Traumatic brain injury (TBI) today is a growing problem in all developed countries with significant prevalence rates and serious economic consequences.
This diagnosis covers a wide range of injuries from concussion to severe contact and intracranial injuries of the skull. Thus, rehabilitation after traumatic brain injury is varied in its strategies, targeting demonstrated symptoms that functionally limit a person's activities, and with the ultimate goal of individual autonomy and reintegration with the community.
Traumatic injury to the skull and brain can significantly impact many cognitive, physical, and psychological skills. Physical deficits include movement, balance, coordination, fine motor skills, and muscular strength and endurance. Cognitive impairment ranges from mild intellectual deficits to severe forms of qualitative and quantitative impairment of consciousness. Psycho-emotional defects are found in defective behavior and emotional spectrum disorders.
Varieties
TBI is differentiated into closed and open forms. With the open version, the skin of the head and the wide tendon plate with which the muscles are fixed are damaged. The damage reaches the skull bones or deeper tissues. If the dura mater of the brain is damaged, then the open form is called a penetrating wound. With a closed version of TBI, the skin may be damaged, but the connecting plate is not affected.
Brain damage is classified into categories depending on the degree of the defect that occurs: mild, moderate (moderate) and severe. The Glasgow Coma Scale, the most commonly used system for classifying the severity of traumatic brain injury, assesses a patient's level of consciousness on a scale from 3 to 15. Diagnosis is based on the results of verbal, motor and visual responses to stimuli. It is believed that an index of 13 and above is a criterion for a mild disorder, from 9 to 12 for moderate (moderately severe), from 8 and below severe.
Causes
Brain damage can occur in many ways. These injuries usually result from accidents in which the head hits an object. Trauma can result in brain damage if someone hits a person hard on the head.
Damage to cranial structures is a common occurrence in head impacts during car accidents. Such situations can arise due to industrial accidents, thermal and chemical burns. Symptoms of CMP may develop as a result of birth trauma. Similar disorders can be caused by a lack of oxygen, poisoning, hemorrhage in the cranial cavity or neuroinfection.
What's the forecast?
If the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations and instructions, then everything ends in a complete recovery. Residual symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, and insomnia may persist for several months. Then they gradually decrease until they disappear completely.
If there are concomitant pathologies and medical recommendations are not followed, as well as with severe injuries, there may be complications in the form of VSD and even epileptic seizures, especially if alcohol habits are present.
What happens with a traumatic brain injury
A mild form of TBI is characterized by one or more of the following symptoms:
- attack of short-term loss of consciousness;
- loss of memory for events immediately before or after the injury;
- any change in mental status at the time of injury;
- focal neurological deficit.
Very often in such cases, the victim looks good outwardly, without realizing that functional problems are developing. Some people suffer from the long-term effects of TBI, known as post-concussion syndrome (traumatic encephalopathy). Persons suffering from this syndrome experience severe headaches, dizziness, decreased performance, weakness, insomnia and intellectual impairment.
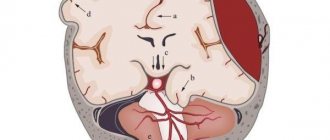
Most traumatic brain injuries result in widespread damage to brain structures. The brainstem, frontal and temporal lobes are particularly vulnerable to local injury from contusions due to their location near bony prominences.
In addition to regulating the basic functions of excitation and inhibition, the brain stem is involved in the processes of attention and short-term memory. Trauma in this area can also lead to autonomic dysfunction: disruptions in metabolism, thermoregulation, respiratory and cardiac activity.
The limbic system helps regulate a person's emotional status. Connected to the limbic system are the temporal lobes, which are involved in many cognitive skills such as memory and language. Damage to the temporal lobes is associated with a number of behavioral disorders.
The frontal lobe almost always suffers from injury due to its large size and location at the front of the skull. The frontal lobe is involved in many cognitive functions and is considered the center of control of emotions and behavior of the individual. Damage to this area can lead to decreased criticality and increased impulsivity.
Signs and symptoms
TBI can cause a wide range of functional short-term and long-term changes affecting cognitive, emotional, and behavioral areas.
As a result of brain damage, the following suffers:
- thinking (the process of modeling environmental patterns);
- attention (concentration and retention);
- memory (memorization, storage, reproduction of information);
- functions of the sense organs (vision, hearing, taste, smell, touch);
- speech activity (communication, expression and understanding of words);
- emotions and behavior (depression, anxiety, aggression, social unacceptableness).
Symptoms that may occur after a TBI:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- convulsions;
- loss of coordination of movements.
TBI can also cause epilepsy and increases the risk of conditions such as Alzheimer's-type dementia, Parkinson's disease and other brain diseases that become more relevant in old age.
Repeated mild brain injuries occurring over a long period of time (i.e., months and years after the initial episode) lead to cumulative neurological and cognitive deficits. Repeated moderate to severe TBIs occurring within a short period of time (i.e., hours, days, or weeks after the first event) can be catastrophic or fatal.
Periods, consequences and complications of TBI
The so-called traumatic disease includes three periods:
- Acute (duration 2 weeks – 2.5 months) – development of defense reactions to a damaging factor.
- Intermediate (duration 6 months – 1 year) – the process of lysis and repair in damaged areas.
- Long-term or final (duration 2-3 years, with complications - until the end of life) - completion of tissue degeneration and restoration of functions.
Complications of TBI in the acute phase:
- Impaired function of the respiratory system (respiratory depression and gas exchange disorders).
- Problems with central and regional (cerebral) circulation.
- Hemorrhagic complications (cerebral infarction, intracranial hemorrhage).
- Dislocation (displacement) of brain parts.
- Complications of a purulent-inflammatory nature: intracranial (abscesses, osteomyelitis, meningitis, encephalitis), extracranial (pneumonia, for example).
Possible consequences of TBI:
- Paralysis of the limbs (partial, complete) on one or both sides.
- Loss of vision, hearing, ability to speak, swallow, and breathe.
- Loss (weakening) of control over the function of the pelvic organs (the patient is not able to control the processes of urination and defecation).
- Tremor (shaking) in the limbs.
- Partial memory loss, deterioration of attention, changes in character and other consequences associated with higher nervous activity (usually after a coma).
In the long-term post-traumatic period, the development of epilepsy (acquired epilepsy), occlusive hydrocephalus, neuroses, and parkinsonism is possible. Also, cases of arachnoiditis and arachnoencephalitis (a disease of the central nervous system - serous (non-purulent) inflammation of the arachnoid membrane of the brain or spinal cord) are not uncommon.
Features of rehabilitation
If a person has suffered a traumatic brain injury, recovery and rehabilitation will be an important part of the treatment program. Rehabilitation can take different forms depending on the needs of the victim and may include physical therapy, vocational assistance, speech therapy, psychiatric care, psychotherapy, psychological correction and social support. All of these types of interventions are necessary to help the victim recover as quickly and fully as possible from the effects of the injury.
In the acute period after traumatic brain injury, rehabilitation is aimed at getting out of a coma and choosing a treatment strategy for a speedy recovery. With mild TBI, most patients recover quickly, but the effects of subsequent injuries can be devastating.
Complications of severe TBI that are functionally limiting and difficult to treat include heterotopic ossification, psychomotor agitation, and spasticity (involuntary movement and spasm of facial muscles). It should be borne in mind that the process of recovery from severe traumatic brain injury can be lifelong.
Psychotherapeutic techniques and exercise, along with pharmacological interventions, also aim to prevent long-term motor and cognitive impairment. In addition, rehabilitation of patients with traumatic brain injury targets long-term symptoms, including sleep disturbances, visuospatial deficits, cephalalgia, and cognitive dysfunction.
Employees of the Community for the Rehabilitation of Traumatic Brain Injuries of Irakli Pozharisky:
- help improve your ability to function fully at home and in the community;
- will reduce or completely eliminate mental and physical problems caused by TBI;
- provide emotional support;
- will tell you how to adapt to the changes that occur during recovery.
Rehabilitation carried out in the community of rehabilitation specialists Irakli Pozharisky can also help prevent complications of traumatic brain injury, such as:
- formation of blood clots (blood clots);
- pain syndrome;
- bedsores caused by prolonged lying in one position;
- breathing problems;
- drop in blood pressure when moving;
- muscle weakness and muscle spasms;
- problems with the intestines and bladder;
- deterioration of sexual function.
Products that are harmful due to concussion
Doctors are unanimous in their opinion and advise excluding the following foods from the diet during a concussion:
- fatty foods, which not only impair blood circulation in the brain, but also lead to gaining extra pounds;
- various spices and seasonings: they are irritants to the nervous system;
- confectionery and various sweets;
- spicy and salty foods;
- alcohol (strictly prohibited in case of injury): it not only destroys neurons, but also has a negative effect on cerebral circulation and the central nervous system;
- strong coffee and tea: they contribute to increased blood pressure.
All of the above products can cause serious harm in case of a concussion. During this period, it is necessary to be especially vigilant about what and in what quantity enters the body.
Proper nutrition is an integral part of injury recovery. It is important to remember that only comprehensive treatment and compliance with all recommendations leads to a quick and complete recovery of the patient. Not only medications and diet are important, but also a good mood, a positive attitude, fresh air and, of course, rest.
A severe concussion requires drug therapy in a hospital, where the patient is under full medical supervision. Only this method guarantees recovery and the absence of any complications.
What are the risks of rehabilitation measures after traumatic brain injury?
TBI rehabilitation performed by qualified and experienced professionals is unlikely to cause problems. But if you are not professionally literate, there is always a risk that parts of rehabilitation, such as physical or occupational therapy, could lead to new brain injuries or worsen existing symptoms. This risk occurs if rehabilitation measures are not carried out properly. This is why it is important to work closely with certified rehabilitation specialists who will take adequate measures to prevent worsening symptoms and prevent problems.
Prohibited and Not Recommended Products
In case of a concussion, it is recommended to remove some products from the menu at least temporarily or significantly limit their volume.
It is advisable not to eat many of the ingredients and dishes prohibited due to injury even after the end of therapy.
Refusal of them will affect your health in the most favorable way.
Diet restrictions for concussion:
- animal fats in large quantities or in the form of fried foods;
- smoked meats, pickles, marinades, ready-made sauces;
- aromatic spices and hot seasonings that have a stimulating effect on the nervous system;
- sugar in its pure form and in other products;
- chocolate, cocoa, confectionery, baked goods;
- semi-finished products, fast food.
The list of restrictions for the patient includes fast food.
If these restrictions are not followed, concussion symptoms will get worse or last longer than normal. They can also cause additional problems and discomfort.
How to prepare for rehabilitation after a traumatic brain injury
Before rehabilitation can begin, the victim must receive nursing care and medication. At the first stage, assistance to the patient includes the following activities:
- emergency treatment by ambulance staff;
- intensive therapy;
- surgery if indicated;
- use of pharmacological agents.
Once the patient's condition is stabilized and not life-threatening, most people who have had a moderate or severe traumatic brain injury require rehabilitation. Patients may need to relearn basic skills such as walking or talking. The goal of rehabilitation interventions is to improve patients' ability to perform daily activities.
Rehabilitation therapy usually begins in the hospital. Recovery from a traumatic brain injury can continue in specialized rehabilitation centers or in public outpatient departments. The type and duration of rehabilitation is different for everyone, and depends on the severity of the TBI and what part of the brain was damaged.
Drinks - what you can and cannot do
In addition to diet, during the recovery period after a concussion, you need to follow a drinking regime.
To calculate the daily volume of permissible fluid, you must consult your doctor. Sometimes a specialist recommends reducing this indicator in order to prevent cerebral edema. The optimal drinks for a patient with a concussion are pure water, green tea, juices, fruit drinks, compotes, and decoctions. All formulations, except the first, contain a large amount of vitamins and minerals. It is important to monitor the relationship between how much fluid the patient drinks and how much urine he excretes. If the first indicator significantly exceeds the second, you should inform your doctor about this. You will have to give up a number of drinks during treatment and recovery. Natural and artificial pathogens found in coffee, cocoa, black tea, sweet soda, and energy drinks pose a danger to the patient. The consumption of alcohol in any form or volume is strictly prohibited.
Who takes part in rehabilitation
Specialists involved in the recovery and rehabilitation process:
A physical therapist is a doctor trained in physical medicine and rehabilitation who oversees and controls the entire process. He teaches targeted movements, teaches how to maintain balance, and helps with walking.
Speech therapist who specializes in speech restoration after traumatic brain injury. It helps a person improve communication skills and use assistive communication devices if necessary
A clinical psychologist who evaluates cognitive impairment and performance helps a person manage behavior. It introduces the patient to coping strategies and also provides information necessary for emotional and psychological well-being.
An vocational psychologist who evaluates the ability to return to work and related vocational opportunities. It provides the client with information resources to solve common workplace problems.
Tour of the “Extramed” hospital
Comparison of the Extramed hospital with a state hospital and a paid department of a state hospital:
| Hospital | State hospital | Paid department of the state. hospitals |
| New treatment methods | ||
| Individual care from staff | ||
| 24/7 care | ||
| Diagnostic base | ||
| Reanimation | ||
| Individual nutrition | ||
| Increased comfort | ||
| Professional responsibility | ||
| Long stay | ||
| Newest medicines | ||
| Accommodation with relatives | ||
| Reception of visitors at any time | ||
| Doctor visiting your home |
What happens during rehabilitation after a traumatic brain injury
Each person's needs and abilities after TBI are different. By contacting the community of rehabilitologists Irakli Pozharisky, the client will have a rehabilitation program developed specifically for him. Many medical professionals and specialists will participate in this program.
An individual rehabilitation program may include any or all of these procedures:
- physiotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- breathing exercises;
- psychiatric correction;
- psychological support;
- psychotherapeutic intervention;
- speech therapy;
- social support.
Duration of rehabilitation
How long it takes to recover from a traumatic brain injury and how much follow-up care is required depends on how severely the brain is damaged and how well the patient responds to therapy. Some people can return to the same level of activity they did before their TBI. Other patients require lifelong care.
It is important to keep in mind that some long-term effects of damage to cranial cavity structures may take years to manifest. In the long term, the affected person may be at increased risk of developing problems such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia.
After rehabilitation, the center’s specialists will give important but simple instructions, including:
- symptoms and signs indicating that you should visit a doctor;
- possible delayed consequences;
- safety tips;
- recommendations for self-care and household organization;
- information regarding alcohol consumption.
Before agreeing to a diagnostic test or rehabilitation procedure, you should obtain information from employees:
- name of the test or procedure;
- the reason why the activity is recommended;
- what results can be expected;
- risks and benefits;
- what are the possible side effects or complications;
- place and time;
- other alternative methods;
- cost of manipulation.
What is recommended for the victim to eat?
The diet of a patient with a concussion is designed so that the food provides the body with everything it needs, but does not overload the organs and systems. Additionally, the menu includes foods and dishes that can calm the nerves, increase cellular immunity, and stimulate brain function.
The menu needs to include foods and dishes that will stimulate brain function.
Rules and principles of the diet recommended for concussion:
- The basis of the diet should be light protein and carbohydrate foods. In this case, it is desirable that most of the proteins are of plant origin, and carbohydrates are slow;
- ingredients are steamed, boiled, baked, used fresh;
- the diet should be enriched with B vitamins. For this purpose, the menu includes legumes, seaweed, asparagus, eggs, buckwheat, nuts, dairy products and lean fish;
- Recovery from a concussion will be faster if the patient receives sufficient amounts of vitamins and iron. Lean meat, cereals, legumes, spinach, beef liver, berries, fruits and herbs will help with this;
- It is beneficial for the patient to regularly consume soy, boiled or baked chicken, and turkey. They contain lecithin, a fat-like chemical compound that improves the condition of the brain center;
- for 1-3 weeks, the victim of a concussion is forced to adhere to bed rest, which negatively affects intestinal motility. Soups, side dishes and salads with fresh cabbage and beets will start digestion, relieving discomfort;
- citruses, spinach, bell peppers and rose hips are rich in vitamin C. Ascorbic acid strengthens the immune system, lifts the mood, and eliminates stress;
- To satisfy the need for sweets, it is recommended to make do with honey, natural candied fruits, and homemade marshmallows.
To satisfy your need for sweets, it is better to use honey.
The contents of the menu largely depend on what medications the patient is taking. If he is prescribed diuretics, then dried fruits, baked potatoes, nuts, beans, milk and dairy products should be added to the diet. They will provide the body with potassium and prevent microelement deficiency.
General Tips
After suffering a traumatic brain injury, after rehabilitation for at least six months, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- get enough good rest;
- do not take on previously habitual loads, increase your work or study time gradually;
- exercise caution and avoid situations where there is a risk of injury;
- do not engage in activities that require extreme concentration (for example, driving);
- avoid exhausting physical work;
- eat fully, balanced and in a timely manner;
- avoid information overload;
- write notes and place them in a visible place so as not to forget about upcoming tasks.
The patient may need help in the future to fully regain speech after traumatic brain injury. Therefore, you should not be afraid to contact specialists again if, after a period of relative well-being, existing problems reappear. The best option for people who have suffered from brain injuries is to undergo a complete physical examination twice a year. Completing this procedure on time will guarantee timely assistance to prevent serious problems.
Sample menu
During treatment for a concussion, you should eat in small portions several times a day (about 5-6 times). In addition to the main meals, it is advisable to include a second breakfast, an afternoon snack and a second dinner in the daily routine. A sample menu for the day might look like this:
- breakfast: porridge with milk, fruit, weak tea;
- second breakfast: yogurt;
- lunch: vegetable or meat soup, omelet;
- afternoon snack: a handful of nuts or an apple;
- dinner: vegetable salad, rosehip broth, stewed meat with vegetables;
- second dinner: a glass of kefir or a banana.
At home, many patients are lazy to follow a diet and quickly switch to their usual food. However, with such nutrition it is impossible to get good results in the near future. The introduction of “forbidden” foods into the diet should occur gradually after the doctor’s permission.
It is especially difficult to organize proper nutrition for older people and small children, since it is difficult for them to follow a diet. It makes no sense for babies who receive nutrients from their mother's milk to change their diet, but their mothers do. A woman should reconsider her diet, removing harmful foods from it and replacing them with healthy ones as much as possible.
There is no specific diet that describes the list of products that should be included in the menu for a concussion. But there are a number of recommendations that, if followed, will allow for a faster recovery and significantly reduce the consequences of the injury.