When going to define this concept, many mean by it aggression, disputes and squabbles, but it covers a wider area of human activity and is not always destructive. The interests of the parties collide in a variety of areas - labor, economic, social, etc. What is conflict is in this article.
Psychology of conflict
When there is no agreement between the parties, when each wants to take a position that is incompatible or contrary to the interests of the other, a clash arises. The concept of conflict is studied by the science of conflictology. It identifies the problem, the motives that prompt the participants to confrontation, their positions and goals. The essence of conflicts is diverse, but tension and negative emotions always arise between the participants, but if desired, you can find a way out of this situation.
Characters
Conflict participants are parties directly involved in the formation and completion of a conflict of interests. There are 2 types of actors: indirect and direct participants in the conflict.
Indirect ones include:
- Provocateur. A person (state, group, society) who provokes another person into a conflict, while in some cases not taking part in the conflict situation itself.
- The provocateur's ally, or "support group." A person who contributes (materially, morally) to the development of a collision.
- Organizer (creator) of the conflict.
- Judge (mediator, intermediary). A person who is a third party in a conflict situation.
Direct ones include:
- The instigator. Sometimes it is a provocateur.
- Subject.
- Sides of the collision.
Sociology of conflict
In any society, clashes are inevitable, because this is the main condition for the development of society. Moreover, the more complex it is, the more groups with divergent and mutually exclusive interests there are, the more reasons for confrontation to arise. Conflict resolution largely depends on the goals pursued by the subjects and their desire to resolve the situation in a positive or negative way. An open struggle between the parties and a real confrontation can be provoked by the incompatibility of needs and values.
Causes of conflicts
This phenomenon is complex and multidimensional, and the factors that gave rise to it vary significantly:
- Values – spiritual, material.
- The causes of conflicts are also related to the imperfection of the developed legal framework.
- A shortage of goods that are of great importance in human life.
- Those who are interested in why conflicts happen should answer that it is due to the characteristics of the psyche. Conflicts in a group arise due to persistent stereotypes of thinking and behavior.
- Poor awareness. Lack of knowledge on certain issues also leads to confrontation.
Structure
The conflict structure includes these components:
- Participants. Individuals and certain social associations, organizations, ideological movements, and other communities can act as participants.
Even states can be participants in a social conflict. - Item. The subject refers to the very essence of the conflict, the contradiction that arose between the participants.
- An object. This is a certain benefit that the parties to the conflict seek to obtain. This could be material wealth, power, maintaining certain spiritual norms, achieving a goal, and much more.
- Macroenvironment and microenvironment. The conditions of the microenvironment and macroenvironment must be taken into account by all parties to the conflict. The microenvironment is the people who surround the conflicting parties and with whom they interact, and the macroenvironment is the social communities that the participants belong to.
Pros and cons of conflict
Experts argue a lot about the role of confrontations in society and highlight the following negative aspects
:
- Time and energy costs, and in some cases material costs.
- Negative emotions that are destructive and can lead to various diseases. This is characteristic of such a phenomenon as interpersonal conflict. Internal struggle, when a person himself does not know how to do it better and more correctly, negatively affects the functioning of the central nervous system, cardiovascular system, etc.
- When thinking about what a conflict is, it is worth noting such a disadvantage as open confrontation, which often leads to physical attacks and hostilities, that is, war.
- Deterioration of relationships and general socio-psychological climate.
- Declining authority and decreased productivity.
On the positive side
include:
- Relieving tension and clarifying the situation. Having found out the opponent’s point of view, it is easier to understand him and determine ways out of the current situation.
- The positive aspects of conflict include the development of new relationships when the dispute ends. Such a collision provides an opportunity to reconsider your views on familiar things and begin to build relationships in a new way. Conflicts in the family, which happen to everyone, strengthen the marriage if the husband and wife are interested in maintaining it. In the case of an organization, this leads to team unity, if this does not contradict general group norms and the foundations of relationships.
- In a social environment, he balances and stabilizes the situation through debates, discussions, compromises, etc.
- The responsibility of the parties increases.
Possible consequences
The end result of a controversial situation can lead to positive or negative consequences. The positive consequences of conflict include progress, growth of an individual or an entire organization. They contribute to a clear formulation of the interests and goals of an individual or company. Participants in a conflict of interests feel involved and useful in solving a task or problem.
Negative consequences destabilize the organization, destroy relationships, weaken further cooperation and communication. Along with emotionality, hostility and mistrust are growing.
Sometimes a showdown requires a third – neutral participant
Types of conflicts
Conflicts between the parties are distinguished by volume and duration, means used, source of occurrence, form, nature of development, etc. Types of conflicts in the sphere of government:
- economic;
- social;
- political;
- organizational.
According to the method of resolution, they can be antagonistic and compromise. In the first case, in the process of confrontation, the structures of all parties are destroyed or one emerges as the winner, and in the second, the interests of all participants are taken into account. Based on the composition of the parties, the following are distinguished:
- intrapersonal;
- interpersonal and group;
- conflicts in organizations.
Classification
Conflicts are divided into:
- Reasons for appearance. There are subjective and objective reasons for the development of the conflict. Objective reasons arise in the absence of control on the part of the individual, while subjective reasons are controlled by him to one degree or another and are closely related to his personality, character, priorities, goals and interests.
- Level of openness. Conflicts are divided into open and closed.
Open conflicts mean situations where the parties directly express their own dissatisfaction: they quarrel, insult opponents, argue, and resort to violence. Closed conflicts are not always noticeable to others; they use indirect methods of influence. - The position of the conflicting parties. If one party to a conflict occupies a higher position and has more power than the other, such conflicts are called vertical. If parties are in conflict, the participants of which are generally equal to each other, such a conflict is horizontal. Accordingly, a conflict between parents and minor children, between a teacher and a student, between a boss and a subordinate, and so on can be considered vertical, while horizontal conflicts usually concern relationships in teams.
- Composition of the parties. If the conflict is not related to differences in ideology or opinion, and the participants do not belong to different ideological communities, such a conflict is called interpersonal. Group conflicts include conflicts in which the parties belong to separate social communities. There are also political conflicts, which are divided into domestic and foreign policy.
- Features of influence on participants. Conflicts can vary in duration (short-term, long-term), degree of scale (global, regional, group, personal), and severity.
- Contents. If the basis of the conflict is the subjective hostility that the parties experience towards each other, then such conflicts are called emotional.
If the essence of the conflict is based on reliable and reasonable argumentation and is not directly related to personal hostility, then this is a rational conflict.
Stages of conflict
In its formation, the collision occurs in several phases:
- At the pre-conflict stage, tension between the parties increases. Up to a certain point, it proceeds secretly, but when any incident occurs, that is, a push, it turns into an open form.
- The stages of conflict include the conflict itself. The parties move to open confrontation and can both challenge themselves and respond to it. The apogee is to cause as much damage to the enemy as possible.
- Those who want to know what a conflict is and what its third stage is, we can answer that at the resolution stage a change of guidelines occurs. Taking into account their capabilities and the capabilities of the enemy, the parties begin to search for ways out of the current situation, and the confrontation loses its intensity.
- In the post-conflict stage, there is a temporary respite or a lasting peace based on consensus.
Conflict resolution
Any conflict situation is sooner or later resolved or frozen. In order to eliminate contradictions and constructively resolve the issue, it is necessary to recognize the existence of the conflict and identify its main participants. Then it is worth organizing a negotiation procedure, discussing pressing issues, searching for compromise solutions and putting the adopted resolutions into practice.
If it is possible to achieve such results, the conflict can be considered a positive phenomenon that has positive consequences.
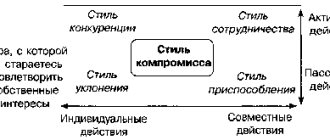
What strategies exist for dealing with conflict?
Insisting on their own, the parties can adhere to the following course:
- Escape, evasion, or accommodation.
In the first two cases, the subject refuses to discuss anything, negotiate, etc. In the latter, he agrees with the other side in everything, fearing to make retaliatory demands. - Strategies for dealing with conflict include smoothing
. The conduct of the parties may consist of apologizing, making promises, etc. - Compromise
is a mutual concession, and what a conflict is in this case will now be clear. Moreover, each of the subjects is satisfied with the solution found. - Coercion or confrontation.
The interests of the other side and its opinion are not taken into account, there is an active confrontation. - Cooperation
. The parties sit down at the negotiating table and jointly look for ways to break the impasse.
Rivalry
Rivalry is a type of behavior when a subject strives to satisfy his own interests, causing damage to the interests of the opposing subject. Following the presented strategy, a person is confident that only one participant can gain the upper hand in a conflict, and victory for one will always mean defeat for the other. A person who prefers competition will “push his line” in every way available to him. They will not take into account the opposite position.
Basic human actions with the “Competition” strategy
- Tight control over your opponent's actions
- Constant and deliberate pressure on an opponent by any means
- The use of deception and tricks to create an advantage in one’s favor
- Provoking your opponent to make mistakes and ill-considered steps
- Reluctance to engage in constructive dialogue due to overconfidence
Pros and cons of the “Rivalry” strategy
Rigidly defending one's position can, of course, help the subject gain the upper hand in the event of a conflict. But such a strategy cannot be applied if the subsequent interaction of people involves long-term relationships, for example, joint work, friendship, love. After all, relationships can develop and generally have the right to exist only if the desires and interests of all people are taken into account, and the defeat of one will mean defeat for everyone. Therefore, if the person with whom you have a conflict is dear to you or the relationship with him is important to you for some reason, it is better not to use the strategy of competition to resolve the conflict.
2
How to avoid conflict?
There are many ways to protect yourself from open confrontation. We need to improve our level of literacy and integrity. After all, the more importance a person places on moral education, the stronger his desire to resolve the situation peacefully, without throwing hysterics and without getting personal. Awareness of the conflict is already a step towards finding a way out of it. Even at the earliest stage, when tension just arises, you can start negotiations, and then analyze the situation and avoid problems.
How to resolve the conflict?
This process consists of three stages:
- Collision diagnostics.
- Finding a strategy for resolving disagreements.
- Execution of a set of methods.
Conflict resolution begins with identifying the problem and discussing it. It is necessary to listen to each side and begin to search for a solution that would suit both, carefully analyzing all its positive and negative characteristics. It is necessary to clarify all the details of the contract, options for action in the event of force majeure. In the future, you need to act according to the adopted plan.
Conflict resolution methods
They pursue the goal of eliminating or minimizing the causes that gave rise to the collision and correcting the behavior of the participants:
- Intrapersonal methods are designed to help a person protect his interests without infringing on the opponent’s positions.
- Structural methods are used in organizations and include clarification of job requirements, existing reward and punishment systems, etc.
- Interpersonal methods.
- Conflict resolution methods include negotiation.
- Retaliatory aggression.
How not to lose in a conflict?
The wise proverb: “Give in - be smarter” contains the whole meaning. Often, by taking a step forward, accepting a person with all his strengths and weaknesses, you can win. The rules of behavior in conflict are always the same - you must try to understand the other, his motives, be honest with yourself and tolerant of others. Sometimes it is useful to involve a third party in the dispute, who will impartially assess the situation and establish contact with each of the parties. Well, the most important thing is to treat your opponent with respect and save face in any situation.
Compromise
Compromise is a partial satisfaction of the interests of all subjects of conflict interaction.
Basic human actions with the “Compromise” strategy
- Focus on equality of positions
- Offering your own options in response to your opponent’s offer of options
- Sometimes using cunning or flattery to gain favor from an opponent
- Striving to find a mutually beneficial solution
Pros and cons of the “Compromise” strategy
Despite the fact that compromise implies satisfaction of the interests of all subjects of conflict interaction, which, in fact, is fair, it is important to keep in mind that in most situations this strategy should be considered only as an intermediate stage in resolving the situation, preceding the search for the most optimal solution, completely satisfactory to the conflicting parties.
5