Make an appointment by phone: +7 (343) 355-56-57
+7
- About the disease
- Cost of services
- Sign up
- About the disease
- Prices
- Sign up
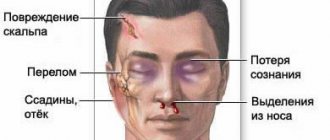
A concussion is a form of traumatic brain injury. In which short-term memory loss may occur, brain dysfunction is reversible. Usually the cause is various traumatic situations. In case of injury, the protective fluid is not able to prevent the impact of brain tissue on the bone tissue of the skull. The injury requires hospitalization and consultation with a specialist.
Classification
Concussion is classified into three degrees:
1.
Mild degree.
The victim is conscious, and within half an hour after the injury there are typical complaints of headache, dizziness, nausea, and disorientation in space. After half an hour the condition returns to normal. 2.
Average.
Consciousness is preserved, short-term memory loss occurs, the symptoms are similar to mild, dizziness persists, there may be a headache, nausea, the victim is disoriented in space. 3.
Severe degree. For her, loss of consciousness lasting a couple of minutes, maybe several hours, is accompanied by retrograde amnesia. Symptoms of headache, dizziness, nausea, disorientation in space can remain for two or three weeks, problems with sleep, and loss of appetite occur. Organic brain lesions lead to the appearance of vascular dementia. This is a secondary disease, that is, occurring against the background of some pathological process. The main reason is a previous ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke.
In what cases should you consult a doctor?
The pulse rate can change in various diseases and pathological conditions:
- respiratory infections, such as pneumonia;
- in general, various infectious diseases that are accompanied by a strong increase in body temperature and dehydration;
- anemia – a decrease in the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood;
- hypotension – decreased blood pressure;
- diseases of the thyroid gland, which are accompanied by an increase in the level of its hormones - hyperthyroidism;
- cardiovascular diseases, including arrhythmias - heart rhythm disturbances.
In medicine, an increase in heart rate above normal is called tachycardia
. And this is a dangerous condition that you should not try to cope with on your own. If your heart rate constantly exceeds 100 beats per minute at rest, this is definitely a reason to consult a doctor who will prescribe the necessary treatment. Especially if you often feel tired or dizzy. Such symptoms cannot be joked about, because over time, more serious disorders of the cardiovascular system may occur, and there is a risk of thrombosis or even sudden death.
Too low a pulse is also not very good. If your heart rate is consistently less than 60 beats per minute, visit your doctor. This condition may be accompanied by symptoms such as dizziness and shortness of breath.
Symptoms of a concussion
General symptoms:
The victim complains of memory loss, dizziness, tinnitus, double vision, intense headache, nausea leading to vomiting, and fatigue. There is sleep disturbance, daytime sleepiness, irritability, and emotional lability. After the injury, confused speech appears, short-term memory loss (retrograde, anterograde amnesia), increased sensitivity to light, noise, balance is disturbed, uncoordinated movements, smell and taste are lost.
Symptoms that may bother you for a longer period:
- intense headache, may be migraine;
- difficulties with reading, remembering, writing;
- absent-mindedness, difficulty concentrating;
- nausea, vomiting;
- drowsiness, weakness;
- dizziness.
Drug therapy
In the acute period, drug therapy is mandatory.
Analgesics and other pain relievers
Headache occurs in almost all patients with a concussion.
To relieve the syndrome, it is recommended to take:
- analgesics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
For mild and moderate, diffuse and episodic pain, Analgin or Baralgin is prescribed. If the pain intensifies and is constantly present, taking Pentalgin, Tempalgin, Sedalgin is indicated.
If the pain syndrome is not relieved by the listed analgesics, NSAIDs are prescribed. They are taken only under the supervision of a doctor, since any medicine from this group can provoke bleeding if the blood vessels of the brain are damaged. Side effects when taking analgesics can also include dizziness and decreased blood pressure.
Analgesics for pain relief.
Sedatives for anxiety and insomnia
Neurological disorders during a concussion manifest themselves in the form of sleep disturbances and increased anxiety. Prolonged bed rest can cause depression and suspiciousness in the patient.
To calm and improve a person’s psycho-emotional state, you should give him mild sedatives:
- Belloid;
- Novo-Passit;
- Persen;
- Corvalol;
- Valocordin.
Sedatives are also used under the supervision of a physician, as they can provoke bronchospasm. With long-term use of this group of drugs, defecation failures are observed due to persistent disruption of intestinal motility.
Sedatives.
Tranquilizers for emotional stability
After an injury, the patient may experience increased excitability, tearfulness, and irritability. This condition negatively affects the effectiveness of therapy.
In order to stabilize the emotional state, a neurologist may prescribe tranquilizers:
- Phenazepam;
- Nozepam;
- Adaptol;
- Phenobarbital;
- Elenium;
- Dormiplant.
Such medications are not recommended for children. With long-term use, side effects may occur in the form of depression of central nervous system functions. For elderly patients, tranquilizers are prescribed in rare cases and under the supervision of a physician.
Tranquilizers to reduce excitability.
Neurotropic agents
This group of drugs includes:
- nootropics;
- sedatives;
- antispasmodics;
- general tonics and adaptogens;
- sleeping pills.
For concussions, nootropic drugs that normalize mental activity are mainly used.
This group includes neuroprotectors that have other useful pharmacological properties:
- antihypoxic;
- anxiolytic;
- sedative;
- anticonvulsant;
- muscle relaxant.
In case of injury, medications are prescribed that improve metabolic processes:
- Piracetam;
- Cinnarizine;
- Glycine;
- Vinpocetine;
- Nootropil.
These drugs can be used for a long time, because they have virtually no side effects.
Neurotropics without side symptoms.
Diuretics for resolving edema
Dehydration therapy is indicated only when there is a threat of cerebral edema.
To normalize intracranial pressure and eliminate edema, use:
- Diacarb;
- Uregit;
- Furosemide;
- Veroshpiron;
- Lasix;
- Arifon.
Diuretics should not be taken by hypotensive patients: the patient may lose consciousness. Diuretics are not prescribed to children under 12 years of age. Even the weakest of them are prescribed taking into account contraindications.
Diuretics.
Supporting vitamin complexes
To shorten the recovery period, maintain general condition, and provide the body with nutrients, vitamin therapy is indicated. Vitamins are taken both in the form of tablets and capsules, and by injection.
After a concussion, vitamins are indicated:
- B1 (thiamine);
- AT 6;
- B3 (niacin);
- folic acid.
Magnesium and phosphorus are prescribed in combination with them.
Vitamin complexes.
Vascular preparations
Vasotropic drugs are recommended for:
- eliminating vascular spasm;
- improving microcirculation;
- normalization of rheological properties of blood;
- prevention of thrombosis and hemorrhage;
- strengthening the walls of blood vessels.
The following medications for blood vessels are recommended:
- Vasotropin;
- Teonicola;
- Cavinton;
- Mexiprima;
- Actovegina.
Medicines are selected individually. For example, hypotensive patients are not recommended to take medications that relax the muscles of the vascular walls. In case of cardiovascular pathology, drugs that stimulate blood circulation are used with caution.
Preparations for strengthening the walls of blood vessels.
Remedies for nausea and dizziness
Nootropic and vasotropic medications help eliminate dizziness. Persistent vertigo from a concussion is rare, so specific medications for dizziness are rarely prescribed.
These include:
- Bilobil;
- Glycine;
- Papaverine;
- Tanakan.
For nausea you can take:
- Dramamine;
- Cerucal;
- Microzer;
- Chophytol;
- Kokkulin.
Mint infusion or menthol lozenges can relieve the condition.
For nausea and dizziness.
Disease prognosis
In the absence of complex combined lesions of the central nervous system and careful adherence to medical recommendations, the injury does not leave any complications and ends with complete rehabilitation.
Within 3-12 months after a concussion, some patients may experience the following symptoms:
- Decreased memory;
- Decreased concentration;
- Manifestations of depression;
- Unreasonable anxiety;
- Headache;
- Insomnia;
- Intolerance to bright light and loud sounds;
Over time, these manifestations completely or partially “disappear.”
Diagnostic methods
To determine the nature and extent of disorders, methods such as CT and MRI are used. During a diagnostic CT study, abnormalities are detected - areas of hemorrhage, damage to parenchyma (nervous tissue), fractures of the bone structures of the skull. Computed tomography is considered the most informative method for identifying indications for emergency surgery.
Other advantages of CT: the ability to examine patients in a state of psychomotor agitation, and quick results. Neuroimaging is mandatory for patients:
- Children under 16 years of age.
- Patients with signs of intoxication.
- Patients with a blurred, erased clinical picture.
- Patients taking anticoagulants on an ongoing basis (as part of a program for the treatment of chronic vascular pathologies).
With a mild concussion, changes in the structure of the brain matter are detected in 15% of cases. If, during the initial examination of the patient, neurological symptoms of a focal type are observed, morphological changes in the nervous tissue are detected with a frequency of 50% of cases.
An MRI study is more sensitive to detecting axonal damage of a diffuse type, changes in the structure of the parenchyma, and hematomas of subdural (under the dura mater) localization. MRI reveals hemorrhagic disorders that are associated with axonal damage.
Shaken baby syndrome
Everyone knows that mothers simply need rest (just like other people who regularly care for a small child). Today we will raise the topic of what can happen if a mother does not rest for a long time and, as a result, burns out.
Babies cry a lot in the first year of life. Sometimes mothers cannot stand it and, in response to prolonged crying, begin to do things that they could not even think of before: they shake the child violently or throw him against something.
After this, 2 scenarios may follow:
1. The baby will be lucky - he will get away with only a minor fright, a couple of bruises and abrasions.
2. The baby will be unlucky - the baby will develop shaken baby syndrome, which poses a threat to his health and life.
What is shaken baby syndrome?
A small child has weak neck muscles, and if the baby is shaken, his head begins to hang freely, and its contents begin to bang against the skull. This causes multiple damage to brain tissue and supply vessels.
Note that the consequences from shaking are much more serious than from a blow when a child falls from a small height.
Of course, shaken baby syndrome can also develop with increased swinging, throwing up and other situations in everyday life. However, this is much less common than what is defined as child abuse.
What's next?
The child has difficulty breathing, convulsions, lethargy and drowsiness. When parents contact a medical institution, the correct diagnosis is made, at best, within a day.
Late diagnosis is usually associated with the following reasons:
1. The parents did not even understand that the symptoms that arose in the child could be the result of shaking, so they kept silent about this fact.
2. The parents realized that the child was experiencing symptoms due to shaking and, fearing the consequences, kept silent about this fact.
Without truthful evidence, it is quite difficult to diagnose pathology, because with a concussion there are usually no external injuries. But it is at this stage that lost time can cause death.
The baby is usually brought to the hospital with nonspecific symptoms: difficulty breathing, drowsiness, vomiting, convulsions, loss of consciousness. In this case, the fact of injury is denied, and there are no external injuries.
Much later, it turns out that the symptoms appeared immediately after shaking (in more than 90% of cases) and this was not the first time the child was shaken (in 70% of cases).
What diagnostics are needed?
The following methods are used to diagnose shaken baby syndrome:
1. Neuroimaging methods (MRI or CT) are necessary to identify hemorrhages and areas of ischemia.
2. CSF analysis - used to confirm the presence of hemorrhage and rule out meningitis (due to the similarity of symptoms).
3. General and biochemical blood test.
4. Ultrasound and radiography – necessary if additional damage is suspected.
The most important and at the same time difficult task for a doctor is to prove that brain damage is associated with an act of abuse, and not just with an injury resulting from a fall (for example, when a baby is just learning to walk and often gets hit).
And it is impossible to determine what is worse - not recognizing an adult who harms a child or blaming an innocent person, thereby destroying a family.
How to help a child?
Shaken baby syndrome is often accompanied by retinal hemorrhage, as well as other manifestations of domestic violence - fractures, hematomas, damage to internal organs, etc.
A child who has suffered a concussion should be treated in intensive care. Doctors need to try to preserve as much brain tissue as possible in the first minutes (by removing the accumulation of blood, sometimes surgically, to eliminate breathing and circulatory disorders). Let us note that about 39% of children require emergency resuscitation upon arrival at a medical facility.
Unfortunately, medical care cannot always help avoid tragedy:
- about 23% of children with shaken baby syndrome die;
- up to 55% of children remain with neurological pathologies;
- up to 65% subsequently suffer from visual impairment.
Thus, the best option is not to let it get to this point and try to find enough time for proper rest.
Clinical picture
A concussion is characterized by short-term depression of consciousness and single vomiting. Primary symptoms after a mild traumatic brain injury - increased breathing, changes in pulse and blood pressure - usually disappear quickly. However, if the patient has a history of hypertension or hypertensive reactions, blood pressure may persistently increase. This is due to the stress factors that accompany the injury.
Body temperature with mild traumatic brain injury remains within normal limits. Vasomotor reactions are possible (pallor, then redness of the face). People who have suffered a concussion are characterized by vegetative phenomena: flushing of the face, anxiety, sleep disturbances, sweating. In some cases, pain occurs when moving the eyes.
Maintaining a daily routine
After a complete examination and the doctor prescribes medications, a patient with a mild concussion can continue concussion treatment at home.
To quickly regain your health, you need to follow these recommendations:
- For any degree of concussion, it is recommended to remain in bed for 3 to 5 days. Sick leave for this injury is issued for an average of 10-14 days.
- It is necessary to temporarily stop using a computer, TV, smartphone, reading regular books and using their electronic analogues, and communicating in large quantities.
- Psycho-emotional overload is not recommended for patients. Their loved ones should protect their loved ones with a concussion from worries and stressful situations.
- If you have photophobia, it is advisable to create a dim light background in the room, cover the windows with blinds and thick curtains.
- Relief of headaches, often observed after a concussion, is carried out without fail with drugs prescribed by a doctor in the recommended dosage.
Symptoms of a mild form of the disease decrease significantly after 3-7 days if the above recommendations are carefully followed. The lack of positive dynamics and the deterioration of the patient’s health should cause concern. Bleeding from the nose and ears is especially dangerous. In this case, emergency medical attention is necessary.