Rokeach's theory
M. Rokeach considered values as a type of stable belief that a certain goal or way of existence is preferable to another.
The nature of human values according to Rokeach:
- the total number of values that are the property of a person is relatively small;
- all people have the same values, although to varying degrees;
- values are organized into systems;
- the origins of human values can be traced to culture, society and its institutions, and the individual;
- the influence of values can be traced in almost all social phenomena worthy of study.
M. Rokeach distinguishes two classes of values - terminal and instrumental:
- M. Rokeach defines terminal values as the belief that some ultimate goal of individual existence (for example, a happy family life, world peace) from a personal and social point of view is worth striving for;
- Instrumental values are beliefs that a certain course of action (for example, honesty, rationalism) is preferable from personal and social points of view in all situations. In fact, the separation of terminal and instrumental values produces a fairly traditional distinction between values-goals and values-means.
Set of values
Values are certain views on life and the whole world . They largely define a person as an individual in society and determine the direction of his activities in any field. A philosophy of life is based on a set of such values.
Sometimes people cannot explain their actions. But everything is interpreted very simply - they have certain values that influence behavior, but these vital priority ideas are stored at the subconscious level. It is difficult to objectively explain and understand them, but it is possible.
In such cases, it is very useful to visit a professional psychologist who will help you understand yourself and find the right solution.
Procedure
INSTRUCTIONS: “You are offered two lists of 18 values. Your task is to rank them in order of importance to you as principles that guide you in your life. That is, you assign number 1 to the most important, etc., so that under the eighteenth number will be the value that is least significant for you.
Work slowly and thoughtfully. If you change your mind during the work, you can correct your answers. The end result should reflect your true position."
| Terminal values | rank | Instrumental values | rank |
| Active active life (fullness and emotional richness of life) | Accuracy (cleanliness, ability to keep things in order, clarity in conducting business) | ||
| Life wisdom (maturity of judgment and common sense achieved through life experience) | Good manners (good manners, ability to behave in accordance with the norms of cultural behavior) | ||
| Health (physical and mental) | High demands (high demands on life and high aspirations) | ||
| Interesting job | Cheerfulness (optimism, sense of humor) | ||
| The beauty of nature and art (experience of beauty in nature and art) | Efficiency (discipline) | ||
| Love (spiritual and physical intimacy with a loved one) | Independence (ability to act independently, decisively) | ||
| Financially secure life (no financial problems) | Intransigence towards shortcomings in yourself and others | ||
| Having good and loyal friends | Education (breadth of knowledge, high cultural level) | ||
| Social recognition (respect from others, the team, colleagues) | Responsibility (sense of duty, ability to keep one’s word) | ||
| Cognition (the opportunity to expand one’s education, horizons, general culture, intellectual development) | Rationalism (the ability to think sensibly and logically, make thoughtful, rational decisions) | ||
| Productive life (maximum full use of your capabilities, strengths and abilities) | Self-control (restraint, self-discipline) | ||
| Development (work on yourself, constant physical and spiritual improvement) | Courage to stand up for your opinion | ||
| Freedom (autonomy, independence in judgment and action) | Sensitivity (caring) | ||
| Happy family life | Tolerance (towards the views and opinions of others, the ability to forgive others for their mistakes and delusions) | ||
| Happiness of others (welfare, development and improvement of other people, the entire nation, humanity as a whole) | Breadth of views (the ability to understand someone else’s point of view, respect other tastes, customs, habits) | ||
| Creativity (opportunity to be creative) | Strong will (the ability to insist on one’s own, not to give up in the face of difficulties) | ||
| Self-confidence (inner harmony, freedom from internal contradictions, doubts) | Honesty (truthfulness, sincerity) | ||
| Pleasures (pleasant, easy pastime, lack of responsibilities, entertainment) | Efficiency in business (hard work, productivity at work) |
Value-oriented unity of the group - what does it mean?
Each group member has certain views on life, attitudes and beliefs.
They form value guidelines. If a group contains people with similar value orientations, we can talk about their unity.
In this case, their positions, views, assessments of what is happening will coincide. All group members will share each other's opinions, which will avoid conflicts and misunderstandings.
According to psychologists, it is very important to achieve this unity, since this leads to a significant increase in the effectiveness of the work performed in the group. The set common goals are achieved much faster, the group is friendly, and the work is carried out harmoniously
The set common goals are achieved much faster, the group is friendly, and the work is carried out harmoniously.
Rokeach test scales
As a result of M. Rokeach’s methodology, the severity of 36 indicators is revealed - value orientations of two types:
Terminal values:
- ACTIVE LIFE
- LIFE WISDOM
- HEALTH
- INTERESTING JOB
- BEAUTY OF NATURE AND ART
- LOVE
- FINANCIALLY SECURE LIFE
- HAVING GOOD AND TRUE FRIENDS
- PUBLIC ACCEPTANCE
- COGNITION
- PRODUCTIVE LIFE
- DEVELOPMENT
- ENTERTAINMENT
- FREEDOM
- HAPPY FAMILY LIFE
- THE HAPPINESS OF OTHERS
- CREATION
- SELF CONFIDENCE
Instrumental values:
- ACCURACY
- EDUCAMENT
- HIGH DEMANDS
- JOY OF LIFE
- PERFORMANCE
- INDEPENDENCE
- INTOLERANCE FOR DISADVANTAGES
- EDUCATION
- RESPONSIBILITY
- RATIONALISM
- SELF-CONTROL
- COURAGE
- STRONG WILL
- TOLERANCE
- HONESTY
- SENSITIVITY
- BREADTH OF VIEW
- EFFICIENCY IN BUSINESS
Content
- 1 Theoretical foundations
- 2 Procedure 2.1 Instructions
- 2.2 Modifications to the test procedure
- 3.1 Groups of terminal values 3.1.1 “Concrete” and “abstract”
- 3.2.1 Ethical values, communication values, business values
- 4.1 Answer form
Interpretation of results
The individual hierarchy of values obtained as a result of the study can be divided into three equal groups:
- preferred values, significant (ranks from 1 to 6);
- indifferent, indifferent (7-12);
- rejected, insignificant (rank 13-18 of the hierarchy).
The ranks obtained for each of the 36 values, reflecting the significance of the value for the subject, can be used in empirical studies to identify differences in groups or to analyze the relationship of value orientations with other psychological phenomena.
Special cases
If the time and effort spent do not produce concrete results, this situation in the analysis of the test may indicate that the respondent is informal . It could be a schoolboy or just a confused young man. In any case, his value system is undergoing many changes; it is just being formed.
There is no point in checking such people. It is advisable for them to pass the test when they are full of determination and have achieved the integrity of their inner world. Otherwise, these are simply incorrect results that will not say anything about the personality of the subject.
M. Rokeach’s method for determining value orientations is applicable only to mature personalities.
Another reason for the inability to correctly analyze the test may be insincerity in the answers. And in this case, the person is a closed book. It's hard to say why he came for testing if his answers are lies. But, most likely, the subject has some prejudices, and he decided to prove to himself or someone else that psychology does not deserve the attention that is paid to it.
An example of analyzing the results of the Rokeach questionnaire
In Fig. Table 3 shows the average values of terminal values of adolescents in the experimental (athletes) and control (non-athletes) groups.
The structure of terminal values of adolescents of both groups is similar: the most significant values are health, love, friends and family; the least significant are beauty, creativity, the happiness of others.
Teenagers from both subgroups are more focused on health, love, family and friends. Focusing on the beauty of nature and art, creativity and the happiness of others is not so important.
I hope this article will help you write a psychology paper on your own. If you need help, please contact us (all types of work in psychology; statistical calculations). Order
Values
This term is understood as the readiness of an individual to be active in relation to a specific object. They can be formed on the basis of social situations and vital needs.
We must not forget that attitudes begin to be laid in childhood. The child is influenced by his immediate environment: family, relatives, friends.
The baby tries to imitate close people. They copy behavior and try to be like those they like.
During adolescence, a person is greatly influenced by famous personalities, actors and singers that they like. The teenager adopts behavior, views, tries to be like his idol, thereby sharing his attitudes.
Each individual may have a thousand attitudes. Some matter more, others less. When making important decisions, a person turns to his attitudes, focusing on them.
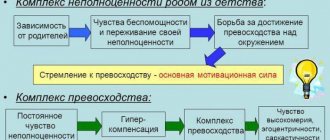
How to get rid of an inferiority complex? Advice from psychologists will help you!
Specifics
Rokeach’s technique also involves analyzing values and dividing them into groups, which is logical, since all beliefs relate to certain areas of life. Accordingly, there are values of personal life and professional self-realization, financial (material) and spiritual. The instrumental type mentioned above includes beliefs regarding communication, ethics, business, altruism, self-affirmation, and other people.
Rokeach's technique, as practice shows, is interesting and effective. Its advantage lies in its versatility, efficiency and convenience. You can “examine” a person with its help very easily, as well as process the results. And the lists of values (otherwise called stimulus material) can be varied, and the instructions can be changed.
True, some also highlight disadvantages. These include social undesirability and the likelihood that the person agreeing to the test will be insincere.
How is testing done?
You will be given 18 tickets, each of which represents a certain value. You are required to arrange them in order of importance. You need to sort it out honestly: what guides you most in life, what is most important to you - you assign the first number to this. And further in descending order, so that the last, eighteenth ticket will be the least significant for you.
It would be better to lay it out slowly, and before taking the test, think about everything and decide what is most important to you. You need to take the test as honestly as possible, otherwise the results will be false.
Methodology for diagnosing personality for motivation to avoid failures by T. Ehlers
Instructions: You are offered a list of words of 30 lines, 3 words in each line. In each line, select only one of the three words and that most accurately characterizes you, and mark it, highlight it in bold or underline it.
| 1. Brave | vigilant | enterprising |
| 2. Meek | timid | stubborn |
| 3. Cautious | decisive | pessimistic |
| 4. Fickle | unceremonious | attentive |
| 5. Stupid | cowardly | unthinking |
| 6. Nimble | lively | prudent |
| 7. Cold Blooded | wavering | daring |
| 8. Swift | frivolous | timid |
| 9. Unthinking | cutesy | improvident |
| 10. Optimistic | conscientious | sensitive |
| 11. Melancholic | doubting | unstable |
| 12. Cowardly | careless | excited |
| 13. Reckless | quiet | timid |
| 14. Attentive | imprudent | brave |
| 15. Reasonable | fast | courageous |
| 16. Enterprising | careful | prudent |
| 17. Excited | absent-minded | timid |
| 18. Cowardly | careless | unceremonious |
| 19. Shy | indecisive | nervous |
| 20. Executive | devoted | adventurous |
| 21. Prudent | lively | desperate |
| 22. Tamed | indifferent | careless |
| 23. Cautious | carefree | patient |
| 24. Reasonable | caring | brave |
| 25. Foresighted | intrepid | conscientious |
| 26. Hasty | timid | carefree |
| 27. Absent-minded | reckless | pessimistic |
| 28. Discreet | reasonable | enterprising |
| 29. Quiet | unorganized | timid |
| 30. Optimistic | vigilant | carefree |