Psychospeech development delay (PSRD) is a group of disorders that are united by clinical symptoms of delayed development of speech and psyche. These include expressive and receptive speech disorders, unspecified diagnoses, as well as mixed specific disorders in the field of human psychological development (specific disorders of speech development, school skills, motor functions without a predominance of one of the symptoms to be able to make an accurate diagnosis).
They are usually associated with atypical functioning of the central nervous system, which ultimately leads to changes in the pace of all mental development and affects the following components:
- memory;
- attention;
- thinking;
- speech;
- emotional-volitional sphere;
- behavior.
Delayed psycho-speech development is not synonymous with a child’s mental retardation. The key difference is that mental retardation can be corrected and compensated for, while mental retardation cannot be corrected. Difficulties may arise if you do not contact a specialist in a timely manner, because... speech problems and cognitive deficits are steadily increasing.
ZPRD syndrome is determined by a doctor (psychiatrist, neurologist) based on the symptoms present. After determining the type of psycho-speech delay, an individual correction plan is developed, as well as a possible referral to a specialized kindergarten, school or development group (if we are talking about a combined institution).
What it is
What does a diagnosis of REP mean? The meaning of this abbreviation is residual encephalopathy. The disease is characterized by the death of neurons and impaired brain function. The word "residual" means "residual."
This pathology is always secondary. It occurs as a residual phenomenon after suffering diseases of the central nervous system. This complication occurs when brain diseases are insufficiently or incorrectly treated.
Parents of children are often interested in what a diagnosis of REP in a child means. The decoding of this medical abbreviation is similar, it is residual encephalopathy. With adverse effects on the embryo or birth injuries, perinatal encephalopathy occurs. This disease is diagnosed in children in the first weeks and months of life. If the treatment of such a pathology was carried out poorly, then REP may develop in the future as a residual phenomenon. Often this complication does not appear immediately, but after several months or even years, and it can be difficult to diagnose.
Symptoms and consequences of perinatal encephalopathy
Symptoms of the disease manifest themselves differently at different periods of a child’s life. To simplify classification and improve diagnosis, it is customary to distinguish three main periods of PEP: acute (during the first month of life), recovery (up to 1 year, less often up to 2 years - mainly in premature infants) and outcome of the disease. There is a possibility that the child’s body - as a self-regulating system, from the point of view of osteopathy - can fully recover and neutralize the symptoms of the disease by adapting to them. This does not mean complete recovery, since the effects of AEDs may appear at a later age. Therefore, if you suspect a disease, you must immediately show the child to an osteopathic doctor, who can make the correct diagnosis and prescribe competent, adequate treatment aimed at ridding the body not of the consequences, but of the causes of the disease.
Causes
The diagnosis of REP is usually made to patients if they show signs of brain disorders after suffering pathologies of the central nervous system and other diseases that adversely affect the state of neurons. Residual encephalopathy most often occurs due to the following diseases and conditions:
- Severe head injuries accompanied by concussion or skull fractures.
- Congenital perinatal encephalopathy. This condition develops after birth injuries and a pathological course of pregnancy in the mother of the child.
- Inflammatory diseases of the brain.
- Excess urea in the body. This deviation is often observed in diseases of the liver and kidneys.
- Stroke and other cerebrovascular accidents. The cause of the pathology can also be vascular atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes mellitus. Endocrine disorders and excess glucose in the body adversely affect the condition of the nervous tissue.
- Toxin poisoning. Heavy metal compounds, certain medications, and alcohol have an adverse effect on the brain.
- Use of narcotic and psychotropic drugs. Even with timely detoxification, patients often retain signs of brain pathology.
Often the causes of this type of encephalopathy are several unfavorable factors. The physician must take a thorough history of the patient before diagnosing REP. This disease can develop after a fairly long period of time after suffering pathologies.
Classification
Encephalopathy that develops in childhood is divided into
- Perinatal . Appears in infancy.
- Residual . Signs and symptoms of this form of cerebral encephalopathy in children are detected after 3 years.
Depending on the provoking factors of the disease, the following forms are distinguished:
- Vascular , caused by progressive diseases of the arteries and veins that impair the blood supply to the brain.
- Discirculatory , associated with blood stagnation and impaired outflow. It is often observed in children suffering from congenital pathologies of cerebral vessels, viral diseases complicated by sepsis, endocrine disorders with persistent changes in the vascular structure. The risk group includes children whose mothers drank alcohol or drugs during pregnancy.
- Post-traumatic , developing after a head injury, including birth. The severity of this disease directly depends on the intensity of the symptoms of the pathology, the age of the child, and problems with blood vessels. Mainly manifested by dizziness and headaches. Characterized by sleep disturbances, weakness, and mood swings.
- Toxic , caused by toxic substances accumulated in large quantities in the blood with damage to brain cells. For example, when pathological jaundice occurs in newborns, when bilirubin, formed during the breakdown of fetal hemoglobin, is not broken down by liver enzymes, but is converted into toxic elements and enters the brain, destroying cells of the nervous system. Often, jaundice in this form occurs due to a progressive blood disease, a mismatch in the blood groups of mother and baby, abnormal structure of the liver and bile ducts, infection with hepatitis or toxoplasmosis.
- Hypertensive , in which dysfunction of the kidneys and adrenal glands, as well as persistent high blood pressure leads to diffuse changes that damage cells of the nervous system.
- encephalopathy . It develops due to a deficiency of B vitamins, which causes insufficient nutrition of neurons and their inevitable destruction.
- Epileptic encephalopathy develops with progressive episyndrome. Against the background of an increase in convulsive attacks, neurons die, forming additional foci of epiactivity, which are recorded by an electroencephalogram.
Symptoms
Residual encephalopathy in an adult patient is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Sudden memory loss. The patient becomes forgetful. He may have difficulty remembering even recent events.
- Decrease in intelligence. The patient's thinking process is disrupted due to the death of neurons and impaired cerebral circulation.
- Emotional lability. The patient's mood often changes, and there is increased irritability and tearfulness.
- Sleep disorders. Patients suffer from insomnia at night, and during the day they feel drowsiness and lethargy.
- Convulsive seizures. Seizures become more frequent as the disease progresses.
- Speech, vision and hearing disorders. The patient slurs his words. Vision and hearing deteriorate due to the death of nerve cells.
- Impaired coordination of movements. The patient's gait becomes unsteady, and he often loses his balance.
- Asthenia. The patient complains of constant fatigue and high fatigue.
- Headache. Migraine-like attacks occur. In this case, the pain syndrome is not relieved by analgesics.
These manifestations of pathology increase as the disease progresses. The more neurons die, the more severe the impairment of brain function.
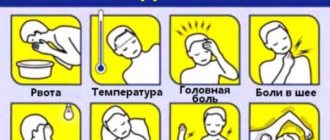
What signs indicate a diagnosis of REP in a child? This disease can sometimes be difficult to identify in young children. After all, the baby cannot complain about feeling unwell. Parents should be alert to the following manifestations:
- tearfulness;
- increased reaction to external stimuli;
- frequent nausea and vomiting;
- weak sucking reflex;
- increased muscle tension;
- arrhythmia;
- exophthalmos (bulging eyes).
In older children, the disease is accompanied by the same symptoms as in adults. Residual encephalopathy has an extremely negative effect on the child’s intelligence. Children lag behind in mental and physical development, experience difficulties in assimilation and memorization of information, and it becomes difficult for them to study. Often, sick children experience sudden fainting.
Features of the course of complex dyslalia
The more complex the combination of disorders, the more difficult it is to cope with it. Accordingly, this affects the general background of the disease. In complex forms, mental and general developmental delays may be observed. It is necessary to engage in in-depth research of the child in the aspect of his psyche, intellectual development, hearing, and vision. Complex dyslalia may be a signal that there are problems with them. People who are hard of hearing often distort or change the “T” sound.
A child with second or third degree hearing loss does not have a metallic tone in his voice. The voice has softness or, in other words, viscosity. Children with vision problems may have dyslalia defects corresponding to its complex types. This is caused by poor visual control. In such patients, sigmatism is observed 4 times more often than in healthy children.
Complications
How dangerous is a neurologist's diagnosis of REP? Without treatment, this type of encephalopathy can lead to the development of the following complications:
- severe dementia in adult patients;
- mental retardation in children;
- dropsy of the brain;
- neurocirculatory dystonia;
- paralysis;
- Parkinson's disease;
- epilepsy.
The likelihood of complications increases if the patient seeks help too late, when a significant number of nerve cells have died.
Pediatric neurologists often talk about minimal brain dysfunction when diagnosing REP. What does this mean? This complication is expressed in mental disorders in young patients. The child becomes restless, hyperactive, excitable, and often makes erratic movements. These manifestations intensify during puberty against the background of hormonal changes in the body.
How do osteopathic specialists evaluate perinatal encephalopathy?
From the point of view of osteopathy, the entire complex of central nervous system diseases, united under this term, is a consequence of mechanical disorders in the body of the fetus of a newborn child. Moreover, they can occur during pregnancy or later - during difficult childbirth and/or caesarean section. The reasons leading to the appearance of the disease are:
- dysfunction of the spinal column or its individual sections;
- disturbances in the functioning of internal organs;
- prolonged oxygen starvation;
- circulatory disorders.
But even if the fetus developed normally during pregnancy, there is a high probability of injury during childbirth, since, passing between the pelvic bones, the fetus rotates 360 degrees, which can cause disturbances in the skeletal structure and muscle tissue. The most common disturbances observed are in the position of the cervical vertebrae. In most cases, in the first weeks of a child’s growth, the effects of damage are completely neutralized by the body on its own. But this is not always the case; any changes or deviations in development can lead to complications, which subsequently provoke disturbances in the blood supply to the brain and the manifestation of perinatal disorder.
Diagnostics
Before diagnosing REP, the doctor questions the patient and examines his medical record. It is necessary to identify all neurological pathologies that the patient suffered in the past. Additional research methods are also prescribed:
- electroencephalogram;
- MRI and CT of the brain;
- clinical and biochemical blood test;
- Dopplerography of cerebral vessels.
Memo to parents
- CPR is not a death sentence; it is a disease that can be fully or partially corrected.
- According to statistics, a schoolchild can be diagnosed with mental retardation by the age of 10.
- To make a diagnosis, one doctor is not enough; you need to collect a PMPK.
- Without a decision of the commission, the child does not have the right to be transferred to individual education, to a specialized class, or to boarding school.
- There should be no pressure on parents from members of the commission.
- Parents retain the right to refuse to undergo the PMPK.
- The diagnosis of the commission is announced without the presence of the child!!!
- To make a diagnosis, a complex of symptoms is taken into account, and not just neurological indicators.
Drug treatment
Treatment of this type of encephalopathy should be comprehensive. To restore normal brain function, patients are prescribed nootropic drugs:
- "Cinnarizine";
- "Piracetam";
- "Cavinton";
- "Noopept";
- "Pantogam"
- "Phenibut";
- "Phenotropil".
These medications improve cerebral circulation and metabolism. It is useful to take them together with B vitamins. This will help restore normal functioning of the central nervous system.
For severe headaches, analgesics usually do not help. Therefore, patients are prescribed non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs:
- "Ketanov";
- "Nise";
- "Ibuprofen."
For severe pain, treatment with corticosteroids is recommended: Prednisolone or Dexamethasone.
If a patient experiences frequent epileptic seizures, it is recommended to take anticonvulsants: Finlepsin or medications based on valproic acid.
For increased irritability and mood swings, doctors prescribe mild sedatives: Afobazol, Glycine, Persen. These medications will help reduce emotional instability. In severe cases, antidepressants and tranquilizers are indicated.
Other therapies
Drug treatment is supplemented with therapeutic massage sessions. This helps stimulate cerebral circulation. Therapeutic gymnastics is also useful. When performing exercises, you need to pay special attention to the collar area. Active neck movements help improve brain nutrition.
A child suffering from residual encephalopathy needs developmental activities. When correcting mental disorders, it is very important to train memory and attention. In cases of severe developmental delay, home schooling is indicated for school-age children.
Pathogenesis of dyslalia
The reasons vary for different types. Accordingly, the correction required is different.
Physiological prerequisites for mechanical dyslalia
The mechanical type is caused by physiological and anatomical defects. They do not make it possible to pronounce sounds correctly, the sound that they heard. This usually occurs due to dental defects - bite, incorrect shape and location of incisors, underdeveloped jaws. Doctors consider the main reasons:
- the frenulum of the tongue is too short;
- structural features of the bones of the jaw and face;
- palate defects;
- pathology of the upper lip;
To get rid of mechanical dyslalia, a dentist and an orthodontist are needed. The child must undergo a special correction course. The best results are achieved at the age of 5-6 years.
Forecast
If the diagnosis of REP was made in a timely manner and the patient completed the full course of therapy, then the disease can be cured. Lost neurons can no longer be restored. But if the process of brain cell death has just begun, then therapy will help maintain the normal function of the central nervous system. Therefore, treatment is effective only at the initial stage of the pathology.
In advanced cases, it is no longer possible to restore lost brain functions. Even after treatment, the patient retains signs of memory impairment, thinking disorders and emotional lability. In children, this can lead to severe mental impairment.
Prevalence of the problem
Dyslalia is a common problem. There are different estimates on this matter, on average, the number of children suffering from this speech disorder is about 25-30% in preschool age. As you get older, this number decreases. At primary school age this percentage drops to 17-20%. At older ages there are only 1-2% of such children.
The disease is a common occurrence, most common in the practice of speech therapists. According to various estimates, the average number of children with such problems in preschool age is 25-30%, in elementary grades – 17-20%, and in older age – 1%.
More often in the practice of speech therapists there are combined articulation disorders that create a barrier to the development of writing. Children, at the same time, have an extensive vocabulary, the structure of speech is not disturbed. All grammatical laws are observed - cases, declensions, endings.
Prevention
How to prevent the occurrence of residual encephalopathy? Prevention of this dangerous disease consists of observing the following measures:
- Injuries and pathologies of the central nervous system must be carefully treated.
- During pregnancy, women need to be under regular supervision by an obstetrician-gynecologist. It is also necessary to avoid any adverse effects on the embryo.
- We must try to prevent traumatic brain injuries in children.
- It is necessary to protect yourself from poisoning with toxic substances, and also stop drinking alcohol.
- Patients who have suffered pathologies of the central nervous system need to be regularly monitored by a neurologist and undergo all necessary examinations.
These recommendations will help avoid the occurrence of residual encephalopathy. It is important to remember that this disease is much easier to prevent than to cure.
Risk factors
Risk factors that increase the risk of developing the disease include:
- chronic maternal illnesses. Often they are not transmitted directly to the child, since they are not hereditary, but at the genetic level they cause the manifestations of various pathologies and abnormalities in the development of the fetus and the already born child;
- infectious diseases suffered during pregnancy. Untreated pathologies that can manifest themselves against the background of a general weakening of the body’s immunity due to pregnancy are very dangerous;
- poor nutrition. During the period of gestation, the mother's body must receive the entire necessary set of proteins, vitamins and minerals. Nutrition should be balanced and agreed with a doctor to avoid food allergies and digestive disorders;
- mother's age is too young. A girl’s body may simply be unprepared to bear a full-fledged and healthy child. If the expectant mother is too young or has insufficient physical development, she should be under the constant supervision of a specialist throughout the entire period of pregnancy and after childbirth;
- metabolic disorder in the mother's body. Since her body is closely interconnected with the body of the unborn child, any disturbances affect the nutrition and health of the fetus. Therefore, proper nutrition, which was mentioned earlier, is so important, as well as the trouble-free operation of the organs responsible for metabolism in the body;
- pathologies during pregnancy. Early and late toxicosis, stress, physical activity and other factors are very dangerous, which can lead to interruption and abnormal course of pregnancy;
- unfavorable environmental conditions. Unfortunately, today this factor is more dangerous than many others, because it is often impossible to avoid the effects of harmful external manifestations. It is recommended to contact specialists (including an osteopath) who will help to significantly neutralize the adverse effects of the environment;
- prematurity or postmaturity of the fetus.
- Thus, most risk factors are associated
specifically with the health of the mother. Therefore, during pregnancy, she should carefully monitor her well-being, listening to the advice of a good doctor. In parallel with other specialists, it is recommended to regularly visit an osteopath, who will also monitor the progress of pregnancy and will be able to correct possible deviations using osteopathic methods, without the use of drugs that can harm the unborn child.