Medical information is reliable Checked by Eremin Alexey Valentinovich
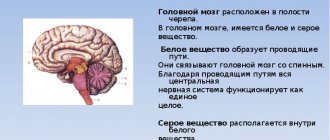
Encephalopathy (or encephalopathic, psychoorganic syndrome) is a condition that occurs when the brain is damaged as a result of congenital, acquired diseases and conditions. Dystrophic changes in nervous tissue are chronic and often lead to permanent disability. Timely treatment of encephalopathy in Moscow will help avoid progression of the disease.
Causes
All causes of this pathological condition in pediatric and adult practice are divided into congenital and acquired. Congenital encephalopathy develops during pregnancy or childbirth; the condition is detected by neurologists at an early age.
Acquired encephalopathic syndrome is more often identified in adults or adolescents. Among the reasons for the appearance are:
- head injuries;
- intoxication;
- infections;
- irradiation;
- metabolic disorders;
- somatic diseases;
- vascular lesions of the brain.
When questioning the patient or his relatives, the psychiatrist will clarify what factors influenced the occurrence of encephalopathy, at what speed the symptoms occurred - acutely or whether the condition worsened gradually.
Why does the violation occur?
As a result of TBI, pathological changes in brain tissue occur. As a result of diffuse processes, parts of the cerebral system stop working normally. Signs of encephalopathy for a doctor are as follows:
- hypoxia resulting from vascular disorders;
- changes in the nature of the meninges (fusion with each other, formation of scar tissue members);
- formation of cysts, hematomas;
- increased size of the ventricles of the brain;
- degeneration of glia and neurons.
It is worth considering that encephalopathy can progress and have a greater or lesser degree of severity. The development of the disease is influenced by several factors:
- severity of the lesion;
- the body's ability to recover;
- general health;
- nature of the injury.
Premorbid and genetic factors are also important. It is desirable that the treatment of TBI itself be timely and effective. In this case, complications can be avoided.
Encephalopathy - symptoms
Encephalopathic syndrome is a complex of pathological symptoms manifested in the form of:
- decreased memory and general intelligence;
- affective instability;
- decreased ability to work and learn;
- deterioration of adaptation to stress.
Mental disorders are often combined with focal brain lesions and in some cases are caused by them.
The speed at which the first signs of brain damage appear and their severity depends on the cause of the disorder. For example, with Gaye-Wernicke encephalopathy, which occurs due to vitamin B1 deficiency, the symptoms develop acutely; the first symptom may be psychosis, followed by severe disturbances in movement, swallowing, and severe memory disorders.
With vascular and some metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, hypertension), a gradual deterioration of the condition over decades is possible. Patients do not consult a doctor for a long time and do not begin treatment for encephalopathy, as they do not notice increasing changes. The functions of dead neurons are taken over by surrounding cells.
Over time, compensatory capabilities are depleted. The development of encephalopathy is often indicated by the following patient complaints:
- irritability, tearfulness;
- weakness, fatigue;
- new information is remembered worse;
- instability of attention;
- difficulties with planning things;
- headaches (with mental stress, weather changes);
- dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- weather sensitivity;
- poor tolerance to hot or cold weather;
- sleep disorders;
- depressed mood;
- apathy;
- unsteadiness of gait;
- visual impairment;
- the appearance of hallucinations.
When the cause of encephalopathy is local brain damage, focal neurological symptoms appear in the clinical picture. Detection of one or more painful manifestations is the basis for contacting a specialist. If the need to come to an appointment and personally talk about your health problems causes embarrassment, you can get primary information for free by calling the clinic. A specialist will answer your questions.
Risk factors
Doctors have been actively studying angioencephalopathy of the brain for several decades, what it is, and the features of its course. Thanks to numerous studies, they were able to identify the so-called risk group, being in which increases the likelihood of developing pathology. It includes people:
- those suffering from addictions (smoking, alcohol abuse);
- experiencing chronic fatigue;
- exposed to daily stress;
- not watching their diet.
In addition, the presence of hypertension among close relatives significantly increases the risk of angioencephalopathy.
Relatives' eye disease
In a situation where the patient does not agree to see a doctor on his own because he does not see the need for this or cannot describe changes in his condition, the family psychiatrist asks the relatives what worries them about the behavior of their loved one.
It is family members who initiate treatment for encephalopathy in the absence of criticism from the patient.
The severity of symptoms and their combination may vary at different stages of the disorder, but relatives or friends say that a loved one:
- became uncollected, absent-minded;
- gets easily irritated and lashes out at relatives;
- became more demanding, intolerant;
- weak-hearted, easily cries for no apparent reason;
- forgets about important dates, current events and plans;
- has difficulty performing normal tasks;
- withdraws from his routine duties;
- looks depressed, but cannot explain the reason for the bad mood;
- has difficulty remembering any words or names;
- uncritical of ongoing changes;
- could get lost on the street, stopped going to familiar places;
- sleeps poorly at night, sleepy during the day.
Diagnostic techniques
A very important point is to study the reason why a person suffered an injury, the degree of its severity and the place where it is localized. This is necessary to prescribe the correct and necessary treatment.
In addition, the doctor has the opportunity to prescribe additional examination:
- Two types of tomography – magnetic resonance and computer. With their help, it becomes possible to determine how deep the injury is and which parts of the brain were affected or damaged.
- Electroencephalography. This examination makes it possible to determine whether any symptoms are observed that lead to the development of epilepsy.
Types of course, forms and degrees of encephalopathic syndrome
There are three types of encephalopathy: stationary, progressive, regredient. In the stationary variant, the severity of the main symptoms remains practically unchanged over time, and decompensation of the condition is possible in response to the action of unfavorable factors.
The progressive course is characterized by a gradual worsening of clinical manifestations as a result of the addition of additional factors or an increase in the severity of the underlying disease. The regressive course is the most favorable - with the treatment of encephalopathy, the patient's condition gradually improves.
Depending on the degree of predominance of certain symptoms, several forms of psychoorganic syndrome are distinguished. Four of them are the most common.
| Form | Symptoms |
| Asthenic form | Asthenic symptoms and emotional instability come to the fore. The patient gets tired quickly and cannot maintain attention on the task at hand. When tired, he becomes irritable and whiny. Has difficulty withstanding emotional overload. The ability to remember new information decreases. Additional symptoms may include senestopathy, paresthesia, and a feeling of derealization. |
| Explosive form | With persistent asthenia and hypersensitivity, gross affective disturbances become increasingly important: anger, irritability, grumpiness. They are combined with tearfulness, emotional instability, slow thinking, and memory impairment. Such patients are prone to developing hypochondria and litigiousness. |
| Euphoric form | Such patients are complacent, careless, and their judgments are facile. Memory impairment is evident. Thinking is slow, detailed. Patients cannot cope with ordinary activities, are passive, and their intelligence decreases. Short attacks of anger are possible, ending in tearfulness and touchiness. |
| Apathetic form | The range of interests narrows, patients become spontaneous, spend a lot of time doing nothing and are not burdened by it. The scope of interest is limited to physiological needs. A sharp decrease in memory and attention. Thinking is viscous, detailed. |
In a number of patients, the syndrome manifests itself in the form of an amnestic form, in which memory impairment comes to the fore.
Treatment of encephalopathy is most effective in the early stages. Psychiatrists note that with a progressive course, the forms of the disease can be considered as stages of development. Depending on the severity, there are 3 degrees of the disorder:
Mild degree. The patient retains self-care skills, and often the ability to work. He gets tired faster, so it takes longer to complete normal tasks. Learning new skills is difficult.
Moderate (moderate severity). The patient loses the ability to work, and partially to self-care. Requires regular assistance to maintain normal functioning. Personality changes are increasing: explosiveness, complacency and lightness of judgment or apathy with lack of spontaneity.
Severe encephalopathy. With this level of impairment, the patient completely loses the ability to self-care and requires constant outside help.
Stages
There are three stages of angioencephalopathy:
- Subjective complaints about deterioration of memory and attention are accompanied by minor focal symptoms: a decrease in the pupillary reflex, the appearance of mild reflexes of oral automatism. Slight changes in gait, lack of self-confidence, irritability.
- At this stage, neurological symptoms increase and one dominant symptom crystallizes. These may be extrapyramidal disorders, pseudobulbar syndrome, ataxia, dysfunction of the cranial nerves. Cognitive function suffers more severely, and professional and social adaptation decreases.
- Several syndromes predominate in patients. Noteworthy are gross gait disturbances, cerebellar disorders, parkinsonism, and disruption of the pelvic organs. At this stage, criticism of one’s condition decreases and there may be no complaints at all. Patients become helpless, like children, because they develop dementia.
Encephalopathy
Discirculatory encephalopathy (or DEP) occurs in 6% of the world's population. With this disease, small cerebral vessels are gradually affected with the development of diffuse or focal dystrophic changes in the brain.
Patients with diseases and conditions such as:
- hypertonic disease;
- systemic connective tissue lesions;
- cerebral atherosclerosis;
- disruption of venous outflow from the head.
- There may be a combination of several factors.
In case of vascular disorders, treatment of encephalopathy in Moscow is often started by mature and elderly people. The most common causes of the disease are prolonged high blood pressure and atherosclerosis.
Clinical manifestations of DEP consist of mental disorders and neurological symptoms. Cognitive, affective and psychotic disorders fit completely into the picture of the progressive course of the psychoorganic syndrome. The outcome of DEP is considered to be dementia (otherwise known as dementia). The predominant symptoms depend on the location of the pathological foci.
During a neurological examination, a specialist may reveal:
- vestibular disorders;
- loss of smooth movement and speech;
- walking and balance problems;
- dysarthria, change in speech timbre;
- violent laughter, crying;
- focal symptoms;
- the appearance of pathological reflexes.
In severe cases, the patient ceases to control the functions of the pelvic organs - urinary and fecal incontinence develops.
What is the danger of the disease?
The consequences of dropsy largely depend on the age at which the disorders occurred and the development of complications:
- Infants experience high excitability, sleep disturbances, and increased muscle tone. The most severe manifestation is developmental delay and mental deviations.
- Preschoolers show aggression, stutter, develop strabismus, and experience developmental delays.
- School-age children experience memory loss and headaches. The learning process is difficult.
- In adults, epilepsy, increased excitability, and hallucinations appear.
The danger of the disease in adulthood is the development of mental disorders, motor functions and motor skills. If urgent measures are not taken, the patient becomes disabled.
Toxic encephalopathy
Toxic encephalopathy is a condition associated with the effect of neurotropic poisons on the brain in everyday life or professional activities. Harmful substances include alcohols, drugs, arsenic, pesticides, heavy metal salts, and bacterial toxins.
The most common cause of the disorder is alcohol abuse. Encephalopathy in this group of patients develops with an experience of ethyl alcohol use of 10 years or more; narcologists indicate that most patients have stages 2 and 3 of addiction. Such patients have a negative attitude towards seeking help; treatment of encephalopathy often begins after interruption of binge drinking, poisoning with surrogates, or the development of severe cognitive and neurological disorders that limit independent alcohol consumption.
Along with the psychoorganic syndrome, patients experience neurological disorders: polyneuropathy, ataxia, and the occurrence of pathological reflexes. Among the common forms:
- acute Wernicke encephalopathy;
- Korsakov's syndrome and Korsakov's psychosis;
- fulminant forms of encephalopathy;
- alcoholic pseudoparalysis;
- alcoholic hallucinosis;
- cerebellar atrophy.
This type of brain damage leads to seizures. The condition is life-threatening and requires a differential diagnosis with epilepsy.
Toxic encephalopathy often develops against the background of metabolic disorders (deficiency of vitamins, nutrients, uncompensated diabetes mellitus). In such cases they talk about toxic-metabolic encephalopathy. If left untreated, dementia may develop.
Possible complications
Patients with angioencephalopathy must be prescribed background therapy with antiplatelet medications to stabilize blood pressure. Untimely treatment of vascular pathologies of the brain can lead to complications such as oxygen starvation, disruption of the integrity of blood vessels and hemorrhage. Over time, such patients develop fits of laughter, followed by hysteria. There is a coordination disorder and manifestations of oral automatism. Against the background of damage to the occipital zone of the brain, a decrease in vision and even its complete loss cannot be ruled out.
Diagnostics
Early detection of encephalopathy is of great importance in case of vascular and metabolic lesions of the brain. Patients with these types of disorders often seek help when painful symptoms begin to limit normal daily activities. The examination begins with a consultation with a neurologist. If necessary, he refers the patient to a therapist, ophthalmologist, endocrinologist, or narcologist. Instrumental diagnostic methods include:
- MRI, CT;
- EEG;
- Doppler ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck.
Laboratory methods include: general blood test, coagulogram, determination of sugar and cholesterol fractions.
Preventive measures
If encephalopathy was diagnosed on time and properly treated, the likelihood of complete healing of the patient is very high. However, a positive outcome is observed only if the brain damage was not too deep. An additional factor influencing the possibility of recovery is maintaining a correct lifestyle.
To avoid relapses and worsening of the condition, the patient should:
- follow all doctor’s recommendations during the treatment of intracranial injury;
- give up cigarettes and alcoholic beverages;
- avoid re-injury.
Athletes should stop working out during recovery, and representatives of law enforcement agencies should take a vacation.
Encephalopathy of the brain - treatment and prognosis
Treatment of encephalopathy in Moscow is carried out by psychiatrists and neurologists in close collaboration with other specialists - endocrinologists, cardiologists, rheumatologists. The scope of help for the disorder varies at different stages and may include:
- Correction of the underlying disease that caused brain damage. In case of chronic somatic pathology, a specialized specialist seeks compensation. Thus, a cardiologist carries out antihypertensive therapy, an endocrinologist adjusts the dosage of sugar-lowering drugs and insulin, a neurologist treats the consequences of a stroke or head injury.
- In the presence of intoxication, it is necessary to stop the flow of poison into the body. To do this, the patient excludes exposure to harmful occupational factors; if the influence of psychoactive substances is present, abstinence from use is necessary. The doctor then administers detoxification therapy. To monitor the condition and prevent complications, this stage of therapy is most effective in an inpatient setting.
- Symptomatic treatment. Aimed at combating the manifestations of encephalopathy. For this purpose, vitamin preparations, vascular agents, and nootropics are used. If episyndrome develops, the neurologist recommends anticonvulsant therapy.
With the development of cognitive impairment, the patient receives means to strengthen memory. Some products require lifelong use. During therapy, the patient remains cheerful, active, and does household chores. If a patient develops severe memory impairment, taking medications helps reduce the burden on relatives or caregivers.
Non-drug treatment of encephalopathy is aimed at preserving the ability to self-care and some social adaptation of the patient. Psychotherapeutic and psychological assistance consists of conducting classes in which the patient trains cognitive skills: memory, attention, and relearns how to cope with everyday situations: cooking, going to the store, or the clinic. Such rehabilitation helps him maintain his dignity and be less dependent on the help of relatives.
The prognosis for encephalopathy depends on the stage, the underlying cause of the disease and the willingness to follow the doctor’s recommendations. It is important to understand that it is impossible to completely eliminate the symptoms of this mental disorder. Damage to nervous tissue is irreversible. However, during treatment it is possible to compensate for the condition:
- reduction in episodes of irritability;
- some improvement in memory and attention;
- normalization of sleep.
Patients receiving maintenance therapy and eliminating or reducing the influence of factors such as high blood pressure or blood sugar, hypercholesterolemia, alcohol, have a longer life expectancy than those who neglect the advice of a doctor.
Taking medications
It is not possible to completely restore brain function with angioencephalopathy. Therefore, the therapeutic methods used for treatment should be aimed at slowing down destructive changes in cerebral circulation and eliminating the microsomatic processes that provoked them.
The chronic form of the pathology does not require hospitalization. The patient can be admitted to the hospital only if there is a somatic defect and a high probability of stroke.
Depending on the stage of cerebral angioencephalopathy, treatment is carried out using the following drugs:
- Nootropics (“Nootropil”, “Actovegin”). Helps improve metabolic processes between cells.
- Antihypertensive drugs (“Lisinopril”, “Nimodipine”). Stabilizes blood pressure and improves its performance.
- Anticoagulants (“Curantil”). With their help, they achieve a decrease in blood viscosity.
- Statins (“Lovastatin”, “Simvastatin”). Drugs from this group are recommended for atherosclerosis, since in this case it is necessary to reduce cholesterol levels.
- Chondroprotectors. Used in the presence of severe problems with the spinal column.
If a patient suffers from diabetes, he is given a special diet and appropriate medications.
Treatment of encephalopathy in adults - how to choose a clinic
The issue of choosing a medical institution and specialist worries both patients and relatives. Treatment of encephalopathy in Moscow is possible in three formats:
- managing patients at home;
- outpatient observation;
- hospitalization in a psychiatric hospital.
To decide on the format of medical care, it is important to clearly assess not only the patient’s health, but also his age and social environment. Often relatives are faced with a lack of criticality of the patient towards the condition:
- refuses to see a doctor;
- does not want to undergo examination in a regular clinic;
- has a negative attitude towards hospitalization.
To discuss the specifics of treatment with a specialist, it is enough to contact the clinic without the patient at any free time: doctors will give a detailed and free consultation over the phone. Obtaining reliable information will allow you to make an informed decision. You should not choose the first institution you come across with lower prices. Please note the following conditions:
- Is there a license to carry out medical activities? In boarding houses and private homes for the elderly, treatment is actually not provided;
- availability of own doctors on staff. Visiting specialists are not interested in the outcome of therapy and help only in acute situations;
- availability of valid certificates in psychiatry and psychotherapy among the clinic doctors;
- the ability to examine the patient in a short time. It is necessary to clarify which diagnostic methods are possible - this is of particular importance when working with negatively inclined or immobile patients;
- possibility of providing primary care at home (calling a doctor). This is important in the treatment of acute toxic encephalopathies, when refusing to visit the clinic;
- hospitalization on the day of treatment without paperwork. Some conditions are life-threatening. Treatment of encephalopathy may be required immediately, and getting to a clinic with decent conditions without waiting in line is not easy;
- comfortable conditions in the psychiatric department. Hospitalization is stressful for the patient. An unfavorable climate in the hospital, crowding of patients in the ward, and the inability to receive care from medical personnel reduces confidence in the doctor and worsens the prognosis.
Encephalopathy is a chronic disorder in which damage to brain tissue develops with the occurrence of mental, neurological, and somatic disorders. Competent treatment allows the patient to maintain quality of life, and in case of severe symptoms, reduce the burden on caring relatives.
Questions and answers
Mom has dyscirculatory encephalopathy. She hardly leaves the house. Is it possible to examine her in a hospital?
Yes. In a psychiatric clinic, experienced doctors will conduct all the necessary studies and select therapy. You can choose comfortable accommodation conditions and get more information about what kind of help is recommended for this condition by calling.
Why does a doctor recommend hospitalization of a patient with encephalopathy in a hospital?
A doctor may refer a patient to a 24-hour department in the following cases:
- the patient is aggressive, has delusions, hallucinations;
- the patient has acute toxic encephalopathy;
- it is necessary to examine a patient with limited mobility;
- selection of therapy with round-the-clock monitoring is required;
- the patient needs assistance, but will not be able to attend the clinic independently.
Is it possible to get information about how much treatment for encephalopathy will cost in Moscow: we are afraid of hidden fees.
When you contact the clinic, you will receive full information about the cost of consultations, examinations, and for inpatient treatment - the price of one day of stay. The institution does not practice “hidden payments” and sudden increases in the cost of treatment. Detailed information is available by calling the hospital or will be provided during a personal visit.
Is it possible to completely cure encephalopathy?
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely eliminate the symptoms of encephalopathy. But properly prescribed treatment can eliminate or reduce painful symptoms and slow down the progression of the disorder.
Prevention methods
Now you know the main causes and symptoms of cerebral angioencephalopathy, what it is. Is it possible to prevent the development of the disease?
First of all, doctors advise undergoing a medical examination once a year to identify pathology at the initial stage. In this case, no specific therapy is prescribed, but constant monitoring by specialized specialists is required.
If you are at risk, you should pay special attention to your own health. You need to establish a sports regime and regularly do exercises for the collar area. The therapist should tell you more about them. Some people benefit from physical therapy sessions. At the same time, one should not forget about proper nutrition. You will need to exclude excessively salty and peppery foods from your diet.