under the heels (sometimes also under the elbows), while the heels will be above the holes in the rings and there will be no pressure on them.
For a patient lying on his side, it makes sense to place fabric rings under the ankles. It is important to examine the body daily so as not to miss the slightest reddish spot that does not disappear after changing body position.
The detected area of redness is considered the first sign of a bedsore and immediate care must be taken to ensure that absolutely nothing presses on this area until the redness disappears. For example, if a red spot appears on your thigh, it means you should not lie on that side for some time. If the skin has changed color on the lower back and heels, the person should stop lying on his back until the redness of the skin disappears. Instead, he may lie on his stomach or side. This will protect the skin from further damage. If a red spot appears on the buttocks, it is necessary to limit sitting for a while and recommend that the patient lie on his side or stomach. This, of course, will create additional inconvenience, but will prevent the formation of bedsores. Do not rub the skin on paralyzed parts of the body vigorously. To prevent bedsores, it is necessary to carry out a light massage and quartz treatment. Treating bedsores that have formed is much more difficult than preventing them.
In case of formation of superficial bedsores, it is necessary:
- >Continue all the above prevention;
- Use wound healing ointments: Iruksol, Levosin, Levomikol, Actovegin, Solcoseryl 2 times a day, covered with a dry bandage. They also have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects;
- Use specialized collagen sponges, patches, wipes;
- If the bedsore, despite all the above manipulations, does not heal, you need to contact a surgeon.
PREVENTION OF PNEUMONIA
During a stroke, the self-regulation of organs and systems and the body’s self-defense are disrupted. In such patients, the drainage function of the respiratory organs very often suffers. The cough reflex is either reduced or completely absent. Healthy microflora is gradually replaced by pathogenic bacteria. The main factors provoking the development of pneumonia include:
- Old or senile age (after 65 years);
- The patient is overweight;
- Chronic diseases of the respiratory system and cardiovascular system;
- Prolonged stay in a stationary position;
- Carrying out artificial ventilation of the lungs for more than 7 days;
Types of pneumonia:
- Aspiration pneumonia.
It occurs when food particles and gastric juice enter the respiratory passages. A segment of the lung affected by a foreign body stops functioning. Bacteria cause inflammation to develop. - Pneumonia is congestive (hypostatic).
Appears in patients who have been lying down for a long time. Prolonged stay in a horizontal position entails impaired blood circulation in the lungs, their ventilation, and the drainage system of the respiratory organs. Thick mucus accumulates and provokes the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, and as a result, purulent inflammation.
Pneumonia Prevention
- Position the patient on the bed with the head end elevated;
- Changing the position of the patient's body in bed 3-4 times a day;/li>
- Daily sanitization of the nasopharynx by rinsing. Oral hygiene after every meal. Feed the patient only in a sitting position or with the head of the bed elevated (even if feeding through a tube);
- Daily wet cleaning and ventilation of the room where the patient is located, if possible - quartzing the room for 30 minutes 2 times a day;
- Physiotherapy of the upper respiratory tract (eg, ultraviolet radiation);
- >Daily chest massage (percussion, vacuum, cupping);
- Early activation of the patient (starting from the second day after the stroke, perform passive movements in the shoulder girdle, gradually expanding the set of exercises and adding active movements);
- Breathing exercises. Do breathing exercises with the patient several times a day: the simplest is inflating balloons (prevention of congestion in the lungs).
THROMBOSIS AND THROMBOEMBOLISM
The possibility of thrombosis formation is associated, first of all, with the patient’s long immobility. Deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities can occur unnoticed. A person may feel bursting pain in the calf muscles. The leg swells a little.
Prevention of deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities and body:
- Passive gymnastics. In the first days you need to do the simplest movements. Either independently, or passively, with the help of relatives. The main thing is to overcome the main cause of thrombosis development every day: the immobile lying position of the patient.
- Raise your legs 6-10 degrees.
- Application of Compression hosiery: use of special (pneumatic compression) stockings (sizes are selected individually by the attending physician or in an orthopedic salon after taking measurements) or bandaging the legs with an elastic bandage) immediately after the occurrence of a stroke. Attention: very tight stockings may cause bedsores! Particular care should be taken when bandaging the feet of patients with diabetes. Leg binding is not indicated for atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities.
- Use of antithrombotic drugs prescribed by the attending physician.
RULES FOR APPLYING COMPRESSION BANDAGE
PREVENTION OF INTESTINAL PARESIS
There is no specific prevention; therefore, only secondary prevention is possible, which includes:
Bowel release
Defecation should always occur at the same time, morning or evening, daily or every other day. In such cases, the hospital uses medications, enemas, and sometimes careful removal of excrement from the anus to restore bowel function. Some people in their care continue the habit of taking laxatives every day at home. However, this leads to constant irritation of the intestines and is therefore undesirable. For constipation, it is more important to teach how to control your bowels and establish a strict bowel movement routine.
To do this, firstly, the patient needs to adhere to a plant-based diet, eat more greens, vegetables, especially beets, and fresh fruits, figs, plums, and bran bread. Some, in order to achieve a laxative effect and regular emptying of the intestines, eat only one type of food or are undernourished. However, this is hardly advisable, since the body is deprived of adequate nutrition.
Secondly, it is important for the patient to learn to have bowel movements at the same time. It is recommended to clarify it with the person himself, so as not to be late to sit on the toilet or bedside toilet. It is important to provide the opportunity to use a sit-down bedside toilet as early as possible. The toilet seat and bedside bowel movement must be stable and well supported when necessary.
Warm drinks or food taken shortly before going to the toilet promote bowel movements (when they enter the stomach, they cause contractions of the intestines, facilitating the removal of excrement).
Bowel training exercises
- Give a person suffering from constipation after a stroke a glass of hot liquid in the morning (200 to 250 ml).
- Place the client on his left side and massage the left lower quadrant of the abdomen to ease the gastric reflex. After 30 minutes, sit comfortably on the bed or toilet seat. You need to lean forward and lift your legs slightly to put pressure on your stomach. Devices that fix the legs will help place them in this position. Maintain this position for 20 minutes or until the patient has had a complete bowel movement.
- it is necessary to stimulate the patient's physical activity:
- actively (turning in bed every 2 hours, early, at the first opportunity, verticalization of the patient, carrying out a complex of exercise therapy);
- passively (stimulating intestinal motility: abdominal massage, increasing chest excursion during breathing);
- adhere to proper nutrition (easily digestible food, drink plenty of fluids - at least 2 liters of liquid per day, including soups, tea...)
- maintain normal intestinal microflora under the supervision of a physician;
- maintain a positive attitude and comfortable emotional state of the patient, help manage stress.
Patients may require an enema, a laxative, and sometimes manual stimulation of bowel movements. Rotate your gloved finger in the anus until you feel the wall of the rectum relax, gases pass and feces go down. Stop after one minute, and repeat this manipulation until the flow of feces stops after two consecutive stimulations. Rectal suppositories also help during bowel movements. Place the suppositories so that they physically stimulate the intestinal walls. Suppositories must be in direct contact with the intestinal wall to be effective. The suppositories are expelled during bowel movements.
Factors influencing the speed and quality of rehabilitation
There are many factors that influence the speed of recovery after a stroke, so predicting the duration of rehabilitation and likely results is quite difficult.
How long rehabilitation after a stroke will last depends on the individual parameters for each person, as well as on other factors:
- volume of damage: an extensive stroke significantly worsens the severity of the patient’s condition, and also causes many neurological complications that adversely affect the timing of recovery and its quality;
- patient’s age: the older the victim, the longer the recovery;
- localization of damage: circulatory disorders of deep structures are difficult to treat;
- type of stroke: hemorrhagic strokes are less common, but occur in a more aggressive form, and also have a high mortality rate, although the prognosis for rehabilitation is more favorable than for ischemic stroke;
- caused by disorders: the presence of multiple cerebral symptoms, comatose states, severe paralysis and sensory disturbances give an unfavorable prognosis for recovery;
- timeliness of therapy: the most positive results of therapy can be achieved by starting treatment measures in the first 4 hours after the onset of the first symptoms; seeking help at a later time worsens the prognosis;
- compliance with medical recommendations: after the patient is discharged from the medical institution, the patient is given recommendations that can improve the quality of life, prevent the formation of relapse and negative complications.
The severity of the lesion has the greatest impact on the likelihood of restoration of lost functions and the timing of rehabilitation. With extensive strokes, violations of the most important functions are observed, even if the prescribed rehabilitation program is followed, the prognosis is rather disappointing. The greatest difficulties arise with the complete return of speech and motor functions. Close relatives who will devote a lot of time to special activities with the patient can positively influence the situation.
Where is the patient transferred from ARC?
Relatives of a stroke patient are interested in where they are transferred after resuscitation in order to be able to visit the person and provide moral support. It depends on the severity of the brain damage:
- uncomplicated cases are treated in hospital for 3 weeks, then follow-up treatment and rehabilitation are carried out on an outpatient basis;
- in case of a severe attack, the patient is transferred from the intensive care ward to the neurological department, where he can stay for a month or longer.
If the risk of a recurrent stroke attack remains or vital signs are not stable, then the patient remains in the anesthesiology and intensive care unit (ARO).
Stroke Prevention
Prevention of heart attack and stroke in women and men are links in one chain of measures that prevent disability and death in people suffering from cardiovascular diseases.
Cardiologists and neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital use modern diagnostic methods to examine patients, allowing them to identify risk factors for vascular diseases and take measures aimed at preventing diseases. Medicines for the prevention of stroke and heart attack allow you to control the course of the disease, reduce the incidence of acute cardiovascular crises, and the likelihood of complications.
Chance of full recovery after stroke
The rehabilitation period is individual; for some, a few months are enough; for others, it will take years to achieve a positive result. The earlier restoration procedures are started, the more favorable the prognosis. At the same time, the patient’s attitude and focus on results is important; The greater a person’s desire to return to a full life, the more effective the classes and exercises.
At the Yusupov Hospital, a well-coordinated team of professionals (neurologists, rehabilitation specialists, therapists, cardiologists, speech therapists, psychologists) takes part in the rehabilitation of patients after a stroke. Doctors create an individual program for each patient, aimed at the best possible result, observing the following principles:
- early start of restorative procedures;
- systematicity and duration of events;
- complexity of procedures;
- multidisciplinarity of classes;
- compliance of procedures with the patient’s condition;
- active interaction between doctors and the patient and his family.
You can make an appointment with the doctors at the Yusupov Hospital and find out how much rehabilitation after a stroke costs by calling.
Duration of non-drug treatment
Physiotherapy is applied in limited courses (from 10 to 30 days), which can be repeated (for example, in spring and autumn).
Psychotherapy is a long-term treatment method. For example, the average course of such a common type of psychotherapy as cognitive behavioral therapy takes several months. Although there are also one-time psychotherapeutic sessions and trainings designed for one or several sessions (the so-called short-term psychotherapy).
What symptoms require hospitalization?
Signs of a stroke are the following:
- speech is impaired, the person has difficulty pronouncing simple phrases, confuses syllables;
- vision deteriorates sharply;
- an acute headache occurs for no particular reason, dizziness appears;
- on one side of the body there is weakness, numbness, even paralysis of the muscles of the face, arm or leg;
- Coordination and gait are impaired.
If at least one of these symptoms appears, emergency hospitalization and initiation of treatment are necessary.
Cost of hospitalization in medical institutions
| Calling a medical doctor (by profile) to your home | Transportation by ambulance in Moscow within the Moscow Ring Road | Diagnosis, treatment and hospital stay |
| 3,000 - 5,000 rub. | 7,000 rub. | check with operators |
The cost of hospitalization is calculated individually depending on the severity of the patient’s condition and the hospital.
You can choose a good hospital, find out about the approximate cost and duration of hospitalization from our service specialists by calling our hotline (24 hours a day)
Advantages of treatment at the clinic of JSC "Medicine"
On the basis of a multidisciplinary medical center (academician Roitberg’s clinic) there is a cardiac rehabilitation center specially created for the treatment of strokes. How does IB differ from a regular neurological or therapeutic department:
- specializes in the treatment of patients with stroke, its staff is trained to care for this group of patients;
- the necessary diagnostic facilities - from computer and magnetic resonance imaging scanners to a laboratory with round-the-clock operation, an intensive care unit;
- work according to local protocols developed on the basis of domestic and international principles of stroke treatment;
- early mobilization and intensive rehabilitation.
multidisciplinary team:
- vascular neurologists;
- nurses are trained to care for stroke patients;
- rehabilitators who help restore physical capabilities and self-care skills;
- speech therapists – restore the ability to oral and written communication, correct swallowing disorders;
- neuropsychologists - working to restore cognitive functions.
In addition, in the cardiac rehabilitation center there is a constant opportunity to consult with doctors of various specialties: cardiologist, neurosurgeon, psychiatrist, urologist, endocrinologist, etc. In developed countries, hospitalization in stroke units has become the “gold standard”. In the UK and Germany, 9 out of 10 patients with stroke are treated in an IB, in Poland - 8 out of 10.