Traumatic brain injury
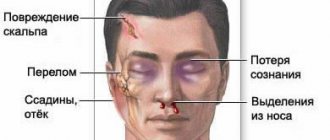
- this is damage to the bones of the skull and/or soft tissues (meninges, brain tissue, nerves, blood vessels). Based on the nature of the injury, a distinction is made between closed and open, penetrating and non-penetrating TBI, as well as concussion or contusion of the brain. The clinical picture of traumatic brain injury depends on its nature and severity. The main symptoms are headache, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, loss of consciousness, memory impairment. Brain contusion and intracerebral hematoma are accompanied by focal symptoms. Diagnosis of traumatic brain injury includes medical history, neurological examination, skull x-ray, CT or MRI of the brain.
What is it and what is the ICD 10 code?
According to the 10 microbial code, concussion can manifest itself as a concussion . With a severe concussion, the victim may lose memory for a short time, and remember everything only when the memory returns.
Subtype of severe wound acquired in war
What does it mean to receive this type of serious injury, and in general - is it a wound or not? Undoubtedly, yes! If the temporal or frontal part is bruised, a person may become speechless. Concussion as a serious injury can be a severe concussion with hemorrhage. Sometimes it leads to seizures.
Symptoms of concussion are very similar to a standard concussion , because you can see blood from the ears and nose. It may also be accompanied by fractures, severe bruises, and damage to internal organs.
Severe injury can cause mental disorders such as headache, dizziness, and excessive irritability. The victims need complete rest and emergency hospitalization.
To heal such a wound, you will have to spend a lot of time.
This is interesting: Traumatic stress
Symptoms of concussion
The main symptom of concussion is loss of creation, which can last several minutes or several days. It is impossible to say for sure about the integrity of the body - you can observe changes in the functioning of cognitive functions and sensory systems.
These may include hearing impairment, vision impairment, memory loss, difficulty speaking, and dizziness. All these symptoms may disappear or remain bothersome for a long time.
This term is associated with a bruise. However, bruise is a narrower concept; it can be applied to a specific area of the body. In this context, you can use the definition of contusion as damage to one of the organs. A synonym for concussion is blast injury.
Kinds
Contusion can be of the following types:
- Brain. It occurs due to bruising of the entire body through mechanical action. This could be an impact on the surface of the water or a blast wave. Often, contusion is expressed as a headache, dizziness. You can observe loss of hearing and vision, vomiting and nausea, as well as breathing problems - hyperventilation, loss of coordination, retardation of movements.
- Eyes. Eye contusion is damage to the eye elements under the influence of the external environment. The cause may be a strong blow from a fall, or a jet of gas or water. Indirect contusion can appear when exposed to different areas. The consequences may be changes in the ocular structure. Blood circulation may be impaired, which will lead to rupture of tissues and blood vessels.
- Ear. Contusion of this organ leads to hearing loss and even anatomical changes. Damage may occur under the influence of a blast wave. This means a sudden, sharp change in pressure on the eardrum. Often it is destroyed. Hearing can be lost partially or completely.
- Easy. Closed injury from a blow may be accompanied by subpleural hemorrhages and crushing of lung tissue. With bruises, hemothorax and pneumothorax are rare. With extensive reproduction, wet or shock lung syndrome can be seen. Hemorrhages are caused by merging shadows, the diameter of which ranges from 2 to 4 cm.
- Guts. Damage to the intestine in peacetime can occur during a transport accident, a fall from a height, or compression between carriages. At the same time, the degree of damage can be different. These can be ruptures of the intestine, their separation from the mesentery. Clinical rupture is determined by the presence of pain in the abdomen.
What it is?
An eye contusion is an injury to the visual organ as a result of exposure to heavy blunt objects or intense mechanical force.
ICD-10 code
Eye contusion according to ICD-10 (international classification of diseases) is designated by code S05 and is one of the most dangerous injuries to the eyeball.
S05 Trauma to the eye and orbit Classification:
- S05.0 Conjunctival trauma and corneal abrasion without mention of a foreign body.
- S05.1 Contusion of the eyeball and orbital tissues.
- S05.2 Laceration of the eye with prolapse or loss of intraocular tissue.
- S05.3 Laceration of the eye without prolapse or loss of intraocular tissue.
- S05.4 Penetrating wound of the orbit with or without the presence of a foreign body.
- S05.5 Penetrating wound of the eyeball with a foreign body.
- S05.6 Penetrating wound of the eyeball without a foreign body.
- S05.7 Eyeball avulsion.
- S05.8 Other injuries of the eye and orbit.
- S05.9 Injury to unspecified part of the eye and orbit.
Possible classifications
Currently, in domestic and foreign traumatology, doctors use several different classifications, each of which reflects certain features of the occurrence of injury and its consequences.
Classification by affected area:
- spinal nerve contusion;
- bone contusion;
- contusion damage to the spinal cord;
- contusion damage to the brain;
- contusion of the organs of hearing and balance;
- contusion of the organs of vision;
- contusion damage to the spinal column;
- contusion damage to the urinary apparatus;
- contusion of the heart and adjacent vessels.
Classification by process extent:
- general contusion;
- local contusion.
General contusion is a uniform damage to all body systems. Local is characterized by the presence of traumatic pathology of one or more organs. Such a contusion is very dangerous and leads to longer treatment complications.
Classification by causes:
- shell shock during military operations;
- concussion due to injuries at work;
- household concussion.
Most often, doctors have to diagnose military personnel with “shell shock”: more than 40% of soldiers had the misfortune to suffer this injury at least once in their lives. In second place in terms of frequency of occurrence is occupational injury among workers at various enterprises. Concussion in everyday life is quite rare.
Classification according to combination with other injuries:
- isolated contusion;
- combined contusion lesion;
- combined contusion.
Classification of concussion severity:
- I degree - mild damage;
- II degree - moderate damage;
- III degree - severe damage.
In the first degree of concussion, a person loses consciousness for no more than 30–40 minutes. In some cases, the stage of absence of consciousness does not occur at all. After the victim wakes up, he is disoriented in space for some time, cannot speak, hear or move normally, and does not remember previous events. Symptoms subside within a few hours.
The second degree is characterized by absence of consciousness for more than two hours. After this, the victim complains of a severe headache, nausea or vomiting, and his pupils may be of different sizes. The duration of cognitive impairment is more than 12–24 hours. Recovery from a moderate concussion takes more than a month.
Severe damage is characterized by complete depression of consciousness up to coma, the duration of which can vary from several days to several months. The patient's reflexes are suppressed, and special life support devices are required to breathe and stimulate the heart. After emerging from a coma, the patient may completely forget some life events and lose self-care skills, speech and some motor functions. The duration of recovery after such an incident can be several years.
Classification according to the presence or absence of complications:
- complicated contusion;
- uncomplicated contusion.
Uncomplicated contusion is the mildest type of traumatic injury and occurs more often in peacetime during everyday interactions. Complicated concussion mainly affects people associated with exposure to some negative factor, as well as the military. This type of pathology is treated only by doctors with special training, and therapy lasts many months.
Concussion - symptoms and consequences
This condition is developing at a rapid pace. The first signs of concussion appear within a couple of minutes after receiving the injury. Some people mistakenly confuse this condition with shock. The only thing they have in common is that the victim, after receiving an injury, does not react in any way to what is happening around him. The onset of concussion can be judged by the following signs:
- Lack of consciousness.
The victim has no reaction to stimuli. In addition, his pupils may differ in size. With a mild type of concussion, a person remains unconscious for only a few minutes (maximum - half an hour), and with a severe type - weeks, or even months. - Disorientation in space.
After the victim comes to, he remains confused for a long time. He cannot figure out where he is, or even say his name or describe the circumstances that led to the injury. - Attacks of nausea and vomiting.
They attack immediately after a person regains consciousness. This is the body’s response to the impact of a shock wave: the functioning of the vomiting center is disrupted. - Sphincter dysfunction.
Due to a long stay in a coma, involuntary urination and defecation occur. - Photophobia.
Each contusion is accompanied by a disruption in the functioning of the brain or spinal cord. Photophobia is an integral part of such damage. Such a symptom can manifest itself within several hours, or even weeks. - Memory impairment.
After a long coma, the victim does not recognize his loved ones and does not remember anything about his past life. In most cases, memories gradually return to the patient.
Brain contusion
Such a lesion is characterized by a specific clinical picture.
A brain injury is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- dizziness;
- hearing and vision impairment;
- paralysis of limbs;
- nose bleed;
- epileptic seizures;
- disorientation in space;
- coma.
Eye contusion
The main flow of information to the brain is delivered by the organs of vision. Contusion of the eyeball leads to the fact that a person loses one of the basic senses.
Such a lesion is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- swelling of the eyelid;
- nystagmus;
- ulcerative lesions of the cornea;
- pupils that differ in size;
- loss of visual acuity;
- hemorrhage in the eyeball;
- clouding of the lens;
- loss of the ability to open and close eyes.
Ear contusion
With a mild degree of damage, the patient is deafened for several minutes; with severe damage, deafness can last for days, or even weeks.
Symptoms of hearing aid contusion:
- disorientation in space;
- unsure gait;
- inability to move without assistance;
- bleeding from the ear;
- when the head turns sharply, balance is lost and the person falls.
Spinal contusion
The clinical picture largely depends on which part is damaged.
Contusion of the spinal cord in the cervical area is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- decreased blood pressure;
- paraparesis of the upper limbs;
- slow heart rate;
- constriction of the pupils.
If the thoracic region is injured, the following signs are observed:
- pneumonia;
- heart dysfunction;
- disturbances in the functioning of the respiratory system;
- loss of sensation in the lower extremities;
- disturbances in the functioning of internal organs.
When the lumbar region is affected, it manifests itself as follows:
- paraplegia;
- leg pain;
- loss of sensation in the perineum.
Contusion of internal organs
If the lower half of the body is injured, the pelvic organs are more often affected. The kidneys are hit harder.
Injury to internal organs is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the presence of bloody impurities in the urine;
- pain when urinating;
- false urges;
- disturbances in the functioning of the organs of the reproductive system;
- spontaneous urination.
Concussion - consequences
The first negative manifestations are observed a few days after the injury. The consequences that arise directly depend on the degree of concussion.
More often the victim experiences:
- dyspnea;
- increased heart rate;
- stuttering and other speech disorders;
- severe headaches;
- intolerance to loud sounds.
Since during this period the restoration of neurons in damaged areas of the brain begins, the shell-shocked person exhibits the following psychogenic disorders:
- epileptic seizures;
- fast fatiguability;
- hysteria;
- increased sweating;
- tearfulness;
- depressive state.
Degrees
- Mild degree (first) . In this case, the damage is minor and the symptoms are not too pronounced. This degree of contusion has no negative consequences and does not require special treatment.
- Average degree (second). The patient may lose consciousness for a while. He may experience diarrhea and vomiting. Often there is some lethargy, aggression, problems with heartbeat and breathing. The functioning of the brain is impaired, so all functions slow down.
- Severe degree (third). In this case, the patient may not regain consciousness for up to 3 weeks. Sometimes a patient can die if first aid is not given and taken to the hospital.
Types and degrees of head contusion
There are 2 main types of such damage.
- The first (general) is the result of a bruise of the entire body. It is characterized by loss of consciousness and amnesia.
- The second type is severe contusion. There are malfunctions in the functioning of all organs and systems, the course is rapid and unpredictable.
ATTENTION: A separate subspecies is eye contusion. Additionally, it is divided into direct - a bruise of the eyeball itself, and indirect - the result of damage to the body
Threatens complete or partial loss of vision.
The degree of concussion damage to the brain depends on the severity of the fall (or the force of the explosion).
- Easy. Symptoms are not expressed, the course is rapid, the signs disappear on their own after 1-3 days. Concussion does not pose a threat to health, but monitoring the victim’s health status is necessary.
- Medium severity. A person may lose consciousness (from 30 minutes to a couple of hours), and will be bothered by nausea. In this state, aggression or lethargy develops, breathing becomes difficult, and the pulse quickens. Brain activity returns to normal only after 1.5 months. Further recovery may be complete or partial. Medical supervision after a brain contusion is necessary for a year.
- Heavy. Unconsciousness can last from a couple of hours to 4 weeks. In addition to disorders in brain function, mental and neurological problems begin. An unfavorable prognosis is death without regaining consciousness.
General information
Traumatic brain injury is a collective concept that includes various injuries to the bone and soft structures of the head. The following clinical forms of TBI are distinguished: concussion, brain contusion, diffuse axonal damage, brain compression. The most common possible traumatic brain injury (about 70% of all TBIs) is a concussion. Mild brain contusion is diagnosed in 10-15% of victims with traumatic brain injury, moderate severity is diagnosed in 8-10% of victims, severe contusion is diagnosed in 5-7% of victims.
Traumatic brain injury
This is interesting: Forest fire
What is cerebral contusion
To understand what a contusion is and understand its consequences, you need to take into account the similarity of the pathology with a closed-type traumatic brain injury. Head contusion occurs due to displacement, compression, and deformation of brain structures. The symptoms and disorders that accompany the pathology depend on the location of the lesion. Concussion is a common occurrence in war, which is associated with a high risk of injury, in particular brain contusion.
The term became widespread after World War I. The risk of such lesions is high among professional athletes. Contusion affecting the brain causes a condition such as stress, which affects neurological reflexes and psycho-emotional sensations. A patient with a mild form of pathology experiences a feeling of vulnerability and helplessness, panic, fear, and loses the ability to reason sensibly and meaningfully.
Mental disorders negatively affect the family life of patients who need constant monitoring and care from relatives. Wartime blast-related injuries negatively impact mental health even years after the event.
People who have suffered a cerebral contusion experience nausea, insomnia, headaches that arise for an unknown reason, memory loss, and inability to concentrate. In medical practice, the phenomenon is called post-traumatic syndrome. For such patients who took part in combat operations in Afghanistan and Iraq, the DVBIC medical center (Veterans with Brain Injury Center) was opened in the United States.
What other outcomes are there?
We can talk forever about what concussion leads to. If the brain is affected, then the person may be bothered by headaches, intolerance to sounds, sudden changes in light, and stuttering. Psychological disorders also often occur here.
If a person receives a second degree contusion, complications may include disruptions in the functioning of the heart muscle of the respiratory system. When suffering from a severe form of the disease, it is important to provide the necessary treatment in a timely manner . Otherwise, death may occur.
Regardless of the degree of the disease, contusion is the presence of a large number of fractures and cracks, as well as concussions. When examining for the presence of disorders, it is important to pay attention to the kidneys, liver, and spleen.
If we talk about preventive measures that are aimed at preventing illness, doctors strongly recommend paying attention to the rules of personal safety. You should avoid places where you can get such severe injuries.
In wartime, it is not so difficult to protect yourself from shell shock. In any case, if the first symptoms appear, you can visit a doctor and get examined.
Read more about contusion of the eye and human ENT organs in separate articles.
Symptoms
With a mild degree of contusion, patients complain of:
- pain in the eyeball;
- lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- burning, stinging;
- It hurts to open your eyelids.
Within a few hours after the impact, the hemorrhage increases, and severe swelling of the tissues is observed. The bleeding then goes away within two or three weeks.
The second degree of damage is characterized by:
- severe pain when trying to open the eye or move the eyeball;
- a foggy veil appears before your eyes;
- vision is practically absent or poorly expressed.
For severe eye damage:
- the patient sees practically nothing, only distinguishes light;
- the pain radiates to the temples, brow ridges, forehead;
- oscillatory movements of the iris are noticeable;
- the lens “trembles”.
Symptoms of the last degree of concussion:
- the functionality of the visual apparatus is impaired;
- complete blindness;
- mobility of the eyeball is limited;
- spots appear before the eyes, which indicates a detachment of the inner membranes.
In critical condition, the eyeball is completely crushed.
The nature of the manifestation of contusion in different parts of the visual apparatus
Conjunctiva
With a mild injury, the conjunctiva may not be affected; with more severe injuries, hemorrhage is observed. In mild clinical cases, treatment is not required; the hemorrhage will go away on its own.
Cornea
A damaged cornea manifests itself as photophobia, lacrimation, pain and burning, and spasm of the eyelids. Severe clinical cases are characterized by clouding of the corneal layer.
Sclera
Damage to the sclera causes vision loss. Its rupture is indicated by a sharp decrease in the quality of vision, a decrease in intraocular pressure, and hemorrhage into the vitreous body.
Iris
A minor injury leads to a narrowing of the pupil; in severe clinical cases, the iris ruptures.
Lens
This part of the visual apparatus may be damaged due to a sharp blow. Subluxation, dislocation or rupture of the lens body is observed. The impact often results in clouding of the lens - cataract.
Vitreous body
Hemorrhage into the vitreous body is characterized by the appearance of dark clots of various shapes before the eyes. This may affect the quality of vision.
Ocular fundus
Damage to the fundus manifests itself in:
- retinal detachment;
- retinal breaks;
- damage to the optic nerve;
- damage to the vascular network.
Bruises around the eye are a consequence of damage to the soft tissue of the periorbital structures.
Symptoms of receiving
Signs of concussion depend on its type.
In the brain
When the brain is damaged in the first degree, it sends the following symptoms:
- Headache and nausea.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Dizziness and nausea.
- Amnesia.
- Tachycardia, bradycardia.
- Arterial hypertension.
The average degree manifests itself as follows:
- Severe amnesia.
- Prolonged headache.
- Disruption of the functioning of important organs.
- Impaired sensitivity.
Symptoms of severe concussion are as follows:
- Loss of creation (about 3 weeks).
- Disturbances in the functioning of internal organs.
- Bradycardia.
- Paralysis of limbs.
- Hearing and speech impairment.
- Profuse hemorrhages.
In the eye
Mild eye contusion manifests itself as follows:
- Decreased vision clarity.
- Changes in the eyeball (corneal edema, erosion).
- Retinal clouding.
Moderate contusion manifests itself as follows:
- Deep corneal erosion.
- Deterioration of vision.
- Local type cataract.
- Presence of hemorrhages.
- Rupture of the ocular sphincter.
The third degree is characterized by:
- Enlargement of the eye.
- Damage to the sclera.
- Hypotension and hypertension.
In the ear
There are first, second and third degrees of ear damage. This occurs due to exposure to sound. If the injury is minor, hearing may be lost for a while. At this point, degeneration of supporting cells and hairs occurs.
If the degree is average, then you can observe injury to the ear canal and organs located next to it. If the degree is severe, then destruction occurs in all cells. In this case, the nerve fibers are affected and hemorrhage appears in the ear canal.
Signs of different degrees
First degree
With first-degree injuries, subarachnoid effusions begin to form.
Loss of consciousness lasts from 30 to 60 minutes. Clinical manifestations are very pronounced - they have a long manifestation and can increase from the second day of injury.
A distinctive feature is a symptom of amnesia. The victim may have trouble remembering why they were injured. This does not appear in all cases. But, since the symptom is transient, relief occurs within a week.
Symptoms of the neurological type after restorative procedures are very distinct - headaches, nausea and vomiting begin. On examination, there may be an incomplete response to light.
It is also important to examine reflex excitability. Changes in the vegetative-vascular system may be the same as with a concussion
Second
The anatomical substrate that determines the second degree of contusion is the development of a planar effusion that can occupy the entire field. Loss of consciousness can last from 1 to 4 hours. Symptoms often include breathing disorders and changes in cardiac activity. But, if the treatment is correct, relief will be noticeable within a day.
After the creature is restored, the concussion will manifest itself with dizziness, headache, and lethargy. Amnesia may last a week or several months.
When examining the victim, you can notice that the nasolabial fold is smoothed, peripheral reflexes are asymmetrical, and horizontal nystagmus is observed. However, such symptoms are transient and not long-lasting. Often the process ends with degeneration of the damaged organ.
Third
The anatomical substrate that determines third-degree contusion is extensive hemorrhages around the impact, hemorrhages in the brain tissue or in the ventricles.
In fact, this degree indicates a hemorrhagic stroke.
Signs of third degree concussion: loss of consciousness occurring for more than 4 hours. You can also observe cranial disorders, Babinski and Kernig symptoms.
Diagnosis of injuries along with hematomas inside the brain is carried out in neurosurgical departments
It is important to hospitalize the victim immediately, since only qualified personnel can provide assistance.
Healing Methods
Treatment of contusion in a medical facility involves a set of measures:
- Drug therapy. The attending physician - a neurologist or traumatologist - prescribes medications depending on the type and severity of the injury. The main efforts are aimed at normalizing water balance, eliminating pain, suppressing the gag reflex, solving neurological problems, and fighting inflammation.
- Surgical intervention. The operation is indicated to normalize intracranial pressure, in case of hemorrhages, or violation of the integrity of the skull. In these cases, the patient cannot be treated only with conservative methods.
- Psychotherapeutic sessions. Elimination of neurasthenic manifestations, depression, pathological fears.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures aimed at restoring motor skills.
- Speech therapy exercises to help cope with the absence or defects of speech.
During rehabilitation, the patient is recommended massage, sanatorium treatment, and soothing baths. Family support, a favorable microclimate at work, and the absence of noise and turmoil are very important at this time. The participation of family and friends is the most important condition for successful recovery.
To clarify the diagnosis of a possible brain contusion, the doctor:
- Finds out the causes of injury.
- Collects anamnesis.
- Interviews witnesses to the incident (if the patient is unconscious).
- Conducts a general examination and evaluates the functioning of important organs and systems.
These actions are carried out at the scene of injury or after the person is transported to the hospital.
In the future, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- X-ray examination reveals violations of the integrity of the bones of the skull (severe head injury is a mandatory indication for this examination).
- Electroencephalography, which allows you to study the brain by recording its bioelectrical activity.
- Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging will help to accurately determine the severity and location of injuries received, even in the deep structures of the brain.
Having established the extent of the damage and identified possible hemorrhage, the specialist prescribes appropriate treatment. It should be noted that during the period of therapy and rehabilitation, the patient will have to be periodically examined so that the recovery process can be monitored over time.
The examination is carried out using instrumental methods - CT, MRI, EEG. Additionally, blood tests and lumbar puncture tests are performed. The degree of neurological impairment is determined using special tests. Level of disturbance of consciousness – according to the Glasgow scale.
First aid
In case of a mild contusion, the victim can cope with first aid on his own. The main thing is not to harm yourself. Therefore, it is prohibited to do the following:
- rub the eye;
- press on the eyelids;
- touch the injured eye with unwashed hands;
- treat damaged tissues with iodine or brilliant green;
- wash the eye in case of penetrating wound or deep damage;
- apply a cotton swab to the eye in case of penetrating injury.
In case of minor damage, apply a compressive bandage to the eye and place an ice pack inside the bandage. This must be done immediately after the injury so that hematomas and swelling do not spread to healthy tissue. After this, you need to go to the emergency room so that the damage is examined by a doctor.
First aid includes the following procedures:
- applying a bandage to protect from light;
- the use of Albucid drops to prevent microbial infection;
- taking sedatives to relieve stress;
- taking analgesics to relieve pain;
- stopping bleeding (if necessary);
- exclusion of sudden movements, pushing, jumping, running.
A bandage is applied to the open wound to isolate the damaged tissue from contact with air and the environment.
If a chemical substance (fungicides, agrochemicals, etc.) gets on the eyeball, you need to rinse it with a large volume of water and go to the emergency room.
What should you do if someone suffers such damage?
Help for a person who has been shell-shocked must be provided taking into account the fact that he is unconscious. He is completely helpless. Therefore, if, for example, he fell face-first into a puddle, he could easily choke. And if there is a spark on the clothes, it can burn.
If the degree is not severe, then consciousness will return quickly enough , and the only help in this case will be to make sure that he breathes well. It is important to check for bleeding and also call an ambulance quickly. There is nothing more you can do to help.
Now you know what to do first if someone is injured and concussed as a side effect of this disaster.
Slave machine in the holds
The 17th century was the peak of the development of the galley fleet, primarily for the Mediterranean countries. France, Spain, and Italy rewrote their codes of laws in such a way as to send as many convicts as possible to galley work, regardless of the term (or indefiniteness) of the punishment. But the most famous exploiter of muscle power on ships was the Ottoman Empire.
Turkey often supported the existence of wild cordon states on its periphery, like the Crimean Khanate or the Persian separate principalities, which lived by robberies and raids, actively providing their Istanbul patron with a resource in the form of manpower - military and civilian prisoners. A certain part of them went to hadorga - that’s what the Turks called galley work. In terrible conditions, ankle-deep in water, under constant lashes, for days on end, a Spanish merchant, a Don Cossack, an Egyptian mullah, a Persian prisoner of war and a subject of the Lithuanian principality, a Russian artisan captured by the Crimeans, pushed with one oar until exhaustion.
Forced men in the galleys. One oar is controlled by several rowersSource: pinterest.com
The mortality rate in the holds, where the human forces of the oar drive were locked and chained, was not so great (for a good move, the oarsmen were often fed better than sailors and marines), how severe was the physical suffering and wear and tear of the body.
The rowers, and these were often former military men or dashing people, often could not stand the torment and started riots. If they managed to escape, then they rowed with much greater force than under the blows of the overseer’s whip, and if not, then those who had lost everything already fought to the death with their oppressors, sometimes destroying the ship. This happened especially often in battle, when the soldiers and sailors were busy fighting, or during stops, when the Turkish team was resting on the shore. Usually, fugitive detachments of rowers ended up with the Venetians or Maltese, who, being enemies of the Turks, greeted them as heroes and wrote letters of accompaniment to Rome.
There, in turn, the Pope met these people with a difficult fate and, having written them letters of safe conduct and allowance, sent them home. The news about the heroes was ahead of them, and the prince or monarch, through whose territory the path of the liberated man (and accompanied by a papal letter) lay, as a rule, greeted him with honors, in every possible way facilitating his passage through his land. In the 17th century, the Ottoman Empire lost on average one galley every 7 weeks due to riots and escapes of captive oarsmen, so the Italian archives contained a lot of documents about escaped convicts, their origins and wide geography: having received the support of the Pope, people went to their homeland, be it Lisbon or Vologda. It is remarkable that documents recording the arrival of such liberated people have been preserved in the archives of their native lands.
Others were less fortunate - interrogation reports testify to captured sailors who served as slaves on Turkish galleys for 15, 20, and 40 years. There was no count of the dead rowers, so we cannot say how much the Mediterranean Sea was diluted with their blood.
Riot against the Ottomans in the galleys. Embittered oarsmen usually did not spare their oppressorsSource: moiarussia.ru
The Maltese and Spaniards often recruited the same captured Turks and North Africans as rowers, but France, Holland and Great Britain had to draw muscle resources from their criminals, literally sending them to hard labor. Peter the Great did the same during the Northern War: in the crews of galleys in the Baltic and Azov Seas, the oarsmen were almost always convicted convicts.
In the 1740s, the importance of the galley fleet fell sharply, the large rowing ships disappeared, and the calm inland seas were left to be plied by merchant and liaison rowing ships with hired crews.
Recovery after concussion
Recovery from injury is a very important period. Medical rehabilitation specialists treat the long-term consequences of concussion. Any patient who has suffered a concussion must be observed by a psychiatrist.
Therapeutic gymnastics and massages
A course of therapeutic exercises to restore muscle and nerve tone is especially important for patients who have been in a coma for a long time. With the help of a trainer, they gradually master the space of the gym, alternating between breathing exercises and physical activity. The duration of therapeutic exercises is several months or years.
Therapeutic gymnastics promotes rapid recovery after injury
Massage of the affected areas is carried out by a specialist. It is recommended to start with slow and smooth patting and stroking movements, gradually adding pinches and intense rubbing of the damaged areas. You can also perform massage on your own, having previously obtained information from a medical rehabilitation specialist about the method of its implementation.
Correction of cognitive impairment
Many patients, after suffering a trauma, experience problems with further socialization and return to society. To do this, after recovering from a coma, they are recommended to visit a psychiatrist. With its help, many people overcome depression and can move on with their lives calmly. The doctor shows the patient some ways to solve the problem, to which he himself did not pay any attention.
All patients who have experienced shell shock should visit a psychiatrist
Treatment of eye contusion
Initially, the victim should be given first aid: give pain relief, apply cold to the eye area, but not to the organ of vision itself. Treatment tactics will depend on the severity of clinical signs of injury and the severity of the injury.
Conservative treatment is based on taking the following groups of drugs:
- anti-inflammatory;
- antiseptics;
- painkillers;
- mydriatics;
- hypotensive;
- antibacterial.
If necessary, a bandage is applied to the damaged organ of vision. Physical activity and alcohol intake are strictly prohibited during the treatment period. Factors that contribute to visual strain in victims should be excluded.
If conservative therapy does not give the desired result or a severe eye injury is diagnosed, surgical intervention is performed. In such cases, in addition to consulting an ophthalmologist, the intervention of a neurosurgeon will be required.
Consequences and precautions
The consequences of such injuries can be determined by the degree of their severity , as well as the structures damaged when following the doctor’s recommendations. Often, complications can appear over time, and this is due to the fact that the brain structure gradually returns to work in a certain order.
Among the consequences the following can be observed:
- Severe headaches.
- Painful reaction to loud noises and lights.
- Sleep disturbances, increased excitability of the nervous system.
- Dizziness.
- Depressive syndrome, manifested by fatigue, apathy, lethargy.
- Stuttering.
If syndromes increase and worsen, it would be a good idea to consult a neurologist or psychotherapist. It may make sense to undergo re-treatment. Some patients are even sent to health resorts to fully recover from injury.
We wrote about the consequences of a cerebral contusion in a separate article.
Prognosis after injury and possible consequences
People who have suffered a mild stage of concussion quite quickly return to their usual rhythm of life. In severe and moderate stages, this process can drag on for many months and even years. It is necessary that family, friends and psychologists be constantly with the victim: this will allow them to realize what happened as quickly as possible and continue to live a measured life, without withdrawing into themselves.
Complications and consequences of concussion:
- hearing loss in one or both ears;
- decreased visual acuity or complete blindness;
- paresis and paralysis of the limbs;
- disorders of urination and defecation;
- sexual dysfunction;
- insomnia and sleepwalking;
- speech and writing disorders;
- migraines, headaches and dizziness;
- asthenovegetative syndrome - weakness, lethargy, adynamia, lack of an emotional component;
- depressive and suicidal conditions;
- sudden attacks of aggression;
- change in the character and behavior of the victim.
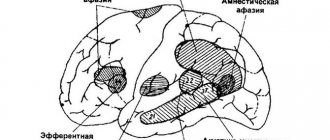
Classification
The classification of TBI is based on its biomechanics, type, type, nature, shape, severity of injury, clinical phase, treatment period, and outcome of the injury.
Based on biomechanics, the following types of TBI are distinguished:
- shock-anti-shock (the shock wave propagates from the site of the received blow and passes through the brain to the opposite side with rapid pressure changes);
- acceleration-deceleration (movement and rotation of the cerebral hemispheres in relation to a more fixed brain stem);
- combined (simultaneous impact of both mechanisms).
By type of damage:
- focal (characterized by local macrostructural damage to the brain matter, with the exception of areas of destruction, small and large focal hemorrhages in the area of impact, counter-impact and shock wave);
- diffuse (tension and spread of primary and secondary axonal ruptures in the centrum semiovale, corpus callosum, subcortical formations, brain stem);
- combined (a combination of focal and diffuse brain damage).
Based on their type, TBIs are classified into:
- closed - damage that does not violate the integrity of the scalp; fractures of the bones of the calvarium without damage to the adjacent soft tissues or a fracture of the base of the skull with developed liquorrhea and bleeding (from the ear or nose);
- open non-penetrating TBI - without damage to the dura mater and open penetrating TBI - with damage to the dura mater.
In addition, isolated (absence of any extracranial damage), combined (extracranial damage as a result of mechanical energy) and combined (simultaneous exposure to various energies: mechanical and thermal/radiation/chemical) traumatic brain injury are distinguished.
Based on severity, TBI is divided into 3 degrees: mild, moderate and severe. When correlating this rubric with the Glasgow Coma Scale, mild traumatic brain injury is assessed at 13-15, moderate at 9-12, severe at 8 points or less. A mild traumatic brain injury corresponds to a mild concussion and contusion of the brain, a moderate one corresponds to a moderate brain contusion, a severe one corresponds to a severe brain contusion, diffuse axonal damage and acute compression of the brain.
The course of TBI is divided into 3 basic periods: acute, intermediate and long-term. The duration of the periods of traumatic brain injury varies depending on the clinical form of TBI: acute - 2-10 weeks, intermediate - 2-6 months, long-term with clinical recovery - up to 2 years.
Consequences for the eyeball
The consequences of an eye contusion can be very serious, including complete loss of vision, without the possibility of recovery.
Corneas
Damage to the cornea is the most common consequence of eyeball contusion. Signs of such defects are erosion of varying depths and areas. They have the ability to change their size upward within a week.
The first indicators of corneal injury include:
- decreased visual acuity;
- unpleasant sensitivity to light;
- uncontrolled production of tears;
- feeling that something is in the eye;
- blepharospasms.
Blurred vision occurs if the central zones of the cornea are eroded. When the stroma is damaged, visual acuity noticeably decreases. Destruction of the endothelium leads to edema in the depths of the stroma, and opacification of the cornea in the form of stripes and latticework leads to the penetration of purulent composition into other areas of the stroma.
Important! In particularly severe cases of corneal defect, 3rd degree eye contusion may develop. At this stage, the eye becomes cloudy and takes on a gray tint.
Lens
Eye contusion is often a consequence of traumatic cataract. The reason is caused by clouding of the lens due to a change in its location (luxation). Due to the fact that moisture enters through microcracks in the capsule of the anterior chamber of the eye, the volume of fluid may increase with visible bruising.
Fibers in the form of a swollen mass fill the entire volume of the capsule if its cracks are significant. Sometimes the fibers block part of the anterior chamber, increasing pressure inside the eye and causing glaucoma. Lens luxation is characterized by deformation of the anterior chamber and displacement of the iris. The lens itself takes the form of a drop filled with fat.
Retina
Retinal injury is one of the most severe types of damage.
With minor injury, the structure of the eye and vision quickly and independently resume their functions. If it comes to severe cases (for example, 2nd degree contusion of the eyeball), then visual acuity is significantly reduced, and bleeding may develop:
- preretinal;
- retinal;
- subretinal.
Brain damage due to explosion in war
Nowadays you can often find such consequences:
- Increased sweating.
- Epilepsy seizures.
- Hysterical attacks.
- Dizziness with concussion.
Dizziness
It can be observed at different stages of the disease. Often the cause of dizziness is a concussion. A sudden fall or beeping sound may cause injury.
Loud noise intolerance
The main reason for intolerance to loud sounds is acoustic trauma to the ear due to contusion. Factors and circumstances of such intolerance may be different :
- Shot from a weapon.
- Powerful explosion.
- Loud music.
- Shout.
And this is not the entire list of reasons that can disrupt the functioning of the hearing aid. Regardless of what factor affects the hearing organs, contusion can begin if the noise level is above 160 dB.
Tachycardia
Tachycardia is another consequence of contusion. It can begin with a heart bruise. Characteristic symptoms are severe shortness of breath and pain in the heart area.
Consequences for the psyche
Of particular danger are:
If you can somehow come to terms with the first consequences of a concussion for the psyche and muffle them, then epilepsy can begin at any time and in any place. Even simple external factors can indicate the onset of epilepsy.
Ear contusion: what is it, could it be from a gunshot?
Ear contusion refers to the category of acoustic injuries that occur when there is a sudden change in pressure in the hearing organs. As a result, a change in the anatomical features of the ear is observed. Quite often, due to exposure to unfavorable factors, there is a rupture of the eardrum, as well as a decrease in hearing function.
Mechanism of development and manifestation
Ear injury in most cases occurs when the eardrums are exposed to excessively loud sounds. There are a significant number of factors due to which the pathological process develops. The occurrence of the disease can be diagnosed after:
- shots;
- loud music;
- explosions;
- loud scream, etc.
The occurrence of pathology can be observed when the sound increases to more than 160 dB. This is why the disease can be diagnosed after setting off fireworks or even a loud kiss on the ear. This can stretch or damage your eardrums.
The appearance of a contusion is accompanied by a sharp and oppressive pain in the middle of the ear. The pain can go away on its own in the shortest possible time. Some people experience pain for a long period of time. If deafness or bleeding from the ear occurs after exposure to loud sounds, then you need to seek help from a specialist who can provide adequate first aid.
Regardless of the severity of the disease, the patient experiences the appearance of corresponding symptoms during concussion:
- The pathology is accompanied by severe pain in the ear.
- Also, after a contusion, the appearance of hearing loss or complete deafness is observed.
- The pathological process in some patients is accompanied by disorientation.
- A fairly common symptom of concussion is ringing in the ears.
- After damage to the auricle, dizziness may be diagnosed.
- When exposed to significant amounts of sound, people experience bleeding from the ear or nasal cavity.
- When this pathological process occurs, vision may be impaired.
- In rare cases, patients experience loss of consciousness.
Contusion is a fairly serious pathological process, therefore, when the first signs appear, the patient should consult a doctor, who, after diagnosis, will prescribe treatment aimed at restoring hearing.
Features of therapy
In case of an ear contusion, the patient must be given first aid, which will have a positive effect on the process of further treatment.
Further treatment
Treatment of contusion is carried out using medications. Most often, patients are prescribed stimulants and tonic drugs - Hoffmann drops, Camphor. If a person develops vasomotor labyrinthopathy, treatment is carried out with Aeron or Aneurin.
Treatment of the pathological process should be aimed at preventing the development of infection. For this purpose, bacteriostatic agents are prescribed. Treatment with Penicillin or Bicillin is quite effective in this case. If the victim has severe pain, then the use of Morphine is recommended to eliminate it.
If there is a mechanical injury or barotrauma, a protective bandage must be applied to the ear. Injecting liquid into the hearing organ is strictly prohibited. For severe damage to the eardrum, surgery may be recommended.
If a patient is diagnosed with increased excitability or insomnia, then he needs to take sedative medications (Sedafiton, Nervohel). During the period of treatment of contusion and recovery, the patient must be provided with complete rest. It is recommended to protect his hearing organs from the negative influence of loud sounds.
Contusion is a rather dangerous pathological process. If first aid is provided incorrectly and the patient is treated inadequately, serious complications can develop. That is why, after receiving an injury, the patient needs to undergo appropriate diagnostic measures, which will make it possible to prescribe adequate treatment.
Contusion of other organs
In 5-7% of cases of chest injury, especially if the blow falls on the anterior chest and sternum, an obvious contusion of the heart is formed. Clinically and according to ECG data, they are similar to myocardial infarction. In 43-47% of cases of closed chest injury, a hidden cardiac contusion is noted, which gives a clinical picture of coronary artery disease, but its cause is revealed only through special studies.
Renal contusion is observed quite often, especially in polytraumas. The main criterion for diagnosis is the presence of obvious hematuria or microhematuria. A full range of examination should be carried out by a urologist for differential diagnosis with damage to other parts of the genitourinary tract.
The diagnosis of contusion of the liver and spleen is valid, but the diagnosis is very difficult with low severity, and more severe contusions form subcapsular ruptures. The same applies to bruises of hollow organs.
, , , ,
Drug treatment
Restoring the functionality of the damaged organ is carried out taking into account the nature of the injury. When treating contusion, it is important to prevent dangerous complications. Therapy is aimed at:
- restoration of the integrity of damaged tissues;
- stopping hydrodynamic processes;
- elimination of foci of inflammation.
Minor damage may not be treated, but the doctor will prescribe Albucid drops to prevent bacterial infection. If you experience any discomfort, you can always make an appointment with an ophthalmologist.
If there are extensive bruises, anti-swelling ointments and antibacterial drops are prescribed.
For any mechanical damage to soft tissue, prophylaxis against the development of a purulent bacterial infection is necessary. Drops and gels for treating damaged eyes
| Albucid | Inexpensive, time-tested drops to prevent the development of bacterial infections. They have an anti-inflammatory effect. |
| Hyphenation | Drops moisturize the mucous membrane of the eye. The lacrimal membrane prevents the development of microbial infection in the mucous membrane of the eye. Relieves irritation, burning and stinging in the eyes, accelerates the healing of injured tissue. |
| Balarpan | The drops contain substances present in the corneal layer. They moisturize the cornea, create a protective layer, and accelerate regenerative processes in the corneal layer. |
| Vitasik | The drops accelerate the regeneration processes of damaged tissues and restore the damaged membrane of the corneal layer. |
| Kornegel | The delicate texture of the gel moisturizes the cornea and mucous membranes, protects against adverse external factors, and fights microbial and bacterial infections. |
| Solcoseryl gel | Moisturizes, protects and nourishes the eye shell with useful substances. Helps cope with the consequences of injury, even treats the consequences of burns. |
Causes and risk factors
Concussion can have several causes. The conditions for the appearance of pathology in everyday life, at work and on the battlefield differ significantly from each other, so approaches to diagnosis and treatment will differ from each other.
Explosion is one of the common causes of concussion
Table: causes of contusion in different conditions
| Military reasons | Production reasons | Household reasons |
| Use of firearms | Powerful vibrations of various equipment | Gas cylinder explosion |
| Military grenade explosion | Explosions of flammable substances in workshops | Fall from a great height |
| Prolonged stay in military equipment while it is moving | Pressure drops when diving to depth | Sudden change in atmospheric pressure |
| Violation of safety regulations during military operations | Collapse of sand or rocks | Physical and mechanical impact on the body (accident) |
| Depressurization of a submarine or aircraft | Excessive noise levels and harsh sounds in production | Strong impact on the water surface |
Table: causes of contusion damage to individual organs
| Brain | Auditory and vestibular apparatus | Visual apparatus | Spinal column |
| Traumatic brain injury | A sharp blow to the ears | Impact with force that deforms the eyeball | Traumatic damage to the bones of the spine |
| Infectious and inflammatory processes in brain tissue, leading to its enlargement | Mechanical rupture of the eardrum | Compression of the eyeballs | Infectious processes in the bones of the spine (syphilis, tuberculosis) |
| Dropsy of the brain | Accumulation of fluid in the middle ear cavity | A sharp increase in intraocular pressure | Changes in atmospheric pressure |
| Violation of the biological and chemical composition of cerebrospinal fluid | Infectious and inflammatory processes in the sinuses of the skull | Impaired blood supply to the eyeball and optic nerve | Bone compression and deformation |
Risk factors
Like any traumatic injury, concussion has certain risk factors. By reducing their number, the possibility of pathology occurring is minimized. But unfortunately, most of them cannot be completely eliminated.
Main risk factors:
- engaging in dangerous sports;
- work in physical and chemical production;
- work related to the effects of vibration on the body;
- long stay in the zone of radiation contamination;
- work with high-power radiation;
- violation of safety regulations when handling weapons;
- violation of the rules of movement in military transport;
- staying in the blast wave zone;
- close proximity to a military training ground where weapons are tested.
Consequences of ear contusion
With an ear contusion, as already mentioned, a rupture of the eardrum occurs, as a result of which the tightness and asepticity of the tympanic cavity is disrupted. As a result, an infectious-inflammatory process develops in it and traumatic otitis media occurs, requiring the use of antibacterial therapy.
The nature of hearing damage depends on the cause of exposure and its intensity:
- With a small perforation, a defect in the eardrum of various locations and shapes is observed:
- round;
oval;
- irregular shape;
- with torn edges.
- With a fresh injury, otoscopy reveals a hyperemic medial wall of the tympanic cavity.
- For isolated membrane perforation, outpatient treatment is sufficient. As a rule, the defect quickly heals on its own, and hearing restoration occurs in full.
- With the development of inflammation, the formation of exudate occurs, and in the absence of treatment, purulent discharge occurs.
- With a fracture or dislocation of the malleus, incus, or displacement and dislocation of the stapes (auditory ossicles), often, but not always, accompanying longitudinal fractures of the pyramid of the temporal bone, blunt trauma of the skull without a fracture of the pyramid, the following are observed:
- deafness;
severe pain in the ear and dizziness;
- lack of coordination;
- feeling of stuffiness, noise on the side of the injury.
- In the absence of perforation of the membrane, which happens less frequently, the diagnosis of dislocation or rupture of the auditory ossicles is carried out using tympanometry.
- Contusion of the labyrinth (inner ear), organ of Corti, is usually combined with brain damage and requires emergency care.
It is the cause of the development of labyrinthine traumatic syndrome, which is accompanied by a violation of both auditory and vestibular function due to the resulting hemorrhage, hypoxic edema of organ structures, and violation of the integrity of moving elements, for example, separation of otoliths. - Perforation of the eardrum occurs when the pyramid of the temporal bone is fractured and a line passes through the tympanic ring.
REFERENCE: it may be accompanied by minor bleeding when the vessels in the area of the malleus handle are damaged, which is self-limiting.
During otoscopy, a defect in the eardrum is visible; in the case of an explosion at close range, traces of gunpowder are visible in the external auditory canal and on the membrane. Hearing loss due to the type of sound conduction disorder reaches 20 dB or less.
IMPORTANT: In addition to the situations described above, severe injuries to the middle and inner ear may cause damage to the cranial nerves.
Damage to the auditory and facial cranial nerves:
- The auditory nerve innervates the cochlea; as a result of its damage, persistent sensorineural hearing loss develops, in some cases reversible.
- The facial nerve passes through the labyrinth of the temporal bone. A disruption of its blood supply, or the transfer of inflammation from the tympanic cavity leads to reversible paresis of half the face. In addition, it may affect the trigeminal and vagus nerves.
Diagnosis of the condition
To distinguish a concussion from a regular bruise, concussion or shock, it is necessary to carry out a wide range of diagnostic measures. Since it is not possible to interview the patient at first after the injury, a brief life history is collected from his closest relatives or friends, and the circumstances of the injury and the first medical measures taken are collected from eyewitnesses of the incident.
After the patient returns to consciousness, the doctor collects complaints and checks the organs of vision, hearing, smell and the patient’s ability to move his limbs. Based on the data obtained, a preliminary diagnosis is made.
Conversation with the patient is an important stage in collecting anamnesis.
Instrumental diagnostic methods
To establish a final diagnosis, specialists resort to modern research methods. They allow us to clarify the severity of the lesion and suggest possible outcomes.
The main methods of instrumental examination are:
- X-ray examination: will determine whether the integrity of the bones (skull, limbs, spine) has been compromised;
- Ultrasound diagnostics: will show the presence or absence of hematomas and soft tissue damage;
- electroencephalography: is a recording of the bioelectric potentials of the brain, with its help you can track the decrease and increase in the activity of a particular segment, which will allow you to find out the location of the damage;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging: will allow you to differentiate a concussion from a bruise, fracture or concussion;
- visual acuity examination and intraocular pressure measurement: will help make a diagnosis of visual contusion;
- hardware diagnostics of hearing acuity using audiometry: will show the degree of damage to the hearing organs;
- static and dynamic functional tests: will allow you to determine damage to the balance organs;
- microscopic examination of the cellular composition of the cerebrospinal fluid using a puncture: will make it possible to diagnose a spinal cord contusion.
Diagnostics
First of all, a physical examination of the victim is carried out: the doctor visually examines the injured eye and finds out how the injury was received and with what object.
To determine the severity of damage to the organ of vision and the risks of complications, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- visometry;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- gonioscopy;
- biomicroscopy;
- radiography of the facial part of the skull;
- MRI of the head;
- Ultrasound of the eye;
- non-contact tonometry.
Standard laboratory tests are carried out only when necessary, since in this case the tests themselves do not have diagnostic value.
Treatment of pathology
Treatment for mild, severe, and moderate contusions can vary significantly. For uncomplicated pathology, the duration of treatment and recovery is about a week.
When treating a contusion injury of any severity, it is necessary to strictly adhere to bed rest, reduce the negative impact on the affected organ and the complete absence of negative stress factors.
First aid in case of concussion
Any person present at the scene of the incident should be able to provide first aid.
Specialized care is provided by emergency room or hospital doctors.
Algorithm of actions for concussion:
- Check vital signs: breathing, heartbeat.
- Determine whether a person is conscious by lightly tapping the face.
- Call emergency medical assistance.
- Place the victim in a horizontal position on his back.
- Turn your head to the side so that the patient does not choke on vomit.
- If there is vomit, it is recommended to remove it from the mouth using a handkerchief or towel.
- If there is bleeding from the nose or ears, it is necessary to make tampons from cotton wool or cotton pads to stop the bleeding.
- If there is a convulsive seizure, you need to gently fix the patient's head and make sure that he does not harm himself or others.
Absolutely forbidden:
- tilt the patient's head back: this can cause vomit to enter the respiratory tract;
- bring the patient to consciousness by hitting or pouring water on the face;
- Perform cardiac massage on a patient with chest injuries;
- try to give the patient a painkiller tablet.
Video: first aid for concussion
Inpatient treatment and medications
After providing first aid in an ambulance, the patient should be sent to a specialized traumatology, resuscitation or intensive care unit. In the first few days after the injury, you must remain in bed. Patients in critical condition are connected to a ventilator.
Medicines used for concussion:
- painkillers: Analgin, Morphine, Methylmorphine and Narcotin will reduce pain and alleviate the condition of the victim;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to reduce tissue edema: Ibuprofen, Nimesulide, Ketorolac, Diclofenac;
- glucocorticosteroids will reduce inflammation and relieve spasm: Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone;
- sedatives help restore neuropsychic balance: tincture of valerian and motherwort, camphor;
- antiemetic drugs block impulses from the center of vomiting, reducing the frequency of nausea attacks: Ondasetron, Promethazine, Cyclizine;
- diuretics relieve cerebral edema and stimulate kidney function: Furosemide, Hydrochlorothiazide, Mannitol;
- antidepressants reduce the risk of asthenovegetative syndrome in the future: Fluoxetine, Sertraline.
Photo gallery: drugs used to treat injury
In cases of combined damage to the body, as well as in the formation of extensive compression or hematoma of various organs, surgical treatment is used. It is aimed at decompression and reduction of intracranial pressure.
Traditional medicine
Traditional medicine methods can only be used for mild, uncomplicated contusions. Before using any product, you should contact a specialist and consult, taking into account the possible consequences. In no case should you use only traditional methods without drug treatment, since they are aimed only at reducing symptoms and not at eliminating the cause.
Traditional medicine is good for relieving symptoms of concussion
To treat mild contusion, you can prepare the following recipes:
- 10 tbsp. l. chamomile, pour 1 liter of boiling water and let it brew for two hours. After the resulting liquid has cooled, you need to remove the flowers and drink the infusion one glass twice a day. Chamomile is believed to have a sedative effect.
- 2 tbsp. l. apple cider vinegar should be dissolved in 0.5 liters of cold water. Then you should moisten a gauze cloth in the resulting vinegar water and place it on your forehead. This method helps cope with migraines.
- 2 large burdock leaves and 10 currant leaves need to be brewed in 1 liter of hot water. After the liquid has cooled, you should soak cotton wool in it and place it on the sore spot, covering it with a towel on top. Keep it for no more than an hour. Such a compress will help relieve swelling in case of local contusion.
New time
By the end of the Middle Ages, the concept of rowing ships had not changed much in appearance. But the technological content has made significant progress: now the oars were made very long, up to 6 people could control one oar, the sails on rowing ships were significantly improved, their systems were borrowed from the thoroughbred sailing fleet. Practice has shown that it was much easier to optimize the performance of single rowers on each oar than several guys on one.
Therefore, with the increase in staff, the so-called “rowing” - the most experienced and strong rower - was placed on each oar. Often he was a mercenary or a sailor, and he had to train new recruits from among the slaves and convicts. The weakest rowers were seated closer to the hull, since the least amount of effort had to be exerted there; they were called oars. In general, the speed of galleys of this period dropped to 5 knots. Galleys - this is how all rowing ships in general began to be called. Those that had developed sailing weapons with several masts were called galleasses; they could equally effectively use both types of propulsion. And of course, in the spirit of the times, the galleys acquired artillery.
The design features, namely the oar decks occupying the entire side, did not allow the installation of guns according to the classical scheme, that is, along the sides. Therefore, the guns were placed at the bow or stern and looked along the course of the ship or against it. On large galleys, superstructures were built at the bow and stern of the ship, where guns, falconets and gunners were located, but even on them the narrowness of the galleys prevented the installation of guns “on board”. This feature determined the combat tactics of galleys - maneuverable oared ships were launched into battle against enemy ships in medium and large groups during periods of calm, approached from an advantageous side and shot at immobilized ships.
Battle of galleys with galleonsSource: wikimedia.org
Thus, the galley fleet destroyed even galleons and formations that nominally outnumbered it in the number of guns. In this way, many unexpected victories were won in the wars between Holland, England, France and Spain in the 16th-17th centuries. The most famous battle of the galley fleet in our history is Gangut, which ended in a decisive victory over the Swedes.
Bottom line
An eye contusion is a serious injury that can lead to critical vision loss. Therefore, immediately after providing first aid, the victim must be checked by a doctor (traumatologist, ophthalmologist), undergo the required tests and complete the course of therapy to the end. An untreated disease is dangerous for the development of complications that are worse than the disease itself.
Sources used:
- Stratton GM Vision without inversion of the retinal image (English) // Psychological Review (English) Russian. : journal. — 1897.
- Eye diseases. Fundamentals of ophthalmology / Edited by Professor V. G. Kopaeva. — M.: OJSC “Publishing House “Medicine”, 2012.
- D. Hubel. Structure of the eye, brain, vision. — ed. A. L. Byzova. - M.: Mir, 1990.
- Department of Ophthalmology - University of Colorado
Health care
Each patient who has suffered a head injury or contusion of varying severity is placed in a medical institution - a neurological or trauma department.
After an examination using MRI, computed tomography, and x-ray examination, the doctor prescribes a course of treatment based on the results obtained. When diagnosing a mild contusion and a moderate degree of brain damage, doctors most often prescribe a traditional, conservative course of treatment - these are nootropics and neuroprotectors, prescribe antihistamines, and also dehydrate the whole body.
Also, taking into account the history of the disease and the patient’s complaints, analgesics, antiemetics, fever relievers and anticonvulsants may be prescribed.
If the patient has suffered a severe head injury and is diagnosed with a severe degree of concussion, the course of treatment is carried out in the intensive care ward.
If necessary, the patient is connected to a ventilator, and after stabilization of the internal organs, surgical intervention can be performed, which is carried out to decompress the pressure in the cranium and brain, so internal bleeding can be stopped and dead, damaged tissue of the gray matter can be removed.
After medical and surgical intervention, the patient may be prescribed physical therapy and classes with a speech therapist, mandatory complete rest and taking vitamins, and normalization of his psychological state.
First aid for concussion:
Treatment
The most important thing during treatment is to provide the patient with peace . He should not hear loud sounds or be in a cramped, stuffy room.
To eliminate hearing loss, it will be necessary to take measures to restore hearing function. In this case, the doctor may resort to restorative therapy. It consists of taking sedative vitamins and medications.
If you have a concussion, you should not listen to music; it is not recommended to watch TV at high volume. The best solution is to avoid places where re-infection is possible.
If any infection occurs, take antibiotics or painkillers. Depending on the patient’s condition, they can calm anxiety and relieve insomnia.