- Types of brain tumor stage 4: classification
- Symptoms of stage 4 brain cancer
- Diagnosis of a brain tumor
- Treatment
- What factors influence survival?
- Survival prognosis
All types of cancer are usually classified into stages, depending on how far the tumor has spread. The stages of a brain tumor vary according to their characteristics:
- most often, the first stage of cancer corresponds to a neoplasm that is located within one organ,
- the second - spread to nearby (regional) lymph nodes,
- the third - spread to neighboring organs.
These stages of brain tumor are significantly different from the fourth. Late-stage cancer is called metastatic because it has distant metastases in various parts of the body. Such tumors are practically untreatable, the prognosis in most cases is unfavorable, the doctor can only slow down the progression and prolong the patient’s life.
For brain cancer, the picture is somewhat different. Such tumors are primarily dangerous not because of metastases, but because they damage nerve centers and disrupt important brain functions.
For brain tumors, grades of malignancy are distinguished. The most significant sign by which a tumor is classified as one or another degree of malignancy is the microscopic structure of the cells. There are 4 criteria:
- Atypia is an “incorrect” cell structure.
- Active cell division.
- Active growth of new blood vessels.
- Areas of necrosis - tissue death due to insufficient blood flow.
Depending on the presence of these signs, 4 degrees of malignancy are distinguished:
- I degree - they grow slowly and never grow into surrounding tissues.
- Grade II - cells have one of four signs of malignancy, usually atypia. These tumors grow slowly but can invade surrounding tissue.
- Grade III - two signs of malignancy are present, but no necrosis. These types of cancer behave like full-fledged malignant tumors. They grow quite quickly and spread into the surrounding healthy tissue.
- IV degree - 3 or all 4 signs are present, necessarily including necrosis. These are the most aggressive and deadly tumors.
Causes of tumor appearance
According to global statistics, brain cancer is the tenth leading cause of death in adults. About forty types of tumors are known, among which there are both benign and malignant. There are several known causes of the disease.
Age
. Cancer most often affects older people. Brain cancer is usually found in patients over fifty years of age. But it can also occur at a young age.
Heredity
. The risk of developing cancer forgetting increases if close relatives have suffered from various forms of cancer. The risk of transmission of the disease through the maternal line is especially high (however, men are more often affected than women).
Influence of external factors
. The risk of the disease is increased among workers of enterprises dealing with chemical, toxic or radioactive substances, as well as among people living in areas with unfavorable environmental conditions. In addition, the risk is increased in people who have suffered a traumatic brain injury.
Causes
The impossibility of identifying the etiological factor excludes the possibility of conservative treatment of a tumor of any stage.
The main theories of the occurrence of brain tumors:
- Genetic determination. Oncologists claim the presence of a genetic predisposition to cancer. Every person has genes that cause cancer. The start time of the activity of the genetic material, localization, intensity of the process - individual characteristics;
- Viral activity provokes DNA changes. A change in the genetic component determines the likelihood of developing an oncological process. The etiological role of papillomavirus in the occurrence of cervical cancer has been proven. Research into infectious agents of intracerebral tumors is ongoing;
- Chemical - supporters of the theory consider cerebral cancers to be a consequence of the action of certain types of chemicals. Taking pharmaceutical drugs with a toxic effect on brain cells, intoxication during illnesses can cause oncological conditions;
- Physical – the occurrence of cancer as a result of exposure to radiation, X-rays, and other types of ionizing radiation.
Literary sources describe other causes of oncology. Until the real causes are identified, it is impossible to treat neoplasms using conservative methods.
Primary and secondary tumor
The tumor is classified according to many factors. According to typology, the tumor can be primary (originally arose in the meninges) or secondary (originated in another organ, and its metastases spread to other tissues). The term “brain cancer” is not entirely correct. The fact is that this is one of the types of malignant neoplasms that develop specifically from epithelial tissues. However, most often we are talking about glioma or glioblastoma: these types of diseases occur in 60% of cases. Such tumors develop from glial cells, which are involved in regeneration and metabolism, and also help conduct nerve impulses. It is these neoplasms that are primary. At the fourth stage, they begin to metastasize and penetrate other tissues of the body. Unfortunately, cancer is most often discovered when it has reached an advanced stage.
Tumors of childhood
Even children can get a brain tumor. Among childhood cancers, brain tumors account for about 20%. This is second only to leukemia. More often they are observed in children of the first year of life. Teratomas are found mainly in children. In older children, benign astrocytomas (more than 30%), primitive neuroectodermal tumors (medulloblastoma, pineoblastoma - 20%) and ependymomas (15% of cases among children over 1 year of age) predominate.
At present, it is not known for certain how brain tumors form in children. It has been established that they develop more often in boys than in girls. The reasons why brain tumors are more common in male children have not been established.
How does a malignant brain tumor develop?
Primary neoplasms develop in the structures of the brain or nearby tissues:
- shells,
- nerves,
- pineal gland.
The mechanism of disease development is characteristic of all cancer lesions. The process starts with the appearance of abnormal cells with a mutated DNA chain, due to which they begin to divide uncontrollably. The mechanism of natural death is switched off, and the immune system is powerless. As a result, the development of mutant cells begins to progress in the tissue, which leads to the appearance of a tumor. In some cases, they turn out to be benign, and then you can get rid of the disease without resorting to radical methods. True, patients do not always seek medical help on time: often the occurrence of such tumors is not accompanied by severe symptoms.
The whole truth about brain cancer
Despite the alarming situation associated with the development of coronavirus infection, our lives do not stop: visits to doctors, timely diagnosis and treatment must proceed according to plan. This is especially true for cancer patients, as well as those who have noticed alarming symptoms. Candidate of Medical Sciences, neurosurgeon, radiosurgeon, head of the Center for High-Precision Radiology Sergei Ilyalov talks about this.
Brain tumors have been shrouded in a veil of fatal hopelessness for many years, remaining the most frightening diagnosis of all possible in oncology. This gloomy confidence is due to the fact that half a century ago there were simply no options for treating many diseases. Thus, brain cancer became synonymous with an incurable disease.
By 2021, the picture has changed significantly, and today we can talk about the variety of methods that modern medicine offers.
What is hidden behind the concept of “brain cancer”?
Strictly speaking, there is no such diagnosis as “brain cancer”. Cancer is a tumor of epithelial cells, and there are no epithelial cells in the brain. However, the brain has a very complex cellular structure and its bulk consists of glial cells (white matter) of various types that support and nourish neurocytes (gray matter), cells of the meninges, cranial nerves and other structures, therefore there are more than a hundred varieties of malignant and benign tumors that primarily develop in the brain. In addition, secondary tumors can develop in the brain as a result of metastasis of malignant tumors of other organs.
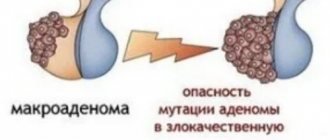
Benign tumors are characterized by a slow growth rate, while they do not penetrate into surrounding tissues, do not metastasize and do not have a toxic effect on the body, but, increasing in size in the confined space of the cranial cavity, they can pose a threat to the patient’s life due to compression of the brain.
Why do brain tumors occur?
There are many reasons for the development of brain tumors. These include heredity, radiation, exposure to carcinogenic substances and others. According to statistics, malignant brain tumors are more common in men, but women are twice as likely to suffer from benign tumors of the meninges (meningiomas).
At various times, the ability to cause brain tumors has been attributed to microwave ovens, mobile phones and wireless Internet, but over the years of research, none of these hypotheses have been confirmed. In recent years, the ability to cause malignant tumors has been attributed to in vitro fertilization (IVF), but not a single domestic or foreign study has revealed the effect of this method on the incidence of tumors either in the brain or in other organs. Pregnancy that occurs after IVF or naturally does not cause tumors, but powerful hormonal changes can accelerate the growth of existing tumors. Fortunately, such cases are extremely rare.
Is there prevention?
Due to the fact that the mechanisms of development of primary brain tumors are not fully understood, specific methods of prevention do not exist today. The vast majority of people do not have a hereditary predisposition, but a risk group, although very conditional, still exists. First of all, these are workers in the field of radiation production and enterprises where carcinogenic substances are involved - they have a higher risk than in the general population, but they also undergo medical examinations more often and more thoroughly.
Also, the risk of developing tumors depends on age. There are tumors that in most cases are characteristic exclusively of childhood, for example, medulloblastoma. In adults, benign and malignant neoplasms occur at any age, but the likelihood of their occurrence increases after 45 years. Hereditary transmission of the risk of brain tumors is characteristic of neurofibromatosis type 2 and von Hippel-Lindau disease.
A separate risk group consists of patients with malignant tumors of various locations - breast, lung, rectum, kidney and skin, which make up the top 5 tumors that most often metastasize to the brain. Therefore, cancer patients should undergo regular examinations even with long-term remission of the disease.
How to identify a tumor?
The clinical picture of the tumor depends, first of all, on its location, since each part of the brain has its own “area of responsibility.” Sometimes the tumor can be located in the “silent zone”, and then the disease is asymptomatic until the enlarging tumor affects other areas or causes an increase in intracranial pressure.
The most common symptoms include:
- intense headache, poorly relieved by analgesics. Sometimes - with nausea and vomiting
- seizures
- visual disturbances (rapid decrease in vision, limited visual fields, double vision, flashes before the eyes)
- movement disorders (impaired limb strength) in half of the body
- problems with coordination, dizziness
- sensory disturbances in half the body
- hearing impairment (ringing or tinnitus, hearing loss)
- problems with speech, memory or thinking
Many of the symptoms that occur with brain tumors can also occur as a result of other diseases, so a neurologist will help you understand the cause of your complaints. A neurological examination allows one to suspect a brain tumor and promptly refer the patient for examination.
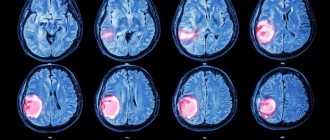
For diagnosis, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with intravenous contrast is performed - this simple and safe method allows you to clearly visualize the structures of the brain and identify any deviations from the norm.
Is there any hope for recovery?
Looking back, we can say with confidence that we are lucky to live in the age of high technology. Today, domestic medicine has all the capabilities to provide high-tech treatment. Firstly, this is an accurate diagnosis, thanks to which it is possible to differentiate active tumor tissue from healthy brain tissue, assess the actual extent of spread and monitor the dynamics of treatment. Secondly, the use of the latest drugs to control the disease. And, of course, the development of surgery and radiation therapy. Modern radiation therapy is developing towards the most precise irradiation of the tumor with minimal involvement of surrounding healthy tissue. Radiosurgery is at the forefront of high-precision radiation techniques.
The use of this technology makes it possible to cure many benign brain tumors and intracerebral metastases without trephination, pain and a long recovery period.
Despite the fact that “brain cancer” has not lost its threatening significance, you definitely shouldn’t be afraid of it - primary malignant brain tumors are statistically quite rare. The incidence rate of the most “evil” tumor, glioblastoma, is about 3 cases per 100 thousand population.
The main thing to remember is that the earlier the disease is detected, the greater the chances of a favorable outcome. This applies equally to malignant and benign tumors. “Folk methods” should be avoided, as there is no reliable evidence of their effectiveness. Self-medication can be fatal, while modern technologies improve treatment outcomes for millions of patients year after year. The best means of prevention is a healthy lifestyle and careful attention to your own health.
Original: https://med-info.ru/content/view/8689
Stages of brain cancer
All types of cancer are usually classified according to the size and prevalence of the disease.
Stage I
. The tumor arises in the membranes of the brain or develops from nerve cells. It is small in size and does not extend beyond the skull. As a rule, at this stage there are no obvious symptoms, and if a tumor is found, it happens by chance, during a regular medical examination.
Stage II
. The disease extends beyond the boundaries of one organ and metastasizes to the nearest lymph nodes. The first general symptoms appear: nausea, headache, dizziness, loss of appetite and others.
Stage III.
Metastases penetrate to other organs, the disease progresses, causing more and more obvious symptoms. Most patients seek qualified help at this stage of the disease.
IV stage
. Metastases have spread throughout the body. The tumor is practically untreatable. The cancer is entering its terminal stage.
Prognosis for glioblastoma
Life expectancy and survival depend on the type of glioblastoma, the location of the lesion, the general condition of the patient and the presence of concomitant diseases.
Without appropriate therapy, only about 10% of patients can survive more than 3 months after diagnosis.
Proper treatment of glioblastoma of the brain in most cases can prolong life to 1.5–2 years, and 5% of such patients live five years or longer.
The exception is the most malignant - glioblastoma multiforme. Even competent treatment does not guarantee survival for more than one year.
Degrees of malignancy
The problem with brain oncology is not even the metastasis of the disease, but the fact that the tumor that has affected the nerve centers disrupts important processes. A person begins to lose his sense of smell, vision, hearing, and touch. Fine motor skills are impaired, and sometimes the sense of reality is lost. For brain tumors, there are several criteria and degrees of malignancy:
- Atypia. Cells mutate, become atypical, “wrong”.
- Active division of the affected elements begins. The cells multiply, causing tumor growth.
- New vessels appear that grow into the neoplasm.
- The appearance of necrotic foci. The tumor compresses the tissues; due to insufficient inflow or outflow of blood, they begin to gradually die.
If the cancer enters the terminal stage, there is virtually no chance of recovery. Life expectancy depends on a number of factors, which include not only the doctor’s experience and the availability of suitable equipment, but also the patient’s desire for life.
How long do people live with stage 4 glyblastoma?
The average survival rate of patients after a diagnosis of stage 4 organic brain damage is about 2 months. This figure is arbitrary, since each patient’s tumor growth differs in intensity, the degree of damage to brain structures, as well as the resistance and reserve forces of the body. Medicine has known cases where patients with stage 4 cancer, undergoing regular courses of treatment, successfully lived for several more years. Such cases constitute a small percentage, since by the time the final stage occurs, the disease has already managed to metastasize throughout the body, affecting important brain structures.
The essence of the 4th stage of pathology
When cancer reaches the terminal stage, doctors classify the disease as stage five. It is this that marks the onset of imminent death. Therefore, when treating oncology, only four stages are considered: here doctors can still, if not cure the patient, then at least prolong his life and improve its quality level. When brain cancer develops, its fourth degree is considered a severe form of pathology. It has several differences:
- Severe form of pathology.
- Aggressive course of the process.
- Accelerated formation and division of malignant cells.
- Damage to healthy tissue closest to the lesion.
- Metastasis to other organs.
The disease is considered inoperable precisely because of the large number of cancer foci in other tissues of the body. However, active therapy helps reduce suffering and prolong the patient's life.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms are usually divided into general and focal. In the latter case, the symptoms depend on where the tumor forms.
General symptoms
The clinical picture is caused by an increase in pressure inside the skull and the toxic effect of metabolites of pathogenic cells on healthy tissue. Common signs include:
- headache not relieved by conventional analgesics;
- various visual impairments, for example, fog, doubling, glare, decreased visual acuity and others;
- loss of appetite, poor health, nausea and vomiting that are not caused by food poisoning;
- changes in the usual emotional state: mood swings, depression or aggressiveness, and others;
- symptoms of an epileptic nature;
- weakening of the brain: it is difficult for a person to concentrate, mental activity is disrupted, there is a loss of concentration, memory problems, etc.
Important. Early signs of cancer are often misunderstood by sick people. They seek help when clinical signs significantly impair quality of life. In this case, the brain tumor is diagnosed late, which significantly complicates treatment and worsens the prognosis.
Focal symptoms
Signs of this type arise due to changes in the functioning of cerebral structures, so the clinic depends on the location of the neoplasm:
- when the hemispheres are damaged, tactile sensitivity decreases, muscles in the opposite part of the body weaken (in the presence of pathogenesis in the right hemisphere, problems arise on the left side);
- disease in the temporal lobe leads to a deterioration in the ability to speak, memory suffers, and the perception of smells changes;
- pathological changes in the cerebellum lead to disturbances in gait and coordination of movements;
- damage to the frontal lobe causes mental and cognitive changes;
- neoplasia in the parietal lobe changes tactile sensations and fine motor skills;
- damage to the occipital zone negatively affects vision, and hallucinations are possible.
Important. The presence of these signs (of any type and intensity) is a good reason to seek medical advice. Early detection of pathologies improves the prognosis of treatment.
Classification of tumors
The term “brain cancer” most often refers to glioblastoma: this is the most aggressive type of the disease. It occurs in 15% of cases and is characterized by rapid development and metastasis. The reasons for its occurrence are not fully understood. The main factor provoking tumor growth is called heredity or genetic disorders. Doctors consider alcohol and cigarette abuse, viral infections and contact with sending substances to be secondary causes. In addition to this aggressive disease, there are:
- Brain stem gliomas.
- Astrocytic tumors of the pineal region.
- Piloid astrocytomas.
- Mixed gliomas.
- Germ cell neoplasms.
- Medulloblastomas.
- Oligodendroglial tumors.
- Anaplastic astrocytomas and others.
Depending on the type of disease and its stage, the correct treatment will be selected. At the fourth stage, it is palliative in nature and is aimed at improving the patient’s quality of life.
Treatment options for stage 4 glioblastoma in medical
Treatment of cancer pathology in the last stage is one of the specializations of medicine (Türkiye).
The long-term cooperation of the Medical Center with the Johns Hopkins Clinic in the USA helps to provide patients with the most modern treatment at the level of world standards.
The Center employs world-famous doctors who provide highly accurate diagnostics and treatment using the most modern methods and technologies.
At the same time, the cost of medical care at Anadolu is approximately 20% lower compared to clinics in the USA and Israel, while treatment and examination are carried out at the same advanced level.
The medical institution has an International Department that helps foreign patients organize and undergo treatment, as well as stay in touch with doctors upon returning home. The clinic organizes free transfer from the airport, helps book a hotel, provides a personal coordinator and translator during treatment.
The center has representative offices in the main regions of Russia and the CIS countries. Order a call back , send a request for treatment and prices , or call us (toll-free within the Russian Federation): 8 .
The material was prepared in agreement with the doctors of the Anadolu Clinic, professor, doctor of medical sciences. Serdar Kahraman and Professor Hale Basak Chalar.
Symptoms of brain cancer
Oncology is very insidious. Up until the second or third stage, the patient may not even suspect the presence of a serious disease. Such tumors are detected only during regular medical examination. At the third or fourth stage, the symptoms become so vivid that it is no longer possible to ignore them. This:
- Regular headaches that are not relieved by analgesics and get worse at night.
- Convulsive seizures.
- Nausea and vomiting, symptoms of body poisoning.
- Impaired cognitive abilities.
- Deterioration of vision, loss of smell.
- Personality changes: mood swings, restless behavior, excessive aggression.
- Loss of consciousness.
Since brain cancer usually develops quite quickly, symptoms increase rapidly. At a late stage of the disease, the general symptoms are similar to the clinical picture of other brain disorders (for example, stroke), so to establish an accurate diagnosis you will have to undergo a series of examinations.
REHABILITATION OF PATIENTS
THE RUSSIAN - JAPANESE ONCOLOGICAL CENTER HAS DEVELOPED REHABILITATION PROGRAMS FOR PATIENTS AFTER TREATMENT, CHEMOTHERAPY AND RADIATION THERAPY.
Rehabilitation is aimed at areas of the brain that are responsible for important body functions: speech, movement, sensory organs, thinking, memory.
With rehabilitation treatment, the risk of complications after chemotherapy is reduced to a minimum. The patient does not experience severe symptoms after the procedures and does not lose quality of life.
Feel the quality of life after rehabilitation!
The patient should never forget that brain cancer is an aggressive type of cancer and develops quite quickly. Relapses are possible, so we make sure to monitor our patients at least 2 times a year and repeat the supporting set of rehabilitation measures after a year or a year and a half.
Our experience shows that treatment of brain cancer is always possible, even regardless of its stage and location.
The developed and tested methods of our Oncology Center are aimed at curing this disease, reducing its symptoms, preventing the progression of the disease and improving the quality of life!
Diagnosis of a brain tumor
An adequate way to detect pathology is to undergo an MRI examination. In addition, in diagnosing the fourth stage of cancer, the following are often used:
- CT. Computed tomography helps detect metastases in other tissues of the body. In addition, it is this examination that helps to find the primary source of tumor spread, establish its actual size and make an accurate diagnosis.
- Biopsy. During this procedure, the doctor removes a small section of the affected tissue, after which the fragment is examined in the laboratory. The sampling is carried out under anesthesia using a special needle under CT or MRI control.
- Additional tests. The doctor may recommend donating blood: if cancer is suspected, this is necessary in order to identify tumor markers in the body. Since some tumors can be easily confused with other diseases, this test will help clarify the diagnosis.
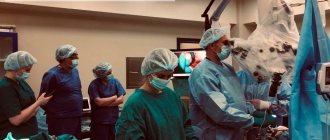
Treatment of stage IV brain cancer
Typically, therapy is exclusively palliative. However, in some cases, this process helps to launch the regenerative functions of the body and completely get rid of the tumor. Properly selected therapy can help extend the patient’s life to 5–10 years.
Surgical intervention.
In advanced forms of cancer, it is often not possible to remove the entire tumor. During surgery, the doctor removes only the largest affected area. However, even such an intervention can prolong the patient’s life.
Radiation therapy
. Even if the operation was successful and the doctor removed 98–99% of the tumor, a recurrence of glioblastoma is possible: it will return due to cancer cells remaining in the body. Radiation therapy, which destroys the remnants of pathology, can help avoid this, prolonging the patient’s life.
Chemotherapy
. Aggressive forms of cancer are resistant to most chemicals. However, using an integrated approach allows one to achieve good results: some chemicals increase the sensitivity of mutated cells to radiation.
What affects survival?
The prognosis for detecting stage 4 brain cancer is based on several important factors:
- Patient's age and gender.
- Type of oncology.
- The size of the tumor, the presence of metastases in other tissues.
- The degree of impairment of nervous functions.
- The presence of certain mutations in the structure of the affected cells.
- Possibility of complete or partial removal of the primary tumor.
- Patient's mood.
In general, the success of treatment is related to the stage of cancer. The sooner you start therapy, the higher the chance of completely getting rid of the disease. However, in the terminal stage of aggressive forms of the disease, especially without proper treatment, the prognosis will always be unfavorable: such patients live no more than a year. With timely and high-quality medical care, it is possible not only to reduce symptoms, but also to extend the patient’s life to 5–10 years while maintaining cognitive and neurological functions.
How long do they live after glioblastoma removal?
When faced with glioblastoma, many patients immediately give up, looking for a complete answer to the question “what is the life expectancy with this diagnosis”? At the same time, realizing that even their attending physician will not be able to give them an exact answer.
The answer to this question depends on:
- patient's age group;
- localization of the tumor;
- presence of metastases.
In order to improve your condition and maintain your body, doctors recommend adjusting your sleep and rest patterns, minimizing stressful situations, eating a balanced diet and giving up all bad habits. Timely detection and seeking qualified medical help can extend the life of a cancer patient by more than 10 years. Such an outcome is possible only with a positive course of the disease and with proper compliance with all the recommendations and prescriptions of the attending physician.
Prevention recommendations
Cancer can affect anyone, including people who lead a healthy lifestyle. In a word, no one is immune from the disease. However, following simple medical recommendations will help to significantly reduce the risk of disease:
- Eat right. The diet should include more fresh vegetables, meat, fish, and dairy products. Store-bought sweets, soda, packaged juices and fast food are recommended to be excluded from the diet.
- Drink more water. The norm of fluid consumption is at least one and a half liters per day.
- Don't forget about physical activity. But you shouldn’t overuse them either: daily walks in the fresh air and morning exercises are enough.
- Give up bad habits. Alcohol and smoking provoke cell mutations.
And of course, do not forget to visit your doctor on time. Annual medical examinations can help identify the disease in its early stages.