The perinatal period is the period from the 28th week of pregnancy to the 7th day after birth, inclusive. If during this period, as a result of exposure to various unfavorable factors, damage to the child’s brain occurs, accompanied by neurological symptoms, then such damage is called perinatal damage to the central nervous system or perinatal encephalopathy.
The concept of perinatal damage to the central nervous system combines several pathologies resulting from damage to brain cells in the perinatal period and leading to dysfunction. Damage to the central nervous system in the perinatal period can lead to the development of serious diseases later (cerebral palsy, delayed psychomotor and psycho-speech development, etc.).
Perinatal encephalopathy manifests itself as various disorders in motor development, impaired speech formation, and mental disorders.
Perinatal encephalopathy is a syndromic diagnosis and requires mandatory clarification. That is, it is necessary to examine the child in order to find out which specific departments are damaged and to what extent, and what functions this damage affects. A detailed examination will allow the doctor to prescribe adequate treatment and minimize the consequences of the damage.
Risk factors
The development of perinatal encephalopathy in the fetus and child can lead to
- chronic maternal intoxication and chronic diseases
- infectious diseases during pregnancy
- disorders of uteroplacental blood flow, placental abruption, fetoplacental insufficiency
- Umbilical cord entanglement
- maternal diseases associated with metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, phenylketonuria, etc.)
- severe toxicosis;
- pathological course of labor, use of obstetric aid, weakness of labor, rapid labor
- prematurity;
- Fetal malformations
Symptoms, how PCNSL manifests itself
Perinatal encephalopathy is a very multifaceted disease. The following main clinical syndromes of PPCNSL are distinguished:
- Muscular dystonia is a pathological increase or decrease in muscle tone. Normally, all newborns have increased muscle tone of the flexors; in the process of growth and motor development, the flexor tone decreases, becoming normal. This transformation allows a newborn child to have the necessary set of protective reflexes, and during the process of growth, a decrease in flexor tone makes it possible to develop movements. In cases where muscle tone has not decreased in a timely manner or does not change symmetrically, this significantly interferes with the normal development of the child’s motor sphere, the formation of postural control and normal movements.
- Neuro-reflex excitability syndrome is a disorder of sleep and wakefulness, an overly active reaction to sounds and touches.
- CNS depression. Lethargy, apathy, decreased tone and reflexes, drowsiness.
- Intracranial hypertension. This syndrome occurs when intracranial pressure increases. Increased excitability, obsessive screaming, regurgitation, bulging fontanel and Graefe's symptom are most characteristic of this syndrome. Intracranial hypertension can lead to the development of hydrocephalus—a decrease in the volume of brain tissue and its replacement with fluid.
- Convulsions (convulsive syndrome) are involuntary contractions of the muscles of the entire body, accompanied by loss of consciousness or simply “freezing” for several seconds. Convulsive syndrome is dangerous because, if left untreated, it significantly disrupts the normal development of the brain and its function.
Osteopathic treatments
Osteopathic treatment of central nervous system lesions in newborns is aimed at eliminating anatomical dysfunctions in the newborn’s body, restoring normal biomechanical relationships of all bones and joints, as well as soft tissues damaged during traumatic birth. Examples of techniques that are included in the osteopathic course of treatment for newborns:
- Fascial decompression of the sacrum, sacrolumbar joints.
- Removal of blocks at the level of the articulation of the first cervical vertebra and the skull.
- Balancing the tone of the thoracoabdominal diaphragm.
- Release (normalization of muscle tone) of the upper aperture of the chest, collarbones, shoulder blades, first rib.
- Decompression of sphenobasilar synchondrosis.
- Balancing the mutual tension membranes of the cranial cavity and spinal cord.
- Elimination of intraosseous damage to the occipital, temporal, and sphenoid bones resulting from injuries during childbirth.
- Correction of blood outflow and cerebrospinal fluid circulation in the cranial cavity.
- Balancing and balancing techniques.
The goal of treatment is to ensure that there are no tensions, blocks, or dysfunctions in the newborn’s body, so that it functions as an ideally tuned biomechanical system. The entire future life of the baby and diseases that may appear due to missed birth injuries depend on this.
Treatment and rehabilitation for PCNSL
Treatment of PPCNS begins with measures to prevent it.
Before birth, mandatory monitoring of the fetal condition is carried out and, if any abnormalities are present, treatment is immediately prescribed. In severe cases, surgical delivery may be required.
During the perinatal period, children with suspected PPCNS are observed by a neonatologist. At this stage, intensive therapy is carried out, the child is in a specialized department.
After stabilization of the condition, in the absence of a threat to life, the recovery process begins - rehabilitation. The goal of this stage is to minimize the effects of brain damage.
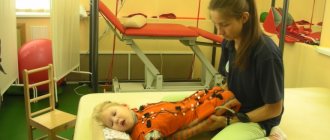
At this stage, medications are used that improve trophic processes in brain tissue, massage to normalize tone and stimulate tactile and proprioceptors, exercise therapy and kinesiotherapy (Bobat, Vojta, etc.) to develop motor skills and prevent the development of contractures, it may also be necessary the use of special orthopedic devices to prevent or correct limb deformities. Botulinum therapy can be used to reduce tone.
The most important thing is to remember that all rehabilitation activities are carried out for one purpose - to provide an opportunity for the child to develop skills and make him as independent as possible in adulthood. Each child’s body is unique and the result of recovery in each specific case is very difficult to predict, however, the correct and consistent use of rehabilitation methods and techniques allows you to achieve maximum results. Cases of partial or complete restoration of central nervous system functions after PCNSL are far from uncommon.
Main complaints
Pathology of the nervous system in newborns does not appear immediately, and this is its insidiousness. After all, the longer the disease remains unrecognized, the more difficult it is to treat it in the future. Only very pronounced disorders make themselves felt in the first days of the baby’s life, usually manifesting themselves in convulsions. Seizures that occur in the first 24 hours after the baby is born are especially dangerous.
Most often, parents pay attention to the child’s hyperexcitability, restless behavior, and sleep disturbances. Also often associated symptoms are excessive regurgitation and choking. Some mothers manage to notice disturbances in motor functions. As a simple home test, you can use a child's skills screening test depending on age.
Screening test. Normal full-term baby:
- By 2 months he can hold his head while lying on his stomach.
- By 6 months, sits independently and steadily.
- At 12 months – the beginning of independent walking.
Children with traumatic lesions of the spinal cord at the neck level are delayed by 1-2 months, however, their developmental delay is not as severe as with damage to the cerebral cortex.
Based on the pace at which the child develops, one can approximately judge the presence of neurological abnormalities and consult a doctor in time. The doctor will conduct more detailed studies that will show the diagnosis and level of damage to the nervous system.
Our rehabilitation programs for PCNSL
We provide comprehensive treatment for the consequences of perinatal CNS damage.
Typically, a rehabilitation program includes:
- Observation by a neurologist. The participation of this doctor is necessary, since the child’s condition must be monitored during the process of rehabilitation measures
- Observation by a physical therapy doctor (rehabilitation specialist). The basis of any rehabilitation is the development and restoration of motor skills. A physical therapy doctor will examine a small patient and plan the rehabilitation process, helping to prioritize physical treatment.
- Observation by a neuropsychologist and sessions with a neuropsychologist. The participation of a neuropsychologist in rehabilitation after PCNSL is necessary starting from 2 years of age. The tasks of a neuropsychologist include diagnosing disorders of higher nervous activity in a child, planning and implementing measures to correct them. Neuropsychologists conduct group and developmental classes with children to develop memory, attention, motivation, and thinking. The neuropsychologist also provides family counseling.
- Exercise therapy and kinesitherapy. We are proficient in various exercise therapy techniques. It is impractical to single out just one among them. Exercise therapy techniques are tools in the hands of a doctor and instructor. We try to select the appropriate instrument for each of our patients. The most commonly used methods in children are Bobath therapy and Vojta therapy. We also use PNF, Neurac, manual therapy techniques and many others in our work.
- Massage. Massage plays an important role in the rehabilitation of children. Naturally, it is not an independent procedure, but its reasonable use allows the child to become more aware of his body and helps him learn to control it. In addition, massage in rehabilitation solves many auxiliary problems - eliminating swelling, improving muscle nutrition, temporary decrease in tone, etc.
- Physiotherapy. We widely use physiotherapeutic treatment in rehabilitation after PCNSL. The objectives of physiotherapy are very diverse and depend on the characteristics of the disease. The most commonly used are medicinal electrophoresis, IR dipole, phototherapy, and magnetic therapy.
- If necessary, a speech therapist may be included in the rehabilitation team. Typically, the need to involve this specialist arises when there is a delay in speech development or alalia.
If you have any questions or want to sign up for a rehabilitation program, call us at: +7 (812) 309-67-26 or leave a request through the contact form on the website.
Development of the central nervous system and signs of pathology
- home
- Archive
- Archive of articles
- Baby
- Development of the central nervous system and signs of pathology
Perinatal damage to the nervous system is precisely this diagnosis that is increasingly being made to newborn babies. Behind these words lies a fairly large group of various lesions of the brain and spinal cord that occur during pregnancy and birth of a baby, as well as in the first days of his life. Periods of the disease During this disease, despite the variety of causes that cause it, it is customary to distinguish three periods: acute (1st month of life), recovery, which is divided into early (from the 2nd to 3rd months of life) and late (from 4 months to 1 year in full-term infants, up to 2 years in premature infants), and the outcome of the disease. In each of these periods, perinatal injuries have different clinical manifestations - syndromes, and several of them may be present simultaneously in one child. The severity of each syndrome and their combination make it possible to determine the severity of damage to the nervous system, prescribe the correct treatment and predict the further development of the disease. Acute period syndromes Acute period syndromes include comatose, convulsive, hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndromes, as well as central nervous system depression and increased neuro-reflex excitability. With mild damage to the central nervous system in newborns, a syndrome of increased neuro-reflex excitability is most often observed, which is manifested by shuddering, increased (hypertonicity) or decreased (hypotonic) muscle tone, increased reflexes, tremor (trembling) of the chin and limbs, restless shallow sleep, frequent causeless crying . With moderate damage to the central nervous system in the first days of life, depression of the central nervous system occurs in the form of decreased motor activity and muscle tone, weakened reflexes of newborns, including sucking and swallowing. By the end of the 1st month of life, depression of the central nervous system gradually disappears, and in some children it is replaced by increased arousal. With an average degree of damage to the central nervous system, disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and systems are observed (vegetative-visceral syndrome). Due to imperfect regulation of vascular tone, uneven coloration (marbling) of the skin appears. In addition, there are disturbances in the rhythm of breathing and heart contractions and dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract in the form of unstable stools, constipation, frequent regurgitation, and flatulence. Often, children in the acute period of the disease show signs of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome, which is characterized by excessive accumulation of fluid in the spaces of the brain containing cerebrospinal fluid, which leads to increased intracranial pressure. The main symptoms that can be noticed not only by doctors, but also by parents are the rapid growth rate of the child’s head circumference (more than 1 cm per week), significant size and bulging of the large fontanelle, divergence of cranial sutures, restlessness, frequent regurgitation, unusual eye movements (nystagmus). ). A sharp depression of the activity of the central nervous system and other organs and systems is inherent in the extremely serious condition of a newborn with the development of coma syndrome (lack of consciousness and coordinating function of the brain). This condition requires emergency care in intensive care. Syndromes of the recovery period During the recovery period, parents should be alert to poor facial expressions, late appearance of a smile, decreased interest in toys and environmental objects, as well as a weak monotonous cry, delayed appearance of humming and babbling. Perhaps all this is a consequence of lesions of the central nervous system, in which, along with others, syndromes of motor disorders and delayed psychomotor development occur. Outcomes of the disease By the age of one year, in most children, manifestations of perinatal lesions of the central nervous system gradually disappear. Frequent consequences of perinatal lesions include: • delayed mental, motor or speech development; • cerebroasthenic syndrome (mood swings, motor restlessness, anxious sleep, weather dependence); • attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: aggressiveness, impulsivity, difficulty concentrating and maintaining attention, learning and memory disorders. The most unfavorable outcomes are epilepsy, hydrocephalus, and cerebral palsy, indicating severe perinatal damage to the central nervous system. Causes of disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system Experts distinguish four groups of perinatal lesions of the central nervous system: 1) hypoxic, in which the main damaging factor is hypoxia (lack of oxygen); 2) traumatic, resulting from mechanical damage to the tissues of the brain and spinal cord during childbirth in the first minutes and hours of the child’s life; 3) dismetabolic and toxic-metabolic, the main damaging factor of which is metabolic disorders in the child’s body, as well as damage resulting from the use of toxic substances by a pregnant woman (medicines, alcohol, drugs, smoking); 4) damage to the central nervous system during infectious diseases of the perinatal period, when the main damaging effect is exerted by an infectious agent (viruses, bacteria and other microorganisms). Help for children with central nervous system damage Infants with central nervous system damage need treatment and rehabilitation as early as possible, since in the first months of a child’s life many of the disorders are reversible without serious consequences. It is during this period that the regenerative abilities of the child’s body are especially great: it is still possible for the nerve cells of the brain to mature to replace those lost after hypoxia, and for the formation of new connections between them, which will be responsible for the normal development of the baby. First aid is provided to babies in the maternity hospital. This stage includes restoration and maintenance of vital organs (heart, lungs, kidneys), normalization of metabolic processes, treatment of central nervous system damage syndromes (depression or excitation, seizures, cerebral edema, increased intracranial pressure). The basis of treatment is medication and intensive therapy. During treatment, the child's condition gradually improves, however, many symptoms of central nervous system damage may persist, which requires transfer to the pathology department of newborns and premature infants or to the neurological department of a children's hospital. At the second stage of treatment, drugs are prescribed aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease (infections, toxic substances) and affecting the mechanism of development of the disease, as well as drugs that stimulate the maturation of brain tissue, reduce muscle tone, improve the nutrition of nerve cells, cerebral circulation and microcirculation. In addition to drug therapy, when the condition improves, a course of massage with the gradual addition of therapeutic exercises, electrophoresis sessions and other rehabilitation methods are prescribed (for full-term infants - from the end of the 3rd week of life, for premature infants - a little later). After completing the course of treatment, most children are discharged home with recommendations for further observation in a children's clinic (third stage of rehabilitation). The pediatrician, together with a neurologist, and, if necessary, with other specialized specialists (ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, orthopedist, psychologist, physiotherapist), draws up an individual plan for managing the child in the first year of life. During this period, non-drug rehabilitation methods are most often used: massage, therapeutic exercises, electrophoresis, pulsed currents, acupuncture, thermal procedures, balneotherapy (therapeutic baths), swimming, as well as psychological and pedagogical correction aimed at developing the baby’s motor skills, speech and psyche. Parents whose baby was born with signs of a central nervous system disorder should not despair. Yes, you will have to put in much more effort than other moms and dads, but in the end they will pay off, and the reward for this work will be the happy smile of the little man.