- Types and types of aneurysms
- Symptoms of an aneurysm
- Causes of damage to the arteries of the brain
- Hemorrhagic stroke and other consequences
- Surgical removal
- Consequences of the operation
- Pregnancy and aneurysm
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of aneurysm
- Taking medications
- Folk remedies for aneurysm
- Recommendations for aneurysm
- Prevention
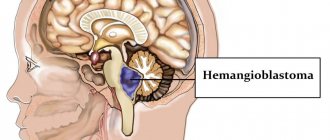
An aneurysm is a pathology of the arteries in which thinning and protrusion of the wall occurs in a certain area. The disease affects the blood vessels in the brain, through which blood circulates under high pressure. This situation poses a serious threat to the health and life of the patient due to deterioration of cerebral circulation and irreversible damage to nervous tissue. With an aneurysm, the vessel increases in size and begins to compress neighboring areas. This causes dysfunction of the central nervous system. A critical condition occurs if a vessel ruptures and cerebral hemorrhage occurs, which often leads to death.
Types and types of aneurysms
The classification of aneurysms is based on their shape and size, causes of occurrence, and number of chambers:
- According to the shape of the protrusion of the walls, they are bag-shaped and spindle-shaped. The first type is more common.
- Depending on the size of the pathology, they are divided into four groups. If the aneurysm is smaller than three millimeters, it is called milliary. A normal size protrusion reaches 15 mm. Large aneurysms grow up to 25 mm; those from 25 mm or more are called giant.
- The pathology can be congenital or acquired as a result of illness or injury.
- Depending on the number of aneurysms, they can be single or multiple. The protrusion may consist of one or more chambers.
Classification
The classification of aneurysms depends on several medical criteria. Basically, based on their structure, experts distinguish saccular and fusiform convexity. In the first case, the violation of the structure of the vessel wall is local in nature, resembling a sac, hence the name. A spindle-shaped aneurysm is a uniform lesion of the vessel wall in diameter and may have a multi-chamber structure.
Based on their location in the brain, the following localizations of aneurysms are distinguished:
- anterior cerebral artery;
- middle cerebral artery;
- carotid artery aneurysm;
- damage to the vertebrobasilar system;
- multiple aneurysms.
In addition to damage to the blood vessels of the brain, there is pathology in other areas. For example, an aortic aneurysm. The disease is an expansion of the walls of the aorta under the influence of various provoking factors.
Types of cerebral aneurysms
In medical practice, aneurysms are classified according to their size into small, medium, large and giant aneurysms. Sometimes the bulge can be up to 2.5 cm in diameter.
Symptoms of an aneurysm
At the initial stages, the pathology may not manifest itself in any way. We are talking about the so-called asymptomatic aneurysm. As it increases, a characteristic neurological picture appears:
- headache;
- loss of sensation in the lower extremities;
- violation of fine motor skills, diction;
- numbness of the face, weakening of the facial muscles, loss of control over facial expressions.
Impaired cerebral circulation changes character and behavior. The person becomes restless and emotionally unstable.
When an aneurysm ruptures, a severe headache occurs, which is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, and pallor. The patient experiences convulsions and develops photophobia. Due to impaired cerebral circulation, a person loses orientation and falls into an unconscious state. If there are signs of aneurysm rupture, you should urgently call an ambulance and take the victim to the neurological department.
First aid for a patient with a ruptured aneurysm
Anyone suspected of having a ruptured aneurysm should be urgently taken to the hospital. Before the arrival of doctors, the patient should be given emergency care, which consists of the following:
- Call an ambulance.
- Place the victim in a horizontal position, with the head raised.
- Open access to fresh air into the room, free your neck and chest from tight clothing.
- If you lose consciousness, you need to check the airways for the presence of foreign objects and perform artificial respiration.
- Apply a bag of cold compress with ice to the area of pain.
- Monitor pulse and blood pressure. If possible, record data for further transmission to doctors.
A person’s life often depends on first aid from others
Important! Sometimes aneurysm rupture causes death within the first minutes. In this case, any actions will be ineffective.
Causes of damage to the arteries of the brain
An aneurysm can develop on any vessels. According to statistics, protrusion is most often diagnosed in the arteries at the base of the skull. This is caused by physiological characteristics: in this area the blood pressure is higher than in the rest, so the risk of damage to the vessel walls increases. If one layer is damaged, then the wall protrudes in this area under the pressure of the blood flow.
All aneurysms can be divided into congenital and acquired. Congenital causes are caused by abnormalities in the development of blood vessels, genetic diseases in which connective tissue weakens. Against the background of a burdened heredity, pathology can develop even at a young age, although the disease is very rare in children.
Most aneurysms are acquired. They arise as a result of traumatic brain injuries and brain tumors. The high-risk group includes patients with hypertension, atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, and people who engage in weightlifting or intense physical labor. The likelihood of an aneurysm increases if a person regularly exposes himself to stress or leads an unhealthy lifestyle.
Protrusion of the artery wall can develop against the background of an inflammatory process - aortitis. It can be caused by a streptococcal or fungal infection. The disease can develop against the background of tuberculosis, syphilis, or after unsuccessful surgery.
Hemorrhagic stroke and other consequences
An aneurysm is a dangerous rupture of the vessel wall, which is subject to constant stress due to blood flow. When a rupture occurs, a hemorrhagic stroke occurs. It is a very serious medical and social problem. Due to hemorrhage, a hematoma is formed, which compresses the brain tissue and puts pressure on neighboring vessels. In the absence of treatment, irreversible changes occur in the affected structures within a few hours.
A hemorrhagic stroke can be suspected by severe headaches, sudden problems with speech and coordination of movements. The person feels disoriented and goes into a state of shock. In this case, you need to urgently contact a medical facility. The pathology requires emergency surgery and long-term treatment. Patients who have suffered a hemorrhagic stroke require long-term rehabilitation.
A complicated aneurysm, which is accompanied by thrombosis, is extremely dangerous. Due to a blood clot, blood circulation in the vessel slows down or stops completely. Another common complication is aneurysm dissection. In this case, a lumen is formed in the inner lining of the vessel through which blood passes.
The presence of an aneurysm significantly impairs the quality of life, especially if the pathology affects an important part of the brain. The larger the protrusion, the stronger the disease manifests itself. Due to neurological symptoms, people are forced to give up their usual activities and constantly take medications for headaches. The patient’s well-being worsens in the presence of cardiovascular diseases, increased stress, and bad habits.
Surgical removal
After diagnosing and assessing the patient’s condition, the doctor selects a treatment regimen. If the aneurysm is large and there is an increased risk of rupture, surgery to remove the protrusion is recommended. The procedure is performed by a neurosurgeon. It can be planned or emergency if a rupture occurs.
During surgery, the aneurysm is coagulated. It can also be excised or bandaged. The method of eliminating the pathology is selected based on the diagnostic results, depending on the characteristics of the clinical case. The purpose of the operation is to exclude the damaged area of the vessel from the bloodstream. Minimally invasive techniques are used during the procedure.
Consequences of the operation
After the operation, the patient spends from several days to several weeks in the hospital. Rehabilitation consists of taking medications, physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, and therapeutic exercises. Patients with severe neurological disorders are advised to undergo sanatorium-resort treatment, which includes comprehensive rehabilitation programs. They help to fully restore your ability to work.
Complications after surgery include spasms and vascular obstruction. They are more likely to affect older patients and people whose bodies are severely weakened by chronic diseases.
Preoperative preparation
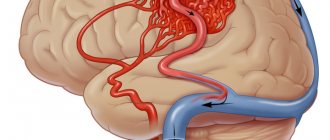
cerebral aneurysm in the picture
During planned aneurysm clippings, specialists have time to thoroughly examine the patient and prepare him for the intervention. As conservative therapy, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed, drugs that normalize heart rhythm in case of arrhythmias, and correction of the lipid spectrum is carried out in the presence of abnormalities.
Before planning the operation, the patient undergoes all kinds of examinations, including blood tests, urine tests, coagulogram, cardiogram, etc., as with other surgical interventions. To localize and clarify the nature of the vascular formation, CT, MRI with contrast, angiography, and ultrasound with Doppler are performed.
In the case of ruptured aneurysms, the patient is admitted to a hospital with a clinic for acute subarachnoid or intracerebral hemorrhage and is sent to the neurosurgical department; there is virtually no time for examinations, so one has to limit oneself to the minimum that allows one to determine the location of the malformation.
Both trepanation and endovasal surgery require general anesthesia, although in the latter case local anesthesia may be used. Before the operation, the patient talks with the surgeon and anesthesiologist (except in cases of coma and acute bleeding), does not eat for the next 8 hours before the operation, and tries to get enough sleep. The hair at the trepanation site is shaved.
Pregnancy and aneurysm
Women who are planning to conceive need to be aware of the threat aneurysms pose. During pregnancy, the risks of hemorrhagic stroke for physiological reasons increase. In the second and third trimester, the volume of circulating blood increases and blood pressure rises. The situation may worsen if the patient has concomitant diseases: hypertension, diabetes.
According to statistics, the frequency of hemorrhagic strokes in pregnant women with an aneurysm is 2-5 cases per 10,000. The disease is accompanied by depression of consciousness, profound motor disorders, and respiratory failure. Neurological disorders pose a threat to the life of the expectant mother and child. Due to respiratory failure, the supply of oxygen to organs and tissues is disrupted, and fetal hypoxia develops. Lack of oxygen is a dangerous condition that leads to pathologies of intrauterine development.
A pregnant woman with a ruptured aneurysm requires urgent neurosurgical treatment and oxygen support.
Women of reproductive age who have been diagnosed with a bulging artery wall should consult a neurologist in advance and undergo treatment.
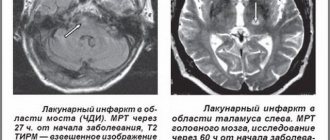
Diagnostics
If you suspect an aneurysm, you should make an appointment with a neurologist. The patient is prescribed hardware diagnostics of cerebral vessels. The following procedures are the most informative:
- Computed tomography, which is also indicated for protrusion rupture. A CT image will reveal where the rupture occurred and assess the extent of tissue damage.
- Vascular angiography is the most popular method that doctors use most often. Such diagnostics helps to identify the location and size of the aneurysm.
- MRI and X-ray are a universal way to assess the condition of blood vessels.
- General and biochemical blood tests and urine tests are prescribed to identify changes in the body.
It should be remembered that with small sizes the protrusion may not create discomfort and may not manifest itself in any way. Many clinical cases are identified during preventive examinations and routine medical examinations. This confirms that such activities should not be neglected.
Medicines
Photo: grud.guru
If a strange and sharp headache occurs, a person must immediately contact the nearest medical institution for qualified help. The disease is not treated with medication, but there is prevention and rehabilitation after surgery.
Surgical intervention is currently the only and most promising method of treating aneurysm. Treatment with special drugs is used only to stabilize the patient or in a situation where surgery is contraindicated or not possible at all.
Chemical drugs cannot eliminate an aneurysm; they only reduce the likelihood of vessel rupture by eliminating critical factors. Some medications are included in a complex of general therapy, which is aimed primarily at alleviating the symptoms of the initial pathology in patients. What vitamins and medications are taken for cerebral aneurysm?
Calcium channel blockers
The main representative of the nimodipine group. The chemical drug reliably blocks calcium channels in the muscle cells of the vascular walls. The vessels dilate. Blood circulation in the cerebral arteries is significantly improved. These drugs are simply irreplaceable in the prevention of dangerous arterial spasms.
Antacids
The principle of action is based on blocking H2 histamine receptors in the stomach. As a result, its acidity decreases and the secretion of gastric juice is significantly reduced. This group includes Ranitidine.
Anticonvulsants
Today, Fosphenytoin is the main representative of this group. The drugs cause reliable stabilization of membranes in nerve cells. Pathological nerve impulses noticeably slow down and do not spread.
Antiemetic drugs
Prochlorperazine is mainly used. The gag reflex is reduced by blocking postsynaptic dopamine receptors in the mesolimbic region of the brain.
Painkillers
Morphine is very effective for pain relief. The level of pain is reduced as a result of the effect on specific opioid receptors.
Antihypertensive drugs
Recently, three main drugs have been used: labetalol, captopril, hydralazine. Due to the effect on enzymes and receptors, the overall tone of the arteries is reduced and rupture is prevented.
Treatment of aneurysm
Aneurysm is treated conservatively and surgically. Therapy is selected by the doctor based on the clinical case. The neurologist assesses the condition of the arteries and the degree of their damage. Based on the data obtained, conclusions can be drawn about the possibility or impossibility of using conservative methods. If the protrusion is significant, which is accompanied by severe neurological symptoms, and there is a high risk of aneurysm rupture, the patient is recommended to undergo elective surgery. This is a radical method that helps prevent possible complications. Urgent surgical treatment is required if rupture cannot be avoided and the patient suffers a hemorrhagic stroke.
Taking medications
The main method of conservative treatment of an aneurysm is taking medications. The patient is prescribed a complex of drugs:
- drugs to lower cholesterol and prevent atherosclerosis;
- painkillers;
- anticonvulsants;
- drugs to normalize blood pressure: amlodipine, atenolol, anaprilin, enalapril (consultation with a doctor is required, there are contraindications)
Drug therapy is also indicated in the postoperative period. It eliminates neurological symptoms and pain, and reduces the likelihood of disease relapse.
What should such patients avoid?
Under no circumstances should you violate the established regime of mobility and physical activity. This can lead to a sharp increase in cardiac output and rupture of the clip (recurrent hemorrhage).
You should not stop taking prescribed medications without permission, as this can lead to complications in the postoperative period. Chronic lack of sleep, fatigue and nervous stress are contraindicated, which negatively affects the condition of the heart.
You should not skip scheduled visits to the doctor or refuse necessary diagnostic measures even after a successful operation.
Folk remedies for aneurysm
Herbal medicines are used to treat diseases that contribute to the development of aneurysm. Folk remedies cannot cure an existing pathology, but they will reduce the risk of its occurrence.
First of all, we are talking about herbal medicines with anti-inflammatory and hypotensive effects. They prevent the development of inflammation and help normalize blood pressure. To improve blood circulation and normalize blood pressure, decoctions and infusions of hawthorn and viburnum berries are used.
For the prevention and treatment of blood vessels, herbal preparations with celandine and dill are used. It should be understood that herbal remedies in the treatment of aneurysm are an auxiliary method. Their effectiveness increases if a person leads a healthy lifestyle.
Development mechanism
The formation of the pathological process is based on a group of common pathogenetic factors. Which ones:
Congenital vascular anomalies
They occur more often than you might think. Another thing is that such conditions and characteristics of the body do not always lead to something as dangerous as an aneurysm.
We are talking about a pathological process that is formed in the prenatal period.
Whether this is due to a mutation or something else does not have much clinical significance. Since this does not affect the consequences in any way, and there is no point in clarifying the issue yet: prevention of genetic abnormalities is not yet possible.
Previous brain injuries
Cerebral structures are not only nerve tissue, but also an abundance of blood vessels. When the fibers are damaged, the arteries themselves undergo changes.
This can have a very negative impact, although it is impossible to guarantee the development of an aneurysm. These are just theoretical risks.
It takes some time: a year or two to monitor the patient’s condition.
Tissue irradiation
Radiation causes cell destruction and changes at the molecular level. The result is decay, gradual or rapid. Depends on the dose.
The result is softening of the vascular wall, tissue destruction at the local level.
Attention:
Especially often this consequence occurs against the background of radiation therapy.
Patients who deal with radiation as part of their professional duties are also at risk. Submariners, nuclear power plant employees and others.
Past infectious pathologies
Mostly viral. For example, some forms of herpes, as has already been proven by theorists of medical science. There are also risks from bacteria, for example, after meningitis or encephalitis.
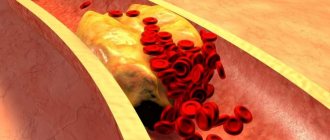
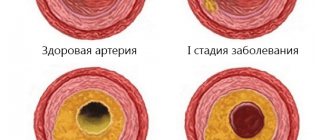
Atherosclerosis
Chronic pathology. It is typically characterized by the deposition of cholesterol on the walls of blood vessels, the inner lining of the arteries of the brain.
Gradually, fats turn into full-fledged plaques, clogging the blood flow.
Pressure at the local level is growing significantly. The vessels are not designed for such loads. A slow or rapid degenerative process begins.
If nothing is done, an aneurysm will form within a few years.
Toxic destruction of vascular tissue
For example, with systematic smoking, consumption of alcohol or drugs. It makes sense to give up the bad habit as quickly as possible.
How quickly the change will develop is difficult to say. How to predict whether it will happen at all. But there are such risks and they are more than real.
Genetic predispositions
If there were patients with aneurysms in the family, the likelihood of a pathological process becomes several times higher.
You need to look at relatives of the direct, ascending line. That is, father, mother, grandparents are involved in the probabilistic analysis.
These are the basic mechanisms. As a rule, they do not intersect. Although certain combinations are possible. For example, long-term smoking causes injury.
The risk of developing an aneurysm in this case will be prohibitively greater, since the pathogenetic factors are numerous.