One of the most common forms of dementia is Alzheimer's disease. An acquired neurodegenerative disease is characterized by the slow death of nerve cells and manifests itself as a persistent intellectual disorder. A person becomes unable to acquire new knowledge and skills, and also gradually loses previously acquired ones. In addition to memory impairment, problems arise with speech and spatial orientation. The patient loses the ability to care for himself, body functions go out.
When diagnosing, behavioral analysis, cognitive reactions, and MRI results are of great importance. Although a cure for Alzheimer's disease has not yet been found, there are ways to prevent its occurrence or reduce the severity of symptoms.
Causes of the disease
Doctors have not yet achieved a complete understanding of the cause of Alzheimer’s and the course of the disease. Apparently, the whole point is the accumulation of peculiar protein deposits in the brain tissue, which are recorded using computer, magnetic resonance and other types of tomography.
The main risk factor is old age. If under the age of 70 Alzheimer's disease is registered in three cases per 1000 people, then in 80-year-olds it is already up to 20 cases, and in 90-year-olds it is 70 cases per 1000 people. The disease is extremely rare in people under 60 years of age. Elderly women get sick more often than men.
Doctors attach great importance to genetic predisposition. A defective gene leading to the appearance of forms of proteins with neurotoxic properties was found in 50% of patients.
According to doctors, other reasons can serve as the impetus for the onset of the disease:
- brain injuries and concussions;
- psychological disorders;
- vascular problems;
- regular alcohol intake, nicotine addiction;
- obesity;
- low intellectual activity.
In patients diagnosed with Alzheimer's, after autopsy, so-called senile plaques are discovered - spherical extracellular foci of brain damage, which have negative consequences on the nervous system and brain functions.
Risk group
Patients who have certain diseases are automatically included in the risk group. These diseases can be grouped together according to one very important symptom - lack of oxygen in brain cells:
It is also worth mentioning separately about the disturbance of protein metabolism, or more precisely about the production of a pathological protein - amyloid. It can be deposited in the brain in the form of plaques and leads to neuronal degeneration and impaired blood supply. A distinctive feature of this protein is that the body is unable to dissolve it or get rid of it on its own. This protein begins to be deposited long before the first symptoms of the disease appear.
Symptoms of Alzheimer's disease
Neither patients nor their loved ones can say exactly when the changes began. The person becomes forgetful and cannot remember individual words. The mood often changes, tearfulness and touchiness occur. Possible sleep disturbances. Poor night sleep gives way to daytime sleepiness.
The first symptoms of Alzheimer's over time are complemented by other manifestations:
- the circle of interests narrows, life becomes monotonous;
- lack of composure, confusion, suspiciousness, and uncertainty are manifested in everything;
- professional skills are lost;
- It becomes more and more difficult to perform everyday tasks;
- a person gets lost in the area, disoriented in space;
- degradation of thought processes occurs.
Visual dysfunction is added to acquired dementia. In the final stages, the sick person does not recognize loved ones, cannot eat, dress, or take care of himself.
How to improve memory. Recommendations from the Neuroscience Center
If you observe alarming symptoms in yourself or in people close to you, indicating memory problems similar to those indicated above, then you need to go to an appointment with a neurologist, neuropsychologist or therapist and undergo a series of special diagnostic tests. If you want to immediately start fighting an undesirable phenomenon before receiving the doctors’ verdict, then take action - start training your memory.
Here are some exercises to improve memory:
- If possible, perform your usual tasks with your eyes closed, from memory;
- If you are a left-handed person, do everyday tasks with your right hand, if you are right-handed, then with your left. Try this rule, for example, writing, ironing clothes, drawing, etc. – You will soon feel a positive result;
- learn Braille, which is used by blind people when reading, or learn sign language - this is useful for memory and can be useful in life;
- type texts on the keyboard with both hands, using all fingers;
- do some handicrafts - start embroidering or knitting;
- learn foreign languages and speak them more;
- try to distinguish the denomination of coins blindly, feeling them with your hands.
In addition, expand your range of interests, read more, visit places and institutions you have not been to before, go to plays and performances, walk in parks, meet and communicate with people, make new friends.
Perform the recommended exercises, follow the listed rules, take care of your health, and your memory will not fail you until old age!
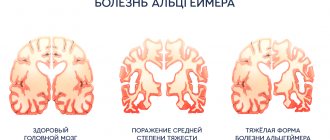
Classification of the disease
Throughout the disease, a pattern of progressive disorders is observed. According to symptoms, there are four stages of Alzheimer's: predementia, early, moderate and severe. Slow degradation occurs over an average of 7 years, ending in the death of the patient.
Initial stage (pre-dementia)
The first manifestations of Alzheimer's disease, such as memory impairment and lack of concentration, are mistakenly perceived by relatives as manifestations of aging. Problems with the performance of everyday functions are still barely noticeable. It is typical that already at this time the person becomes apathetic, which persists throughout the disease.
Early stage
Memory continues to decline. The patient retains clear consciousness and high sensitivity, but the ability to normally perceive information is lost. For example, a person does not recognize or partially recognizes familiar faces. Or he cannot determine which objects in his environment have the same color. Clumsiness in performing daily tasks appears, fine motor skills are impaired. With some manipulations, the patient requires help, although he can still do many things on his own.
Moderate stage
The condition is worsening, as evidenced by obvious speech impairments. To replace a forgotten word, a person often selects the wrong words. Consistent movements are difficult. Most everyday tasks require significant effort. Psychiatric deviations appear, for example, the idea of vagrancy. Irritability can come and go quickly. Symptoms of delirium often occur. The person becomes whiny. It happens that he resists help. In order to smooth out the increase in general stress, relatives often move the sick person to a hospital for care.
Severe stage
At this stage, the patient cannot live without outside help. He is able to pronounce individual words and phrases, understands other people's speech and can show emotions. The condition is characterized as apathetic, exhausted. In the end, even small actions are impossible without the participation of others.
Based on its form, Alzheimer's disease is divided into presenile and senile. The first is a disease detected before age 65. The senile form refers to patients older than this age. Presenile dementia is characterized by rapid progression, family history, and rapid impairment of speech functions. The pace of progress depends on the standard of living, type of activity, heredity, and the presence of chronic diseases.
Senile dementia develops slowly at first. The first stages last 2-4 years. Temporary improvements in condition are characteristic. An elderly patient remembers the past perfectly, but does not perceive new knowledge. As it progresses, false memories arise, and people from the current environment are associated with people from their youth. There is no complete breakdown of speech. On the contrary, a sick person can speak vividly to the end and retain a rich vocabulary.
Early dementia
This stage of diagnosis, as there is a further deterioration in the general condition of the patient: the symptoms are becoming more pronounced. In addition to short-term memory impairment, speech impairment, motor impairment, and the first symptoms of long-term memory impairment appear. Disorders of long-term memory manifest themselves individually in everyone, ranging from the inability to remember information that the patient memorized several years ago, ending with memories of the correct use of cutlery. There is a violation of the speech apparatus, however, it is hardly noticeable.
Preventive actions
Preventive, that is, prophylactic measures, can slow down the development of the disease, but whether it can be prevented, scientists do not have a consensus.
To prevent Alzheimer's disease, it is recommended for older people to:
- lead an active life;
- be interested in new electronics;
- master the computer and use of gadgets;
- stimulate brain activity, read, find new hobbies.
Moderate physical exercise, especially outdoors, is very beneficial. At this time, the blood is saturated with oxygen, the brain structures begin to function better, which reduces the risk of vascular disorders.
When cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases are detected, it is important to treat them promptly. Normal organ function prevents the development of Alzheimer's type dementia.
Differential diagnosis
To carry out differential diagnosis, a biochemical study of the patient’s blood is performed to exclude all possible inflammatory diseases. In the early stages of the disease, you can perform a CT or MRI to exclude the possibility of tumors in the brain and stroke, and angiography to look at the patency of blood vessels and the presence of atherosclerosis. Psychological tests are used to identify specific organic thinking disorders and to determine concomitant depression, anxiety, and other symptoms that may aggravate the course of dementia.
At later stages, CT and MRI will show significant brain atrophy in characteristic areas. It is also advisable to conduct a chemical analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid to detect pathological or disease-specific cellular elements in it. Genetic analysis will determine predisposition to this disease, as well as detect mutations characteristic of Alzheimer's disease.
Treatment and patient care
Therapy for Alzheimer's disease includes a set of measures, including drug treatment, psychosocial correction, and patient care.
There are no medications that can cure the disease. To treat cognitive impairment, doctors prescribe chemicals from the group of inhibitors that can delay the course of physiological processes in the body, as well as NMDA receptor antagonists, designed to reduce the manifestation of negative symptoms.
Behavioral correction involves the use of art therapy, music therapy, communication with animals and stimulation of any type of activity in the patient. The goal is to improve the patient’s quality of life.
No care is required at first. We are talking only about help in performing certain functions, possible tips. Relatives cope with this successfully. But in the last stages of Alzheimer's disease, the patient requires complete care. If relatives do not have the opportunity to constantly be with the patient, a nurse is hired for these purposes. Many people choose help from specialized institutions.
A good example is the private boarding house “Idyll” in Yekaterinburg. The cost of the stay is comparable to the pension of many patients. The institution employs doctors and medical staff who are well acquainted with the specifics of diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. Elderly people are provided with 24-hour care. Restorative and cultural events are being carried out.
Diagnostics
It is very difficult to recognize the disease, since when diagnosing one has to rely on symptoms and complaints - in the early stages it is very difficult to differentiate the disease from stress or from the processes of physiological aging. And in most cases, the patient does not immediately turn to a specialist, since the symptoms may not bother him much. In the later stages, the diagnosis is easier to make – the characteristic symptoms become more pronounced. But it is worth remembering that other diseases can manifest themselves similarly:
- Stroke;
- Parkinson's disease;
- Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- Neoplasms of the brain.
For correct diagnosis, it is very important for the doctor to collect a complete medical history of the patient:
- When did the first symptoms appear?
- What symptoms does the patient have?
- How severe are the symptoms?
- Accompanying illnesses;
- Presence of injuries.
Due to the nature of the course of the disease, the patient cannot always independently answer all the doctor’s questions, so making a diagnosis can be difficult. If possible, all the necessary information is provided to the doctor by knowledgeable relatives of the patient.
Diagnosis also includes neuropsychological tests, which help assess the severity of cognitive impairment, and PET scans, which are used to detect amyloid accumulations in the brain.
Where can you improve your memory in St. Petersburg
Where should you go if it becomes clear that memory impairment is affecting your quality of life and you urgently need to take action? Why did my memory deteriorate? A specialist neurologist at our Center for Neurology, Professor Zhulev, can answer these questions.
Make an appointment with a doctor using the phone number listed on the website. If you notice that your ability to remember dates, faces and other data has sharply deteriorated, then you need to undergo an examination and identify the reasons. Don't let your health take its course. If memory has sharply deteriorated, then this is a signal from the body about problems that have arisen, and the sooner the doctor diagnoses them, the better.
We are located in the Central district of St. Petersburg, the work schedule and map can be found in the Contacts section.