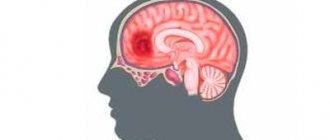
Lipoma and skin atheroma are two common types of benign neoplasms. They require exceptionally attentive treatment, since in some cases (though, fortunately, not often) they can degenerate into malignant tumors. The appearance of atheroma may not cause suspicion - at first it usually does not cause much inconvenience. However, even if the tumor is not painful, you should still see a doctor. Often a lump (lipoma) on the neck or scalp gradually increases in size, in this case you need to visit a doctor urgently - the new growth will need to be examined to determine whether there is a risk of developing cancer.
Lipoma and atheroma are often similar in appearance, and patients often do not distinguish them from each other, defining them under the general name “wen.” Let's try to figure out what the difference is between a lipoma and an atheroma, and also what to do if you have one of these formations.
Why does a lump appear?
A bump on the head from a blow appears due to damage to small vessels. At its core, it is a type of hematoma. Upon impact, the capillaries rupture and blood flows out. When other parts of the body are bruised, a bruise appears on the skin, but there is usually no swelling. This is due to the fact that the subcutaneous tissue absorbs blood on the body and limbs. Therefore, swelling does not form.
There is no fiber on the head. Blood pours out under the skin. In this case, the liquid is not absorbed, but only accumulates. For this reason, a head injury leads to the appearance of a lump. This does not exclude the simultaneous formation of a bruise if the blow was strong enough.
Examination methods
To diagnose hematomas, you need to contact a traumatologist. When the hemorrhage is localized deep in muscle tissue, joints or internal organs, a visual examination provides too little information for the doctor to objectively assess the severity of the lesion and the degree of danger of injury. In such situations, the patient is prescribed:
- Ultrasound of a damaged body part, organ or joint;
- X-ray of the damaged part of the body;
- CT or MRI;
- puncture (puncture with a special needle) of a joint or organ in which blood is believed to have accumulated.
Based on the examination results, the doctor prescribes appropriate procedures.
Causes
A hematoma on the head does not occur with every bruise. In order for a lump to appear, a fairly rough mechanical effect on the skin is necessary. Swelling usually occurs as a result of the following injuries:
- Bumps on a child’s head from an impact are most often caused by falls. Small children often fall out of strollers. Such injuries also occur when a child learns to walk.
- Adults are more likely to get bumps when hitting hard surfaces. This happens with awkward movements or when an object falls on a person from above.
Levomekol in the treatment of burns
For burns, Levomekol is needed to prevent infection of the wound surface with pathogenic infections, as well as to accelerate tissue healing. Levomekol also copes with inflammation, which can lead to suppuration of the wound. The ointment cleanses the affected area well from both purulent discharge and necrotic cells.
The treatment system for a small area burn of 1-2 degrees is as follows:
- before applying the ointment, the wound is washed under running water;
- the ointment is applied to a sterile gauze pad, which is applied to the wound surface;
- the bandage is applied for a day;
- dressings are done every day - up to 5 times a day.
The burn is treated until the tissue is completely healed. The total duration of the course for minor household burns is 5 – 14 days.
Symptoms
How to distinguish a hematoma from other types of edema and tumors? Bumps on the head from a blow have the following features:
- A hematoma always forms exclusively in the place that has been subjected to mechanical stress. For example, if a person hurts himself on the top of his head, the bump cannot appear in the frontal region.
- The size of the formation may vary. It depends on how severe the bruise was.
- The color of the cone may vary. Sometimes it does not differ from the rest of the skin color, but it may also be bluish due to hemorrhage. But in the head area there are no bruises of such a bright color as on other parts of the body.
- The skin around the lump looks swollen.
- When you press on the lump, pain is felt.
On average, swelling can last from 2 to 7 days. With intensive treatment and proper first aid, the lump goes away quite quickly.
Atheroma
The origin of atheroma is fundamentally different from lipomas. Atheroma develops from the sebaceous glands of the skin. For various reasons, the gland duct becomes clogged, secretion accumulates in the gland, which gradually begins to increase in size. Atheroma is defined as a small (from 0.5 to 2 - 3 cm) formation, which always rises somewhat above the skin and is always fused to it (i.e. the skin above the atheroma does not move), and can grow slowly. Atheroma always has a capsule and contains atheromatous masses resembling crushed lard.
Because The atheroma is connected to the external environment by a duct; there is always a threat that it will become infected through the duct and suppuration will occur. In this situation, moderate pain appears in the area of the previously “quiet” atheroma, the formation quickly (over several days) increases in size, redness appears around it, and body temperature may rise. Suppuration of atheroma requires urgent surgery.
Features of bruises in children
A bump on the head after a blow in a child is a very common occurrence. After all, children love a mobile and active lifestyle. Babies have delicate scalp, so a hematoma can form even with a minor blow.
However, head injuries in children are often accompanied by concussion and other unpleasant consequences. Therefore, you need to pay attention to the baby’s well-being. Many children cry a lot when they are bruised, but most often this is due to fear rather than pain. You need to let the baby calm down, and then take a closer look at his condition. If you have the slightest doubt, you should contact a pediatric traumatologist.
The size of the hematoma does not always indicate the danger of injury. For example, with forehead bruises, huge bumps always form. However, the frontal bone is the strongest and protects the brain well, so unpleasant consequences from bruises in this area are rare.
Let's sum it up
The main causes of bruising and increased fragility of blood vessels are listed above, but not all of them. There are quite a few of them, and treatment tactics in each specific case can differ radically. Moreover, completely different specialists can treat pathology: vascular surgeons/phlebologists, dermatologists, rheumatologists, infectious disease specialists. It is impossible to give any general recommendations without seeing the patient and without knowing the entire clinical picture. From a relatively harmless, which can have an effect, and in most cases does not harm, we can recommend eating more foods rich in vitamin C, vitamins P, or taking their synthetic analogues. But even here, allergic reactions to these drugs and food are possible, and there are also restrictions for certain groups of patients (for example, pregnant women).
Cold
Let's say that a child or adult has a bump on their head from a blow. What to do first? A few minutes after the injury, blood continues to flow from the burst vessels, and the lump grows. If the blow was very strong, then the swelling increases right before our eyes.
First of all, you need to stop the subcutaneous hemorrhage. To do this, apply cold to the damaged area. Its effect will help narrow blood vessels and reduce hematoma, as well as reduce pain. The following available tools are suitable for this purpose:
- Ice. If the injury occurred at home, you can take ice from the refrigerator, put it in a bag and wrap it in a towel. Apply an ice compress to the bruised area. This procedure must be repeated several times during the day. Instead of ice, you can use freezer items or a bottle of cold water.
- Compress with cold water. You need to moisten the cloth with cold water and apply it to the bump. As soon as the compress warms up, it must be replaced. This procedure is repeated several times.
- If you don’t have anything cold on hand, regular vegetable oil can help. It should be applied to cotton wool or a bandage and applied to the bruise for half an hour. With the help of such a folk remedy, you can completely avoid the appearance of a bump if the blow was not too strong.
Cold must be applied within the first 24 hours after injury.
Why does a hematoma change color?
Doctors identify three distinct stages of a hematoma through which it must go before completely disappearing. Each of them is characterized by a certain skin color, through which the hemorrhage is visible.
- Appearance of a bruise. Immediately after a soft tissue bruise, a sharp pain is felt, the area of skin in the damaged area becomes purplish-red and swells due to tissue swelling, then the red color gradually changes to blue. The red color comes from red blood cells containing large amounts of hemoglobin. After a few hours, hemoglobin begins to break down, and the bruise site turns blue. Due to swelling and inflammation of the tissue in the damaged area, the temperature rises.
- Greening. After two or three days, swelling and temperature decrease, the condition of the tissues more or less returns to normal, but minor pain when pressed remains. The blue tint of the skin gradually turns into a greenish color.
- Yellowing. By about the fifth day, the swelling completely disappears, the remaining hemoglobin disintegrates and is removed from the tissues. The site of the bruise becomes yellowish, then acquires its normal color.
Visual symptoms of hematomas are most clearly visible in cases where the effusion of blood occurs in the subcutaneous layer. If a clot forms in the deeper layers of soft tissue, then only a small but painful swelling is noticeable on the outside. Such formations are much more dangerous, since the process occurs unnoticed and can be accompanied by complications.
Are you experiencing symptoms of a hematoma?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Exposure to heat
Cold is a first aid remedy for bumps on the head from a blow. How to treat the hematoma further? Many people limit themselves to only cold compresses on the first day. However, this is not enough. On the second day, the sore spot must be warmed up. Under the influence of heat, the swelling subsides and the lump begins to dissolve.
You can apply a warm boiled egg to the bruise. Table salt, heated in a frying pan and wrapped in a cloth, is also suitable. You should not use compresses that are too hot, so as not to burn your already injured skin.
In the following days, the lump is treated with pharmaceutical ointments or folk remedies.
How to remove hematomas?
After establishing the nature and characteristics of the hematoma, treatment is prescribed in accordance with the information received:
- prescribe UHF procedures;
- a surgical opening is performed to remove accumulated clots and rinse the cavity;
- the patient is hospitalized in the surgical department for opening and drainage, followed by antibiotic therapy.
Recovery time depends on the extent of the lesion, the presence or absence of infection and other factors.
Ointments
How to anoint a bump on the head from a blow after first aid? In pharmacies you can buy various local remedies for bruises. Let's look at some of them:
- "Troxerutin." This is a drug in the form of a gel that helps resolve swelling after a bruise. The product is well absorbed into the skin, but it is not recommended to apply it to damaged epithelium. The treated sore spot should be protected from exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
- "Troxevasin". The gel strengthens the walls of damaged blood vessels and promotes their healing. It reduces swelling and relieves pain. The cone should be treated with gel in the morning and evening.
- "Rescuer". This gel stops the inflammatory reaction and heals the injured area of the skin. In addition, it has disinfectant properties.
- "Heparin ointment." The product is intended to combat thrombosis. However, it is also effective for bumps on the head from a blow. The ointment acts as an anticoagulant and promotes the resorption of hematomas.
- "Lyoton 1000". This gel also has anticoagulant properties and dissolves blood mass under the skin after a bruise.
- "Mirralgin." The product is a plant-based balm. It improves blood circulation in damaged tissues, relieves pain and swelling. This harmless herbal remedy is especially indicated for young children.
These medications must be used until the lump disappears completely. Treatment may take varying periods of time, depending on the severity of the injury.
Treatment of formations on the head
Heparin ointment has an analgesic and absorbable effect.
You can smear a bump on the head from a blow with medicines and natural remedies. The first group includes absorbable and analgesic drugs:
- Troxerutin. Decongestant gel that quickly relieves swelling from hematomas. However, it should not be used on damaged areas of the skin.
- Troxevasin. A soothing gel that restores blood vessels and relieves inflammation.
- Heparin ointment. An inexpensive analogue of anti-inflammatory drugs with a powerful analgesic and absorbable effect.
- Gel Rescuer. A product aimed at regenerating the skin. Activates the growth of new cells, removes infection.
- Lyoton 1000. Gel with a resolving effect, aimed at quickly removing blood clots from under the skin.
- Mirralgin. Balm made from herbal ingredients to relieve pain and swelling.
In children, it is better to smear the bump on the head after blows with natural remedies without antibiotics and strong NSAIDs.
If the lump hurts a lot, adults can anoint it with NSAID-based gels. However, the tablets should not be taken orally. They can hide some important symptoms.
Creams and gels must be applied strictly according to the instructions, without exceeding the treatment period. For children, therapy is prescribed by a doctor. For children, smaller dosages and a shorter course of treatment are used. The drugs are most often used 2-3 times a day.
Traditional recipes for bruises on the head
Raw grated potatoes help to quickly eliminate hematoma.
This group of medicines includes all natural mixtures, as well as the restorative properties of herbs and products:
- a compress with vegetable oil is made from heated sunflower or olive oil;
- crush the cabbage leaves and boil them in milk for a few minutes, then apply them to the head along with gauze for 1 hour;
- wrap a boiled egg and warm the bruised area with it several times a day; salt can be used in the same way;
- prepare a decoction of thyme - 1 tbsp. l. for 1 glass of water, moisten gauze and apply to the head;
- Fresh wormwood juice has absorbent properties;
- you can make a paste from raw potatoes, 1 tsp. starch and water;
- a compress of honey, salt and a small amount of mustard powder helps relieve pain and swelling;
- fresh aloe also helps with infection, pain and swelling. Use plant leaves over 3 years old.
After applying compresses, you can apply an iodine mesh to the bump, which will enhance the effectiveness of natural products.
Before using any folk recipes, especially those involving heating, be sure to consult a specialist. In some diseases and purulent processes, heat is the real enemy.
You can use natural products externally only if you are not allergic to them.
Surgery
Surgeon intervention is required only for large benign formations. All patients with malignant tumors undergo radiation therapy or chemical treatment followed by removal of the tumor.
If the lump does not go away after the blow for a long time, you need to carefully examine it. Sometimes it is enough to undergo a longer course of therapy, combining medications and home remedies. In some diseases, the lump becomes a side effect and persists for a long time. It can be reduced surgically, but only under strict doctor’s instructions.
Folk remedies
Bumps on the head from a blow can also be cured using folk remedies. Everyone knows the wound-healing properties of aloe and Kalanchoe juice. These plants can be used to make a compress that will help reduce tissue swelling. You need to take a leaf of the plant, remove the top layer from it, put it on the sore spot, and then cover it with film and cotton wool. The compress is kept for about 2-3 hours.
You can use regular cabbage leaves. They need to be crushed and boiled in milk. Then put the mixture on a napkin or cloth and apply it to the bruise. Keep the compress for about 1 hour. This remedy helps relieve swelling.
Bumps on the head from a blow in adults can be treated with a mixture of iodine and alcohol (1:1 proportions). This remedy is especially useful for swelling of a bluish and pinkish color, accompanied by severe subcutaneous hemorrhage.
Indications for use of Levomekol ointment
Since Levomekol ointment has an antibacterial effect, and at the same time stimulates the restoration of tissue structure, the drug is indicated for the following diseases:
- infection of wounds with pathogenic microflora, ulcers and purulent abscesses on the epidermis;
- burns (mostly 2nd and 3rd degree);
- violation of tissue integrity due to injuries;
- necrotic processes;
- weeping and dry eczema;
- calluses;
- trophic ulcers;
- frostbite of the extremities (superficial layers of the skin);
- pimples, acne, carbuncles, boils;
- otitis and sinusitis (including with purulent discharge);
- treatment of sutures after surgery
- bedsores;
- haemorrhoids.
Levomekol ointment can be used for children
"Levomekol" can be used for children from 1 year. But before this, it is imperative to consult a pediatrician.
Possible consequences
It should be remembered that a bump on the head from a blow is not always a harmless phenomenon. After all, the cranium contains the brain, many vessels and nerve nodes. Damage to these anatomical structures can lead to serious consequences:
- concussion;
- skull fracture;
- rupture of cerebral vessels.
It is important to remember that serious head injuries often lead to severe disruptions in the functioning of the central nervous system. Such pathologies often require long-term treatment. Therefore, everyone should know in what cases a lump can be dangerous.
Further actions in case of injury
If for the first day the most correct and effective method is exposure to cold, then after this time, actions should be aimed at carefully warming up the impact site. Heat will help get rid of the swelling, relieve swelling, as a result of which the lump will resolve and disappear.
Heated salt retains heat for a long time. Wrapping it in a not very thick cloth, you need to keep the compress on the sore spot. A boiled egg will also remain warm for a long time and can be used for application.
When a doctor's help is needed
It is necessary to consult a doctor if the bump on the head after the blow does not go away within a week. If swelling does not disappear for a long time, this may indicate trauma to the bone tissue.
Seek immediate medical attention if a child or adult experiences the following symptoms:
- pain in the head and neck area;
- dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- blurred vision;
- strabismus;
- discharge of blood or clear fluid from the nose or ears;
- increase in pain syndrome;
- disorders of speech and consciousness;
- pain that increases when turning the head;
- seizures;
- bleeding from the wound that does not stop for more than 10 - 15 minutes.
These warning signs may indicate a severe head injury. It is necessary to put the patient to bed, call an ambulance and monitor his consciousness and breathing until the doctors arrive.
Levomekol or Vishnevsky ointment. What's better?
Let's start with the fact that Vishnevsky ointment and Levomekol, although they are used in similar cases, still have a multidirectional spectrum of action. Thus, Vishnevsky ointment is effective when the wound is in the process of regeneration. Therefore, it cannot be used when the wound is suppurated or severely inflamed. Yes, the drug contains an antiseptic, but its concentration is not enough to provide a bactericidal effect. Moreover, tar and castor oil stimulate blood circulation in the affected area, which worsens the situation.
This is why Vishnevsky’s ointment is not as effective, since Levomekol has higher antibacterial activity due to the presence of an antibiotic in it and accelerates the process of outflow of pus from the wound. Also important are the following distinctive features that determine the superiority of Levomekol ointment:
- no unpleasant odor;
- higher repair characteristics;
- does not provoke irritation in the treatment area;
- when treating boils, Levomekol quickly initiates an abscess and opening of the abscess, followed by wound healing.
But if Vishnevsky ointment helps the patient, then there is little point in changing it.
Is a lump always associated with a bruise?
A soft bump after a head hit is not dangerous if there are no signs of trauma to the brain or bones of the skull. It is important to remember that a hematoma from a bruise never has a solid structure. If the lump looks like a lump, it is most likely not related to an impact.
Very often, people associate tumors on the head with the fact that they accidentally hurt themselves. However, such bumps may have a completely different origin.
The following formations may occur in the forehead and scalp area:
- Atheromas (wen). They look like balls filled with greasy contents. Festering wen can be painful.
- Hemangioma. This tumor of blood vessels is very similar to a lump after a bruise. However, such a neoplasm has a more intense color than a regular hematoma.
- Fibroma. The tumor consists of connective tissue and is benign. With trauma, malignant degeneration is possible.
- Lymphadenitis. In children, lymph nodes often become enlarged due to inflammation and infections. They look like red, painful bumps. They are usually located on the back of the head or behind the ears.
The appearance of a bump on the head should not be associated solely with the blow. Many of the above tumors require surgical removal. Therefore, if you are not sure that the lump is caused by a bruise, then you need to consult a specialist. Only a doctor can determine the exact cause of the tumor.
To sum up all of the above, we can say
- Lipoma and atheroma are benign formations of different natures - lipoma simply consists of altered adipose tissue, and atheroma is made of a sebaceous gland with a capsule filled with secretion - sebaceous atheromatous masses.
- Conservative, incl. Treatment of lipoma with folk remedies, as well as treatment of atheroma, is absolutely ineffective and often harmful.
- A small (2-3 cm) lipoma can not be operated on, but observed. In case of growth, as well as any discomfort, surgery to remove the lipoma is indicated.
- Removal of atheroma is always desirable, because they tend to increase in size and fester.
- If you find a subcutaneous formation in yourself, you need to consult a doctor, because... under the guise of a lipoma or atheroma, other formations can develop - dermatosarcomas, liposarcomas, hygromas, lymphadenitis, etc.
Dr. Elshansky I.V. has been involved in the diagnosis and surgical treatment of benign formations of the skin and subcutaneous tissue for many years.
Inspection of the impact site and provision of first aid
The ability to provide first aid to a child is 50% of the successful course of the disease after an injury.
If a child falls, you must immediately examine the sore spot and determine how severe the injury is.
It doesn’t matter where the head was hit (forehead or back of the head), the main thing is to determine the degree of severity and provide quick assistance
In this case, you need to immediately apply ice to it. If you don’t find it in the refrigerator, a cold container with liquid or just a cloth moistened with running water will do. Keep the compress on your head for a few minutes, this will help reduce swelling and relieve pain.
During the blow, an abrasion appeared, and blood flows from it.
Take a cotton swab and soak it in hydrogen peroxide. Treat the scratch carefully to prevent infection. If blood flows heavily from a wound and cannot be stopped, call medical attention.
An examination of the head revealed no injuries.
In this case, you need to monitor the baby’s condition and pay attention to strange behavior. He may become moody, get tired quickly, sleep for a long time, complain of headaches
These may be signs of a concussion and other conditions. If the child’s condition worsens, he loses consciousness, feels sick and vomits, call an ambulance.
After the blow, calm the baby down and put him in his crib
He needs peace and attention. Sit next to him, tell him a story, let him know that nothing bad happened and soon he will be able to run again
The main thing is not to let your child fall asleep for several hours. This is necessary to determine the severity of his condition and notice alarming symptoms if they appear.
Wake up your baby at night and check his coordination. If everything is fine with the child for several days, then you can calm down, most likely the bruise passed without complications.
After hitting your head, it is useful to spend more time in the fresh air, just try to avoid active games. It’s better to take your child for a leisurely walk in the park.