Nuchal contusion is a large and heterogeneous group of injuries with an incidence of 100–500/100,000 inhabitants per year. During life, these lesions are registered in 3.7% of men and 2.4% of women. The increase in head and cervical spine injuries is explained by civilizational factors: 45% of injuries are due to road accidents, 30% to falls, 20% to professional and sports injuries. Why can’t you hit the back of the head, why are such injuries dangerous?
Consequences of a bruised head
In the vast majority of cases, a blow to the back of the head during a fall occurs without complications. Unfortunately, this cannot be said in advance. What are the dangers of such an injury?
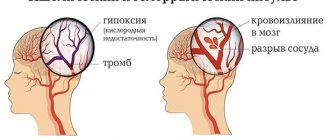
If the back of the head is contused, the consequences may include swelling of the brain, which usually develops within 24 hours. People who do not lose consciousness or who quickly emerge from unconsciousness require special attention. Such people are often perceived as completely healthy, and the risk of complications is not taken into account. After injury, the brain behaves like other parts of the body. If your ankle is injured, no one will be surprised by its swelling only on the 2nd day. The same thing happens to the brain. But unlike the ankle, the brain has no room to expand. It can only expand within the hard skull, but the space between it and the main cranial bone is a maximum of 0.5 cm, it is filled with almost incompressible cerebrospinal fluid, therefore, swelling, the brain contracts, which leads to its damage.
Sudden severe headaches after a blow to the back of the head are very dangerous. Headache, nausea, vomiting, and memory impairment are symptoms that suggest a suspected concussion. A medical examination and a CT or MRI are required.
The same applies to conditions when not only does the head hurt after a blow to the back of the head, but other symptoms are also present:
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- visual disturbances;
- loss of sensation in the hands or feet;
- stiffness of the facial muscles.
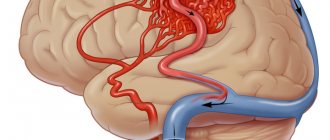
Bleeding into the brain may occur.
Bleeding into the brain is dangerous not by the amount of blood lost, but by the fact that even a very small hemorrhage suppresses the brain.
Important! The fact that an injured person who hits the back of their head quickly recovers from unconsciousness or does not lose consciousness at all does not mean that their condition will not worsen the next day.
First aid
If a person hits the back of their head, it is recommended to apply a cold compress to the affected area. You can use ice wrapped in a cloth or a bottle filled with cold water. You need to keep the compress for 15-20 minutes, then take a half-hour break and repeat the procedure. It is extremely important to monitor your pulse and breathing. If blood appears, the wound should be disinfected and bandaged.
A severe concussion is accompanied by poor circulation and severe hematomas around the eyes. The injured person should be kept at rest. The victim may feel sick, so it is necessary to turn him on his right side so that the vomit can come out freely and air can enter the lungs. It is recommended to tilt your head back slightly and tilt your face closer to the floor. Limbs should be placed at an angle of 90 degrees to prevent fractures during convulsions. It is necessary to call an ambulance and not take any action until the doctor arrives.
It is not recommended to give painkillers, as they interfere with the diagnosis of the injury.
Types of occipital headache after a blow
Types of pain that occurs after a blow to the back of the head:
- superficial (superficial) – better localizable, localization depends on the number of afferent fibers; there is sensitivity of the lips, tongue, hands;
- deep somatic - pain transmitted from the periosteum, muscles and ligaments, has a dull nature, longer duration; most often occurs in sports (when a person is hit in the back of the head - martial arts);
- visceral – characterized by transmission to various superficial areas; pain is transmitted along the surface of the body innervated by the same spinal segment;
- radicular - occurs when the dorsal roots are irritated, pain can affect the entire area of innervation of the affected segment, the pain is sharp, irregular attacks are typical;
- neuralgia - pain in the area of the brain or spinal nerves, can be caused not only by injury, but also by infection; the pain is caused by the hypersensitivity of neurons, i.e. we are not talking about a morphological lesion;
- causalgia - nerve damage that causes irritation of the dorsal spinal roots; the pain is paroxysmal.
First aid for head injuries
First aid for a blow to the back of the head is necessary for the victim immediately after the incident, without waiting for the ambulance to arrive. Of course, an ambulance also needs to be called, since in the future the wounded person will need professional treatment from doctors. What to do in this situation:
- Place the injured person on the floor or sofa (depending on location) so that he remains at rest.
- Apply a compress to the bruised area. This could be a frozen product from the freezer or a piece of ice wrapped in a towel; also use a bottle with cool liquid. The compress should be applied for no more than 15 minutes, then removed for half an hour and applied again.
- If the victim experiences a feeling of nausea, he must be turned on his side.
Note! You only need to do what will alleviate the condition of the wounded person, but you should not give painkillers immediately after a bruise until an ambulance arrives. This may interfere with the examination and diagnosis of the injury.
Treatment of trauma to the occipital part of the head
In case of injury in the back of the head, a medical examination and a calm regime are necessary. According to the dynamics of subjective symptoms and objective neurological results, a CT scan is sometimes performed, an examination that can detect increases in brain depression, subdural or epidural hematoma. In this case, neurosurgical intervention is necessary - elimination of the hematoma. Rare post-traumatic hydrocephalus is usually resolved by inserting a shunt. The cervical spine is secured with a cervical collar. Appropriate medications are used to suppress other associated symptoms of neck injury:
- symptomatic analgesics;
- weak opioids;
- NSAIDs;
- tricyclic antidepressants.
Rehabilitation treatment is added later.
Important! If you hit the back of your head, a difficult-to-control protracted pseudoneurasthenic syndrome sometimes develops.
If you hit the back of your head and there is a suspicion of damage to the cervical spine, you need to be careful in your actions to prevent deterioration of your general condition during manipulation.
It is advisable to relieve increasing pain from the very beginning with medications from the NSAID group (Brufen, Ibalgin, Ibuprofen). If pain persists, consult a doctor.
If no serious damage is found during the inspection, the following measures may help:
- Massage. After determining the location of the injury, massage of a specific group of muscles in the back of the head effectively eliminates the consequences of the injury. The correct technique of the procedure is important, so massage is performed only by a professional.
- Physiotherapy. The physiotherapist creates a combination of suitable exercises designed to involve all injured muscles and ligaments in the back of the head. Therapeutic exercise improves blood circulation, which provides good results in eliminating and preventing the consequences of injury.
- Physiotherapy. Physiotherapeutic methods include magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, ultrasound or laser treatment.
- Chiropractic. Carrying out this method belongs only to the hands of a specialist!
- Acupuncture. This therapeutic method is advisable when signs of neuralgia appear.
- Regime measures. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is an important part of treating the consequences of neck injuries.
Prescribing treatment without proper examination, determining the causes and localization of damage is unacceptable!
Pharmacotherapy
In recent years, pharmacotherapy has been overused and often inappropriately. Without careful clinical evaluation, drug treatment is useless. In addition, drug treatment primarily does not affect the underlying cause of the disease, but only its consequences. Therefore, proper rehabilitation is a much better solution. For acute painful symptoms after a blow to the back of the head and injury to the cervical spine, NSAIDs are most often used in combination with muscle relaxants. The essence of this therapy is the analgesic effect and the effect on reflex muscle spasms.
Muscle relaxants help relax muscle spasms and relax skeletal muscles. Depending on the mechanism of action, they are divided into 2 groups:
- peripheral;
- central.
Peripheral muscle relaxants block the action of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. They are used in anesthesia or when short muscle relaxation is necessary. In contrast, central muscle relaxants are active in the brain stem and spinal cord, where they dampen reflexes. They are often used to treat acute painful muscle spasms after injuries to the back of the head or when spinal problems occur.
Diagnostic methods
The degree of damage is assessed using MRI images.
In order to diagnose damage caused by trauma to the occipital part, it is necessary to consult a neurologist. The specialist will evaluate the biomechanics of the cervical spine, determine range of motion and muscle tone.
Clinical diagnosis is based on examination results. If it is impossible to clarify it, additional procedures are carried out. MRI, CT and echoencephalography are usually prescribed.
Types of head injury
If a person falls and hits his head, it is necessary to consult a specialist for advice. The impact can cause serious traumatic brain injury. There are three types of injuries:
- Concussion. In this case, there is nausea, loss of consciousness, vomiting is possible, and bright light and noise can be irritating.
- Brain contusion. Loss of consciousness can last for several hours, speech is impaired and facial muscles become paralyzed. If the injury is severe, the victim may fall into a coma for several days, while the pupils practically do not react to light.
- Compression of the brain. It is considered the most severe injury. The cause may be a hematoma formed due to a bruise or fragments of cranial bones may put pressure on the brain.
Important! If the brain is compressed, urgent surgical intervention is necessary.
Does protective equipment help prevent injury?
One of the most common misconceptions is that you can rely on protective equipment to completely avoid injury. In fact, protective equipment cannot guarantee perfect safety for a fighter. Some damage is actually reduced due to specialized equipment. This, in particular, reduces the force of the impact and slows down its speed of movement.
But protection cannot protect the central nervous system from damage during blows to the head , since there are many nerve endings under the vault of the skull. For this reason, head protection has become more common in martial arts. For example, in a form of martial arts such as wrestling, special headphones are required.
Basically, of course, they protect the ears, since the cartilaginous parts of the ears break quite easily, but they can also somewhat soften the force of a blow to the head. In boxing, protective helmets are often used, which reliably protect against various impacts, and at the same time provide sufficient visibility. This innovation is believed to have contributed to a significant reduction in injuries among boxers. Important: An athlete may lose consciousness due to a strong blow to the neck or to the area of the so-called solar plexus. The latter is a particularly vulnerable point on the human body. If the abdominal muscles are relaxed at the moment of impact, then the likelihood of shock from pressing the nerve endings to the spine is very high.