The brain stem is one of the important parts of the human central nervous system, since its sections contain nerve centers responsible for the regulation of all vital processes in the body, as well as the nuclei of the oculomotor and other cranial nerves, the function of which is to control the muscles of the face. For this reason, even minor damage to the brain stem by various neoplasms threatens the patient with disorders in the functioning of internal organs.
Types of lesions
Most often, brain stem tumors are diagnosed in children in the first years of life and in adolescence, with the peak incidence usually occurring at 4-6 years of a child’s life. Most of these neoplasms histologically represent gliomas of various formations:
- Astrocytomas. Occurs in more than 50% of clinical cases. It develops as a result of tumor damage to glial tissue cells - astrocytes, which perform a protective and auxiliary function in relation to neurons. Depending on the structural structure, all astrocytomas are divided into 2 categories: malignant and benign tumors. The former include pilocytic and fibrillar neoplasms, and the latter include anaplastic and multiform neoplasms.
- Ependymomas. They are rare, but they cause hydrocephalus and increased intracranial pressure even in the early stages of development.
- Oligodendrogliomas. They can reach large sizes, while the neoplasm has clear boundaries and does not grow together with the surrounding tissues.
- Glioblastoma. It is an aggressive type of glial malignant tumor.
According to the nature of their location in the tissues of the trunk, glial tumors are of 2 types:
- Expansive neoplasms. They have a clear location and do not merge with surrounding structures. Thanks to this feature, they can be easily removed surgically, after which in half of the cases the patient recovers completely.
- Infiltrative neoplasms. These include diffuse glioma of the brain stem, which, on the contrary, does not have a clear location, and its cells grow into the surrounding tissues and displace them, which is why the affected part ceases to function properly. Due to the fact that such a tumor cannot be removed without affecting the functional parts, the prognosis of the disease in most cases is unfavorable.
Total information
Pathological formations of the trunk are detected in children under the age of 15 years - up to 70% of operated patients. Most of the patients are children 5-6 years old. Of the total number of brain tumors, stem tumors make up 10-15%. Of this amount, 90% are brain gliomas. The high level of morbidity in childhood, the difficulty of diagnosis, the complexity of treatment and the high mortality rate make stem tumors a vital problem in oncology, neurology, pediatrics and neurosurgery.
Specifics of the disease
Due to the fact that the sections of the trunk contain nuclei of the regulatory formation, which are responsible for performing a large number of functional tasks of the human central nervous system, their damage by neoplasms is manifested primarily by the appearance of deviations in the functioning of certain internal organs, which significantly complicates diagnosis.
Initially, damage to the brain stem is manifested by the appearance of characteristic neurological abnormalities, for example, it may be a hearing disorder or uncontrollable twitching of the facial muscles. Further, as the tumor grows, the symptoms will intensify, headache and increased intracranial pressure will appear, which indicates the development of edema of healthy tissues.
As the situation worsens, the patient, to one degree or another, develops a syndrome of damage to the medulla oblongata, which is expressed in disruption of the functioning of internal organs and the development of central hemiplegia on the side of the body opposite to the tumor. For these reasons, when the first signs of damage to the trunk appear, the patient should seek medical help as soon as possible.
As practice shows, in a quarter of patients, the brain stem tumor is a benign neoplasm that can be removed surgically. At the same time, the remaining diffusely developing neoplasms are usually treated with radiation therapy.
Symptoms of the clinical picture of the disease
The nuclei of the cranial nerves, nerve pathways, centers - all components of the brain stem influence the development of many symptoms of its damage. The compensatory properties of children's nervous tissue provoke a long-term course of the disease in children. The occurrence of a tumor process affects the initial symptoms of the disease; further manifestations depend entirely on the type of tumor.
Probably, the development of main paresis of the facial nerve with a violation of facial symmetry, nystagmus, strabismus, as well as the occurrence of motor coordination disorders, unsteadiness of gait. Symptoms include dizziness, hand tremors, hearing loss, difficulty swallowing and a sore throat. Decreased muscle activity, paresis of the arms, legs or half of the body are added to the main symptoms. In a later period of the disease, symptoms of hydrocephalus appear - headache, nausea, vomiting. The death of the patient occurs due to disorders of cardiovascular functioning and the respiratory center of the brain stem.
Main symptoms
A glial tumor of the brain stem leads to organic damage to brain tissue, displacement of sections, and also causes circulatory problems in the organ, which causes symptoms characteristic of this disease:
- Headache. The appearance of this sign of damage to the brain substance is observed in 90% of clinical cases and is caused by an increase in the pressure of the neoplasm on the cranial nerves and blood vessels. Dizziness, darkening of the eyes, tinnitus and other manifestations of oxygen deprivation may also be present.
- Nausea, vomiting. Usually occurs during a headache attack and does not depend on food intake.
- Psychological deviations. It is observed in 65% of patients and manifests itself in changes in consciousness, irritability and apathy towards others.
- The patient experiences deterioration in clarity of vision, disordered pupillary reactions, loss of the inner halves of the visual fields, and paralysis of the facial muscles.
- The development of bulbar syndrome, which is characterized by the appearance of disturbances in the functioning of the functional centers of the medulla oblongata, that is, the patient has dysgraphia, aphonia, anarthria with impaired swallowing and articulation. Further, other manifestations of brainstem lesions arise: impaired cardiac activity, decreased blood pressure and the appearance of peripheral paralysis of the tongue muscles.
Also a distinctive feature of brain stem damage is an increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the subarachnoid space and, accordingly, an increase in the volume of the head.
Trunk stroke: what is it, prognosis for recovery, consequences
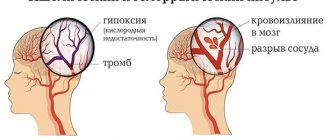
Stroke is an acute pathological condition in which the blood supply to a certain area of the brain is disrupted. As a result, neurons are starved of oxygen and die, which leads to the loss of brain functions controlled by this area.
A stroke can affect both the brain and the spinal cord (called a spinal stroke). A separate form is a brain stem stroke, a disease in which an acute circulatory disorder occurs in the brain stem. Why does a brainstem stroke occur, what is it and is recovery possible for patients who have suffered an attack?
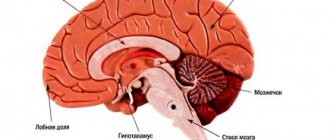
Brainstem stroke: what is it, recovery prognosis, consequences The brainstem connects the spinal cord to the brain, it is one of the most important structures of the nervous system
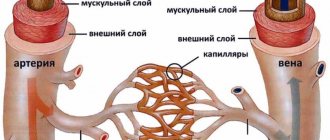
The brain stem is an important part of the nervous system. It is located at the base of the skull, through which pass pathways connecting the spinal cord and the cerebral cortex. The brain stem includes the medulla oblongata, pons and midbrain, contains cranial nerves and their nuclei, vasomotor, respiratory nerve centers. Thus, the brain stem ensures the interaction of central nervous system structures, transmits commands from the brain, carries out reflex reactions, chewing, swallowing, regulates muscle tone, is responsible for breathing, blood circulation, autonomic reactions, thermoregulation, balance, and participates in the functioning of the organs of hearing and vision.
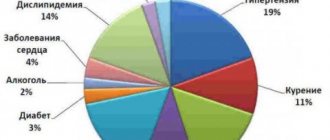
Alcohol abuse and smoking, poor and irregular diet, excess weight, sedentary lifestyle, stress, and overwork increase the risk of stroke.
Types of strokes
Depending on the etiology, a stroke can be ischemic or hemorrhagic.
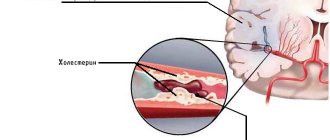
Ischemic brainstem stroke occurs due to blockage or compression of the vessels carrying blood to the brain, a detached thrombus, a blood clot, or, in rare cases, droplets of fat or air bubbles. Compression of the vessel may occur due to a tumor or scar formed after an injury. Ischemic stroke develops much more often than hemorrhagic stroke and has a more favorable prognosis.
A hemorrhagic stroke develops as a result of a rupture of a vessel, in which not only the nutrition of a certain area of the brain is disrupted, but the blood permeates and compresses the brain tissue, forming a hematoma. With a hemorrhagic brainstem stroke, life-support nerve centers are damaged in the brainstem.
Due to a lack of oxygen, the nerve cells of the stem brain cease to perform their functions, as a result of which the coordinated work of all internal organs ceases.
Causes
Among the pathologies leading to brain stem stroke, the most common are the following:
- arterial hypertension - causes irreversible changes in the arteries and arterioles of the brain, the walls of blood vessels become brittle, and sooner or later they may rupture with hemorrhage;
- atherosclerosis - observed in most older people, leads to the appearance of cholesterol plaques in the arteries supplying the brain, as a result of which the plaque clogs the vessel;
- aneurysms and vascular malformations – cause strokes in young patients without concomitant pathology or in combination with it;
- diabetes mellitus and other metabolic disorders affecting blood vessels;
- rheumatic diseases;
- heart diseases - valve pathologies and congenital defects;
- bleeding disorders, including when taking thrombolytic drugs prescribed to cardiac patients.
- 2/3 of cases of brain stem stroke are fatal; the most dangerous period in this regard is the first two days.
Alcohol abuse and smoking, poor and irregular diet, excess weight, sedentary lifestyle, stress, and overwork increase the risk of stroke.
Symptoms of a brainstem stroke
The deterioration of the condition occurs suddenly, the following signs are observed:
- articulation and clarity of speech are impaired (slurred speech);
- there is a lack of coordination;
- dizziness occurs, gait becomes unsteady;
- facial skin may become pale or red;
- blood pressure rises, pulse quickens;
- the temperature decreases and then increases;
- sweating develops.
In the future, these symptoms may be accompanied by respiratory and circulatory disorders. Breathing during a stroke becomes hoarse, rapid, shallow, with difficulty inhaling and exhaling. The patient may lose consciousness.
At the first signs of a stroke, the patient must call an ambulance, since treatment is most effective in the first 3 hours
In some patients, brain stem stroke is accompanied by the development of locked-in syndrome. In this condition, as a result of disruption of the transmission of impulses from the brain to the muscles of the body, paralysis of the limbs and complete loss of motor function occurs. The patient retains consciousness and is able to understand and evaluate what is happening. For such a patient, active participation in his rehabilitation is possible.
Even minor symptoms of a stroke cannot be ignored, as a stroke can lead to irreversible consequences. When the first signs appear, you must immediately seek emergency medical help, and until doctors arrive, provide the patient with rest in a lying position and an influx of fresh air.
Treatment tactics
The prognosis for stroke directly depends on the time of initiation of treatment. A patient with acute cerebrovascular accident must be taken to the neurosurgical department of the hospital as quickly as possible. How long does the treatment take, what kind of therapy is carried out in the hospital, and what is the likelihood that the patient will recover from a stroke?
The possibility of successful rehabilitation depends on which functional centers of the brain stem were affected and which functions were affected.
In the first few hours after a hemorrhagic stroke, surgery may be necessary to stop the bleeding.
If necessary, platelet mass is infused into the affected area. This method is especially effective in the first few hours after the onset of the disease. Studies show that patients who received such therapy had a faster improvement in the trophism of ischemic tissue, a faster recovery of motor functions and a lower risk of death. Among other things, platelet infusion reduces the risk of late complications.
In the first 1–3 days after a stroke, treatment is carried out in a hospital setting. After stabilization of the patient’s condition, diagnostics are carried out to determine the extent of damage to the stem structures. In accordance with the test results, treatment is prescribed, which has the following goals:
- restore and maintain vital functions of the body;
- restore physiological blood supply to areas of the brain affected by stroke;
- relieve swelling and inflammation of damaged brain tissue;
- maintain the rheological properties of blood and normal coagulation;
- support the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Specific treatment is also prescribed, which depends on the location and size of the lesion.
After discharge from the hospital, treatment at home continues for several weeks, including drug therapy, massage and exercise. This is followed by a rehabilitation period that may take several months.
Prognosis for recovery from brainstem stroke
2/3 of cases of brain stem stroke are fatal; the most dangerous period in this regard is the first two days. This is due to a violation of basic life functions.
Even minor symptoms of a stroke cannot be ignored, as a stroke can lead to irreversible consequences.
The prognosis largely depends on the timeliness of medical care provided; treatment is most effective in the first three hours after the attack. The prognosis depends on the patient’s age: in old people, the body’s regenerative abilities are reduced.
Post-stroke rehabilitation is carried out over several months
The possibility of successful rehabilitation depends on which functional centers of the brain stem were affected and which functions were affected:
- breathing - a disorder occurs when the respiratory center of the brain stem is damaged. The patient cannot breathe on his own and in most cases becomes dependent on a ventilator. However, if the respiratory brain center is not completely destroyed, recovery is possible;
- swallowing – one of the main signs of brainstem infarction is dysphagia, or swallowing disorder. This disorder occurs in most people who have had a brainstem stroke. Dysphagia threatens with life-threatening consequences: aspiration pneumonia, exhaustion and dehydration. The prognosis for recovery of patients with dysphagia is uncertain; constant drug therapy is required;
- coordination of movements - an early sign of a stroke is dizziness, an unsteady gait and loss of balance. Usually these signs disappear during treatment and rehabilitation. The prognosis for restoration of this function is generally favorable;
- motor skills of the limbs - with a stroke, control of the movements of the arms and legs is impaired, often on one side. A favorable prognosis for such a disorder can be made only in the first 2–3 months after a stroke, then the dynamics of recovery of motor functions decreases. After 6 months, complete or partial restoration of motor control is extremely rare;
- thermoregulation – a stroke may be accompanied by a violation of thermoregulation, which indicates a serious condition of the patient. A persistent increase in temperature above threshold values indicates damage to the thermoregulation center and aggravates ischemic damage to brain tissue. A decrease in body temperature for every degree doubles the likelihood of a favorable outcome;
- vision – when the oculomotor center, which is located in the brain stem, is damaged, eye movements are impaired. The chances of restoring visual functions with proper therapy are quite high.
Source: healthwow.ru
Treatment of neoplasms
Previously, there was a widespread belief that stem tumors are not subject to surgical treatment due to the fact that they have an infiltrative nature and are capable of diffusely growing into stem elements.
Despite the fact that among all stem structures, most tumors have diffuse germination, sometimes there are delimited nodular formations that are easily removed. Before choosing treatment tactics and deciding on the possibility of surgical intervention, the patient needs to consult a neurosurgeon.
The preferred method of eliminating a brain stem tumor is the maximum possible resection of the tumor with minimal damage to brain structures. Microneurosurgical surgical techniques are developing and provide a chance for a higher level of treatment.
Almost 80% of brain stem tumors are considered inoperable forms. Chemotherapy and radiation treatment are used for inoperable forms, in the preoperative and postoperative period. Cytostatic agents are used in combination form for chemotherapy. 75% of patients receive symptom relief from radiation therapy. The vast majority of cases of the disease end in the death of the patient. Radioisotope treatment can prolong the life of children with similar tumors. The life expectancy of 30% of children who underwent radiotherapy increased by 2 years.
Stereotactic radiosurgery is the newest method for treating brainstem tumors. Two types of radiosurgery can be performed:
- gamma knife - a special helmet is placed on the patient’s head for irradiation from multiple points. The rays converge at one point where the tumor focus is localized. Healthy tissues are practically not affected by this effect. Each beam has a small amount of gamma energy, but the total effect of all beams contributes to achieving maximum effect.
- cyber knife - performed using a robot and is an automated procedure. The device independently concentrates radiation into the area where the tumor is located. The patient's movements and breathing prevent any confusion in aiming the beam of rays.
Studies prove the validity of these methods in the treatment of benign neoplasms up to 3.5 cm in size.
Diagnostics
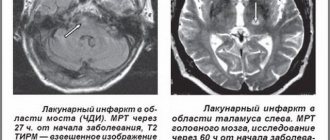
Based on the medical history information obtained by the neurologist and the results of detailed neurological diagnostics, a preliminary diagnosis is established. For confirmation, neuroimaging examinations are used - computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, MSCT.
MRI using a contrast solution provides particularly complete and accurate information about the tumor. High-resolution imaging can detect small tumors that are not visible on CT scans.
MRI results suggest determining the histological structure of the tumor, determining in advance the growth pattern, the extent of exophytic growth of the tumor element and the level of infiltration of the medulla. It is necessary to conduct a detailed collection of all data to determine the likelihood and rationality of surgical treatment of the tumor.
Interpretation of MRI examination data reveals the concentration of the tumor, the forms of accumulation of the contrast agent - uniform, uneven, ring-shaped. If the tumor has a diffuse or infiltrative structure, the outlines of the staining do not correspond to the actual size of the pathogenesis.
In T2 mode, the MR signal changes its propagation to areas where the contrast agent has not accumulated. These areas may be an area of swelling of brain tissue, a space for its growth, or both. The simplest neuroectodermal formations are determined by the presence on MRI images of implantation metastases in the ventricular system of the brain, in the subarachnoid spaces.
It is important to differentiate tumor processes in the brain stem from multiple sclerosis, brain stem inflammation, demyelinating encephalomyelitis, ischemic stroke, intracerebral hematoma, and lymphoma.