Clinical manifestations directly depend on the toxin that caused the disease. In case of an overdose of salicylates, general malaise, nausea with vomiting, ringing or noise in the ears, speech impairment, auditory and visual hallucinations initially occur. Sometimes there is a convulsive syndrome, cognitive disorders, and coma. Carbon monoxide poisoning is accompanied by general cerebral symptoms, memory impairment, hallucinations, ataxia, hypertonicity of skeletal muscles, choreic hyperkinesis and depression of consciousness.
TE in hydrogen sulfide poisoning is characterized by intense persistent headache, dizziness, small-scale tremor, state of intoxication, slowdown of active movements and other manifestations of akinetic-rigid syndrome. With mercury encephalopathy, the first signs are vegetative-vascular disorders and neurasthenia syndrome, combined with severe gastrointestinal disorders. Large-scale tremor, “mercury erethism”, cerebellar ataxia, dysarthria and dementia gradually develop.
Lead TE is characterized by severe diffuse headache, general weakness, malaise, memory impairment, static tremor, severe visual impairment, central paresis and paralysis. In some cases, damage to the motor and mixed cranial nerves and epileptic seizures are determined. A typical manifestation is a lilac-gray border that appears along the dentition (Bruton's sign). In case of ethylene glycol poisoning, horizontal nystagmus and a general condition simulating alcohol intoxication are noted. In severe poisoning, convulsive syndrome, stuporous state or coma occurs.
TE caused by FOS is accompanied by ataxia, severe cephalalgia and dizziness, myoclonus of individual muscles and disorders of the autonomic nervous system. In severe poisoning, hallucinations and delirium are observed. Manganese TE is manifested by muscle hypotonia, general lethargy and drowsiness, emotional lability, walking disorders, forced smiling or forced laughter, tremor of the tongue and lips. In severe cases, “manganese madness” is formed.
Acute alcoholic encephalopathy is characterized by pronounced cerebral symptoms, ophthalmoplegia, strabismus, nystagmus, loss of tendon and periosteal reflexes, hyperkinesis, cerebellar incoordination, vegetative-vascular dysfunction and mental disorders. In the chronic form of alcoholic TE, autonomic and neuroendocrine disorders, insomnia or disturbing dreams, tremor, and dementia occur.
Toxic encephalopathy of the brain: what kind of disease, main causes
The toxicogenic effect of most neurotropic poisons is based on their negative impact directly on neuronal membranes and the mechanisms of nerve impulse transmission. Violations of energy and plastic metabolism play an important role in the pathogenesis of the disease. In addition, some toxins inhibit the hematopoietic and circulatory systems, breathing, which also causes toxic hypoxic encephalopathy. Due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure, cells localized in the cerebral cortex, cerebellum and hippocampus are especially sensitive to the influence of pathological factors, which causes the clinical manifestations of the disease.
Major neurotoxins
The main causes of toxic encephalopathy include:
alcohol and volatile solvents: destroy cell membranes, receptors, cause changes (irreversible with long-term exposure) in energy metabolism;- psychoactive substances (opiates, cannabinoids, amphetamines, cocaine, ephedrine, hallucinogens, some drugs, etc.): pathologically affect the reuptake system and the production of norepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin
- heavy metals (mercury, lead, manganese, arsenic, thallium, etc.): have a direct destructive effect on the structures of the central nervous system and also affect the functioning of the peripheral nervous system.
Accordingly, the risk of toxic brain encephalopathy is especially high among people working in hazardous industries. These are, for example, chemical, construction, metallurgy, and agriculture, where insecticides and pesticides are used. The disease is often diagnosed in alcoholism and drug addiction. The pathology is less common among artists; those who use neurotoxic paint solvents are at risk.
Types of course, forms and degrees of encephalopathic syndrome
There are three types of encephalopathy: stationary, progressive, regredient. In the stationary variant, the severity of the main symptoms remains practically unchanged over time, and decompensation of the condition is possible in response to the action of unfavorable factors.
The progressive course is characterized by a gradual worsening of clinical manifestations as a result of the addition of additional factors or an increase in the severity of the underlying disease. The regressive course is the most favorable - with the treatment of encephalopathy, the patient's condition gradually improves.
Depending on the degree of predominance of certain symptoms, several forms of psychoorganic syndrome are distinguished. Four of them are the most common.
| Form | Symptoms |
| Asthenic form | Asthenic symptoms and emotional instability come to the fore. The patient gets tired quickly and cannot maintain attention on the task at hand. When tired, he becomes irritable and whiny. Has difficulty withstanding emotional overload. The ability to remember new information decreases. Additional symptoms may include senestopathy, paresthesia, and a feeling of derealization. |
| Explosive form | With persistent asthenia and hypersensitivity, gross affective disturbances become increasingly important: anger, irritability, grumpiness. They are combined with tearfulness, emotional instability, slow thinking, and memory impairment. Such patients are prone to developing hypochondria and litigiousness. |
| Euphoric form | Such patients are complacent, careless, and their judgments are facile. Memory impairment is evident. Thinking is slow, detailed. Patients cannot cope with ordinary activities, are passive, and their intelligence decreases. Short attacks of anger are possible, ending in tearfulness and touchiness. |
| Apathetic form | The range of interests narrows, patients become spontaneous, spend a lot of time doing nothing and are not burdened by it. The scope of interest is limited to physiological needs. A sharp decrease in memory and attention. Thinking is viscous, detailed. |
In a number of patients, the syndrome manifests itself in the form of an amnestic form, in which memory impairment comes to the fore.
Treatment of encephalopathy is most effective in the early stages. Psychiatrists note that with a progressive course, the forms of the disease can be considered as stages of development. Depending on the severity, there are 3 degrees of the disorder:
Mild degree. The patient retains self-care skills, and often the ability to work. He gets tired faster, so it takes longer to complete normal tasks. Learning new skills is difficult.
Moderate (moderate severity). The patient loses the ability to work, and partially to self-care. Requires regular assistance to maintain normal functioning. Personality changes are increasing: explosiveness, complacency and lightness of judgment or apathy with lack of spontaneity.
Severe encephalopathy. With this level of impairment, the patient completely loses the ability to self-care and requires constant outside help.
Treatment
The main goal of therapy is to improve blood circulation in the brain, protect nerve cells from oxygen starvation and ischemia. Depending on the underlying cause of the disease, treatment may include:
- antihypertensive, hypoglycemic drugs;
- diet to lower cholesterol and drugs that lower it;
- calcium channel blockers, phosphodiesterase inhibitors and other agents to improve cerebral hemodynamics;
- antiplatelet agents, most often for lifelong use;
- neuroprotectors, for example pyrrolidone derivatives;
- vitamin complexes.
Diagnosis and treatment of DEP are carried out by a neurologist. In severe cases, for example, when the lumen of the internal carotid artery narrows by more than 70%, which causes encephalopathy, surgical intervention is recommended. Anomalies of the vertebral arteries are also treated surgically.
Even properly selected treatment can only slow down the progression of the disease, and then mainly at the first or early second stage. The third stage is practically incurable, and it becomes impossible to control the symptoms. In addition, in some people the disease progresses quickly - no more than 2 years pass between stages.
Treatment of encephalopathy in adults - how to choose a clinic
The issue of choosing a medical institution and specialist worries both patients and relatives. Treatment of encephalopathy in Moscow is possible in three formats:
- managing patients at home;
- outpatient observation;
- hospitalization in a psychiatric hospital.
To decide on the format of medical care, it is important to clearly assess not only the patient’s health, but also his age and social environment. Often relatives are faced with a lack of criticality of the patient towards the condition:
- refuses to see a doctor;
- does not want to undergo examination in a regular clinic;
- has a negative attitude towards hospitalization.
To discuss the specifics of treatment with a specialist, it is enough to contact the clinic without the patient at any free time: doctors will give a detailed and free consultation over the phone. Obtaining reliable information will allow you to make an informed decision. You should not choose the first institution you come across with lower prices. Please note the following conditions:
- Is there a license to carry out medical activities? In boarding houses and private homes for the elderly, treatment is actually not provided;
- availability of own doctors on staff. Visiting specialists are not interested in the outcome of therapy and help only in acute situations;
- availability of valid certificates in psychiatry and psychotherapy among the clinic doctors;
- the ability to examine the patient in a short time. It is necessary to clarify which diagnostic methods are possible - this is of particular importance when working with negatively inclined or immobile patients;
- possibility of providing primary care at home (calling a doctor). This is important in the treatment of acute toxic encephalopathies, when refusing to visit the clinic;
- hospitalization on the day of treatment without paperwork. Some conditions are life-threatening. Treatment of encephalopathy may be required immediately, and getting to a clinic with decent conditions without waiting in line is not easy;
- comfortable conditions in the psychiatric department. Hospitalization is stressful for the patient. An unfavorable climate in the hospital, crowding of patients in the ward, and the inability to receive care from medical personnel reduces confidence in the doctor and worsens the prognosis.
Encephalopathy is a chronic disorder in which damage to brain tissue develops with the occurrence of mental, neurological, and somatic disorders. Competent treatment allows the patient to maintain quality of life, and in case of severe symptoms, reduce the burden on caring relatives.
Diagnostic principles
The diagnosis is based on objective symptoms, results of laboratory and instrumental examinations and anamnesis. In addition to the mandatory examination by a therapist and neurologist, the following are indicated:
- general clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- biochemical blood test with determination of glucose, ALT, AST, bilirubin, urea, creatinines and electrolytes;
- according to indications: analysis to determine immunospecific status, neurospecific factors;
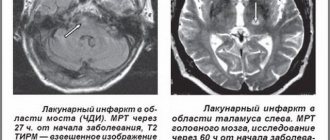
- CT, MRI, angiography;
- specific tests to detect heavy metals and narcotic substances in the body.
If symptoms indicate damage to internal organs, additional research or consultation with specialized specialists may be required. Differential diagnosis is carried out with other forms of encephalopathies and neurodegenerative diseases.
Clinical guidelines for the treatment of toxic encephalopathy
The basic principles of disease treatment are as follows:
- restoration and maintenance of the full functioning of internal organs and systems;
- stopping further entry of the neurotoxin into the body (limiting work activity, giving up alcohol and/or drugs, etc.);
- speeding up metabolism to eliminate poison as quickly as possible, using specific antidotes;
- symptomatic treatment.
In the acute period, therapy is carried out strictly in a hospital setting under round-the-clock medical supervision. As the patient’s well-being improves, the patient is transferred to an outpatient regimen. For a long course the following is prescribed:
- nootropic drugs;
- drugs that improve metabolic processes in the brain;
- neuropeptides;
- antioxidants;
- means for normalizing the tone of cerebral vessels;
- vitamins and dietary supplements (group B, nicotinamide, riboxin, succinic, ascorbic acid, glycine, etc.);
- if necessary, tranquilizers from the group of benzodiazepines, antidepressants, sleeping pills.
Symptoms of toxic encephalopathy are a mandatory indication for contacting a neurologist. No treatment with folk remedies - only comprehensive, individually selected therapy in combination with physical procedures, dietary correction, and lifestyle changes. Don't hesitate to start therapy! To make an appointment or call a specialized specialist at home, call us 24/7 at 8(969)060-93-93.