Cerebellar stroke is still one of the least studied diseases of the central nervous system. The variability of clinical manifestations, their similarity to symptoms of damage to the cerebral hemispheres and other features significantly complicate diagnosis. This pathology occurs relatively rarely: approximately 2% of patients with acute disorders of cerebral circulation have a localization of the lesion in the cerebellum. Men of middle and retirement age suffer more often. What are the characteristic symptoms of the disease and how to treat such a stroke? The answers to these questions are in our article.
Types of cerebellar stroke
According to the standard classification based on pathogenesis, two types of cerebellar stroke are distinguished:
- ischemic;
- hemorrhagic.
According to statistics, the first type significantly predominates. Ischemic lesions of the cerebellum, according to various sources, account for 80 to 90 percent of cases. However, according to expert forecasts, within 50 years the number of diseases with a hemorrhagic nature is expected to double - the result of aging and changes in the racial composition of the planet's population.
Ischemic cerebellar stroke
The development of ischemic damage to the cerebellum is based on partial or complete blockage of blood vessels bringing arterial blood by a thrombus. In this regard, nerve cells stop receiving oxygen and nutrients. As is known, nervous tissue is very sensitive to hypoxia, and if blood flow is not normalized, neurons begin to die.
Hemorrhagic cerebellar stroke
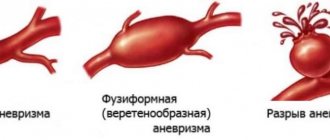
With the hemorrhagic nature of the disease, a sharp disruption of the blood supply to the cerebellum occurs due to rupture of the artery or capillary feeding this structure. Due to the anatomical features of blood circulation, the consequences of a vascular accident are very difficult to predict, since the brain stem is often involved in the pathological process.
Diagnostics
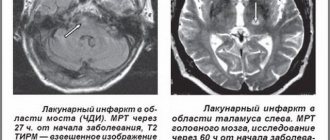
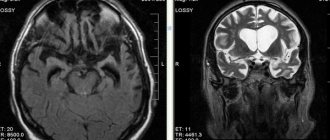
To confirm the diagnosis of cerebellar stroke, an ultrasound is performed. The study allows you to determine the displacement, see the area of edema, and detect a damaged artery.
An informative diagnostic method is magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography. Both methods provide an accurate picture of the changes, the size of the damage, the depth, and detect the cause of the disease.
A blood test is taken for general formula and biochemistry. The data will allow you to identify the level of sugar, cholesterol, and other substances that are signs of the diseases that provoked the attack.
Symptoms of cerebellar stroke
The clinical picture of both ischemic and hemorrhagic disorders of the blood supply to the cerebellum is varied, but there are characteristic symptoms that make it possible to suspect damage to the blood vessels in this particular area. These include cerebellar ataxia. This syndrome is associated with the functional activity of the cerebellum and includes:
- Balance imbalance. The patient cannot stand steadily and sways in different directions when walking.
- Changes in speech. Disturbance in the flow of arterial blood into the cerebellum is accompanied by scanned speech. The patient loudly tries to pronounce ordinary words.
- Loss of precision in movements. It is difficult for the patient to control fine motor skills, movements become sweeping.
- Tremor. Trembling of the limbs, head, and torso appears.
- Nystagmus. The eyeballs make involuntary oscillatory movements. Their frequency can reach several hundred per minute.
Among the general symptoms characteristic of acute cerebral circulation disorders are headache, dizziness, spontaneous vomiting, fever, loss of consciousness, difficulty swallowing, and muscle paralysis.
Causes and factors of cerebellar stroke
The ischemic type of cerebellar stroke is usually considered the outcome of atherosclerotic disease. The thrombus travels through the vertebral or basilar artery through the bloodstream. Embolism can also occur with fresh myocardial infarction or atrial fibrillation. Surgical interventions on the neck are very dangerous, since during their implementation it is possible to traumatize the vertebral arteries with further disruption of blood flow.
The main causes of hemorrhagic stroke of the cerebellum:
- high blood pressure or sudden changes;
- cerebral amyloid angiopathy - deposition of amyloid in small blood vessels through which blood enters the central nervous system;
- taking antithrombotic drugs (“blood thinners”);
- neoplasms;
- inflammatory diseases of the walls of blood vessels.
Wrong lifestyle
In addition to the immediate causes, risk factors play a significant role in the development of cerebellar stroke. One of the key ones is the wrong lifestyle. It includes:
- low mobility during the day;
- food based on foods high in fat and sodium;
- smoking, alcohol abuse, taking narcotic drugs;
- constant nervous tension, chronic stress.
These factors contribute to disruption of normal blood circulation in organs, including the nervous system.
Diseases and medications
Diseases of the internal organs can provoke a cerebellar stroke. The relationship between cerebral circulatory disorders and the following somatic diseases has been proven:
- arterial hypertension;
- metabolic syndrome, accompanied by high levels of cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins in the blood;
- diabetes mellitus and other endocrine pathologies;
- cardiac ischemia;
- diseases in which blood clotting increases.
Uncontrolled use of medications that affect the functioning of the heart, change hormonal levels, and thin the blood can also cause acute impairment of cerebral circulation (including in the cerebellum).
Other reasons
Other causes of vascular accident include genetic predisposition and age factor. A number of genes are currently being studied that are potentially associated with an increased risk of cerebral circulatory disorders.
Causes of hemorrhage
The trigger mechanism for hemorrhage in the cerebellum is most often hypertension. Basically, the reasons for this type of hemorrhage do not differ from the reasons for the occurrence of other types of strokes that affect the brain. Most often these are the following phenomena and conditions:
- A sharp rise in blood pressure;
- Severe anxiety, stress;
- Physical fatigue;
- Intense mental activity;
- Taking inappropriate medications;
- Alcohol consumption;
- Excessive overheating (in the sun, in a bath, a very hot bath, and so on);
- Smoking can cause vascular damage, which, in turn, starts a whole chain of diseases, ultimately leading the patient to stroke, paralysis or death.
First aid for stroke
When providing first aid, it is necessary to understand what a cerebellar stroke is, otherwise there is a huge risk of harming the patient. The main goal is to prevent further death of neurons, and inept and incorrect actions can lead to extremely negative consequences. Recommend:
- Lay the patient on the bed, if the circulatory disorder occurred at home, or on the ground, slightly elevate the torso.
- Turn your head to the side to avoid vomit getting into your respiratory tract.
- Seek medical attention immediately.
- Try to calm the victim down and calm down yourself.
- Provide sufficient fresh air and avoid tight clothing.
Stroke treatment
The volume, tactics and duration of treatment depend on the type of vascular disorder. Common activities include:
- Ensuring the supply of oxygen to brain tissue.
- Correction of blood pressure indicators.
- Prevention of convulsive syndrome.
- Maintaining water-electrolyte and energy balance, normal body temperature.
Drug treatment of cerebellar stroke
The use of medications is possible only after the cause of the vascular accident has been established. For the treatment of ischemic stroke of the cerebellum, the following is used:
- Thrombolytics. Such drugs are able to dissolve blood clots in blood vessels, relieving areas of nervous tissue from ischemia.
- Neuroprotectors. Used to reduce the sensitivity of neurons to oxygen starvation. The use of these drugs allows you to avoid further death of nerve cells and gradually restore the functions of damaged areas.
- Diuretics are medications that help fight swelling of the brain.
In the treatment of acute circulatory disorders in the cerebellum of the hemorrhagic type, neuroprotectors and diuretics are also used, but the key drugs are hemostatic agents.
The amount of drug therapy is selected individually for each patient. It expands in the presence of paralysis, concomitant somatic or endocrine pathology.
Surgery
In parallel with drug treatment, the issue of surgical intervention is being resolved. Its functions:
- Removal of a blood clot or hematoma.
- Redistribution of blood flow to supply affected areas of nervous tissue.
- Stopping bleeding when drug therapy is ineffective.
Traditional surgery is performed openly or using an endoscope.
Rehabilitation
During the recovery period, a set of measures is used: physiotherapy, drug treatment, massage, classes with psychologists and speech therapists.
Depending on the clinical picture and each individual case, rehabilitation courses are selected individually.
Their main goals are:
- restoration of motor functions and motor skills;
- renewal of everyday skills;
- speech restoration;
- memory restoration.
The rehabilitation period depends on the severity of the disease. On average, it takes six months or more for the patient to feel significant improvements.
After a stroke, to minimize the possibility of relapse, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- monitor blood cholesterol levels;
- undergo MRI periodically;
- control blood pressure levels;
- avoid stressful situations;
- do not give in to bad habits: smoking, drinking alcohol;
- If possible, play sports and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Recovery and rehabilitation after cerebellar stroke
Early initiation of rehabilitation treatment makes it possible to more effectively activate the relationship between neurons, returning lost functions to nerve structures. Rehabilitation measures should be varied and include both medications and physical procedures, special physical exercises, and occupational therapy. The main goals of rehabilitation treatment:
- regaining control over motor activity;
- normalization of speech;
- restoration of lost self-care skills;
- improvement of muscle tone after paralysis;
- prevention of complications (contractures).
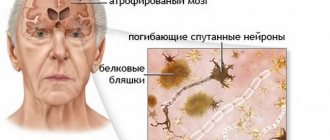
The cerebellum and its functions
Below the occipital hemispheres in the lower part of the skull, close to the spinal column, is the cerebellum. It consists of two hemispheres and a worm. The weight of an adult reaches 160 g. At the time of birth, the child is very small, but is distinguished by noticeable development during the first year of life. By the age of 6 it reaches the minimum size for an adult.
On top, the cerebellum is covered with gray matter, inside it consists of white matter - it contains four nuclei.
Nutrition is provided by three cerebellar arteries, originating from the vertebral and main trunks.
The cerebellum receives information about the current position of the body or its parts. At the same time, an adjustment comes to him from the cerebral cortex regarding what next movement needs to be made. This allows him to correct voluntary and involuntary actions.
The main functions of this part of the brain are coordination of movements, regulation of muscle tone, balance, and muscle memory.
- Stroke on the left side: consequences and features of recovery. How long do people live with this diagnosis?
Stroke in the cerebellum: possible consequences, prognosis
Despite its low prevalence, cerebellar stroke has a poor prognosis for the patient and is accompanied by high mortality, reaching thirty percent or more. Common consequences of cerebellar stroke:
- Disability. According to statistics, only 20% of patients who have suffered an acute cerebellar circulatory disorder are able to care for themselves independently by six months from the onset of the disease. The rest of the victims need help from others.
- Paresis and paralysis. Restoration of motor activity in damaged limbs is slow and not always complete.
- Speech impairment. Some patients still have scanned speech.
Often such severe consequences of a cerebellar stroke cause despair in the patient. However, you should not give up: daily rehabilitation activities can partially or even completely restore lost skills.
Forecast
At the moment, acute manifestations of cerebellar stroke are practically impossible to treat. Unfortunately, almost all patients with severe manifestations of hemorrhage in the cerebellum do not survive, even if they receive appropriate medical care in a timely manner.
Basically, hemorrhage into the cerebellum, the consequences of which can be very severe even if the patient survives, is characterized by high mortality and dangerous complications. The situation is also aggravated by the age of the patient - mostly old people have a large “set” of chronic diseases and a greatly weakened body, which has difficulty resisting such a serious lesion as a stroke.
For a faster and better recovery for a patient who has experienced hemorrhage, it is important to create a calm, friendly, emotionally balanced atmosphere. His family and friends will have to show maximum tact, as the patient can be irritable, capricious and even whiny. Only a gentle attitude and love, combined with competent professional treatment, can return a person to a normal, fulfilling life.
Stroke Prevention
To prevent acute cerebral circulatory disorders, WHO specialists have developed simple recommendations:
- Control and correction of blood pressure.
- Prevention of heart rhythm disturbances.
- Minimizing risk factors.
- Annual examination of the condition of the great vessels.
- Monitoring blood parameters.
Cerebellar stroke is an extremely serious disease, but a number of modern diagnostic and treatment methods increase patient survival and improve their quality of life in the future.
First aid
If there is a suspicion that a stroke is developing, then the most important thing is to immediately call an ambulance .
Then you need to check whether the person can breathe, help him by emptying the oral cavity in a position lying on his side. If possible, record blood pressure and pulse readings. If the patient is on the floor, then lay him on his back, placing a towel folded in several layers under his head. It is very important to establish when the attack occurred, this will help in the correct prescription of therapy. You cannot independently lower blood pressure, give water, and especially feed the patient.
First aid for stroke