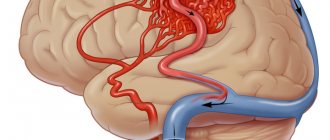
Cerebrospinal fluid continuously circulates in a closed system, maintaining stable intracranial pressure. The expansion of the external cerebrospinal fluid spaces of the brain in adults is caused by the accumulation of fluid in the subarachnoid space, which leads to disruption of the functionality of the central nervous system.
What types of external hydrocephalus of the brain are there?
External hydrocephalus of the brain refers to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (cerebrospinal or cerebrospinal fluid) outside the cerebral hemispheres - in the subarachnoid space. Due to the large accumulation of fluid, the subarachnoid fissures widen, which causes increased pressure on the cerebral cortex and the resulting negative consequences.
The nature and level of complexity of the disease directly depend on the specific type of dropsy. Several criteria are used for classification. The most common ones are:
- intensity of manifestation (pronounced - accumulation of a large amount of cerebrospinal fluid, causing neurological symptoms; moderate - minimal amount of fluid, no signs);
- degree of impact on brain structures (compensated - cerebrospinal fluid does not affect the brain; decompensated - there is a deterioration in the functioning of the nervous system and brain);
- causes of occurrence (replacement - more often diagnosed in older people and is accompanied by the death of brain cells; acquired - occurs due to the spread of infections and mechanical traumatic brain injuries);
- nature of the course (chronic form - a gradual increase in neurological disorders; acute form - a sharp deterioration in the patient’s well-being).
Employees of the Department of Neurosurgery of the City Clinical Hospital named after. Eramishantsev will first determine the type of external hydrocephalus and only then begin treatment. Particular attention is paid to diagnostic data and a thorough study of the symptoms of the identified disease.
Symptoms of external hydrocephalus
The clinical picture in each specific case will be different, and the nature of the manifestation of the disease depends on the severity of the pathological process and the state of the central nervous system. Common symptoms are frequent headaches, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, and weakness. By the way, pain is more localized in the frontoparietal region and in the area of the eyeballs. A person with dropsy experiences pain in the first half of the day, with sudden movements, coughing, sneezing, or severe physical exertion.
Symptoms may vary depending on the severity of the disease. Scientists distinguish 3 stages, and each has its own characteristics:
Mild external hydrocephalus. With a minimal amount of dropsy, the human body will try on its own to cope with such a problem as impaired circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid. In this case, you will feel a slight malaise, periodic dizziness, short-term darkening in the eyes, and a tolerable headache.
The middle stage of development of the disease. At this stage of the spread of the disease, symptoms appear intensely and are more pronounced. Due to an increase in intracranial pressure, severe headaches occur during physical activity, swelling of the optic nerve and facial tissues, increased fatigue, nervousness, depression, and surges in blood pressure.
Severe form of the disease. Signs of pathology in severe forms of external hydrocephalus are reduced to convulsive seizures, frequent fainting, a state of apathy, loss of intellectual abilities, memory loss and inability to care for oneself. Progressive dropsy can even lead to death, so there is no need to delay going to the doctor. It is better to do this at the first suspicion and a slight deterioration in health.
With chronic accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid, symptoms such as unsteady gait, paralysis of the upper and lower extremities, urinary incontinence, nighttime insomnia and daytime sleepiness, depressed mood, and a complex of psychoneurological disorders can be observed.
Symptoms of expansion of subarachnoid spaces
In children and adults, the pathology manifests itself differently. So, in children of the first year of life, the following signs help to suspect something is wrong:
- Negative reaction to noise, medium-level sounds, light;
- Frequent regurgitation;
- Poor sleep, anxiety;
- Strabismus, different pupil diameters;
- Head growth that does not correspond to age;
- Bulging and slower overgrowth of the fontanel;
- Weather sensitivity, anxiety when weather changes;
- Trembling, tremors of the chin, arms or legs.
As you can see, the symptoms are quite non-specific. They may more likely indicate hydrocephalus with intracranial hypertension secondary to expansion of the subarachnoid space. These signs cannot make an accurate diagnosis, but they should prompt an immediate visit to a neurologist or pediatrician.
In adults, one of the main symptoms of expansion of the subarachnoid space is headache, which can be quite intense and prolonged. Patients often complain of severe dizziness and nausea, inability to perform work duties, weakness, restlessness, and anxiety.
Cranialgia is especially pronounced early in the morning and may be accompanied by vomiting, dizziness, hypersensitivity to light and sounds. During the day, patients are often drowsy, at night they cannot sleep, or their sleep is restless and intermittent. An increase in headache, its pulsating nature, and the appearance of vomiting at the height of pain are characteristic symptoms of increasing intracranial pressure.
Diffuse expansion of the subarachnoid space and an increase in the volume of the lateral ventricles will sooner or later cause atrophic and dystrophic changes in the cerebral cortex, which will manifest itself as symptoms of encephalopathy - decreased memory and attention, visual impairment, and intelligence. Autonomic symptoms are often associated in the form of tachycardia, pressure surges, unmotivated anxiety and even fainting.
Movement disorders are more typical for cerebellar localization of pathology. In this case, symptoms may include unsteadiness and uncertainty in gait, dizziness, loss of coordination and fine motor skills.
Constant fatigue, repeated attacks of severe headaches, and the inability to get a good night's sleep disrupt the emotional state of patients, who can become irritable, anxious, and prone to depression. Secondary changes in the brain impair the ability to work and limit active life.
compression of the brain due to subarachnoid hemorrhage
Uneven expansion of the subarachnoid space is possible after trauma, brain surgery, or with tumors that locally compress the membranes of the brain and the cerebrospinal fluid pathways. In this case, focal neurological symptoms are observed in the form of disturbances in sensitivity, speech, hearing, etc. A severe course of the pathology is indicated by convulsive syndrome or epilepsy.
Depending on the width of the intershell space, there are light (1-2 mm expansion), moderate (up to 4 mm) and severe (over 4 mm) degrees of expansion. To a certain extent, such a division is arbitrary, especially with uneven or local changes in the liquor spaces.
The described symptoms usually occur with severe variants of the pathology, severe hydrocephalus and intracranial hypertension. Most often, mild and even moderate degrees of impairment are manifested only by periodic headaches, fatigue and autonomic dysfunction.
Why does dropsy of the brain occur?
In adult patients, acquired hydrocephalus is often encountered, which develops either due to any mechanical damage to the head, or as a result of the development of pathological processes. Why does cerebrospinal fluid accumulate outside the cerebral hemispheres? The explanation is simple: brain structures are disrupted, adhesions appear in the veins, arachnoid villi are destroyed, and as a result, the cerebrospinal fluid does not circulate as it should.
If we delve deeper into the question of the causes of such a disease as external dropsy of the brain, we can identify some factors:
- infectious diseases (tuberculosis, meningitis, encephalitis);
- post-stroke condition, development of sepsis, extensive hemorrhage;
- concussion, head or cervical spine injury;
- malignant tumors that develop in the stem region.
Frequent intoxication of the body leads to the appearance of external hydrocephalus. For example, alcohol abuse, which damages neurons and leads to tissue death. Those patients who suffer from metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus, multiple sclerosis, encephalopathy, and atherosclerosis are also at risk. Another reason that deserves due attention is irreversible age-related changes that cause aging of blood vessels and brain tissue.
Main services of Dr. Zavalishin’s clinic:
- consultation with a neurosurgeon
- treatment of spinal hernia
- brain surgery
- spine surgery
Reasons for development
Acquired hydrocephalus can develop due to pathological processes that result in adhesions in the vessels of the brain and destruction of arachnoid villi.
Make an appointment
External open hydrocephalus of the brain in adults develops for the following reasons:
- inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system;
- violation of the stability of the cervical vertebrae;
- pathology of cerebral blood vessels;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- discirculatory encephalopathies;
- developmental defects of the central nervous system;
- brain tumors;
- surgical interventions on the brain.
The main signs of external hydrocephalus in adults are headache and increased intracranial pressure due to a decrease in brain volume and filling of the free space with cerebrospinal fluid.
Atrophic hydrocephalus occurs due to age-related changes in cerebral vessels, metabolic disorders, diabetes mellitus, and arterial hypertension. With external hydrocephalus, zones with reduced density of brain matter are formed. They atrophy, and the vacated space is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. The cause of the development of external hydrocephalus can be constant alcohol intoxication.
Diagnosis of external hydrocephalus in adult patients
Studying the symptoms and visual examination of the patient is not a sufficient condition for determining external hydrocephalus of the brain. Indirect signs, of course, are important, but you can’t do this without professional diagnostics. Today, 6 methods for detecting dropsy are used:
- Ultrasound examination (US) of the neck and head to assess the condition of blood vessels;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) helps to identify changes in soft tissues and most accurately determine the type of hydrocephalus and the stage of development of the pathology;
- computed tomography (CT) is intended to determine the degree of damage to brain tissue, the size of subarachnoid fissures, and the presence of neoplasms;
- X-rays with the introduction of a contrast agent are aimed at identifying disturbances in the outflow of venous blood and damage to the vascular bed;
- a spinal puncture is prescribed if there is a suspicion of the development of dropsy after encephalitis or meningitis and you need to find out what level of cerebrospinal fluid pressure;
- ophthalmological examination - an opportunity to determine whether the patient has swelling of the optic nerve and atrophy of the tissues of the ocular apparatus.
IMPORTANT! If the diagnosis of “chronic external hydrocephalus of the brain” is confirmed, it is advisable to carry out an additional diagnostic examination after 6 months. The intensity of further visits to the doctor depends on the data obtained and is determined individually.
Treatment of external hydrocele in adults
Treatment methods are selected at a consultation with a neurosurgeon or neurologist after diagnosing the disease. Intervention must be timely, otherwise the risk of various neurological complications increases. It is important to take into account both the type of pathology and the characteristics of the patient’s body.
In the Department of Neurosurgery of the City Clinical Hospital named after. Eramishantsev practice only effective methods of treating external hydrocele of the brain. Methods are divided into two large groups: conservative (medicinal) and surgical (operative), each of which has its own characteristics and advantages.
CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT
Drug treatment is only relevant at a mild stage of the disease. Special medications accelerate the outflow of fluid from the brain, increase urination, relieve inflammation and swelling, strengthen blood vessels, and normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular system. To combat severe headaches, your doctor may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
Common groups of medications are vascular, neurotropic, venotonics, diuretics. But in acute illness they will be ineffective. Mixed hydrocephalus is poorly corrected. In this case, conservative treatment will not get rid of the disease, but will only restore or improve the functioning of individual systems and functions of the human body. Often surgical intervention is not possible.
SURGERY
If acute external dropsy is diagnosed, in most cases drainage of the cerebral ventricles is prescribed. The main technologies are endoscopy and open surgery.
In the first case, we are talking about manipulations that are characterized by minimal trauma, a very low risk of complications, and fairly rapid postoperative recovery. Endoscopy methods allow, with minor intervention, not only to remove excess cerebrospinal fluid, but also to eliminate vein defects, hematomas, and blood clots.
Currently, open surgery is chosen only in exceptional cases. Why? It is difficult to imagine performing open surgery without craniotomy. And trepanation always means increased risks and a long postoperative recovery period.
Another way to get rid of external dropsy is bypass surgery. Doctors use a system of valves and silicone tubes to remove excess cerebrospinal fluid from the skull. The fluid is redirected to other cavities of the body, in particular to the abdominal cavity, right atrium, and superior vena cava. According to statistics, the effectiveness of this technique is 85%.
Is it possible to protect against the occurrence of external hydrocephalus of the brain? This is a very difficult question. But, if you completely give up bad habits and avoid traumatic brain injuries, there is a high probability that trouble will bypass you. Another important point is the timely and professional treatment of such serious diseases as encephalitis, polio, meningitis, as well as other infectious diseases.
Treatment and prevention of hydrocephalus
For patients with mild external hydrocephalus, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe drug therapy. Taking medications that block production and accelerate the release of cerebrospinal fluid can reduce intracranial pressure. For this purpose, patients are prescribed osmotic and loop diuretics (urea, mannitol, furosemide) and sauletics (diacarb). Taking corticosteroids can quickly relieve swelling and inflammation.
Nootropic drugs (vasotropil, cavinton, noofen) and venotonics (actovegin, glivenol) improve brain functioning. Panangin and asparkam restore the concentration of potassium in the blood, which is excreted from the body in large quantities when taking diuretics. For severe headaches, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that have an analgesic effect (nimesulide, ketorolac, diclofenac) are prescribed.
If drug treatment does not eliminate the signs of external hydrocephalus, the treatment is considered ineffective. In such cases, patients at the Yusupov Hospital are consulted by a neurosurgeon. At a meeting of the expert council with the participation of professors and doctors of the highest category, a collegial decision is made regarding the advisability of performing surgical intervention.
In the acute form of hydrocephalus and severe symptoms of the disease, conservative therapy is ineffective. The main treatment method in this case is bypass surgery. During surgery, a special system is installed in the brain cavity through which cerebrospinal fluid is drained into the abdominal or thoracic cavity, occipital cistern, atrium or pelvis.
Complications may develop after bypass surgery:
- Hypodrenage;
- Hyperdrainage;
- Breakdown of the shunt system;
- Sepsis.
If complications occur, neurosurgeons replace the shunt. Despite the presence of certain risks of developing negative consequences of shunting, surgery is the only method that can improve the quality of life for patients with hydrocephalus.
Less traumatic are endoscopic operations that are performed in partner clinics:
- Endoscopic ventriculocisternostomy of the floor of the third ventricle;
- Septostomy;
- Ventriculocystocysternostomy;
- Endoscopic removal of tumors inside the ventricles;
- Aqueductoplasty.
The essence of endoscopic operations for hydrocephalus is that the neurosurgeon inserts endoscopic instruments with a miniature video camera into the skull through a miniature hole. The doctor sees the cavity of the ventricles of the brain and monitors the progress of the intervention. The endoscopic method allows you to create an outflow path for cerebrospinal fluid. Most often, neurosurgeons perform ventriculocisternostomy of the floor of the third ventricle. After surgery, the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricular system occurs into the cisterns of the brain.
Conservative treatment of external hydrocephalus in adults
In the presence of mild hydrocephalus of the brain in adults, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital provide drug therapy. Patients are prescribed the following medications:
- diuretics;
- plasma replacement solutions;
- barbiturates;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- analgesics.
The rehabilitation clinic provides physiotherapeutic procedures and physical therapy. During treatment, it is important for the patient to adhere to a special diet with low fatty foods.
Neurosurgical operations for hydrocephalus
Neurosurgeons perform palliative interventions in the presence of open hydrocephalus and the impossibility of performing radical surgery for closed hydrocephalus. Doctors perform spinal and ventricular puncture. After taking 100 ml of cerebrospinal fluid, the patient's condition temporarily improves.
Ventriculoperitoneal shunting is a radical neurosurgical operation. Using a valved system, a catheter diverts cerebrospinal fluid into the abdominal cavity, where it is absorbed into the bloodstream. During the Küttner-Wenglovsky operation, a drain is placed through which the cerebrospinal fluid passes from the ventricle of the brain into the subdural space.
In order to reduce the release of cerebrospinal fluid, the choroidal components of the cerebral ventricle are removed during a neurosurgical operation. If there is a speck, they are dissected. Fluid also drains from the posterior wall of the ventricle into the spinal canal.
Prevention of hydrocephalus consists of timely and adequate treatment of the pathologies that cause the disease. For patients with arterial hypertension, cardiologists at the Yusupov Hospital select optimal antihypertensive drugs and adjust drug doses. Patients with infectious diseases of the brain are prescribed the latest generation of antibacterial drugs. When the initial stage of hydrocephalus is detected, regular examination is carried out and computed tomography is performed.
If you have symptoms of external hydrocephalus of the brain, call the Yusupov Hospital. Contact center specialists will offer a time convenient for the patient to consult a neurologist. After a comprehensive examination, the doctor will determine the severity of the disease and prescribe treatment depending on the severity of symptoms, the presence of indications and contraindications for surgical intervention.