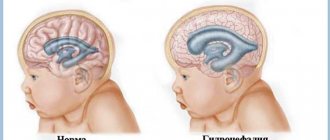
Hydrocephalus is an excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cranial cavity, which results in an increase in the size of the subarachnoid spaces, basal cisterns, and ventricles of the brain. All conditions have been created for the treatment of patients with hydrocephalus at the Yusupov Hospital. The neurology clinic employs candidates and doctors of medical sciences, doctors of the highest category. Neurologists have the knowledge and experience to quickly diagnose the disease and provide adequate therapy.
Causes of hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus develops due to the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cerebrospinal fluid system of the brain in the event of the production of an excess amount of cerebrospinal fluid, impaired absorption or disturbance of the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. In case of exposure to damaging factors on the fetal brain during intrauterine development, congenital hydrocephalus occurs. Acquired hydrocephalus develops under the influence of various pathological mechanisms after the birth of a child.
The following causes of congenital hydrocephalus are known:
- intrauterine infections (hydrocephalus, toxoplasmosis, cytomegaly, syphilis);
- birth injury;
- defects in the development of the cerebrospinal fluid system (atresia of the foramina of Magendie and Luschka, stenosis of the Sylvian aqueduct, structural defects of the subarachnoid space, Dandy-Walker syndrome);
- developmental anomalies of the skull and spine (congenital basilar impression, Chiari malformation).
Acquired hydrocephalus occurs as a result of inflammatory processes of the brain and its membranes, traumatic brain injuries, acute and chronic vascular disorders. Hydrocephalus in adults often develops against the background of a colloid cyst of the third ventricle and intracerebral tumors (germinomas, astrocytomas, ganglioneuromas) growing into the ventricles of the brain or compressing the cerebrospinal fluid tract, disrupting the normal circulation of cerebrospinal fluid and its outflow from the cranial cavity.
Make an appointment
Types of hydrocephalus in adults
There are open (communicating), closed (occlusive) and replacement hydrocephalus. Open hydrocephalus of the brain in adults involves free communication of spaces through which cerebrospinal fluid circulates. It develops when there is an imbalance in production and reabsorption of cerebrospinal fluid. There are hyperproductive, aresorptive and mixed forms of hydrocephalus.
Replacement hydrocephalus can be a consequence of physiological aging of the body or develop in pathological conditions of the central nervous system, accompanied by atrophic changes (Alzheimer's disease, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease). This form of the disease does not refer to true hydrocephalus, caused by impaired cerebrospinal fluid dynamics, but occurs as a result of the filling of “free” spaces inside the skull with cerebrospinal fluid.
In accordance with the location of the expanded cerebrospinal fluid spaces in relation to the brain tissue, the following types of hydrocephalus in adults are distinguished: internal (intraventricular), external (subarachnoid) and mixed. Depending on the level of intracranial hydrocephalus, hypertensive and normotensive hydrocephalus are distinguished. In functional and clinical aspects, progressive (increasing), stabilized (not changing over time) and regressive (decreasing) hydrocephalus are distinguished. Progressive hydrocephalus can be decompensated or subcompensated.
In acute hydrocephalus, no more than three days pass from the moment of the first symptoms of the disease to severe decompensation. Subacute progressive hydrocephalus develops within one month from the onset of the disease, and chronic hydrocephalus develops within a period of 3 weeks to 6 months.
Source
- Methodological manual for students of medical institutes. Compiled by: Gubsky L.; Borkina P.; Abovich Y.; Evstifeeva N.; Timakov V. link
- Orlov Yu.A. Hydrocephalus. – Kyiv, 1995. – 75 p.
- Cerebral lateral ventricular asymmetry on CT: how much asymmetry is representing pathology? Kiroğlu Y1, Karabulut N, Oncel C, Yagci B, Sabir N, Ozdemir B.Surg Radiol Anat. 2008 May;30(3):249-55. doi:10.1007/s00276-008-0314-9. Epub 2008 Feb 6. link
- Grosman H, Stein M, Perrin RC, Gray R, St Louis EL. Computed tomography and lateral ventricular asymmetry: clinical and brain structural correlates. (1990) Canadian Association of Radiologists journal = Journal l'Association canadienne des radiologists. 41 (6): 342-6. Pubmed
- Shapiro R, Galloway SJ, Shapiro MD. Minimal asymmetry of the brain: a normal variant. (1986) A.J.R. American journal of roentgenology. 147(4):753-6. doi:10.2214/ajr.147.4.753 - Pubmed
- Gijn, Jan van et al. “Acute Hydrocephalus After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.” Journal of Neurosurgery 63.3 (1985): 355-362. link
- Dupont, Stefan and Alejandro A Rabinstein. “CT Evaluation Of Lateral Ventricular Dilation After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Baseline Bicaudate Index Balues.” Neurological Research 35.2 (2013): 103-106. link
- Morphometric Changes in Lateral Ventricles of Patients with Recent-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Junghyun H. Lee, Sujung Yoon, Perry F. Renshaw, Tae-Suk Kim, Jiyoung J. Jung, Yera Choi, Binna N. Kim, Alan M. Jacobson, In Kyoon Lyoo. Published: April 4, 2013 “PLOS one”.link
- "Third and Fourth Cerebral Ventricular Sizes among Normal Adults in Zaria-Nigeria." Ahmed Umdagas Hamidu, Solomon Ekott David, Sefiya Adebanke Olarinoye-Akorede, Barnabas Danborno, Abdullahi Jimoh, Olaniyan Fatai. Year:2015, Volume:2, Issue:2, Page:89-92 link
Symptoms of hydrocephalus in an adult
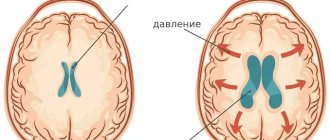
The accumulation of an excess amount of cerebrospinal fluid in a limited space of the cranium leads to an increase in intracranial pressure, which causes the most typical signs of hydrocephalus: intense headache that cannot be relieved by analgesics, nausea and vomiting, a feeling of pressure on the eyeballs.
These symptoms of hydrocephalus in an adult patient can occur acutely or increase gradually, having a transient nature at the onset of the disease. Replacement hydrocephalus often occurs without signs of increased intracranial pressure. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital detect it only after additional examination of the patient. Hydrocephalus of the brain in an adult in the photo has characteristic signs: an increase in the volume of the head and frontal bone.
In most cases, hydrocephalus in adults is accompanied by neurological symptoms. It is caused both by compression of brain structures by expanded cerebrospinal fluid spaces and by the underlying disease, which is the cause of the development of hydrocephalus. With hydrocephalus, vestibular disorders are observed: gait instability, dizziness, noise in the ears and head, nystagmus. Visual function is impaired: there is a significant decrease in visual acuity and loss of certain areas of the visual field. During ophthalmoscopy, ophthalmologists identify congested optic discs. With prolonged hydrocephalus, atrophy of the optic nerves develops.
Hydrocephalus in adults can occur with disturbances in the motor and sensory spheres:
- paresis and paralysis;
- decrease or complete loss of all types of sensitivity;
- increased tendon reflexes and muscle tone;
- formation of spastic contractures of the limbs.
Occlusive hydrocephalus, caused by impaired circulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the posterior cranial fossa, is characterized by symptoms of cerebellar ataxia: changes in handwriting, large-scale disproportionate movements, impaired gait and coordination.
Patients suffering from hydrocephalus develop mental disorders over time, manifested by disorders of the emotional-volitional sphere: neurasthenia, emotional instability, causeless euphoria with a rapid transition to a state of apathy. With a sharp increase in liquor pressure, patients begin to behave aggressively.
General mechanism for the development of disturbances in the activity of cavities
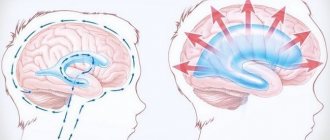
At the first stage, there is difficulty in the outflow of cerebral fluid into the subarachnoid space from the ventricles. This provokes expansion of the cavities. At the same time, compression of the surrounding tissue occurs. Due to the primary blockage of fluid outflow, a number of complications arise. One of the main ones is the occurrence of hydrocephalus. Patients complain of sudden headaches, nausea, and in some cases vomiting. Disorders of autonomic functions are also detected. These symptoms are caused by an acute increase in pressure inside the ventricles, which is characteristic of some pathologies of the liquor-conducting system.
Diagnosis of hydrocephalus
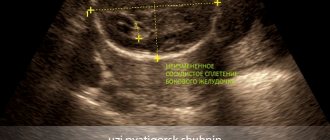
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital conduct a comprehensive examination of patients with hydrocephalus. Computed tomography currently occupies a dominant position among methods for diagnosing hydrocephalus. The procedure is carried out to determine the size and shape of the ventricles, identify developmental anomalies and neoplasms, cysts.
Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to determine the shape and severity of hydrocephalus. Using this diagnostic method, the cause of cerebral hydrocele is determined. Neurosonography helps assess the degree of expansion of the ventricles of the brain. The procedure is used only when diagnosing the disease in children with an open fontanelle, since the skull blocks ultrasound. Neurosonography is used to diagnose hydrocephalus in utero.
Cisternography is a research method in which a radioactive substance is injected into the cerebrospinal fluid. It is used to clarify the type of hydrocephalus and determine the direction of cerebrospinal fluid flow. During an angiography, a contrast agent is injected into the arteries that supply blood to the brain. After some time, anomalies at the level of blood vessels and pathological processes are detected. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use innovative methods for diagnosing cerebral vascular diseases - magnetic resonance angiography, which does not require the administration of contrast agents. A neuropsychological examination involves conducting a survey to identify abnormalities in the functioning of the brain.
Indicators of normal sizes
In the human body, the ventricular system consists of several cavities that anastomize with each other. They communicate with the subarachnoid space, as well as the spinal cord canal. A special liquid, cerebrospinal fluid, moves directly inside the cavities. With its help, tissues receive nutrients and oxygen molecules.
The largest intracerebral hollow formations are, of course, the lateral ventricles. They are localized below the corpus callosum - on both sides of the midline of the brain, symmetrical relative to each other. In each, it is customary to distinguish several sections - the anterior and lower, as well as the posterior horns and the body itself. The shape resembles the English S.
The normal size of the ventricles is assessed taking into account individual anatomical characteristics - there are no uniform standards. Experts focus on average parameters. It is important to know these sizes for babies under one year old - for the purpose of early diagnosis of hydrocephalus.
- What is heart dilatation
Normal values for children:
| Anatomical unit | Newborns, mm | 3 months, mm | 6 months – 9 months, mm | 12 months, mm |
| Lateral ventricle | 23.5-/+ 6.8 | 36.2 -/+3.9 | 60.8-/+6.7 | 64.7-/+12.7 |
For adults, the parameters should be in the range - the anterior horn of the lateral ventricle is less than 12 mm in people under 40 years of age, while its body is 18–21 mm in people under 60 years of age. Exceeding the age-related size of the brain ventricles by more than 10% requires additional research to identify and eliminate the root cause.
Treatment of hydrocephalus
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital take a differentiated approach to treating patients with hydrocephalus. In case of a regressed form of the disease, drug therapy is not used. To reduce cerebrospinal fluid pressure, patients are prescribed diuretics: Diacarb, mannitol, Lasix. Nootropics, venotonics and angioprotectors improve the functional activity of the brain.
For progressive hydrocephalus, neurosurgeons at partner clinics of the Yusupov Hospital perform shunt operations. If there is an obstacle to the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, the space-occupying lesion is removed or the adhesions are cut. If a hematoma is present, it is removed surgically.
An innovative method of treating hydrocephalus is endoscopic surgery:
- endoscopic ventriculocisternostomy of the bottom of the third ventricle;
- endoscopic installation of a shunt system;
- septostomy;
- aqueductoplasty;
- ventriculocystocysternostomy;
- endoscopic removal of intraventricular brain tumor.
Endoscopic operations have a number of advantages compared to bypass interventions: they restore the physiological flow of cerebrospinal fluid, are less traumatic, and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Treatment with endoscopic methods
Endoscopic treatment of hydrocephalus, or dropsy of the brain, is a priority in neurosurgery, since this disease is common among both children and adults. Hydrocephalus of the brain occurs due to impaired absorption of cerebrospinal fluid into the venous system.
Endoscopic surgery
Endoscopic interventions for hydrocephalus of the brain are used to reduce intracranial pressure. Surgeries for dropsy are most effective in comparison with drug therapies, which help slow the progression of the disease, but do not eliminate it. Endoscopic surgery for hydrocephalus, the cost of treatment of which is determined by the severity of the disease, is divided into several types:
- Septostomy;
- Ventriculocisternostomy of the floor of the third ventricle;
- Ventriculocisternostomy;
- Installation of the shunt system endoscopically;
- Removal of intraventricular tumors endoscopically;
- Aqueductoplasty.
The most widely used is endoscopic ventriculocisternostomy of the bottom of the third ventricle. The main task of the surgeon with this technique is to create pathways for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles into the cisterns of the brain, through which the cerebrospinal fluid is absorbed into the vascular walls, as in a healthy person.
Advantages of endoscopic operations
Endoscopic surgery can only be effective if it is performed by a good specialist. One wrong move by the surgeon during brain surgery can lead to irreparable, severe consequences. When shunts are installed, they are often blocked by blood clots, tumor cells, etc. During endoscopy, no foreign objects remain in the body, and accordingly, the development of such complications is excluded.
In severe cases, patients are given brain drains. Such an event is very dangerous, since the infection can easily penetrate the brain through the drainage. With endoscopic intervention this complication does not occur.
Bypass surgery
Many people who have been diagnosed with the disease wonder where to treat hydrocephalus: in a public medical institution or a modern clinic. Yusupov Hospital is equipped with the latest equipment. Doctors regularly improve their skills and master new treatment methods. The clinic staff ensures a comfortable stay for patients.
Shunt surgery for hydrocephalus in adults, the price of which varies depending on the characteristics of the disease, is performed safely and efficiently at the Yusupov Hospital. Installation of a shunt system ensures the removal of cerebrospinal fluid. The procedure lasts about 90 minutes and is performed under general anesthesia for patients of any age.
Bypass surgery is a safe intervention, but there are certain risks when using it, which the neurologist informs the patient about. For example, a reaction to anesthesia or bleeding may develop. Shunt surgery allows the patient to restore normal brain function.
Prognosis and prevention
The consequences of asymmetry of the lateral ventricles are varied. Their severity and severity directly depend on the size of the pathological expansion and the age of the patient. Thus, in mild forms of the disorder, children experience short-term developmental delays, both intellectual and physical. With timely medical care, hydrocephalus is completely eliminated.
Whereas with severe dilatation of the cavities, various neurological diseases are formed - for example, cerebral palsy, or persistent mental disorders. There is no specific prevention of ventricular asymmetry, since it is almost impossible to predict its occurrence. However, experts point out that when the expectant mother strives for a healthy image, she contributes to the birth of a baby with normal sizes of brain cavities. To do this, you need to give up bad individual habits even before pregnancy, eat right, get good sleep, and avoid psycho-emotional and stress overload.