Lacunar stroke is a type of ischemic stroke. Some authors consider it appropriate, taking into account the peculiarities of the mechanism of development of the pathology, to introduce the general term “ischemic brain disease”.
The identification of this form is based on cavities identified as a result of the disease in the subcortical structures. The disease was not diagnosed for a long time during the patient’s lifetime, since it does not manifest itself with any symptoms for a long time.
As new diagnostic techniques developed, it became clear that lacunar stroke accounts for up to 15% of all cases of cerebral infarction.
According to the International Classification of Diseases, the pathology is included in the group of cerebrovascular diseases and is interpreted as a stroke of unspecified origin (infarction or hemorrhage).
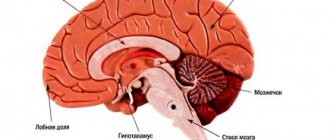
Features of brain damage
Studies have shown that the lacunar form develops mainly in patients with hypertension with severe atherosclerosis. This points to older age as the most vulnerable risk group. Against the background of damage to the main vessels by atherosclerotic plaques, patients already have signs of the onset of chronic cerebral ischemia.
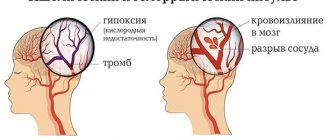
Unlike hemorrhagic and ischemic forms of stroke, with this pathology the patency of not the main arteries is impaired, but the smallest capillaries located inside in relation to the cortical centers of the brain (penetrating). The diameter of these vessels is several tens of microns. With normal blood circulation, they are responsible for supplying the deep layers of brain cells.
Intracerebral arteries are characterized by:
- very low possibility of replacement by collateral (auxiliary) vessels;
- strict local type of pathological damage in areas no more than 10 mm;
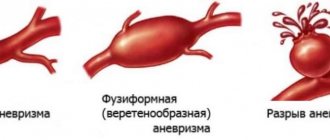
- the possibility of transformation into microaneurysms with subsequent hemorrhage;
- they do not belong to the type of arteries affected by atherosclerosis (they are not vessels of the muscular elastic type, such as the aorta, femoral artery, coronary vessels).
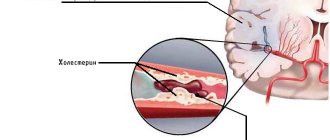
Atherosclerosis worsens the overall nutrition of the brain, contributes to the progression of hypertension and thereby complicates the position of intracerebral vessels.
It is important that the cortical part of the hemispheres is not affected. Small blood clots first cause areas of softening, then cavities (lacunae) form in their place. The size ranges from 10 mm in diameter to 1.5 cm, merging into larger formations is possible. Giant lacunae are cavities larger than 2 cm, but they are rare. Inside the lacunae there is blood or plasma with fibrin. The walls are a “bag” that can rupture under physical stress, a sharp increase in blood pressure, or head injury.
Research, statistics
Frequency of strokes, incl. lacunar, in our country is 2 times higher than in other countries of Western Europe. It is the third leading cause of death in the world. In 85% of cases, the disorder is caused by blockage of blood vessels and interruption of the supply of oxygenated blood to a certain part of the brain.
In 90% of cases, stroke occurs in people over 45 years of age, mainly in men. But in women the condition is more dramatic. This is often associated with the hormonal burden of women (childbirth, menopause, hormonal therapy, contraception) and a higher incidence in older age groups.
Determining the cause of the increased incidence in our country is not easy. A number of studies show a connection with an unhealthy lifestyle, lack of physical activity, type of diet, and a large number of smokers. But to some extent, unfavorable statistics are also associated with underestimation of risk factors leading to stroke.
Causes
A significant role in the formation of pathological changes in the penetrating arteries of the brain is assigned to:
- hypertension with uncontrolled changes in blood pressure, frequent crises, lack of or inadequate treatment;
- the consequences of metabolic changes (impaired carbohydrate metabolism and ionic balance) in diabetes mellitus;
- conditions and diseases accompanied by increased blood clotting and a tendency to thrombus formation (extensive injuries and burns, shock, large loss of fluid with prolonged vomiting, diarrhea, dehydration, polycythemia and others);
- diseases of the arteries of an inflammatory nature (arteritis and vasculitis) with infectious or allergic causes that impede the general blood flow through the cerebral vessels;
- hereditary changes in the structure of the vascular wall.
Rarely, the cause of a lacunar stroke may not be ischemia with tissue necrosis, but a small area of hemorrhage in the adjacent area. Instead of atherosclerosis with the presence of cholesterol plaques from the inside, the penetrating vessels become denser, lose hyaline and become sclerotic.
Pathogens
The described disease can manifest itself as a result of a failure in the blood supply in one of the perforating vessels of the arteries. In almost 80% of lesions, the area of change is the white matter of the cerebral region, located in the subcortical zone and the inner shell, in the remaining 20% - in the base and bridge. Typically, the main cause of progression of deformities is chronic arterial hypertension. Due to this, anomalies begin to appear in the walls of the vascular canals. In the case of such a process, the patient experiences a decrease in the lumen of the artery, which entails problems in the circulatory system, which supplies a certain area of cerebrotissue. After this, signs of ischemia and death appear in the affected lobe; subsequently, a hole is formed in place of the removed cells.
The main etiological sources of the disease are:
- Chronic disease of the arteries of the elastic and muscular-elastic type, renal failure with an increased number of creatinine in the blood cells.
- Diabetes.
- Alcohol abuse.
- The chronic stage of obstructive disorders occurring in the pulmonary apparatus.
- Infectious agents that have entered the body.
- Autoimmune diseases, etc.
Clinical manifestations
Lacunar stroke, unlike other forms, is not accompanied by acute impairment of consciousness, speech, vision, or motor functions, since cortical structures are not involved in the pathological process.
All symptoms arise and increase gradually, depending on the location of the cavity, pressure on a specific subcortical center or its destruction. Complexes of symptoms are combined into syndromes; about 20 of them have been identified. Neurologists speak of a “lacunar state” of the brain.
When passively trying to flex and straighten the limbs, the doctor determines increased resistance
Main syndromes:
- motor - partial or complete loss of movement develops in half the body or one limb and face, all other functions are preserved (half of all stroke cases);
- ataxic hemiparesis - weakness in the arm or leg, more in the hand and feet, with preserved strength;
- combination of hemiparesis and loss of sensitivity (35% of cases);
- dysarthria and “awkward hand” - a combination of speech changes and weakness in the hand, difficulties in the functioning of the joints, possible disturbances in the contractions of the muscles of the face and legs on the same side;
- hyperkinesis (multiple excessive movements) - accompanied by large tremor of the hands, obsessive movements of the torso, twitching of the shoulders and head, at the same time there is a violation of tone in certain muscle groups;
- isolated sensory syndrome (5% of cases) - typically a violation of sensitivity in half the body to complete loss, the temperature of objects, the sharp and blunt end of a needle are not felt, sometimes combined with a change in pain.
Other symptoms include:
- cramps and increased muscle tension on both sides;
- memory loss;
- staggering when walking, impaired balance;
- loss of control of the pelvic organs, involuntary urination and bowel movements.
Neurologists pay attention to the deterioration of the patient’s condition in the morning. Patients report a headache in the evening, which is associated with fatigue and overwork, and take painkillers. Lacunar stroke occurs in a sleepy state. The patient wakes up and discovers changes.
Lacunar formations may be located in “silent” zones and not manifest clinical symptoms.
Preventive actions
Lacunar stroke affects not only the elderly, but also the younger generation.
What is most noteworthy is that men are more susceptible to this disease than women. The main causative agent of cerebral infarction is an unfavorable lifestyle, being in a stressful state, constant stress on the neurons of the brain, blood vessels and heart. Despite the seriousness of the situation, the best medication for preventing the disease is Aspirin. It significantly reduces the risk of recurrence of the lesion. In this case, the drug should be taken only in its pure form.
In addition, to protect yourself from illness, you should take care and reconsider your lifestyle:
- It is imperative to follow a diet that does not contain foods with high sugar, cholesterol and other harmful substances;
- At the same time, it is recommended to take preventive medications, which are prescribed by a doctor during periodic examinations, which should be carried out at least once every six months;
- Blood pressure should always be monitored; it is best to measure it several times a day (and it is better to note all readings in a diary);
- if any of the symptoms of the disease appear, you must immediately contact a specialist;
- and of course you should completely give up alcohol and smoking;
- Get out into nature as often as possible and breathe fresh air.
Do not forget that overwork, stress and excessive loads only increase the likelihood of illness, so everything should be in moderation, and conflict situations should be avoided altogether. Sports should be present in life, but in such a way that it does not harm health.
Diagnostics
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor must identify the connection with hypertension and confirm the gradual development of symptoms. A repeat examination after a few days may indicate worsening dynamics and the appearance of additional signs.
A modern way to identify lacunae in brain tissue is magnetic resonance and computed tomography. It indicates the smallest formations with reduced density and dimensions of 1.7 mm in the subcortical system, determines the shape and localization. On the seventh day of the disease the picture is clearer.
The arrow shows the lacuna identified on MRI.
Unfortunately, with small lacunae sizes, neither MRI nor CT scans detect pathology.
Angiography of cerebral vessels does not help in diagnosis either.
Treatment problems
Treatment of lacunar stroke must begin in the hospital with the correction of antihypertensive therapy. Without blood pressure control it is impossible to achieve results. Therefore, great importance is attached to:
- a therapeutic and protective regime (sufficient sleep, absence of negative emotions and stress, friendly attitude of relatives and staff), the patient will be required to stop smoking if he has not already quit;
- diet in accordance with table No. 10 (limiting salt, fatty and spicy foods, coffee, sweets), fermented milk products, chicken meat products, vegetable salads, unsweetened fruits are recommended.
The basic principles of therapy do not differ from the general requirements for the treatment of all ischemic strokes; they are divided into basic and specific measures.
Basic treatment includes:
- use of antihypertensive drugs to optimize blood pressure;
- regulation of blood clotting;
- measures against cerebral edema;
- if necessary, anticonvulsants.
Cerebrolysin is prescribed as a neuroprotector
Specific treatment includes:
- carrying out thrombolysis in the first 6 hours (intravenous administration of fibrinolysin according to the scheme);
- connection of drugs that reduce thrombus formation (aspirin), anticoagulants according to indications;
- protection of brain cells with neuroprotectors.
The prognosis of lacunar stroke is relatively favorable: restoration of lost functions occurs with proper treatment and patient behavior after 3–6 months.
Complications and prognosis
If the patient has once suffered a lacunar stroke, the prognosis for him is favorable. Lost brain functions are completely restored, only in some people partial disturbances of movement and sensitivity may remain.
If attacks recur, they can cause complications such as lacunar brain disease, which is common in people with vascular dementia.
As for life expectancy, the probability of death is 2%.
It is impossible to say exactly how long a person lives after a lacunar stroke. Much depends on the patient’s age, the location of pathological foci, the development of concomitant diseases, and the timeliness of medical care.
The formation of gaps in the brain stem is especially dangerous, because this is where the respiratory and cardiovascular centers are located.
The likelihood of death increases with a recurrent stroke.
What vascular agents and neuroprotectors are most active in cerebral ischemia?
To support and develop collateral blood flow, drugs such as Cavinton, Nicergoline, Cinnarizine, Eufillin are used. In modern neurology, these drugs are not recommended due to the identified “steal syndrome” (increased blood flow through dilated collaterals further increases the ischemic area, since blood flows into a new direction).
The need to activate metabolism and energy production in damaged brain cells requires drugs with neuroprotective and antioxidant effects. For this purpose: Glycine, Semax, Cerebrolysin, Nootropil, Mexidol, Cortexin are used.
The modern level of medicine takes into account the evidence base of clinical effectiveness. And, unfortunately, it does not exist for these drugs. However, many neurologists consider the use to be practically effective and justified.
What does untreated lacunar stroke lead to?
Violation of the regime and treatment, instead of complete recovery, leads to repeated strokes. The most common consequence of lacunae in brain tissue is a gradual change in the patient’s mental status:
- “gaps” of memory develop, a person forgets not only names, but also loved ones;
- communication becomes difficult due to increased nervousness, reaching the point of hysteria and tearfulness;
- a person is disoriented in place and time, does not understand where he is, and “relives” the period of his youth again.
The patient becomes helpless, loses criticality towards his actions, and requires constant patient care
Classification
Clinical classification is based on clinical symptoms and is discussed in the section on symptoms of lacunar infarction.
In the development of the disease there are:
- the most acute period is the first 3 days;
- acute – 28 days;
- early recovery – the next 6 months after suffering a circulatory disorder;
- late recovery – for 2 years.
Due to mild symptoms and the absence of pronounced motor, speech and sensory disorders, it is very difficult to describe the features of each interval. Therefore, this division is of secondary importance.
What to do for prevention?
Prevention of lacunar ischemia does not differ from general measures to prevent cerebrovascular accidents:
- providing “relief” from nervous overstrain at work and in the family by engaging in feasible sports, walking, hiking;
- mastering the methods of self-hypnosis, yoga therapy;
- maintaining body weight within age norms, fasting days if necessary;
- adherence to the principles of an anti-sclerotic diet, refusal after 40 years of contraindicated foods;
- monitoring blood pressure levels;
- treatment of hypertension when detected;
- carrying out a full course of rehabilitation measures in the event of an acute stroke or myocardial infarction;
- as prescribed by a doctor, taking medications that prevent thrombosis with monitoring of the prothrombin index;
- seeking medical help if new brain symptoms occur.
Patients with risk factors are recommended to undergo magnetic resonance imaging annually. The method allows you to compare and identify positive or negative changes. Timely correction of treatment depends on it.
Rehabilitation period
During the rehabilitation period, a whole range of measures is carried out, both medical and pedagogical, legal, social and psychological. All of them are aimed at restoring lost functions as a result of a lacunar stroke.
Principles of the rehabilitation program:
- If rehabilitation measures are started as early as possible, for example, from the first days of the onset of symptoms of the disease, recovery occurs much faster and more fruitfully. This is an excellent chance to avoid possible secondary complications, such as contractures, congestive pneumonia, thrombophlebitis and others.
- Rehabilitation should be carried out only under the supervision of specialists. If events are organized incorrectly, the chance of full recovery will be significantly less.
- Recovery requires the participation of a physical therapy methodologist, a neurologist, a physiotherapist, a psychotherapist, an occupational therapist and a speech therapist.
- The rehabilitation process involves the presence and support of the patient’s loved ones. It is best to entrust the patient with the most basic household chores on weekends or in the afternoon.