Traumatic brain injuries are the most common ailments that result in visits to emergency rooms and forensic medical examinations.
The relevance of the issue of the severity of different types of damage is due to the increasing increase in the number of general cases of injuries and citizens seeking help, and cases of concussion and other harm to health have begun to occur more often.
This diagnosis sounds scary, so let’s try to understand the details so that people can be more knowledgeable on this issue.
What is a traumatic brain injury?
This is a closed (CTBI) or open (depending on the classification) traumatic brain injury, damage to soft tissues, cerebral membranes, blood vessels and nerves of the brain. Most often, injuries are caused by mechanical impact and most are combined - they include several types of trauma (bruises, fractures, ruptures).
Traumatic brain injury is divided into two main types – open and closed.
- In the first option, there are ruptures of the skin and connective tissue, as well as a possible violation of the integrity of the skull. If an open injury is accompanied by involvement of the subdural membrane, then the injury is considered penetrating.
- With the closed type, there is no damage to the connective tissue aponeuroses of the head, although the skin may be cut.
How to recognize a concussion in young children?
In general, a concussion in infants is a rather rare phenomenon; everything in them is so soft and elastic that the risk of getting a concussion is very small, and, as the saying goes: “A child falls, God lays down the straw.” However, there is still no need to relax too much; parents should be constantly on alert and know the main signs of a concussion in a child:
- Frequent regurgitation, refusal to eat, which, however, can be caused by other reasons (intestinal colic, weather change, ARVI).
- Increased excitability, anxiety or, conversely, lethargy and drowsiness also do not mean much.
- Twitching of the muscles of the limbs.
- Unnatural paleness or redness of the face.
You should especially pay attention to the appearance of unusual signs if the child hit his head the day before.
More often this happens to children who have learned to roll over, sit and crawl, but have not yet acquired a sense of danger. Such a fiend needs an eye and an eye, but he already has more symptoms of concussion than very small ones, for example:
- The child hit himself, was silent, and then began to cry bitterly (he may have lost consciousness for a few seconds).
- In such “big” children, it is easier to distinguish vomiting from regurgitation and notice sleep disturbances, since the time of play and wakefulness has increased.
In a word, with children who have emerged from the newborn state it is already possible to somehow “agree” and understand the cause of the anxiety.
Unfortunately, there are often cases when a visit to the doctor is postponed or even canceled, time passes and everything seems to return to normal, but the harm to health caused by a seemingly insignificant blow can be significant, and the consequences are not comforting:
- Intense headaches following a concussion many years ago can last a lifetime.
- Vegetative-vascular disorders.
- Disorder of thinking processes, poor assimilation of the school curriculum.
- Convulsive syndrome.
Classification
In medical terminology, skull injuries are distinguished by severity, depending on the clinical form and combination of injuries.
According to the degree of severity, they are distinguished:
- A mild one is a concussion or bruise of the brain.
- Moderate – moderate brain injury.
- Severe – acute compression of brain tissue and severe brain injury.
Another classification includes a combination of injuries. I distinguish between isolated cases, in which the patient only experiences damage to the cranial bones. Combined - combined with trauma to other organs, and combined - when the mechanism of injury combines several types of effects (mechanical, electrical, thermal, radiation).
For clinical variation, we can distinguish:
- Fractures.
- A concussion is a health injury caused by mechanical impact and a violation of neurological functions. It goes away on its own after a few days, but persistence of symptoms is a more serious injury.
- Bruise in varying degrees of severity.
- Damage to white matter as a result of braking force. Accompanied by small focal hemorrhages and axonal separation.
- Compression - occurs when the space of the cranium decreases.
- Intracranial hemorrhage is divided into subarachnoid, intracerebral, ventricular and epidural.
For clinical forms, a combination of different types is possible.
Next video on the topic:
Diagnostic methods
In addition to external manifestations - the type of injury, the mental state of the victim, studies of brain functions are carried out:
- electroencephalography , in which electrodes are attached to the head and connected to a machine that records the bioelectrical activity of the brain);
- ophthalmoscopy - examination of the fundus of the eye, which is used to determine signs of increased pressure inside the skull;
- ultrasound Dopplerography , with the help of which the speed of blood movement in the vessels of the brain is studied and the general condition is assessed;
- otoneurological study , which includes the study of the functions of the vestibular, auditory, olfactory and gustatory apparatus.
Facts about the circumstances of the accident are very important when diagnosing a concussion.
An X-ray of the cervical spine and skull should also be taken to exclude the presence of fractures and cracks in the skull, as well as displacement of the cervical vertebrae, since it is important to be sure that the injury is closed so that brain hemorrhage and stroke do not occur.
Kinds
Speaking about determining the severity of harm to health when receiving a brain injury, one must rely on the Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated April 24, 2008 No. 194n “On approval of Medical criteria for determining the severity of harm caused to human health.” Only it describes in detail all the signs on which the forensic medical expert relies when analyzing the victim and making his decision on the degree of severity.
Since we are talking about brain injuries, we draw attention to paragraph 6.1 of the Order and its subparagraphs. Now in more detail.
In forensic medical practice, the basis of the conclusion for closed craniocerebral injuries is assessed based on the duration of the health disorder. Attention should be paid to the clinically proven diagnosis made by a neurologist. To do this, functional tests, EEG, and cerebrospinal fluid puncturing should be performed for research. Based on the results of the study, long-term health problems may be established due to possible functional disorders - hydrocephalus, encephalopathy and vegetative-vascular dystonia.
The bruise is often combined with a concussion. One of the complications of such an injury is the development of inflammation of the sphenoid sinus. These signs can be observed with a mild concussion or bruise of the brain; they are regarded as causing harm of moderate severity due to the delayed consequences of the damage and an unfavorable outcome, which can lead to permanent loss of performance.
For moderate brain contusions, it is necessary to evaluate brainstem symptoms and the duration of the health disorder. If there are no signs of damage to the trunk and the health disorder lasted less than 120 days, the damage is assessed as moderate. If a concussion affects the functions of the medulla oblongata, midbrain and cerebellum, then only severe harm to health, and in no case any minor harm. This is due to the development of danger to life at the time of injury.
Attention! All open craniocerebral injuries are classified as causing grievous harm to health, even in the absence of damage to the brain matter.
Severe bruises, intracranial bleeding, crush injuries, the presence of focal and brain stem symptoms are defined only as severe bodily injuries, according to paragraph 6.1.3. Part two of the order on assessing degrees of severity.
Symptoms of bruise
Common symptoms of a concussion include:
- lethargy;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- slow speech;
- nausea or vomiting;
- problems with coordination;
- double vision;
- fear of light and sounds;
- memory losses;
- pain when moving the eyes.
At a moderate degree it occurs:
short-term memory loss;- prostration;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- weakening of reflexes;
- decreased heart rate;
- constriction of the pupils.
For severe forms:
- brain contusions with intracranial hematomas are detected;
- the main symptom is loss of consciousness;
- difficulty swallowing as a result of fluid entering the respiratory tract;
- severe pallor;
- slow pulse;
- exhaustion;
- lack of reflexes;
- small pupils;
- disappearance of reaction to light;
- shallow breathing.
Qualifying features
Qualifying criteria include aggravating conditions of the crime. The corpus delicti necessarily takes into account the premeditation of the action, the number of participants and the motive.
The qualifying signs of causing grievous harm to health in accordance with Article 111, Part 2 and Part 3 include:
- An act against a person in the performance of official duties.
- A crime with special torment and bullying.
- If the actions were performed on a person in a helpless state.
- It was done with danger to society and carrying great destructive power.
- Performed for hire.
- Had antisocial motives.
- Committed by a group – refers to the category of particularly aggravating circumstances.
- Caused death by negligence.
According to this article, a crime that occurs without the above listed qualifying features is punishable by imprisonment for 8 years. In the presence of aggravating circumstances, the court provides for liability for up to 12 years.
According to the last point, when the act entailed death through negligence, two motives are regarded - intentionality of causing harm and subsequent death. For this offense, the offender faces up to 15 years in prison.
With regard to the qualifying characteristics under Article 112 “Intentionally causing harm to health of moderate severity”, the same circumstances are considered as for Art. 111. Exceptions include clauses on execution for hire, creating a public danger and causing death by negligence. A crime without qualifying characteristics is subject to liability - imprisonment for up to 3 years or forced correctional labor for up to 3 years.
In aggravating circumstances under Art. 112 according to part 2 is punishable by arrest for up to 5 years.
Important! In these cases, the assessment of the degree of responsibility is based more on the danger of the act than on medical criteria.
Short-term complications of concussion
Some patients who have suffered a concussion may experience so-called post-stress disorders:
- persistent headaches lasting 7-14 days, the intensity of which decreases when taking analgesics or painkillers of other groups;
- attacks of dizziness, difficulty concentrating, difficulty performing any normal activities (reading, writing, etc.);
- periodic vomiting for no apparent reason, feeling of nausea.
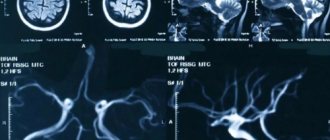
Most often, the side effects of a concussion disappear after some time without treatment; if they bother the patient for several months, you should visit a doctor and get an appointment for a consultation with a neurologist or a brain tomography (magnetic resonance, computer) to clarify the diagnosis.
Restrictions from other species
Intentional harm of moderate and severe severity should be distinguished from beatings and torture:
- Batterings are most often characterized by inflicting injuries of mild severity. A head injury that occurs as a result of numerous beatings is regarded as severe or moderate harm. Which automatically equates the act to Articles 111 and 112.
- Torture is characterized by the infliction of suffering, both physical and psychological, but the main thing is the systematic infliction of damage to a person. This punishment is considered provided there are no serious consequences for health and loss of performance from parts 2 and 3 of the articles on causing harm.
- Separately, it is worth considering the third part of 111 about the grave consequences of bodily injuries in the head area that resulted in death due to negligence. It is distinguished from murder, since this crime also contains intent, but the accused did not foresee the lethal outcome or believed that the actions would not entail consequences.
Diffuse axonal brain injury
Diffuse axonal brain damage is typically characterized by a prolonged coma after a traumatic brain injury, as well as pronounced brain stem symptoms. Coma is accompanied by symmetrical or asymmetrical decerebration or decortication, both spontaneous and easily provoked by irritations (for example, painful ones). Changes in muscle tone are very variable (hormetonia or diffuse hypotension). A typical manifestation is pyramidal-extrapyramidal paresis of the limbs, including asymmetric tetraparesis. In addition to gross disturbances in the rhythm and frequency of breathing, autonomic disorders also appear: increased body temperature and blood pressure, hyperhidrosis, etc. A characteristic feature of the clinical course of diffuse axonal brain damage is the transformation of the patient’s condition from a prolonged coma to a transient vegetative state. The onset of this state is indicated by spontaneous opening of the eyes (with no signs of tracking or fixation of gaze).
Diagnosis
The CT picture of diffuse axonal brain damage is characterized by an increase in brain volume, as a result of which the lateral and third ventricles, subarachnoid convexital spaces, and also the cisterns of the base of the brain are under compression. The presence of small focal hemorrhages in the white matter of the cerebral hemispheres, corpus callosum, subcortical and brain stem structures is often detected.
Brain compression
Brain compression develops in more than 55% of cases of traumatic brain injury. The most common cause of brain compression is an intracranial hematoma (intracerebral, epi- or subdural). Rapidly increasing focal, brainstem and cerebral symptoms pose a danger to the life of the victim. Availability and duration of the so-called the “light gap” - expanded or erased - depends on the severity of the victim’s condition.
Diagnosis
A CT scan reveals a biconvex, less often a flat-convex, limited zone of increased density, which is adjacent to the cranial vault and is localized within one or two lobes. However, if there are several sources of bleeding, the area of increased density can be significant in size and have a crescent shape.
Treatment of traumatic brain injury
When a patient with a traumatic brain injury is admitted to the intensive care unit, the following measures must be taken:
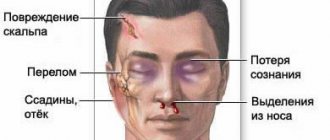
Examination of the victim’s body, during which abrasions, bruises, joint deformities, changes in the shape of the abdomen and chest, bleeding and/or liquor leakage from the ears and nose, bleeding from the rectum and/or urethra, and a specific odor from the mouth are detected or excluded.
Comprehensive x-ray examination: skull in 2 projections, cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine, chest, pelvic bones, upper and lower extremities.
Ultrasound of the chest, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space.
Laboratory tests: general clinical analysis of blood and urine, biochemical blood test (creatinine, urea, bilirubin, etc.), blood sugar, electrolytes. These laboratory tests must be carried out in the future, daily.
ECG (three standard and six chest leads).
Testing urine and blood for alcohol content. If necessary, consult a toxicologist.
Consultations with a neurosurgeon, surgeon, traumatologist.
A mandatory method of examining victims with traumatic brain injury is computed tomography. Relative contraindications to its implementation may include hemorrhagic or traumatic shock, as well as unstable hemodynamics. Using CT, the pathological focus and its location, the number and volume of hyper- and hypodense zones, the position and degree of displacement of the midline structures of the brain, the condition and degree of damage to the brain and skull are determined. If meningitis is suspected, a lumbar puncture and dynamic examination of the cerebrospinal fluid are indicated, which allows monitoring changes in the inflammatory nature of its composition.
A neurological examination of a patient with a traumatic brain injury should be performed every 4 hours. To determine the degree of consciousness impairment, the Glasgow Coma Scale is used (state of speech, response to pain and ability to open/close eyes). In addition, the level of focal, oculomotor, pupillary and bulbar disorders is determined.
For a victim with impaired consciousness of 8 points or less on the Glasgow scale, tracheal intubation is indicated, due to which normal oxygenation is maintained. Depression of consciousness to the level of stupor or coma is an indication for auxiliary or controlled mechanical ventilation (at least 50% oxygen). With its help, optimal cerebral oxygenation is maintained. Patients with severe traumatic brain injury (hematomas, cerebral edema, etc. detected on CT) require monitoring of intracranial pressure, which must be maintained below 20 mmHg. For this purpose, mannitol, hyperventilation, and sometimes barbiturates are prescribed. To prevent septic complications, escalation or de-escalation antibacterial therapy is used. For the treatment of post-traumatic meningitis, modern antimicrobial drugs approved for endolumbar administration (vancomycin) are used.
Patients begin feeding no later than 3 days after TBI. Its volume is increased gradually and at the end of the first week following the date of the traumatic brain injury, it should provide 100% of the patient’s caloric needs. The route of nutrition can be enteral or parenteral. To relieve epileptic seizures, anticonvulsants are prescribed with minimal dose titration (levetiracetam, valproate).
The indication for surgery is an epidural hematoma with a volume of over 30 cm³. It has been proven that the method that provides the most complete evacuation of the hematoma is transcranial removal. Acute subdural hematoma with a thickness of more than 10 mm is also subject to surgical treatment. In comatose patients, acute subdural hematoma is removed by craniotomy, retaining or removing a bone flap. An epidural hematoma with a volume of more than 25 cm³ is also subject to mandatory surgical treatment.
Prognosis for traumatic brain injury
Concussion is a predominantly reversible clinical form of traumatic brain injury. Therefore, in more than 90% of cases of concussion, the outcome of the disease is the recovery of the victim with full restoration of ability to work. Some patients, after the acute period of concussion, experience certain manifestations of post-concussion syndrome: disturbances in cognitive functions, mood, physical well-being and behavior. 5-12 months after a traumatic brain injury, these symptoms disappear or are significantly smoothed out.
Prognostic assessment in severe traumatic brain injury is carried out using the Glasgow Outcome Scale. A decrease in the total number of points on the Glasgow scale increases the likelihood of an unfavorable outcome of the disease. Analyzing the prognostic significance of the age factor, we can conclude that it has a significant impact on both disability and mortality. The combination of hypoxia and arterial hypertension is an unfavorable prognosis factor.
Is it possible to determine the degree yourself based on the symptoms?
After receiving an injury, you should still seek help from a medical facility. Specialists will provide a reliable diagnosis and also provide qualified treatment. Determining the disease in case of a closed craniocerebral injury, and specifically a concussion, will help to accurately determine the severity of the harm to health.
You can do this, in fact, it’s not difficult. We turn to the same Order that we described above and look for a brain injury that matches the injury received by the victim. If there is one, we look at what degree of severity it is.
If not, the same Order contains an Appendix - “Table of percentages of permanent loss of general ability to work.” We are looking for trauma in it. Found - we look at the % of loss and correlate it with paragraphs 7.2 and 8.2 of the Order (moderate severity = from 10 to 30% inclusive, mild = up to 10%, the rest = severe).
Of course, this is just a rough definition. A forensic medical expert will tell you exactly - only his word will be authoritative.
Or, you can do it simpler: knowing your diagnosis, you can approximately determine the severity of the damage:
- A concussion or mild bruise is regarded as causing moderate harm to health - more details.
- For open craniocerebral injuries, only a severe degree is assigned - more details.
- Severe and moderate bruises, bleeding, cerebral hematomas, etc. are also severe.
Treatment
The main principle of treatment is rest . The victim should get more rest. You should also exclude reading, watching TV, computer games, and listening to headphones.
- In case of a concussion, you should immediately place the victim on his right side.
- If possible, bend your left arm and leg at an angle of 90˚. In this way, air passes freely through the bronchial tree, the tongue does not sink, and vomit, saliva and blood can flow out without entering the respiratory tract.
- It is also important to go to the emergency room, where doctors can diagnose the extent of the damage and make an accurate diagnosis.
After an injury, bed rest is required (2-3 days) , then it can be extended or the victim can be discharged to a day hospital if there are no complications in the patient.
In the presence of a second degree concussion, treatment is carried out in the neurological department, and in case of a 3rd degree - in the neurosurgical department. It is necessary to follow all doctor's recommendations. Treatment consists of improving brain function, relieving pain and removing stress from the person.
For this purpose medications are used:
- Painkillers:
- Ibuprofen;
- Ketoprofen;
- Baralgin;
- Sedalgin.
- To relieve dizziness:
- Betaserc;
- Piracetam;
- Microzer;
- Tanakan.
- Sedatives:
- motherwort tincture;
- valerian.
- Sleeping pills:
- Phenobarbital;
- Reladorm.
- To improve blood flow in the brain, vasotropic (Cavinton, Sermion, Teonicol) and nootropic drugs (Nootropil, Cerebrolysin, Picamilon) are combined.
- To improve your general condition:
- Pantogam;
- Vitrum.
- To tone up and improve brain performance:
- tincture of ginseng and eleutherococcus;
- Saparal;
- Pantocrine.
With timely comprehensive treatment, the victim will feel well again in a week, but taking medications should last from 3 weeks to 3 months. Full recovery occurs after 3-12 months .
After a severe concussion, you should be monitored by a neurologist for a year. Come for examination once every 3 months. This will reduce the likelihood of complications arising from a concussion.
How to stop beatings and bring the offender to justice?
The sooner you contact a forensic expert, the easier it will be for specialists to establish the fact of harm. This can be done even before writing the application.
You can contact both specialized authorities - a forensic medical examination, and a hospital, having received a certificate from a traumatologist or neurologist.
If you write a statement about beating, then an examination will be ordered by law enforcement agencies.
What to do when contacting the police:
- How to stop beatings and bring the offender to justice? Write a statement with a detailed description of the crime, the characters involved, the methods of inflicting pain and the locations of the blows.
- Examination by an expert in the direction of the police, followed by a conclusion on the severity level.
If you decide to identify harm yourself, then you should adhere to the following algorithm:
- Visiting a clinic, hospital, or emergency room. There, a certificate is issued with the diagnosis upon application, the nature of the injuries and the time of admission to the medical facility.
- With all the documents, go to the police to write a statement.
- Repeated examination with the participation of forensic doctors.
The last point is not always fulfilled, since the investigation may only need documents from the hospital.
Important! Battery is a serious offense. Do not be afraid to seek help from law enforcement agencies; beatings can be repeated and lead to more serious consequences.
Possible complications and consequences
Complications from a concussion often occur in those who have a history of nervous system disease or in those who did not follow doctor's orders. In 3-5% of cases there are complications. The likelihood of complications increases with each subsequent concussion .
Post-traumatic epilepsy may occur within 24 hours after injury. This occurs due to the appearance of an epileptic focus in the frontal or temporal region of the brain. A couple of days after a concussion, meningitis and encephalitis may appear in the brain, which cause purulent or serous inflammation of the brain.
also occur, which includes :
- headaches;
- lack of sleep;
- absent-mindedness;
- exhaustion;
- memory loss;
- fear of light and sounds.
Consequences of a severe concussion, which can appear 1 year or 30 years after the injury.
These include:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia – disorders of the autonomic nervous system that lead to disturbances in the activity of the heart and blood vessels;
- emotional disturbances - depression, attacks of increased activity or aggression without significant reasons, increased irritability and tearfulness;
- intellectual disorders - memory impairment, decreased concentration, changes in thinking.
We invite you to watch an informative video about the consequences of a concussion:
If the consequences of a concussion occur, you should immediately consult a neurologist. Self-medication with folk remedies is undesirable. To get rid of complications of injury, you need to undergo a course of treatment with medications that improve brain activity and regenerate connections between nerve cells.