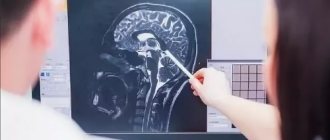
A series of MRI scans of the brain obtained images of sub and supratentorial structures in the axial, coronal and sagittal planes.
In the white matter of both hemispheres, subcortically, periventricularly, areas of pathological signal intensity are detected (hyperintense on T2 V.I. and FLAIR I.P.), with clear uneven contours up to 4 mm, of vascular origin. There is an expansion of the perivascular spaces along the perforating vessels of the brain at the level of the basal ganglia and subcortically. The median structures are not displaced. The lateral ventricles are symmetrical. The III and IV ventricles are without features. The subarachnoid space of the convex is not expanded. The cerebellar tonsils are located at the level of the foramen magnum.
Let's try to figure everything out in order
“In the white matter of both hemispheres, subcortically, periventricularly, areas of pathological signal intensity are detected (hyperintense on T2 V.I. and FLAIR IP), with clear uneven contours up to 4 mm, of vascular origin.” “There is an expansion of the perivascular spaces along the perforating vessels of the brain at the level of the basal ganglia and subcortically.” It looks complicated and unclear. But in fact, this is a description of small areas of altered tissue characteristic of vascular diseases of the brain, primarily atherosclerosis and vascular damage in hypertension.
Unfortunately, atherosclerosis (narrowing of blood vessels by cholesterol plaques) develops by a certain age in almost everyone and naturally manifests itself in various organs, including the brain - in the form of the development of dyscirculatory encephalopathy. In this case, due to a local lack of blood supply, small areas of non-functioning tissue appear in the brain, and they are described by the doctor. You can see them in the photographs in the form of small light spots with clear, uneven contours. The location of these areas, indicated by the doctor in the description, is also very typical for vascular changes in the brain.
What is hidden behind the diagnosis of dyscirculatory encephalopathy?
"Cerebral suffering due to impaired circulation." You probably haven't come across such a diagnosis. However, this is how it could be translated from Greek.
Encephalopathy. What kind of disease is this? Is this a disease at all? We talked about this and much more with Natalya Vladimirovna Umerenkova, a neurologist, leading specialist in the neurology department of the Expert Kursk Clinic.
— Natalya Vladimirovna, on the Internet you can find information that the diagnosis of discirculatory encephalopathy hides a lack of diagnosis. Is this really true or is dyscirculatory encephalopathy a disease?
This is actually a disease. Another question is that it can be called completely differently. For example, an equal sign can be placed between it and such pathologies as chronic cerebral ischemia, chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency. The problem is that none of these terms are reflected in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10). The term “dyscirculatory encephalopathy” is a legacy of medicine in the USSR and the post-Soviet era (as well as the countries of the post-Soviet space). It is rarely found in foreign medical literature.
Read the material on the topic: Vegetative-vascular dystonia: diagnosis or fiction?
As for diagnosis, sometimes the diagnosis of “dyscirculatory encephalopathy” is made redundantly - for example, simply focusing on the patient’s age (which is not always correct). Therefore, it is not always justified.
— Does dyscirculatory encephalopathy have degrees?
No, there are no degrees. There are stages of development of the disease (there are three of them), with manifestations characteristic of each of them.
— What are the symptoms of dyscirculatory encephalopathy?
In the first stage, minimal clinical manifestations are observed. These include general weakness, increased fatigue, a slight deterioration in concentration, some sleep disturbances, increased anxiety, higher emotional instability, headaches, and mild dizziness. An objective neurological examination and MRI of the brain also revealed minimal changes.
Read the material on the topic: What diseases can cause dizziness?
In the second stage, the symptoms become more clear and defined. These are headaches, imbalance, distinct dizziness, more pronounced cognitive and emotional-volitional disorders that are amenable to neuropsychological objectification. MRI reveals more distinct changes in the brain substance.
Read the material on the topic: If an MRI of the brain showed...
At this stage, some difficulties with daily activities appear. For example, some difficulties may be associated with obtaining new information, the need to read a lecture, find a new route to the store, etc., i.e. going beyond the boundaries of the “comfort zone”. Everyday forgetfulness is noted. At the same time, using habitual behavior patterns, skills and knowledge does not cause any problems.
The third stage of discirculatory encephalopathy is characterized by signs of parkinsonism, movement disorders, significant deterioration of cognitive functions and memory. The patient's critical attitude towards his condition suffers. Pelvic disorders are possible (urination suffers more often).
Read material on the topic: What is Parkinson's disease and how does it differ from parkinsonism?
With this disease, personality changes may be observed in the form of irritability, tearfulness, touchiness, and greater “viscosity” of thinking. Fine motor skills may deteriorate, there may be unsteady gait (even falls), episodes of forced laughter or crying, and some difficulty swallowing. There may be a change in the rate of speech, the appearance of dysarthria (fuzzy speech - as if there is “porridge in the mouth”).
— For what reasons does dyscirculatory encephalopathy occur?
They are varied. This is damage to large and small vessels, even small foci of previous strokes (including those that the patient may not know about and they may turn out to be an accidental finding during magnetic resonance imaging of the brain), etc.
Read the material on the topic: How to protect yourself from a stroke?
If we conceptually try to answer the question “why does discirculatory encephalopathy occur,” then one way or another it is associated with a disruption of the vascular bed and, accordingly, a deterioration in the blood supply to the brain. This can be caused by unstable blood pressure figures in hypertension, vascular atherosclerosis, vascular changes in diabetes mellitus, heart rhythm disturbances with a transient deterioration in blood supply to brain tissue or an increased risk of blood clots, independent disorders in the blood coagulation system (with increased thrombus formation) and some others .
— Who is at risk for dyscirculatory encephalopathy?
These are people with high blood pressure, atherosclerotic lesions of cerebral vessels, diabetes mellitus, pathologies of the blood coagulation system and vascular wall, smokers, and people suffering from physical inactivity.
Read the material on the topic: It's off scale! Looking for reasons for high blood pressure
— What other neurological diseases can masquerade as dyscirculatory encephalopathy?
They can be of very different nature. Similar manifestations can occur with brain tumors, hydrocephalus with normal cerebrospinal fluid pressure, tension headaches, and some types of migraine. This diagnosis can be mistakenly made if a person has dizziness that occurs against the background of phobic disorders or pathology of the inner ear. Similar manifestations occur in anxiety and depressive disorders, as well as a number of others.
Read the material on the topic: What is a tension headache?
— What methods does the diagnosis of dyscirculatory encephalopathy include?
Careful collection of complaints and medical history, as well as a detailed neurological examination.
Of the instrumental methods, as a rule, ultrasound of the vessels of the neck is performed (ultrasound duplex scanning of brachiocephalic vessels, not only arteries, but also veins), MRI of the brain (it is advisable to carry out with the vessels of the brain).
Read the material on the topic: Why is MRI of cerebral vessels prescribed?
The blood coagulation system is being studied.
According to indications, consultations with narrow specialists are prescribed - a cardiologist, an endocrinologist, an ophthalmologist.
— How are patients with dyscirculatory encephalopathy treated? Can its development be stopped?
If the diagnosis is correct, the correct treatment is prescribed and the patient fully adheres to it - yes, the disease can be stopped. The principles of treatment are to normalize blood pressure, blood sugar and lipids, and the rheological properties of blood (here “rheological” means “blood fluidity”). A proportionate level of physical activity and smoking cessation are required.
The drugs used are those that have a positive effect on the “nutrition” of brain tissue, improving blood circulation in it, etc. In severe stages, drugs against dementia and parkinsonism may be prescribed. A consultation with a psychiatrist may be necessary.
It should be remembered that drug therapy alone without eliminating the factors leading to the disease will not be very effective and, at best, will provide a temporary effect.
— What is the risk of dyscirculatory encephalopathy if it is not treated? Is it that dangerous?
Lack of treatment will lead to progression of the process. The prognosis directly depends on timely diagnosis and proper treatment.
You can make an appointment with a neurologist here
Please note: consultations are not available in all cities
— Natalya Vladimirovna, is it possible to prevent discirculatory encephalopathy? Tell us about the prevention of this condition
Fortunately, it is possible to prevent its development. No matter how simple it may sound, it is maintaining a healthy lifestyle: a balanced diet, an adequate level of physical and intellectual activity, and the absence of bad habits. If there are diseases and conditions that increase the risk of developing discirculatory encephalopathy, their timely and competent treatment is necessary.
Other
What is encephalopathy and why is it dangerous?
Every person experiences headaches from time to time. Many people do not take into account the reasons for feeling unwell and prefer to take painkillers. However, recurrent headaches can be caused not only by fatigue or changes in blood pressure. Is this often how encephalopathy manifests itself? a common brain disease caused by oxygen starvation and lack of nutrients. We will talk further about whether this pathology can be cured and prevented.
What is encephalopathy?
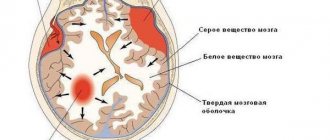
This is a non-inflammatory disease in which the brain tissue receives insufficient blood and, therefore, oxygen. As a result, nerve cells die, stagnant processes appear, and swelling of the meninges forms in local areas.
Encephalopathy? this is a general concept that unites degenerative processes in the brain. Very often, pathology is not defined as an independent disease, but is detected against the background of other diseases. There are no age restrictions for encephalopathy.
| ! | The optimal rate of blood supply to the brain is 45-50 ml of blood every minute per 100 g of brain matter. Reducing this figure to 18 ml per minute is considered critical. |
Causes of the disease
Encephalopathy can be congenital or acquired. In each case, the causes of the disease are different factors, but they are united by a persistent violation of cerebral circulation.
| Congenital | Acquired |
|
|
In the case of newborn children, the presence of the disease is not always obvious. As a rule, the diagnosis is made closer to a year in the presence of specific symptoms. In adults, pathologies caused by vascular disorders are widespread. For example, with atherosclerosis, the lumen of blood vessels decreases as a result of the deposition of lipids on their walls. Blood flow to the brain decreases, ischemia develops. In difficult cases, the lumen of the vessel is blocked by a blood clot or cholesterol plaque, a stroke occurs, as a result of which brain cells die.
Types of encephalopathy
Two main forms of the disease? perinatal (congenital) and acquired. The first includes a decrease in blood supply to the brain that occurred between 28 weeks of intrauterine development of the fetus and the 7th day of the child’s life. All other types of encephalopathy? acquired.
Each type of disease has its own specific symptoms and treatment methods. For this reason, it is important to see a doctor in time to undergo diagnosis and treatment. The manifestations of the disorders depend on which area of the brain is affected.
- Vascular encephalopathy.
It occurs as a result of impaired blood supply to the brain and oxygen starvation of cells. The pathology may be atherosclerotic or hypertensive in nature. In the first case, atherosclerotic plaques are present in the blood vessels, and in the second, high blood pressure is observed with a complication in the form of cerebral edema.
- Traumatic.
In this case, encephalopathy develops as a result of a traumatic brain injury. The disease may cause degenerative, dystrophic, and scarring changes in brain tissue. Most often, the pathology is observed in athletes, drivers and passengers of vehicles, as well as newborn children.
- Radial.
The disease can result from exposure of the brain to ionizing radiation. This type of encephalopathy can be observed among specialists involved in eliminating the consequences of radiation accidents, as well as among those who work with related equipment.
- Metabolic (toxic).
Brain damage can be caused by intoxication of the body due to liver failure, diabetes, carbon monoxide poisoning, heavy metal salts, etc. Toxic poisoning also leads to severe neurological disorders.
- Alcoholic.
The breakdown products of ethyl alcohol, entering the brain through the bloodstream, cause irreversible metabolic disorders. Does Wernicke's encephalopathy also belong to this group? damage to the midbrain and hypothalamus due to alcohol abuse, as well as vitamin deficiency and other reasons.
- Inflammatory.
Most often we are talking about inflammatory processes in the walls of blood vessels. The severity and specificity of manifestations depend on the affected area.
- Vaccine.
This is a rare type of neurological disorder that occurs in response to the vaccine. The most common reaction is to whooping cough medications.
- Discirculatory.
Brain dysfunction occurs due to gradually increasing insufficiency of blood supply. Dyscirculatory encephalopathy directly affects cognitive abilities and neurological disorders.
- Residual encephalopathy (residual).
Structural changes in tissue occur in the brain due to previous injuries, ischemic disease, and infections.
- Spongy.
This type of encephalopathy combines severe diseases in which the brain turns into a spongy body. Among them are Getsmann-Straussler-Scheinker syndrome, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, etc.
Symptoms of encephalopathy
The disease is characterized by a variety of clinical manifestations, which depend on the causes of brain dysfunction. Encephalopathy can have an acute and chronic course.
In the first case, symptoms appear suddenly and very quickly lead to a deterioration in the patient’s condition. The main cause of acute encephalopathy is toxic damage to the body.
In the second case, signs of brain dysfunction appear gradually in the form of headaches, forgetfulness, and emotional instability.
The disease goes through several stages in its development, which are characterized by the following manifestations:
| Stage 1 | Stage 2 | Stage 3 |
|
|
|
| ! | The main manifestations of encephalopathy at the initial stage? headaches, dizziness, tinnitus. Symptoms may occur when the weather changes, physical fatigue, or stress. When they appear, it is necessary to undergo examination. |
Diagnosis of the disease
Modern examination methods make it possible to establish the localization, nature of the pathology, and the mechanism of its occurrence. Diagnostics may include:
Blood tests to determine the levels of hormones, lipids, cholesterol, sugar and other elements that may indicate the development of dyscirculatory encephalopathy.
Rheoencephalography (REG) to measure blood flow in the brain, determine the elasticity and tension of the walls of blood vessels.
Magnetic resonance imaging
to analyze morphological changes in brain tissue. MRI allows you to differentiate encephalography from other diseases of the nervous system: Alzheimer's disease, stroke, tumors, etc.
Doppler ultrasound
to determine the speed of blood flow in an individual blood vessel and clarify the location of the atherosclerotic plaque. Provides information about the state of cerebral circulation.
Ultrasound scanning
to clarify the cause of vessel obstruction? the presence of a spasm, plaque, blood clot, etc. The method has no contraindications and allows you to quickly obtain a reliable result.
Ultrasound monitoring
to determine the cause of blood clot formation? thrombi and emboli. The method also allows you to assess the risk of stroke.
Can encephalopathy be cured?
The disease requires long-term course therapy and observation by a neurologist. For successful treatment and elimination of the symptoms of the disease, diagnosing the causes of its occurrence is of paramount importance.
Acute encephalopathy is an indication for urgent hospitalization and detoxification therapy in a hospital setting. The chronic form of the pathology requires following a certain diet and taking medications as prescribed by a doctor 2–3 times a year.
For hypertension (high blood pressure), the doctor may prescribe Enalapril, Captopril, Lisinopril, Fosinopril and other drugs.
Medicines for hypertension require strict adherence to the dosage schedule, usually 2–3 times a day. Many patients require lifelong use of medications to normalize blood pressure. The dosage and type of medication should be prescribed by the attending physician, since each of them acts with different intensity and is excreted from the body differently.
Modern antihypertensive drugs are divided into the following groups:
- ACE inhibitors (angiotensin-converting enzyme);
- diuretics;
- beta blockers;
- calcium antagonists;
- direct renin inhibitors;
- combination and other drugs.
To improve brain metabolism, Cavinton, Vasobral, Corinfar, Tseliprol, Nikoshpan, Picamilon and other drugs of various groups are prescribed.
Medicines help restore cerebral circulation and thereby eliminate symptoms such as:
- headache and dizziness;
- increased fatigue;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- memory problems;
- insomnia;
- mood swings, etc.
The main groups of drugs to improve cerebral circulation:
- vasodilators;
- blood thinners;
- nootropic;
- vascular strengthening;
- blood microcirculation correctors, etc.
Do free radicals accumulate in the human body during life? reactive oxygen species that destroy cells and lead to diseases of the nervous and cardiovascular systems. To protect tissues from their effects, are antioxidants prescribed? “Actovegin”, “Tiogamma”, “Emoxipin”, “Quertin”, “Riboxin”, “Mexidol”, “Cerakson”, etc. The drugs improve capillary blood flow, strengthen the walls of blood vessels, prevent or slow down atherosclerotic changes, reduce the risk of stroke and heart attack.
| For encephalopathy, the treatment regimen is developed individually for each patient, taking into account data from laboratory and instrumental studies. Almost all drugs for the treatment of chronic forms of the disease are available in pharmacies with a doctor’s prescription. In addition to the listed groups of drugs, the patient may be prescribed anticonvulsants, antidepressants, antiplatelet agents and other drugs. |
Consequences and complications of encephalopathy
Delaying treatment for a long time leads to extensive brain damage. As the disease worsens, the patient may experience:
- constant headaches;
- disorder of consciousness;
- deterioration of vision and hearing;
- facial expression disorders;
- movement coordination disorders;
- tremor of limbs, tic, convulsions;
- sexual function disorder;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia and much more, depending on the area of brain damage.
Prevention of encephalopathy
For successful treatment, elimination of symptoms of the disease and prevention of degenerative processes in the brain, the patient is recommended:
- adjust your diet? give up foods high in cholesterol and fast carbohydrates in favor of vegetables, fruits, and herbs;
- to refuse from bad habits ? smoking and drinking alcohol;
- Exercise regularly to keep your body in good shape.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner and detect encephalopathy in the early stages, the prognosis is positive. The effectiveness of treatment will largely depend on the causes of the pathology. Severe cardiovascular (ischemia, stroke, heart attack) and neurological (osteochondrosis, traumatic brain injury) diseases may require lifelong course therapy. In each case, the treatment and prevention program should be drawn up by the attending physician.