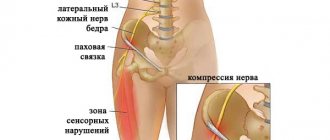
The nature of pain in neuralgia
Pain in neuralgia occurs as a result of spasm of the intercostal muscles or due to pinched nerve endings in the spinal column.
In the latter case, the problem may be an exacerbation of osteochondrosis, the appearance of a hernia or protrusion. The following symptoms are typical for this type of pain:
- Most often, the pain is severe, but it can also manifest itself in the form of some discomfort.
- It intensifies after changes in body position (bending, turning), as well as during coughing or sneezing.
- Manifests itself as constant or paroxysmal.
- The sensations are burning, stabbing, pressing.
- Duration – from 1-2 hours to several days or more.
- Even a slight touch to the intercostal spaces or at paravertebral points makes the pain unbearable.
- Irradiation is observed in the arm, back, neck, and left anterior chest. It is this symptom that often leads to a false interpretation of the cause of the disease, as it resembles a heart attack.
- The skin along the pinched nerve changes sensitivity. Paresthesia (distorted sensation) is observed in the form of burning, crawling, tingling. Sometimes a person complains of numbness in the affected area.
- The attack is often accompanied by sweating, paleness, and muscle spasms. The latter symptom is caused by impaired blood flow in the area and irritation. The local temperature drops and the body area becomes cool.
All of the above symptoms can occur simultaneously. But sometimes only one or two signs appear. The degree of their severity depends on the sensitivity threshold and other individual characteristics.
Causes of intercostal neuralgia and risk factors
Intercostal neuralgia can develop for a variety of reasons. Among them are:
- injuries to the thoracic nerves, chest and spine;
- surgical interventions, long-term immobilization of a person in a certain position;
- poisoning with chemicals, prolonged use of medications;
- congenital developmental anomalies, hereditary diseases;
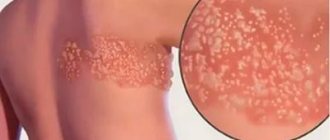
- infectious processes (shingles, tuberculosis, brucellosis and others);
- some neurological diseases, such as radiculitis and multiple sclerosis;
- diseases of the spine (osteochondrosis, deforming spondylosis, herniated intervertebral discs);
- compression of nerve branches in the bone-connective sheaths, for example, in the presence of scar changes, benign or malignant neoplasms;
- immunodeficiency (HIV infection, cancer, etc.);
- allergic reactions;
- diabetes;
- various metabolic disorders in nervous tissue and its hypoxia;
- lack of B vitamins in the body;
- alcohol abuse;
- osteoporosis;
- pathology of nearby anatomical structures (aorta, lungs, pleura);
- various systemic diseases (atherosclerosis, rheumatism, anemia, thyrotoxicosis, etc.).
More often, chest neuralgia appears due to several causes. Therefore, it is typical for older patients with vascular, degenerative and metabolic disorders. Sometimes symptoms of neuralgia appear after excessive physical activity, sudden movements or prolonged stay in one position. They can also occur after hypothermia or severe stress.
More often, intercostal neuralgia is observed on the left or right; less often, there is a bilateral lesion. In most cases, the pathogenesis is based on muscle spasm, leading to compression of nerve fibers. Pain occurs in response to nerve damage.
In children, signs of intercostal neuralgia are rare. When they appear, parents should definitely show the child to the doctor, as this may be a signal of the presence of a serious pathology. The doctor will determine the possible causes and explain how to cure intercostal neuralgia in this case.
Heart diseases with similar symptoms
I want to say that there are many cardiac and vascular pathologies that are accompanied by similar symptoms. I propose to consider the most common abnormalities, this will help to understand whether the heart or neuralgia is the cause of the pain.
Angina pectoris
Pain in this case occurs in the area of the heart muscle (but do not forget that there are atypical attacks). It has a diffuse nature, a person is not able to indicate the exact location. Its strength and description are variable: it can be pressing, piercing, cutting, baking. It radiates to the left arm, under the shoulder blade, neck, lower jaw. It does not depend on the position of the body, but can be provoked by physical overload, nervous stress, as well as sudden hypothermia or overheating.
At this moment, there is a fear of death, shortness of breath with difficulty in inhaling. The attack can be one-time, occurring 1-2 times a day or more often. Its duration ranges from 3-5 to 20 minutes. Almost the same signs are characteristic of myocardial infarction. But unlike angina, the attack usually lasts a long time. The patient takes a certain position in bed - sitting with his legs down or lying on several pillows. You can read more about angina pectoris and how to deal with it in the article at the link.
Myocarditis
Inflammatory diseases are accompanied by moderate pain, which is monotonous. Occurs in 90% of all patients. They describe it as aching or pressing. In the acute period, signs of inflammation are observed (fever, body aches), shortness of breath with impaired inhalation or exhalation. The history often reveals a recent infectious disease. There is no clear dependence on physical activity.
Often myocarditis simulates angina pectoris, especially in older people, when pain and lack of air come to the fore, and the rest of the symptoms are smoothed out or do not appear.
Perikadite
The pain of pericarditis gradually increases, but when effusion appears, it can significantly decrease or go away completely. It stings, cuts, radiates to the neck, back, shoulder, to the right side, and lasts for a long time. Some relief occurs in a sitting position with anterior tilt.
In acute dry inflammation, an attempt to make a deep entrance increases the pain, so with this disease a person breathes quickly and shallowly. During auscultation, in this case, I clearly heard the pleural friction noise. The heart most often hurts with this type of pericarditis in the apex area.
A complete collection of information about pericarditis and its treatment methods is here.
Aortic aneurysm
The symptoms of this acute condition are largely reminiscent of myocardial infarction. A sharp increase in blood pressure, stress or physical activity can be a provocation. The pain is tearing, bursting, localized in the retrosternal region, radiating to the neck, lower jaw, right side of the chest, and sometimes runs along the spine. Has a wavy character. In some cases, it spreads to the projection area of the abdominal aorta and even to the legs.
At the same time, sharp pressure surges appear; when the pressure drops, a collapsible state may occur. There is an asymmetry of the pulse on the left and right arms. As blood begins to accumulate under the inner lining of the aorta, symptoms of anemia (pallor and blueness of the skin, dizziness) quickly develop.
Pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism is accompanied by sharp and severe pain, which is localized in the center of the sternum, as well as to the left or right of it. It can last from a few minutes to 3-5 hours and is associated with respiratory movements of the chest. At the same time, a lack of air comes to the fore, a sharp decrease in pressure, up to collapse. Clinical manifestations depend on the location of the thrombus and its size. When the lumen of a large vessel is blocked, cyanosis appears in the upper part of the body, arrhythmia with an increase in pulsation frequency. When small arteries are blocked, the skin develops blue, shortness of breath, the pain is most often moderate, cough and sputum streaked with blood are observed.
Neuralgia or heart pain
Service price from 900 rub.
Very often, when discomfort appears in the chest, a person has a question: what kind of pain is this? Does the heart hurt, or is the problem in the nerve fibers? Our leading neurologist, osteopath and acupuncturist Larisa Aleksandrovna Baldorzhieva will help answer these questions. The doctor will conduct a differential diagnosis between heart pathologies and neuralgia and prescribe appropriate treatment. You can make an appointment using the telephone numbers provided.
Neuralgia or heart: how to distinguish
Localization, intensity of manifestation and even seasonality will help distinguish heart pain from pathology of the nervous system:
- Local soreness. Neuralgia in the heart area often develops when the intercostal nerves are compressed or irritated, so this situation is characterized by local pain on palpation along the nerves along the chest. The pain often makes it difficult to breathe normally and intensifies during movement.
- Region. Cardiac pathology is manifested by discomfort in the heart area and can radiate to the left (more often) and right (less often) upper limbs, scapula, right and left hypochondrium, and lower jaw. Neuralgia is characterized by pain along the distribution of peripheral nerves.
- Seasonality of the disease. Angina pectoris and myocardial infarction occur regardless of the time of year. Neuralgia, on the contrary, is observed more often in the autumn-spring period, when hypothermia begins.
- Connection with physical activity. Cardiovascular pathology is characterized by the appearance of pain when walking and climbing stairs. Neuralgia can also occur with physical activity. However, provoking factors for it are sharp bends, turns, and heavy lifting.
- Discomfort at rest. Cardiac pathology is characterized by the appearance of pain after physical or emotional stress. If it occurs at rest, it often occurs in the evening hours. With neuralgia, discomfort appears after a long stay in one position, regardless of the period of the day.
Some diagnostic points
In some cases, neuralgia can develop in people suffering from heart pain. Pain signs and instrumental examination data will help to distinguish diseases in this situation:
- The pain of neuralgia is acute, sharp, tingling. It prevents a person from performing even ordinary movements - turning the body, bending forward. The pain can radiate to the back, lower back, or under the shoulder blade. Neuralgia pain is often prolonged, does not subside even during sleep, and intensifies when coughing, sneezing, or taking a deep breath. The attack lasts several seconds or minutes, then gradually subsides. But pain discomfort may remain, but of low intensity.
- With classic angina, the pain syndrome is short-term, lasting from three to twenty minutes. The pain is pressing, burning, squeezing, its character does not change during inhalation, exhalation or change in body position. Taking nitrate-containing drugs, such as nitroglycerin, for 2-3 minutes leads to its disappearance. With myocardial infarction, the pain syndrome is stronger than with angina pectoris, lasts more than half an hour and may be accompanied by changes in blood pressure and pulse. The appearance of sweating and anxiety is typical. The pain is not relieved by nitroglycerin.
- ECG - pathology of the nervous system does not show any obvious changes in this study. In case of cardiac pathologies, this diagnosis helps to identify characteristic deviations from the norm. Electrocardiography is especially effective during an attack. Outside of an attack, pain may not manifest itself in any way. In this case, to confirm the diagnosis, our clinic uses a stress ECG.
To accurately determine whether a person is bothered by heart pain or neuralgia, our Private Practice clinic uses an integrated approach. A full examination by a neurologist, cardiologist and an ECG or exercise test allow us to make a diagnosis with high accuracy and correctly prescribe treatment.
The initial consultation is carried out by neurologist Larisa Aleksandrovna, who is a highly qualified specialist with many years of experience. If she rules out neuralgia, she refers the patient for further examination to a cardiologist at our clinic. After identifying the true cause of the pain, qualified doctors at our medical center prescribe an individual treatment regimen.
You can make an appointment at the medical office every day at a time convenient for you. The cost of a qualified consultation and appointment with a neurologist and osteopath Larisa Aleksandrovna Baldorzhieva is 900 rubles. Our clinic provides high-quality medical care and comprehensive diagnostics exclusively using modern equipment. We are waiting for you every day from 9.00 to 21.00.
How to distinguish
To distinguish heart pain from neuralgia and other pathologies that are successfully masked by cardialgia, it is necessary to take into account the following factors:
- duration;
- localization and depth;
- provocative factors;
- drugs to relieve symptoms.
When trying to determine the cause, I always pay attention to the accompanying signs. This allows you to fairly accurately diagnose the disease, even at the stage of a preliminary survey, before using additional research methods.
Angina pectoris lasts 3-20 minutes, and a heart attack is characterized by a long-lasting attack (the same pain is observed with myocardial inflammation, pericarditis and aneurysm). Suffering of varying intensity and duration is observed with pinched nerves and myositis.
It is necessary to determine the depth and localization of pain. In case of cardiac pathology or vascular problems, it is internal, as if going outward. Superficial sensations are characteristic of neuralgia and muscle inflammation. In this case, it is possible to distinguish pinching from pain in the heart using palpation.
Provoking factors for the development of IHD are psycho-emotional stress or physical overload. The latter factor can also provoke an exacerbation of osteochondrosis and hernia. Myositis occurs against the background of general inflammation, hypothermia or intoxication.
If the attack is relieved by sublingual nitroglycerin, then angina pectoris should be suspected. For a heart attack, acute aneurysm or thromboembolism, this action will not have a significant effect; in this case, only narcotic analgesics, which are administered to the patient immediately after admission to the department, will help. To distinguish intercostal neuralgia from cardiac pain, you should know that the first pathology can be easily eliminated with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the use of muscle relaxants, but cardiac problems cannot be solved in this way.
Differentiation of neuralgia and heart pain
It is important to know the difference between heart pain and neuralgia in order to provide or receive timely help.
Important differences in the manifestation of pathologies:
- pain syndrome. With neuralgia, any body movements, including inhalation and exhalation and normal walking, lead to increased pain. When there is pain in the heart, its intensity does not change depending on the depth of breathing;
- duration of the attack. Heart pain can be relieved in 15-20 minutes by taking medicine (validol, nitroglycerin). These drugs will not help with neuralgia;
- arterial pressure. Cardiovascular disorders lead to increased blood pressure during a painful attack and increased heart rate. Neuralgia does not cause changes in blood pressure;
- nature of pain. Coronarogenic pain in the heart is strong, pressing, with neuralgia it is burning and short-lived;
- localization. In case of heart problems, the pain is concentrated on the left or behind the sternum, neuralgia is accompanied by pain along the affected nerve;
- additional symptoms. Coronarogenic pain syndrome can be accompanied by cold sweat, pallor, and a feeling of shortness of breath. If the pain is of neurological origin, sweating, increased blood pressure, and limited mobility are possible;
- provoking factors. Heart pain can be associated with physical and emotional stress. Neuralgia is caused by sudden movements and uncomfortable posture;
- reaction to medications. Pain in the heart is relieved by treatment with nitroglycerin; neuralgia can be relieved by taking NSAIDs.
These signs are key in recognizing the nature of pain. But for an accurate diagnosis, additional examination is required. To identify the nature of the pathology, specialists from the IntegraMed CDC (formerly NDC) in St. Petersburg prescribe the following procedures:
- appointment with a cardiologist;
- appointment with a therapist;
- CT scan;
- Ultrasound;
- ECHO-cardiography;
- MRI of the spinal column.
Necessary examinations
When I encounter such phenomena, I immediately refer the patient for an ECG. This is especially true for people over 45 years of age, even if the signs are not typical for myocardial ischemia. It is better to make sure that the person is not in danger, and only then calmly carry out treatment for neurological or other abnormalities. If you have angina, you should do an ECG with stress, since it may not show any changes when pain is eliminated.
In some cases, it is necessary to use other instrumental methods:
- Coronary angiography. It is carried out using contrast injection and helps determine the presence of narrowing in the vessels of the heart.
- EchoCG. Ultrasound is used for this. It allows you to see the structure of the chambers of the heart muscle, the condition of the valves, the thickness of the walls, and the presence of inflammatory processes.
- Tomography of the spinal column (or MRI). Performed after ruling out cardiac pathology. During the manipulation, the size of the intervertebral spaces and the condition of the bone tissue, the presence of disc protrusions and pinched neurovascular roots are assessed.
The laboratory evaluates biochemical markers (ALT and AST), their increase indicates the development of a heart attack or myocarditis. More modern ways to determine acute necrosis are to increase the concentration of troponins in the blood.
How to eliminate pain
Providing assistance depends on the cause of the pain, it is carried out as follows:
- "Nitroglycerin" and "Aspirin" during angina pectoris.
- "Analgin" or "Ibuprofen" for pinched roots. Simultaneous use of ointments and gels “Deep-relief”, “Menovazin”.
- In case of a heart attack, aneurysm or embolism, the attack is stopped in intensive care with the use of narcotic analgesics.
If pain radiates to the abdominal area, you should not self-prescribe treatment until a doctor arrives. This will help eliminate acute conditions of the abdominal organs.
Diagnosis of intercostal neuralgia
Make an appointment Shpigel Anna Yakovlevna Neurologist, massage therapist 33 years of experience. The specialist receives: - newborn children and schoolchildren - adults - athletes Reviews from patients Consultation from 3000 rubles.
Acute intercostal neuralgia is a reason to contact a competent, qualified neurologist. Since symptoms in adults with damage to the thoracic nerves can be disguised as other diseases, the patient must undergo a comprehensive examination to exclude possible pathology. The doctor must conduct a survey and examination.
The person’s posture is noteworthy when he leans towards the healthy side, so as not to provoke a painful attack. Palpation of the chest reveals pain. Trigger points are identified at the lower edge of the rib, where the affected nerve passes. If neuralgia affects several nerve branches, which often happens, this leads to a decrease or complete loss of sensitivity in the corresponding area of the body.
First of all, the doctor must distinguish the symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the left from cardiovascular pathology. For this purpose, the patient undergoes an ECG. If indicated, a cardiologist is consulted. In order to correctly diagnose and treat intercostal neuralgia, the doctor also excludes diseases of the respiratory system, digestive tract, musculoskeletal system, infectious processes and other diseases. He may prescribe a number of additional tests (laboratory tests, x-ray of the lungs, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, MRI of the spine, etc.).
Thoracic neuralgia is an indication for electroneurography. This method allows you to determine the condition of nerve fibers by assessing their structure and functionality.
Chest neuralgia can be a manifestation of benign and malignant tumors. It is often the first symptom of a herniated disc and degenerative changes in the spine. Therefore, early identification of its causes is considered an important task for the neurologist and the patient.
Expert advice
If severe pressing pain appears in the chest area, I recommend that a person adhere to the following tactics:
- calm down and take a position in which some relief is felt;
- stop any active movements;
- take Aspirin and put a Nitroglycerin tablet under your tongue;
- in the case where a history of angina pectoris was diagnosed, during a prolonged attack, continue to use sublingual nitrates every 15-20 minutes;
- Call an ambulance and, before it appears, try to determine the nature of the sensation (dependence on breathing, posture, movement).
It is very important to tell the doctor what preceded the attack, after which it began, and what measures were taken to eliminate it.
Forecast and prevention of intercostal neuralgia
In most patients, intercostal neuralgia can be completely cured. If thoracalgia occurs against the background of a herpetic infection, relapses are possible.
If adequate treatment of neuralgia does not bring the desired result, a more “deep” diagnosis is carried out to search for the possible cause of this condition. First of all, spinal hernias, benign and malignant tumors are excluded.
To prevent neuralgia of the intercostal branches from recurring, and its symptoms in adults to manifest themselves less painfully, doctors recommend the following preventive measures:
- follow the canons of a healthy lifestyle: give the body adequate physical activity, eat right, actively relax in the fresh air, give up bad habits, etc.;
- maintain normal functioning of the immune system;
- monitor posture and spinal health;
- promptly treat chronic diseases and infectious processes;
- if possible, visit the pool and harden yourself;
- undergo preventive examinations on time;
- undergo regular scheduled examinations by an osteopath approximately once every six months.
If a person has previously had thoracic neuralgia, he should not be overcooled, be in a draft, expose the body to excessive physical stress, perform sudden movements or remain in an uncomfortable position for a long time. In addition, it is necessary to eliminate or minimize as much as possible stress and any unfavorable factors that can cause symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the left, right or both sides.
Did you like the article? Add the site to your browser bookmarks
Case from practice
A 56-year-old woman came to see me with complaints of chest pain that radiated to her arm.
She noticed her first attacks 1.5 years ago, with a history of large-focal infarction of the anterior wall. Palpation reveals increased sensations in the area of the 6-7 thoracic vertebrae. Some relief is noted after lying on a flat, hard surface. After taking an ECG and conducting additional drug tests, cardiac pathology was excluded. The patient was referred for consultation to a neurologist. An MRI reveals an intervertebral hernia. Treatment is rest during an exacerbation, NSAIDs, massage, electrophoresis with novocaine, traction. After completing the full course, my condition is satisfactory.