Signs and causes of sensory aphasia
Sensory aphasia can result from a wide range of causes. This disease can be caused by both diseases of the cardiovascular system and traumatic injuries to the head and central nervous system. The most common causes of sensory aphasia are:
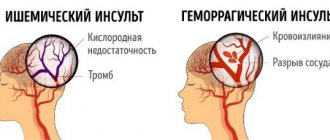
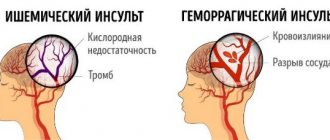
- Acute and transient disorders of cerebral blood flow, for example, embolism or hemorrhagic stroke. Embolization can occur as a result of the presence of an unstable atherosclerotic plaque in the bed of one of the carotid arteries or as a result of thrombus entry from the left atrial appendage in arthimogenic conditions.
- Traumatic head injuries, most often occurring in transport accidents. Contusions and traumatic brain injuries can lead to immediate damage to cortical and subcortical structures or delayed damage with the development of cerebral edema.
- Oncological processes localized in the cranium. Benign or malignant tumors can be a significant factor in the development of sensory aphasia.
It is important to note that the following branches entering the middle cerebral artery basin are most often involved in the formation of the lesion:
- Inferior branch of the middle cerebral artery;
- Posterior temporal artery;
- Artery of the angular gyrus.
Manifestations of the disease
The group of symptoms that manifests itself to a greater extent depends on which area of the brain is affected when sensory aphasia occurs. In any case, this is Wernicke’s area, where the speech analyzer is located, but the specific characteristics of sensory aphasia depend on whether the left or right hemisphere is affected: the perception or reproduction of speech is more impaired.
For a patient with sensory aphasia, words are just a collection of sounds. In some cases, recognition is partially preserved: the patient can identify the object shown to him as living or non-living, large or small. But he is unable to name the object itself. At the same time, the patient, as a rule, can perform simple actions on command - stand up, raise his hand, turn around. Without treatment, the disease progresses and leads to a complete misunderstanding of what is being said. Your own words are also not perceived as speech. Due to the lack of control by hearing, words become incoherent and are pronounced incorrectly and sometimes unrecognizable. Intonation also suffers. Pronunciation may be restored, but the construction of phrases will not appear on its own. Patients try to talk, and get angry when those around them do not understand them: a patient with sensory aphasia is sure that he speaks clearly.
Writing is also impaired to the same extent as speech. But the ability to read is lost only slightly - mainly due to confused stresses that distort the meaning of words.
Forms of sensory aphasia
There are several significant clinical forms of sensory aphasia that are characteristic of sensory aphasia. When additional pathological foci of the cortical substance join the affected Wernicke's area, new symptoms of impaired speech function appear. In this regard, neurologists distinguish the following forms of aphasia:
Semantic aphasia
With this aphasia, there is a violation of the recognition of logic and the relationship of words and objects. This is especially true for spatial perception.
Acalculia-aphasia
In this case, the key symptom is the formation of a localized disorder of speech function. Namely, counting violations. At the same time, the patient’s other forms of speech are not affected.
Sensorimotor aphasia
Lack of speech awareness is associated not only with damage to the cortical part of the auditory analyzer, but also with a violation of articulatory function. In other words, a person cannot correctly evaluate gestures when pronouncing a specific word like another person. Same with myself. The patient himself is not aware of his illness and is very irritated in situations where he is not understood.
Total aphasia
With this option, the victim has a combination of different types of functional speech disorder. The patient has impairments in written and oral speech. In this case, the patient does not perceive someone else’s speech and also cannot answer anything himself.
Difference between aphasia and other speech disorders
Aphasia differs from other speech disorders:
- with aphasia, unlike dyslalia, in addition to impaired pronunciation, the patient loses the ability to understand words;
- Unlike dysarthria, with aphasia there are no problems with tongue mobility. The activity of the articular apparatus in dysarthria is constantly limited;
- hearing loss – hearing impairment, with aphasia there are no auditory abnormalities;
- with aphasia, the child experiences mental retardation. It is secondary in nature, so this disorder should not be confused with mental retardation.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations of sensory aphasia have a number of specific signs that help make a quick and effective differential diagnosis. These signs include:
- Fluent speech or logorrhea, replete with a large number of allegorical expressions and paraphrases. The patient misses nouns, and I compensate for such speech defects with a large number of verbs, prepositions and conjunctions. Speech becomes verbose, but uninformative.
- “Jargnonic aphasia” is a continuous stream of neologisms, proverbs, sayings and paraphrases.
- Strong excitement up to the development of a paranoid state.
- Impaired understanding and perception of speech. The patient has difficulty or does not perceive simple questions at all, for example, a request to introduce himself or say who he is, but is able to follow simple commands, for example, turn his head or introduce himself. It is also important to note that the patient does not understand his own problem and becomes very irritated when the interlocutor does not perceive his speech well.
- Right-sided hemianopsia or upper quadrant hemianopsia. Loss of visual fields - when reading books, the victim will completely not notice the left page when reading the text.
- Smoothing of the nasolabial fold - the face becomes like a mask.
- Impairment of written speech.
There is also pure sensory aphasia (subcortical), when only the understanding of oral speech is impaired, but the understanding of written information, and therefore what is read, is preserved. Another form is also distinguished - transcortical sensory aphasia, which is characterized by the preservation of the ability to repeat oral speech, despite the lack of its perception and understanding. The main problem is that the patient hears the address to himself, but cannot interpret the meaning of what the interlocutor said. The native language is perceived as if it were foreign.
Sensory aphasia in rare cases occurs as an independent lesion of the auditory zones located in the brain, since in almost 85% of cases the damage involves several areas of the brain responsible for a wide variety of functions of the victim’s body. For example, with a stroke, sensory aphasia is often combined with paresis or paralysis of skeletal muscles on the side opposite the lesion. In the case of an infectious-inflammatory process: abscess, meningitis, encephalitis, there will be signs of general intoxication of the body and febrile syndrome, as well as cerebral symptoms. In the case of encephalitis, specific changes will be added to the cerebrospinal fluid - cerebrospinal fluid.
Specific signs of sensory aphasia in children
Sensory aphasia in childhood can be confused with alalia - the primary absence of speech, but there is a difference: if with alalia speech does not shift from the initial level of development, i.e. does not progress and does not undergo regression, then with aphasia a sharp degradation in the development of speech function, which has already been formed in a person, is noticeable. Since in childhood the speech function is not yet fully formed, there are specific signs for aphasia:
- As a rule, there is a rapid development of the disease and rapid recovery of speech function. Lack of recovery progress over several weeks is a poor prognostic sign for further recovery and indicates more serious brain damage.
- Restoration of speech function is carried out by increasing the activity of neighboring areas of the cortex, which to some extent are able to compensate for the neurological deficit. In adults, the restoration of speech function is carried out due to the formation of new logical connections and a developed conceptual apparatus.
- Scanty symptoms. Very often, it is difficult to determine the specific type of aphasia in children, since their speech function is not sufficiently developed. As a result, the conditions for revealing the full clinical picture of sensory aphasia are not created.
Advantages of visiting the Yusupov Hospital
Treatment of aphasia of various forms in Moscow is carried out by experienced specialists from the neurological department of the Yusupov Hospital. By trusting us with your health, you can be sure of receiving qualified medical care. Each patient is guaranteed an individual approach. In their work, doctors use proven modern techniques, which ensures a positive result of therapy.
Despite the high quality of services provided, prices are affordable (more details on the price list can be found on the website). In addition to neurology, services are available in other areas, including oncology, surgery, and therapy. For convenience, payment for treatment can be made in cash or by bank transfer. To make an appointment with a specialist, just call the numbers provided or fill out an application online, leaving your contact information.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of sensory aphasia is primarily aimed at identifying the cause of the disease. The diagnostic study must be comprehensive and consist of the following stages:
- Consultation and questioning of the patient to determine the history of life and illness. Also, during the initial appointment, the doctor examines the patient and studies specific symptom complexes. The neurologist looks for concomitant diseases that manifest themselves not only by external signs, but also by conducting additional tests and studies. During the examination, a specialist neurologist determines the lesions, the nature and course of the pathological process, assesses the general condition of the patient, as well as the blood supply to the brain. Makes a prognosis and subsequent treatment plan in accordance with the patient’s age. Its individual characteristics and concomitant somatic diseases. As well as the level of damage to the central nervous system.
- Consultation with a speech therapist, psychologist and other specialists. They determine the severity of the speech function defect and coordinate further tactics for restoring lost functions with the attending physician.
- Conducting additional instrumental and laboratory studies to verify and clarify the clinical diagnosis. Studies such as computer and magnetic resonance imaging, electroencephalography, angiography of cerebral vessels are carried out. These studies are carried out to identify the level and area of brain damage, the presence of space-occupying formations in the nervous tissue, aneurysms and hemorrhages in the brain tissue, foci of abscess, and the consequences of a stroke.
Our specialists
Tarasova Svetlana Vitalievna
Expert No. 1 in the treatment of headaches and migraines. Head of the Center for the Treatment of Pain and Multiple Sclerosis.
Somnologist.
Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Doctor of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 23 years.Derevianko Leonid Sergeevich
Head of the Center for Diagnostics and Treatment of Sleep Disorders.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Vertebrologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 23 years.
Bezgina Elena Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 24 years.
Dyachenko Ksenia Vasilievna
Head of the center for the treatment of dizziness and balance disorders.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category.
Angioneurologist. Neurorehabilitation specialist. Physiotherapist. Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 19 years.Drozdova Lyubov Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist. Vertebroneurologist. Ozone therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 17 years.
Zhuravleva Nadezhda Vladimirovna
Head of the center for diagnosis and treatment of myasthenia gravis.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Experience: 16 years.
Palagin Maxim Anatolievich
The doctor is a neurologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 6 years.
Treatment
The treatment process aimed at restoring the consequences resulting from aphasia requires a long time and enormous dedication, both from the patient and his relatives, and from medical personnel and specialists who have undergone special training. The restoration work of such a pathological condition consists of the following points:
- Pharmacological (drug) therapy. It mainly includes the use of drugs from the group of nootropics, drugs that increase the metabolism and trophic potential of the brain, vitamin therapy with neuroprotective B vitamins. Additional therapy is selected individually and prescribed in accordance with the cause of sensory aphasia. For example, in the case of a stroke, thrombolytic or hemostatic drugs are added, in the case of an infectious inflammatory lesion, antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or antifungal agents are added.
- Session with a speech therapist. The main difficulty that arises when attempting to contact the victim is the lack of understanding of the specialist’s approach to the patient. Violation of communicative activity requires long-term correction and perseverance. There are also difficulties in interpreting what the patient says. Because his speech is uninformative. It is very difficult to identify the main idea. Consultations with a speech therapist help restore the patient’s vocabulary, correct pronunciation of sounds and meaningful speech. With the help of special exercises and equipment, you can actively interact with the patient even at home.
- Surgical interventions. In some cases, with deep or severe brain damage, the patient requires emergency surgery to eliminate the threat to life. In case of an aneurysm, clipping or sclerosis of the aneurysm can be performed using X-ray control. If aphasia is caused by tumor growth, then stereotactic surgery can be performed to destroy the tumor focus.
- Additional treatment methods can speed up the recovery processes in the victim’s nervous tissue, and also increase the effectiveness of the main therapy. In the treatment of sensory aphasia, methods such as physical therapy, massage, physiotherapeutic methods, and the use of computer programs that stimulate the speech center and improve speech abilities are used. A positive effect has also been noted in contact with animals, so the following can be used in therapy: hippotherapy, feline therapy and dolphin therapy.
At the Clinical Institute of the Brain there is a specialized rehabilitation and recovery center that deals with the correction of disorders in patients with aphasia. Together with treatment, we manage to achieve a quick, step-by-step recovery process. There is a close connection between treatment and rehabilitation, which helps to quickly adapt the patient to new living conditions, thereby significantly increasing the effectiveness of therapy and recovery.
Stroke: restoration of speech. Exercises
Patients diagnosed with aphasia and speech disorders are concerned with the following questions: is it possible to fully recover from a stroke and how long will it take?
First of all, it is necessary to take into account the irreversibility of the process of destruction of brain cells. To restore the patient’s ability to speak, specialists will need to select means of recovery after a stroke that will help switch speech functions to the closest areas of the brain not affected by the disease. And the timing depends, among other things, on the high inertia of brain cells - after all, it is necessary to switch them to functions unusual for them
Many methods have been developed for restoring speech after a stroke that can speed up this process - speech, melodic, visual, artistic, etc. These speech therapy methods are used along with drug therapy - the patient is prescribed drugs that can stimulate the formation of new neural connections.
The method of intonation (melodic) therapy is based on “singing”. The patient is asked to sing words that cannot be pronounced clearly. Visual therapy uses the ability to form associations between words denoting an object and their visual image.
The most common method of treating aphasia is speech therapy. Classes on the method are conducted with a speech therapist-aphasiologist and are included in the course of intensive rehabilitation of patients after a stroke to the extent necessary for a particular patient.
Exercises to restore speech after a stroke begin with a complex that is designed to gradually restore the patient’s articulatory skills. This could be pronouncing individual sounds, syllables or words, or pronouncing tongue twisters. The exercises are performed with a speech therapist, and the results are consolidated independently in your free time. The more intense the exercise, the greater the likelihood of recovery.
Rehabilitation
Only daily classes with a speech therapist and other specialists will contribute to an active rehabilitation process. It is very important to correctly build a rehabilitation plan from simple to complex. To begin with, the victim must be adapted to new conditions. Only after a course of psychotherapy can one begin rehabilitation measures, since the patient must be motivated to recover.
The patient can also perform the following exercises at home:
- Simple questions: the patient is first asked questions with monosyllabic yes or no answers, then later they move on to open questions.
- Thematic dialogues are practiced with the gradual development of dialogue on specific topics;
- Writing and reading. Correction of the spelling and pronunciation of letters begins. Then syllables, which the patient then puts into words. In the future, with successful progress, they move on to writing dictations and reading short texts. The patient is asked to retell in his own words the story he read and answer questions about its content;
- A task aimed at matching pictures and text. The patient is asked to build a story, while laying out the pictures sequentially;
- Structuring pictures according to general properties and characteristics. The patient is given the task of arranging the pictures according to categories and highlighting common characteristics, for example, to separate some animals from others.
Diagnosis and treatment methods for aphasia in Moscow
The problem can be resolved with the help of qualified specialists. The disease requires elimination of the main cause and further correction. The speed of its correction largely depends on the degree of brain damage, so it is important not to delay a visit to a specialist. Diagnosis and treatment of speech disorders is carried out by specialists from the Department of Neurology.
At the initial appointment, the doctor collects anamnesis, collects complaints (in the case of aphasia, if it is impossible to independently describe the condition, close relatives are involved in the diagnosis), conducts a general examination for the presence of external abnormalities (in particular, drooping corners of the lips, decreased tone of the limbs).
Additionally, an examination by a neurologist in a team with a speech pathologist-speech pathologist is required so that the nature of the disorder can be assessed and appropriate corrective measures can be selected. Initiation of therapy requires testing, including assessment of the following symptoms:
- Spontaneous speech. Speech is assessed by the number of words spoken, the presence of spontaneous errors, and the frequency of pauses to select suitable words.
- Understanding. The patient is asked to point to objects that the specialist names and answer basic questions (“yes” or “no”).
- Enumeration of objects. The patient is asked to say the name of the specific object that the specialist points to.
- Reading and writing. The patient is given the task of writing any phrase and saying it out loud. This allows you to assess the degree of understanding and pronunciation.
- Semantic activity. The doctor demands to name all the animals that the patient remembers in one minute.
Up the steps
Sensorimotor aphasia can occur with varying degrees of severity. During correction, the stages change from more severe to easier, so the recovery process can be compared to climbing up the stairs - from complete muteness to normal speech function. Unfortunately, if the patient is not treated, the situation gets worse. This is especially true for children: not being able to communicate through speech, they begin to lag behind in mental development.
With sensorimotor aphasia, the following degrees of damage to the speech apparatus are distinguished:
- mild - understanding and reproduction of speech are slightly impaired, the patient confuses sounds, admits agrammatism, but in general he can be understood;
- pronounced - automatic speech is preserved, understanding addressed speech causes significant difficulties;
- deep (gross) sensorimotor aphasia - automatisms are inaccessible, monosyllabic answers to simple questions are possible;
- total - the patient makes inarticulate sounds and does not respond to spoken speech.
Total sensorimotor aphasia is a difficult case both for the patient and for rehabilitation specialists, but even in such a situation there is not only hope for a complete recovery, it has serious grounds.
Capacity in cases of gross and total sensorimotor aphasia, as a rule, is partially limited, since the person does not understand the speech addressed to him and there is no confidence that he fully understands the text. But to temporarily deprive a person of certain rights in each specific case, a court decision is required, which will request the expert opinion of doctors. We must not forget that in children sensorimotor aphasia is most often a transient phenomenon. The potential for speech restoration is also high in adults. A residual speech defect in itself, with preserved understanding of the conversation and text, is not a reason to deprive a person of the right to make transactions.
Efferent motor aphasia
Efferent motor aphasia occurs when the premotor parts of the frontal lobes of the brain (Broca's area) are damaged and is accompanied by symptoms such as movement disorders
and difficulties in mastering the motor program.
In severe cases, when there is poor circulation after a stroke, speech may be completely absent. The motor function of the articulatory apparatus suffers, since the signal about the beginning and termination of a speech act is delayed, which causes inertia, stereotypical speech, and perseveration
- repetitions of the same syllable or word. The patient cannot switch from one articulatory posture to another in a timely manner, which is why expressive speech suffers. Difficulties arise in repeating a series of sounds or syllables, in naming objects. In conversation, patients miss verbs, prepositions, and swallow endings. Speech is ungrammatical, reminiscent of telegraphic style. In written speech, they confuse the order of letters in a word and find it difficult to choose the correct letter. In severe cases, reading and writing are completely impossible. In mild cases, the patient can write down the word by ear, omitting sounds at the junction of consonants or rearranging them. Understanding of speech is also impaired, especially the figurative meaning of expressions and polysemantic words.
Acoustic-mnestic aphasia
Cause
acoustic-mnestic aphasia - damage to the middle and posterior parts of the temporal region.
It is characterized by symptoms such as a decrease in auditory-verbal memory
due to inhibition of auditory control. When listening to each new word, the patient loses understanding of the previous one, hence the repeated repetition of the same syllable or word. An aphasic who suffers from the acoustic-mnestic form cannot repeat 3-4 words in a row with different meanings. For example, sky, hand, grass, spoon, repeats either the first or the last word. Phonemic hearing and correct articulation are preserved, which results in verbosity that compensates for communication difficulties. The nominative function of speech, retelling based on plot pictures, suffers. Misunderstanding of the meaning of words leads to verbal paraphasia - substitution of words in a sentence, merging one word into one in writing. Along with writing, counting and reading are impaired.
Up