Stuttering
Stroke
Encephalitis
5308 March 30
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Stuttering: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
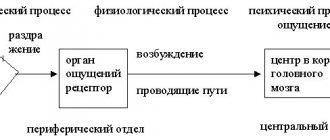
Oral speech is a complex multicomponent process in which not only the structures of the maxillofacial apparatus, but also the brain centers located in the cerebral cortex take part. It is in these structures that in most cases certain pathological processes leading to the development of stuttering are localized.
Stuttering (stammering) is understood as a speech feature characterized by frequent repetition or prolongation of sounds, syllables or even words in combination with frequent pauses, which disrupts the fluency of oral speech.
Today, different figures are given that characterize the number of people who stutter - from 1 to 5%. However, all experts are unanimous that among males stuttering occurs 4 times more often than among females, and also that in 90-95% of cases stuttering occurs between the ages of 2 and 7 years.
This speech defect often leads to problems in communication, which consist not only in the difficulty of perceiving such speech on the part of the listener, but are also associated with the internal emotional experiences of a stuttering person.
Types of stuttering
There are the following types of stuttering:
- Neurotic stuttering, the development of which is usually based on some psychotraumatic factor. This type of stuttering is psychogenic and is not based on structural damage to the brain or peripheral parts of the speech apparatus.
- Neurosis-like stuttering - unlike neurotic stuttering, it develops against the background of organic damage to the nervous system.
- Mixed stuttering develops against the background of both a psychogenic factor and true damage to the nervous system.
Possible causes of stuttering
Stuttering is based on various muscle spasms of the speech apparatus. They develop due to abnormal impulses emanating from the motor speech centers of the brain. The cause of the pathological functioning of these parts of the central nervous system can be both structural and functional disorders. The latter are characterized by the presence in some part of the brain of a focus of excitation, which activates the motor speech center and leads to the development of convulsive readiness of the muscles involved in articulation and voice formation.
If tonic convulsions develop, a prolonged muscle spasm occurs, resulting in speech delay. Unlike tonic convulsions, clonic convulsions are a series of short-term convulsions that lead to involuntary repetition of sounds or syllables.
Both types of seizures lead to impaired speech fluency and stuttering.
Diseases that cause stuttering
Among the factors influencing the development of stuttering, doctors identify the following diseases and conditions:
- emotional lability and dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system;
- mental trauma;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- infectious brain damage;
- stroke;
- perinatal damage to the central nervous system of the child, associated, as a rule, with a violation of the supply of oxygen to brain structures in the prenatal period of development, during childbirth and in the first hours and days of life.
Which doctors should I contact if I stutter?
Traditionally, the initial examination of a patient with stuttering is carried out. After a detailed interview with the patient, the purpose of which is to clarify the circumstances of the appearance of stuttering and possible provoking factors, the doctor specifically examines the nervous system for the presence of other signs of neurological abnormalities. In the treatment of stuttering, doctors resort to the help of a speech therapist and psychologist. Often, to treat stuttering, especially in the absence of organic damage to the nervous system, the neurologist refers the patient to a consultation with a psychiatrist in order to identify some mental abnormalities that lead to the development of stuttering.
Diagnosis and examinations for stuttering
Diagnosis of stuttering begins with a neurological examination, during which a neurologist may suspect the presence of a structural brain lesion or, conversely, receive no evidence of the presence of organic damage. In this case, the doctor resorts to additional laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods in order to confirm or exclude various organic lesions. EEG and neuroimaging methods are coming to the fore.
Electroencephalography (EEG) is one of the integral methods of additional research of a patient suffering from stuttering. EEG helps differentiate neurotic and neurosis-like stuttering by identifying signs of convulsive activity in individual areas of the brain.
Role of the family
Family is the first and main environment for children. Close people can become a pathogenic organism that provokes the prosperity of the disease, but, on the other hand, have a beneficial effect on eliminating the defect.
A large role in the formation of logoclonia is played by the educational model. The risk of developing pathology increases in those families where the baby is raised in an environment of authoritarianism, hypersocialization, and increased emotional connection with the mother. The child is not perceived as he is, the right to develop as an individual is taken away, and his rights are infringed upon. Parents do not have an adequate understanding of the baby and his role in society. There is no attention to age needs.
The atmosphere in the family is another provoking factor for logoneurosis. Scandals, showdowns, misunderstandings between parents act as a chronic stressor. Particular importance is given to violence and dictatorship in a family environment. When faced with the problem of logoneurosis, many parents subconsciously choose the wrong path of response. The first reaction is resistance, rejection of the disease, the desire to get rid of the defect as quickly as possible.
Relatives who are little informed about the disease make fatal mistakes in teaching their children. They show increased control, anxiety, and force the baby to repeat phrases several times. The anxiety of loved ones is transmitted to the patient. In such a situation, the defect worsens. The mother's negative attitude towards the disease provokes increased attention to the speech defects of young patients, increasing sensitivity to the problem.
An examination of parents whose children suffer from logoneurosis revealed the following deviations in the mental state of adults, and, above all, the mother: guilt, anxiety, confusion, hopelessness, worry about the future of the baby. Futile attempts to eliminate the disease disorganize the family. Therefore, parents should pay attention to their condition, which is reflected in the psychological background of the little patient.
Based on the data obtained during conversations with mothers of sick children, it was possible to identify the following models of attitude towards the problem:
- an obstacle that needs to be overcome - we tried everything, this is the last hope;
- undeserved punishment, retribution for sins - why do we need this;
- a disease that needs treatment - he is sick because he is weak;
- tarnished reputation - where does this come from in our educated, wonderful family;
- manifestation of a difficult character - grimacing from harmfulness;
- absence of a problem - different things happen, and so it will pass.
All of these positions are destructive in relation to progress in the treatment of logoneurosis. Considering that children in most cases imitate the reactions of adults, it is hardly worth expecting an adequate assessment from the patient himself, and therefore a positive trend in the treatment of logoclonia.
The only correct response to a problem is to unite the family team. WITH
It is necessary to create a favorable atmosphere in the family for children, adequate participation in treatment without overprotection, but with support.
Parents must remember that their behavior has a powerful impact on the potential of their child.
How to reduce the risk of occurrence and save a child from early stage stuttering
- Speak to your child slowly and smoothly , evenly and rhythmically. Set a leisurely, relaxed pace for your conversation yourself, rather than asking your child to speak more slowly. By these actions you will help your child speak more fluently, as you will set an example for him.
- Take pauses in your speech , leave empty spaces, especially after the child’s phrases - this gives him the opportunity to say something else, and for you to think about his words. Don't speak just because you need to fill a gap in the conversation. Let your child understand and feel that he can talk for as long as he needs.
- Ask fewer questions , make fewer commands. Questions put pressure on the child and make him feel limited in time to answer. Comment and describe what you are currently doing with your child - this significantly reduces the pressure due to lack of time.
- Directives and commands sometimes contain judgment and criticism. It’s better to start such phrases with the words: “Come on,” “How about...”, “What do you think?”
- Sometimes repeat after your child to make it clear that you listened carefully. The main goal is to reduce the number of questions, orders, commands and use the form of speech in the form of comments and statements. Make your child's speech flow smoothly in conversation.
- Listen to the child , do not interrupt, let him feel that his statements are the most important thing at the moment. Allow your child to start a conversation and choose a topic for conversation. Make relevant comments on the topic. Try not to constantly control the conversation.
- Make eye contact . Don't look away if your child begins to stutter, otherwise you will show that you are uncomfortable. Let your child finish the sentence, even if he has to wait.
- Accept that speaking can be difficult . Sometimes it is so difficult for a child to pronounce a word that he may cry: “I can’t say it,” “I can’t do it.” At this moment, demonstrate an accepting attitude towards the child with phrases: “that was difficult to pronounce,” “that’s a difficult word.” Use these phrases only when your child is very upset, scared, or stressed. In other cases where your child's speech is slurred, maintain eye contact and wait as long as necessary for the child to finish his sentence.
- If at the moment you cannot pay attention exclusively to the child, then tell him that you are doing some work, and after it is completed, give him your full attention and be sure to fulfill your promise!
- Set aside special time for conversation and communication, playing with your child. This greatly helps to increase speech fluency. Use this time to develop a slower pace for your speech. Let your child choose the activity and decide when to start the conversation. By devoting time to your child, you greatly increase his self-esteem, and this helps him slow down his speech rate.
- Give your attention exclusively to the child. Children often lack the exclusive attention of loving parents, this is exactly what children dream of!
This way you will create a positive background around you and your child and give him a flow of positive emotions. Fight for your child's speech!
What should adults say?
To prevent relapses of speech disorders (and they may well occur), you as parents need to change or carefully monitor your own speech. This applies to your conversations with each other. Children actively perceive the conversation around them and unconsciously imitate it:
- Speak clearly, intelligibly, without mistakes and without rushing.
- Try to pronounce the phrase a little slower than usual.
- Avoid complex words that are incomprehensible to the baby.
- Various “scary” topics of conversation are taboo.
- It is not recommended to speak in syllables or sing phrases.
Try to get your baby to make friends with balanced children who have well-developed speech. If his speech activity is too high, artificially limit it by giving him the opportunity to silently play alone with himself for some time. Try to get your child to listen more than talk.
Treatment and prognosis
Today, the treatment of such children includes not only medical, but also pedagogical influence.
- Use of medications. A huge number of different groups of drugs can be used in the treatment of stuttering. Let's look at the most common of them:
- 1. Nootropics (piracetam, pantogam, pantocalcin, phenibut).
- 2. Sedatives (valerian, phenibut, glycine, persen, afobazole, adaptol, novo passit). It is worth noting that many nootropics also combine sedative effects.
- 3. Vitamins, especially B vitamins (combilipen, compligam B, larigama).
One of the treatment methods is sessions with a speech therapist.
There are a huge number of methods for overcoming stuttering in children, as well as groups of drugs that can be used in individual cases. Many of you are interested in the question: “Can we help a child on our own, at home and without running to doctors? Is it possible to completely cure stuttering in a child? There are separate techniques that allow you to improve pronunciation and so on by practicing at home, but they are also selected by a specialist. As for the forecast, there is no clear statement. It can be assumed that the younger the child, the more cheerful and positive his behavior, the fewer concomitant psychopathological disorders, the weaker the manifestations of seizures, the better the prognosis.
How can you tell if your child has a speech disorder?
The easiest way to treat stuttering is when it is discovered at a very early stage, before the brain has yet “fixed” the speech defect, before it turns into a reflex and affects the child’s psyche. Therefore, when he turns 3-4 years old, we recommend paying attention to the following points:
- when pronouncing phrases, the child stops, breathes quickly, as if gathering strength;
- stammers, repeats the same syllables and words;
- pronounces additional sounds before the phrase (i, a, e);
- refuses to speak at all, becomes abruptly silent;
- becomes withdrawn.
Any of these symptoms is a reason to consult a doctor. The sooner you do this, the faster and without consequences the problem will be solved.
What should parents do at home?
It is ineffective to cure logoneurosis without the help of parents at home, since the main support should come from them. Therefore, get ready for the fact that you will also have to contact a psychologist and learn from him. To correct psychological problems in a child, you need to change your daily routine and lifestyle at home. The best way to prevent stuttering is to avoid situations that make it worse.
Mode
Organize your daily routine so that periods of intellectual and emotional stress alternate with proper rest and relaxation.
Dream
Children must sleep at least 8 hours a day, so you need to organize your daily life, home space, and sound atmosphere in such a way as to ensure this minimum.
Intonation
The baby should feel the confidence and calmness coming from the parents, so you need to address him slowly, quietly, calmly, without interrupting him. It is important to explain to loved ones that this is exactly what needs to be done.
Praise
Develop your baby's self-confidence by praising him for any success. Create situations in which he could show his best side. However, praise for success should not be confused with pampering.
Situation
In family relationships, quarrels should remain prohibited. It is impossible to cure a child and prevent stuttering in an aggressive and tense atmosphere. The same applies to visiting noisy companies or places.
Leisure
Limit watching programs, movies, cartoons or games that cause emotional overstimulation. Leisure should be calm, aimed at developing creative abilities.
Communication
Gradually and delicately expand your child's social circle by inviting him to visit public places that do not evoke strong emotions. Introduce him to interesting people. They will help him adapt to the outside world.
Activity
Dosed physical activity has a positive effect on the nervous system, as well as muscle development. Therefore, physical education, swimming, running, just walking, playing in the fresh air should become the norm.
Restrictions
Under no circumstances use punishments that can have a negative impact on children's emotions (punishments should also be calm, no matter what offense the child commits). It is strictly forbidden to leave a child alone in a dark room.
Severity
When assessing the severity of the pathology, the severity of symptoms, their impact on the child’s communication with other people, and the presence of concomitant disorders are taken into account.
Highlight:
- mild degree - it is characterized by rare, unexpressed hesitations that do not interfere with talking and communicating. But even with this degree, parents need to contact a specialist in order to begin correction in a timely manner before the deviations become entrenched;
- medium - hesitations are more noticeable and make communication more difficult;
- severe - speech impairments are pronounced, they make communication almost impossible. Other symptoms also appear.
If stuttering is not eliminated, the cause of the pathology is not eliminated, then it gradually progresses, and very quickly.