- Symptoms of hydrocephalus in adults
- Symptoms of hydrocele in children and adolescents
- Diseases that cause dropsy of the head and its main causes
- Atrophic hydrocephalus
- Types of hydrocephalus
- Flow
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of dropsy of the head
Hydrocephalus is an excess of cerebrospinal fluid in the cranial cavity, in the cerebrospinal fluid system of the brain.
CSF is cerebrospinal fluid that is produced by the choroid plexuses of the ventricles of the brain. Normally, cerebrospinal fluid enters the subarachnoid space, which lies above the brain, and is then absorbed by the lining of the spinal cord and brain. From there, the cerebrospinal fluid enters the blood. If this process is disrupted for any reason, excess fluid accumulates and leads to the appearance of negative symptoms. Hydrocephalus is otherwise called hydrocephalus. It is not an independent disease, but accompanies neurological pathologies. They can be congenital or acquired. Hydrocephalus most often occurs in newborns. Mature and elderly people face a similar problem, which is caused by degenerative processes in the brain. Another reason for excess fluid accumulation in the cranial cavity is diseases that are accompanied by increased production of cerebrospinal fluid or worsening of its outflow.
Symptoms of hydrocephalus in adults
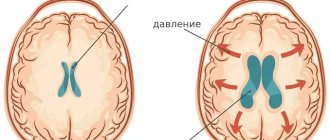
Hydrocephalus results in increased intracranial (intracranial) pressure. It causes compression of brain structures and manifests itself in a number of pronounced symptoms of neurological pathology:
- persistent headaches that do not respond to analgesics;
- vomiting and nausea;
- a feeling of squeezing in the eye area, which is accompanied by blurred vision;
- dizziness, poor coordination of movements, including unsteady gait;
- noise in ears;
- deterioration of muscle tone, including paresis and paralysis of individual muscle groups;
- decreased or loss of sensitivity;
- frequent mood swings, emotional lability, in which the patient may fall into apathy or show aggression for no reason.
In severe cases, hydrocephalus causes death of the optic nerve, mental disorders, complete or partial loss of mobility and other disorders that lead to disability.
Symptoms of hydrocele in children and adolescents
In young children, hydrocephalus occurs differently than in adults. This is due to the age-related properties of the skull bones, which may diverge in children. Thanks to this feature of the child’s body, intracranial pressure will remain normal, despite the accumulation of fluid. You can suspect hydrocephalus in an infant or young child based on the following signs:
- increased head size;
- swelling of the veins and divergence of the sutures of the skull;
- restriction of eyeball movement;
- The large fontanel does not pulsate.
Dropsy of the head has a negative effect on the child and causes retardation in physical and intellectual development. Babies later than their peers master the ability to hold their head up and roll over on their own. With severe or progressive hydrocephalus, the child’s vision deteriorates as the optic discs swell. The head looks spherical. If left untreated, there is a decrease in muscle tone, which leads to inactivity. Due to lack of mobility, a child may develop problems with excess weight. Mental disability is also a consequence of excess accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
In adolescents, hydrocephalus most often develops due to infectious diseases and injuries. The symptoms of dropsy of the head in adolescents are the same as in adults. In addition to the previously listed signs, the child may experience convulsions and loss of consciousness.
Causes and types of minor external hydrocephalus
Moderate external hydrocephalus is a disease in which the production, absorption or flow of cerebrospinal fluid along the cerebrospinal fluid pathways is impaired. Adults and children are susceptible to the disease. Minor external hydrocephalus is characterized by compression and deterioration of blood supply to the brain, which reduces its functional activity.
Moderate external hydrocephalus in children develops for the following reasons:
- infectious diseases suffered in utero;
- genetic pathology;
- birth trauma and infection of the fetus during passage through the birth canal.
The cause of moderate external hydrocephalus in adults can be inflammatory diseases of the substance and membranes of the brain, neoplasms of the cerebellum and brain stem, cerebral atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, and diabetes mellitus. Provoking factors are traumatic brain injuries, alcohol abuse, and intoxication.
According to the form of the disease, several types of external hydrocephalus are distinguished:
- moderate open external hydrocephalus of the brain - characterized by impaired absorption of cerebrospinal fluid, but the spaces in which the cerebrospinal fluid is located communicate freely;
- closed hydrocephalus – develops when the patency of the cerebrospinal fluid passages is disrupted by space-occupying formations or adhesions;
- External replacement hydrocephalus of the brain is a separate form of the disease in which the space vacated due to brain atrophy is filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Replacement hydrocephalus is dangerous because it is asymptomatic for a long time.
Moderate replacement hydrocephalus
Various pathological conditions of the brain are accompanied by moderate external replacement hydrocephalus of the brain. Hydrocephalus is a disease characterized by an imbalance between the production and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid. Early diagnosis and adequate treatment help improve the quality of life of the vast majority of patients with hydrocephalus. The Yusupov Hospital employs candidates and doctors of medical sciences and neurologists of the highest category. They are leading experts in the field of diseases of the central nervous system.
Moderate replacement hydrocephalus is asymptomatic over a long period of time. It develops against the background of various diseases of the cardiovascular system, diabetes mellitus, acute and chronic cerebrovascular accidents.
Replacement hydrocephalus of the brain is a consequence of diseases accompanied by a decrease in the volume of the brain matter. The vacated space is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Excessive amounts of cerebrospinal fluid compress the brain, which leads to disruption of nerve functions.
The following causes of moderate external replacement hydrocephalus of the brain are known:
- traumatic brain injury;
- stroke;
- brain tumors;
- infectious diseases.
Mild external hydrocephalus can occur in patients suffering from arterial hypertension, cerebral atherosclerosis, and diabetes mellitus. Provoking factors for moderately severe external replacement hydrocephalus include alcohol abuse, metabolic disorders and instability of the cervical spine.
Moderate replacement hydrocephalus does not manifest itself with pronounced clinical symptoms. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital identify the disease using additional research methods. As the disease progresses, the pressure of excess cerebrospinal fluid on the brain substance increases, which leads to the following symptoms:
- intense headache developing into migraine;
- numbness of the upper or lower extremities;
- darkening of the eyes;
- impaired coordination of movements and gait;
- nausea and vomiting.
Patients develop a shuffling gait. They complain that their legs feel like they are stuck to the floor. An unfavorable prognostic symptom of replacement hydrocephalus is drowsiness. It increases on the eve of increased neurological symptoms and the development of a coma. Timely surgical intervention can stabilize the patient's condition.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use modern methods for diagnosing hydrocephalus:
- ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels;
- computed or magnetic resonance imaging;
- craniography;
- cisternography;
- angiography.
After analyzing the examination results, doctors at the neurology clinic make a final diagnosis and treat the patient.
When a patient is diagnosed with moderate external replacement hydrocephalus of the brain, treatment is aimed at reducing cranial pressure, improving the nutrition of the brain and eliminating the pathology that caused the disease. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe dehydration therapy to patients. Diacarb reduces the production of cerebrospinal fluid and removes excess fluid from the body. The drug is used in combination with Lasix or furosemide.
For patients with cerebral atherosclerosis complicated by hydrocephalus, neurologists prescribe drugs that lower blood cholesterol levels. If there is a high risk of blood clots and ischemic stroke, antithrombotic therapy is administered with acetylsalicylic acid or clopidogrel. An integrated approach to the treatment of patients with moderate replacement hydrocephalus allows doctors at the Yusupov Hospital to influence not only the symptoms, but also the cause of the disease. After stabilization of blood pressure, cerebral hypertension and symptoms of hydrocephalus decrease.
A more modern method of surgical treatment of replacement hydrocephalus is endoscopic surgery. With their help, the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is restored. Neurosurgeons at partner clinics perform the following endoscopic operations:
- aqueductoplasty;
- endoscopic ventriculocisternostomy of the bottom of the third ventricle;
- ventriculocystocysternostomy;
- endoscopic installation of a shunt system;
- septostomy;
- endoscopic removal of an intraventricular brain tumor.
Endoscopic operations have a number of advantages compared to bypass interventions. After surgery, the patient's physiological outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles into the basal cisterns of the brain is restored.
Moderate mixed hydrocephalus of the brain
With atrophic mixed hydrocephalus, intracranial pressure may increase, decrease, or remain unchanged. In case of increased intracranial pressure, hypertensive liquor syndrome develops. Moderate mixed non-occlusive hydrocephalus is asymptomatic for a long time and patients do not seek medical help. Despite the patient’s normal state of health, over time, signs of cerebral circulatory disorders appear. By contacting a neurologist in a timely manner, it is possible to avoid the unpleasant consequences of the disease.
When cerebrospinal fluid pressure increases, patients with mixed hydrocephalus experience headache, nausea, vomiting in the morning, and drowsiness. Ophthalmologists determine congestion in the optic nerve head. Magnetic resonance imaging shows displacement along the axis of the brain.
The following signs of mixed atrophic hydrocephalus are also distinguished:
- speech disorder;
- seizures;
- weakness in the limbs;
- impairment of short-term memory;
- passivity and lack of initiative of the patient.
With further progression of the disease, severe intellectual impairment develops. Patients lose the ability to self-care and answer questions posed inadequately. Over time, urinary incontinence develops.
Moderate internal hydrocephalus of the brain
The acute form of moderate hydrocephalus of the brain is accompanied by high intracranial pressure. Patients suffer from headaches in the morning. Its intensity decreases throughout the day. In the morning, digestive disorders may occur, including nausea and vomiting. If vomiting reduces the intensity of the headache, this indicates a problem with the brain. As intracranial pressure increases, drowsiness increases, which is an unfavorable prognostic sign.
Moderate external hydrocephalus of the brain occurs as a result of the following diseases:
- infectious diseases of the central nervous system;
- cerebrovascular accidents;
- intraventricular, parastem or stem brain tumors;
- encephalopathies of various origins;
- non-traumatic, traumatic and intraventricular hemorrhages.
Hydrocephalus of the brain can be hereditary or acquired. Based on the location of fluid accumulation, internal and external hydrocephalus are distinguished. Internal hydrocephalus occurs due to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain. External hydrocephalus develops as a result of the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the subarachnoid and subdural spaces.
The main symptoms of moderate hydrocephalus include:
- migraine-like headache
- vomiting and nausea;
- violation of vestibular functions;
- constant drowsiness;
- involuntary urination;
- diplopia (double vision).
With moderate external replacement hydrocephalus, intracranial pressure may remain normal. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital use modern methods for diagnosing hydrocephalus:
- computed or magnetic resonance imaging;
- craniography;
- cisternography;
- ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels;
- angiography.
Patients with hydrocephalus are consulted by an ophthalmologist and a neurosurgeon. Patient management tactics are discussed at a meeting of the expert council.
Diseases that cause dropsy of the head and its main causes
There are three pathological mechanisms that lead to an excess of cerebrospinal fluid:
- excessive formation of cerebrospinal fluid;
- disruption of its movement;
- insufficient absorption of fluid by the membranes of the spinal cord and brain.
Pathology can occur under the influence of one factor or a combination of them. Depending on the etiology, hydrocephalus can be divided into congenital and acquired. Each type has its own reasons.
Congenital hydrocephalus occurs with the following diseases:
- anomalies in the development of the cerebrospinal fluid system and subarachnoid space;
- congenital craniovertebral defects;
- intrauterine infections, including toxoplasmosis, rubella, syphilis;
- birth injury.
In the above cases, signs of “dropsy” of the head appear immediately after the child is born or during the first years of life.
Acquired hydrocephalus is caused by tumor and inflammatory processes in the cranial cavity, injuries, and complications after surgery. Dropsy of the head is accompanied by the following diseases:
- inflammation of the membranes of different parts of the brain;
- skull injuries, unsuccessful surgical interventions;
- cerebral hemorrhage during a hemorrhagic stroke;
- intracerebral hematomas;
- cysts and other tumor diseases of the brain that create compression and disrupt the movement of cerebrospinal fluid.
Causes of the disease:
Congenital hydrocephalus often occurs in children after the mother has suffered a severe infection during pregnancy. It occurs more often if a woman was ill in the first trimester - the fetus’s brain structures begin to develop incorrectly, which is why hydrocephalus, meningoencephalitis and other diseases can occur. Traumatic brain injury, tumor, hematoma, hemorrhage after a stroke are the causes of acquired hydrocephalus. In older people, it develops against the background of atherosclerosis, a significant increase in blood pressure over a long period of time.
Types of hydrocephalus
For reasons of appearance, dropsy of the head is divided into open and closed. With open hydrocephalus, the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid remains normal, but its production is increased, or the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid by the meninges is impaired.
The cause of closed hydrocephalus is compression of certain areas of the cerebrospinal fluid system of the brain. This occurs due to a cyst, tumor or hematoma.
Depending on the focus of the pathology, internal and external dropsy are distinguished. With internal, cerebrospinal fluid is concentrated in the ventricles of the brain, with external - in the subarachnoid space.
How is the procedure performed?
MRI of the brain is performed with or without contrast enhancement. In the first case, the patient is injected intravenously with special drugs that create a clear image of the affected areas and improve the quality of visualization. For example, with this approach, not only the tumor itself is clearly visible, but also its exact boundaries.
No special preparation is required for the procedure, but before it begins, you will have to remove all metal jewelry. The tomography machine itself looks like a large cylinder, inside of which there is a movable platform. The patient is placed on it lying on his back. To protect against the noise produced by the device, earplugs are used.
The table slides inside the tomograph, and the doctor performs the procedure from an adjacent office, controlling the device using a computer. Throughout the examination, voice communication with the doctor is maintained, so the patient can report unpleasant or uncomfortable sensations at any time.
The tomograph sequentially takes a series of images, which ultimately form the finished image. In order for the images to be of high quality, the patient must remain completely still. On average, the procedure takes about 30-45 minutes.
Flow
According to the severity of symptoms, dropsy of the head can be acute, subacute and chronic. In acute hydrocephalus, signs of the disease rapidly increase. This process takes from one day to several days. Subacute “dropsy” of the head develops within a few weeks or a month, and with chronic hydrocephalus, the stage of decompensation occurs within six months.
The prognosis largely depends on how quickly the disease progresses. With compensated hydrocephalus, intracranial pressure remains normal, neurological symptoms do not increase. With a progressive form of the pathology, the patient's condition gradually worsens due to increased intracranial pressure. The disease does not respond well to conservative treatment, and due to constant compression, atrophy of brain tissue develops.
Forms of pathology
The form of hydrocephalus determines the nature of the disease and its severity. The following criteria are most often used for classification:
- The intensity of the manifestation of the pathology - when severe, a lot of fluid accumulates, which disrupts the activity of the nervous system. In this case, the disease is accompanied by severe neurological symptoms. A moderate degree is characterized by the accumulation of a small volume of cerebrospinal fluid and the absence of symptoms;
- The degree of impact on brain structures - in a compensated form, the liquid has no effect on the brain; in a decompensated form, it worsens its functioning;
- The nature of the course - hydrocephalus of the brain in the chronic form is accompanied by a gradual increase in symptoms, in the acute form it leads to a sharp deterioration in the person’s condition.
Modern diagnostic measures allow determining the type of disease, its form and developmental features.
Diagnostics
If you have signs of hydrocephalus, you should consult a neurologist. To assess the patient’s health status, a set of diagnostic procedures is prescribed:
- X-ray of the skull;
- computed tomography or MRI;
- echoencephalography;
- Ultrasound;
- ophthalmoscopy.
Hardware techniques help to identify possible anomalies in the structure of the cerebrospinal fluid system, the presence of trauma, cysts, hematomas, tumors. A lumbar puncture may be performed to identify the cause of the disease. This is an invasive procedure in which cerebrospinal fluid is taken for examination. Such an analysis will determine the infectious nature of the disease and identify the degree of increase in intracranial pressure.
What is needed for the initial diagnosis of hydrocephalus in Israel
To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a primary diagnosis. To do this you need:
- Blood test – $280
- Computed tomography – $630
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – $1350
- Consultation with a neurosurgeon based on examination results – from $660
To get tested, you can sign up:
- Call us at: +972(77)4450-480.
- By leaving a request on the website.
We will contact you quickly.
Treatment of dropsy of the head
Conservative and surgical methods are used to eliminate hydrocephalus. Conservative treatment is primarily aimed at eliminating the inflammation or other disease that has led to the accumulation of fluid in the cranial cavity. To reduce the degree of hydrocephalus with increased intracranial pressure, Furosemide and other diuretics are prescribed.
Newborns with congenital pathologies are prescribed surgical treatment, which helps eliminate abnormalities in the structure of the cerebrospinal fluid system and thereby get rid of excess fluid accumulation. The same applies to patients of any age with tumors, cysts, intracranial hematomas, and brain abscess. During the operation, tumors that compress blood vessels and brain tissue are eliminated.
In some cases, even surgical intervention does not completely eliminate the cause of the disease. To reduce intracranial pressure, the patient undergoes shunt surgery. Their goal is to create additional pathways for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the cranial cavity and normalize the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Methods and principles of treatment
The main task is to eliminate the accumulated excess cerebrospinal fluid in order to restore its normal flow.
In some cases, drug therapy is performed. Improvement from conservative treatment of hydrocephalus usually occurs when the disease is a complication of an infectious or inflammatory disease or traumatic exposure. When medications do not provide the desired effect, surgery is performed to install special shunts. This element ensures the drainage of fluid to the abdominal cavity, where it is absorbed by the body. As a result, pressure decreases and the size of edema in the brain decreases.
Another surgical treatment option is to create an opening in the 3rd cerebral ventricle to allow cerebrospinal fluid to flow between brain regions. Both methods allow you to relieve symptoms and block the development of dangerous complications. If the disease is caused by the appearance of a tumor, it is removed.
The earlier hydrocephalus is detected, the better the prognosis for treatment.
If the operation is timely and successful, the patient can return to normal life, and a full recovery is possible. Advanced stages of the disease not only worsen the quality of life, but also lead to dangerous consequences, including death. That is why accurate diagnosis, primarily MRI, plays an important role. Rate this article: (1 rated 5 out of 5)