Ischemic stroke
Treatment of the consequences of ischemic stroke can be divided into several areas:
- Restoration of movement (sessions with a physical therapist, aquatherapy, exercises on simulators, use of modern techniques: Bobath therapy, Exarta, PNF method);
- Returning independence in everyday life (sessions with an ergotherapist in a specially equipped training apartment);
- Restoration of speech and swallowing;
- Drawing up a menu with the recommendations of the attending physician;
- Blood pressure control and drug therapy;
- Hygiene procedures (including ostomy care and ostomy removal);
- Symptomatic treatment (prevention or treatment of bedsores, pain relief, etc.);
- Restoring control of the pelvic organs;
- Treatment of depression, help from a psychologist.
The rehabilitation program is carried out in three stages.
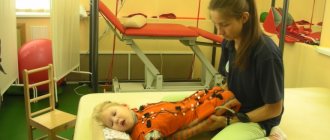
The first stage begins in the first days after an ischemic stroke. The possibilities for active rehabilitation are limited, since the patient is in bed and inactive. The patient is turned over, massaged, and breathing exercises are performed.
It is important to communicate with the patient, even if his own speech is impaired or he cannot respond. Speech perception affects the functioning of functional areas of the brain and has a positive effect on the emotional and physiological state of a person.
The second stage lasts up to several months after the stroke. It can take place either directly in a hospital or in a specialized rehabilitation center. During this period, massage, therapeutic exercises, and physiotherapy are prescribed. Specialists work on speech and cognitive functions (memory, thinking, imagination). This stage can last up to six months: it all depends on the severity of the stroke.
In the late, third, rehabilitation period, active methods are used to restore functions and skills. Fine motor skills and self-care skills are restored. It is also important to develop the patient’s commitment to rehabilitation measures and a positive attitude.
In some cases, one or two courses of rehabilitation are sufficient (the patient is discharged with detailed recommendations and a set of exercises to be performed at home).
deals with treatment after ischemic cerebral stroke. Each specialist conducts an individual examination of the patient and sets time-bound and achievable goals. Team members interact and exchange information to ensure that rehabilitation is effective.
Treatment and rehabilitation after stroke
Therapeutic physical education (PT)
The most important method of restoring motor functions. It is prescribed as soon as the patient’s condition allows him to make feasible movements. The main goal is full or partial restoration of motor function of the body, strength and dexterity in the limbs, and coordination of movements.
In the early period, the patient engages in passive gymnastics together with a physical therapy specialist. Exercises help normalize the tone of the limbs and eliminate the risk of bedsores.
The next stage is active gymnastics. The patient first learns to get out of bed, maintain balance, then walk with support, and then independently. An important component is the restoration of fine motor skills, which is necessary for the patient’s social adaptation. Specialists help to relearn eating, personal hygiene skills, dressing independently, etc.
Massotherapy
Along with exercise therapy, it is an integral part of the rehabilitation program for the return of physical activity. Massage helps relieve pain, eliminates muscle spasms, preserves joint function, and prevents the formation of bedsores at the initial stage, when the patient moves little. In addition, massage prevents pulmonary complications. It also improves blood circulation and normalizes the general condition of the body. Massage is carried out throughout the entire rehabilitation period.
Speech rehabilitation
Speech impairment occurs in more than a third of people who have had a stroke. Moreover, this dysfunction may include not only the loss of the ability to pronounce words independently, but also impaired understanding of the speech of others, forgetting the names of objects and actions. In addition, the articulation of sounds is often impaired, and reading and writing skills are lost. To combat these disorders, long-term classes are required to restore speech functions, which are conducted by a speech therapist-aphasiologist.
It is necessary to start classes already in the initial period, when the level of consciousness allows. Then the exercises become more complicated and the duration of the sessions increases. It is also important for the patient’s family and friends to get involved here. For rehabilitation, not only professional exercises are important, but also constant speech contact at the everyday level.
Drug therapy
It is impossible to achieve stable results without medications. With the help of medications, doctors relieve pain and improve blood circulation, which is necessary to restore the functions of the affected areas of the brain. Medicines also help eliminate the risk of complications. Therapy is carried out only as prescribed by the attending physician. After discharge from the medical center, be sure to take medications!
Psychological therapy
A psychotherapist constantly works with patients during rehabilitation. It helps to cope with depressive emotions, eliminate obsessive thoughts and believe in yourself.
Diet
As a result of a stroke, the blood supply to the brain and blood vessels are affected. Therefore, it is extremely important to reduce your intake of foods containing cholesterol. It is recommended to exclude fatty fried foods and fatty meats from the diet, and reduce salt intake to a minimum. The basis of nutrition should be foods high in fiber and complex carbohydrates. These are vegetables, fruits, cereals. You need to eat foods with polyunsaturated fatty acids: fish, seafood. Low-fat dairy products, boiled or stewed lean meat, bran bread, etc. are also suitable.
In the initial stages of treatment, when it is still difficult for a person to chew, it is necessary to give him only boiled food, preferably pureed. If you are undergoing inpatient therapy, specialists will develop a special diet for the patient and ensure that only the right foods are consumed.
Which doctors treat stroke?
Most patients with ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke are subject to urgent hospitalization in a specialized neurovascular (stroke) department or center, or, in the absence of one, in a neurological department. In case of violation of vital functions, they are hospitalized in the intensive care unit, in case of epi-, sub-, intracerebral hematomas - in neurosurgery.
The leading doctors in the treatment will be neurologists, neurosurgeons and neurovascular specialists. In addition to them, doctors of instrumental and laboratory diagnostics, cardiologists, ophthalmologists, psychologists, speech therapists, endocrinologists, rehabilitation specialists and physiotherapists, and other specialists take part in the treatment process.
Symptoms, signs of stroke
All symptoms of a cerebral stroke develop sharply, quickly, and appear suddenly:
- weakness, numbness, loss of sensitivity, paralysis of one half of the body or face, arms, legs;
- intense headache, described by patients as the worst in life;
- speech impairment (a person cannot speak or has difficulty doing so), misunderstanding of the interlocutor’s speech;
- deterioration in clarity of vision, it is unfocused or completely absent in one eye;
- dizziness, loss of coordination of movements, balance, walking, and sometimes loss of consciousness;
- nausea, vomiting.
Important: if you witness such symptoms, call an ambulance immediately! A stroke is an emergency condition that requires immediate emergency hospitalization!
Uninformed people can easily mistake such signs for alcohol or drug intoxication, so it is extremely important to know and distinguish the symptoms. After all, the speed of medical care plays a key role here - literally minutes count, death from stroke is directly related to delay. The sooner the victim is hospitalized, the less the consequences of a stroke will be and the higher the chances of saving life.
To make it easier to determine the occurrence of a stroke, doctors recommend using three basic recognition techniques. They are called the “UZP” rule, an abbreviation for the first letters of the words denoting the action that a person is asked to perform:
- U - smile. During a stroke, the smile often looks “crooked”, unnaturally skewed, when one corner of the mouth is lowered and the other is raised.
- Z – speak. Say a simple sentence like “Today they promised good weather.” Often (but not always!) there is incorrect pronunciation.
- P – raise your arms at the same time. If one arm involuntarily lags behind in movement or drops, there is a high probability of stroke.
When calling an ambulance, be sure to describe your symptoms to the dispatcher; such cases require calling a specialized resuscitation team and transporting them to a specialized clinic. You should not try to transport the patient to the hospital yourself, since not all medical institutions can provide the required set of emergency medical measures and precious time will be lost.
First aid for stroke
Before the medical team arrives, you need to provide assistance to the patient:
- Place in a horizontal position, raising the shoulders, neck and head 30° relative to the body (place a pillow, a cushion of clothing).
- Provide access to fresh air (unfasten tight clothing, open a window).
- Turn his head to the side to prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract.
Under no circumstances should you give food or water - partial paralysis of the swallowing organs can cause food or drink to enter the respiratory system and subsequent suffocation. In other words, a person may choke or choke, which is likely to cause death due to stroke.
Cost of initial appointment, research, treatment
It is advisable to talk about the price of the initial appointment during a preventive examination, when there is no stroke as such, but the person has pathologies that increase the risk of its development. The cost of diagnostic procedures for stroke can be found in the corresponding table, but it must be taken into account that many studies are used repeatedly to monitor the treatment process.
It is quite difficult to determine even the approximate cost of stroke treatment in Moscow. Much depends on the type of stroke, the extent of brain damage, the patient's condition, the timeliness of medical care and other important factors. In any case, the cost of medical services will be justified - after all, we are talking about preserving life.
Treatment of patients in specialized stroke departments, cardiology centers - stroke units (IB) - reduces mortality and disability by 20%, reduces financial costs at all stages of treatment.
Causes of stroke
A stroke can be caused by several reasons. The most important risk factors for this condition are smoking, a sedentary lifestyle, alcohol abuse, obesity, and genetic predisposition (cases of strokes in close relatives can be considered an indirect sign). The cause may vary depending on the type of stroke. The two most common types are described below:
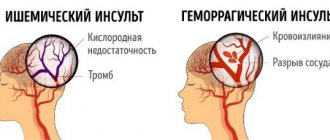
A hemorrhagic stroke occurs due to internal bleeding when a blood vessel inside the brain ruptures. Other names for hemorrhagic stroke are cerebral hemorrhage or intracranial hemorrhage. Among the causes of hemorrhagic stroke are:
- inactive lifestyle;
- increased stress levels;
- alcohol abuse;
- obesity;
- smoking.
Hemorrhagic stroke can also be caused by abnormal formation of blood vessels or rupture of dilated vessels (a complication of cerebral venous insufficiency).
Ischemic stroke occurs due to circulatory problems. A typical case is a blood clot blocking the lumen of a vessel. The cause of ischemic stroke can be:
- diabetes;
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- obesity;
- high cholesterol (causing cerebral atherosclerosis);
- smoking;
- arterial hypertension.
Atrial fibrillation, a type of irregular heartbeat, is another cause of ischemic stroke.
3-type-stroke Deathstroke
Stroke is one of the most common causes of premature death. In Russia, about 200 thousand people die from it every year. Approximately another 200 thousand become disabled. Of these, only 8% return to normal life.
Stroke is a non-infectious disease and means damage to blood vessels in the brain. For a long time it was defined by the word “apoplexy” - translated from Latin as “strike”. In fact, this is a blow to the blood vessels of the brain.
If you do not take strokes resulting from injuries or provoked by any congenital diseases or genetic abnormalities, they can be divided into three groups - ischemic, hemorrhagic and subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Non-traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage is less common, but this type of stroke is the most dangerous - almost 50% of cases are fatal. And even with early diagnosis and timely adequate treatment, a person is more likely to remain severely disabled for the rest of his life. The main symptom is an acute sharp headache like a “blow to the head,” often with pulsation in the occipital region; there are also vomiting, convulsions, and consciousness.
Hemorrhagic stroke, or bleeding in the brain, leads to death in 40% of cases. Symptoms - fever, headache, blurred vision - may not even have time to be noticed, because... A stroke develops quickly, usually during the daytime. Its causes can be either banal overexertion or hypertension, atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases, and at a young age – cocaine addiction.
Ischemic stroke, or cerebral infarction, is the most common. To recognize it, it is enough to remember the word “asymmetry”, because the area of the brain responsible for the motor function of the right or left part of the body is affected. A person cannot raise both arms and legs at the same time or smiles from one corner of his mouth. In addition, he may have confused speech, or he may lose the ability to respond to calls to him.
Risk factors leading to the development of ischemic stroke before old age include arterial hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, smoking and diabetes mellitus. All these factors often depend on the person himself: to prevent them, you need to not smoke, eat right and be physically active. What does it mean to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Prevention
Prevention should be aimed at identifying and correcting the main risk factors.
Atherosclerosis
It is necessary to constantly monitor the level of blood lipids - total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, VLDL, TG, CA. If you are prone to high cholesterol, you must follow the prescribed diet. If following a diet does not provide the desired reduction in cholesterol levels, statins are prescribed - drugs that lower blood lipid levels.
Arterial hypertension
If a diagnosis of “Arterial hypertension” is made, you should take all prescribed medications without skipping, even with normal blood pressure values. You need to keep a blood pressure diary, where you should enter your blood pressure and pulse readings. If blood pressure is unstable, there is a tendency to crises, the diary should be filled out 2 times a day - morning and evening. Such a diary will help the doctor choose the optimal therapy.
Rhythm disorders
Rhythm disturbances can be the result of many heart diseases, incl. myocardial infarction. If there are rhythm disturbances in the atria, most often atrial fibrillation, a person may not feel anything; these disturbances can be detected by taking an ECG. Atrial fibrillation causes the formation of thrombi - blood clots that can cause not only strokes, but also heart attacks of other internal organs.
If atrial fibrillation is detected, anticoagulants are prescribed - drugs that prevent thrombus formation. Taking anticoagulants increases the risk of bleeding. Anticoagulants should not be interrupted, and the drug or dose should not be changed without the doctor's permission.
When PMI or stroke occurs in people under 45 years of age without cardiovascular disease, rarer causes should be excluded.
Stroke is easier to prevent than to treat its consequences. In severe cases, patients remain bedridden despite all the efforts of doctors and relatives. In other cases, rehabilitation can take months or years. The network of boarding houses has created special programs for recovery after a stroke in boarding houses, which are aimed at speedy recovery under the supervision of specialists.
There are two types of stroke:
Ischemic – blood vessels in the neck or brain become blocked. More common, it can be triggered by thrombosis, embolism, or arterial stenosis. More often it occurs at night, while clarity of consciousness is maintained. With a mini-stroke, the blockage of blood flow is temporary, but the condition also requires immediate hospitalization.
Hemorrhagic (intracerebral) - occurs in 10-15% of cases, but 30-60% of them end in death. The blood vessel ruptures completely, allowing blood to flow into the brain. Often a stroke is provoked by an aneurysm, in less than 1% of cases - by an arteriovenous malformation (usually congenital). This type of stroke usually occurs during the day, as a result of excessive physical or emotional stress.