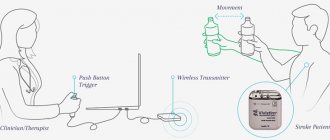
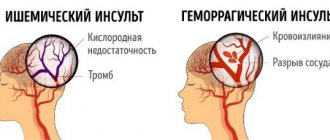
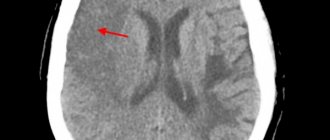
Risk factors for stroke and heart attack
Planning a preventative treatment regimen is based on addressing risk factors that are largely similar for heart attack and stroke.
Metabolic risk factors include:
- dyslipidemia (impaired lipid metabolism - organic compounds, including fats and fat-like substances);
- arterial hypertension;
- obesity;
- metabolic syndrome;
- diabetes mellitus and other endocrinopathies;
- coagulopathies (diseases that develop as a result of disorders of the blood coagulation and anticoagulation systems).
Common markers of heart attack and stroke are:
- previous cardiovascular diseases;
- peripheral vascular pathology;
- calcium index;
- stress test results;
- hypertrophy (thickening of the wall) of the left ventricle.
Atherosclerotic stenosis of the carotid arteries and brain tumors increase the risk of stroke. The provoking factors of a heart attack are:
- atrial fibrillation;
- dysplasia (developmental disorder) of connective tissue;
- arteritis;
- diabetes.
Although the incidence of stroke is higher in men, it is more severe in women, and about half of deaths from stroke occur in women.
Make an appointment
Why does muscle weakness occur?
Causes of weakness in the limbs
When considering the origin of skeletal muscle weakness, it is worth separating the concept of paresis associated with damage to nerve pathways and symptoms caused by defects in synaptic transmission and muscle damage. Often we are talking about blockade or increased destruction of acetylcholine, primary or secondary muscle pathology, reflex syndromes. Among the most well-known causes of weakness are the following:
- Myasthenia.
- Myasthenic syndromes:
Lambert-Eaton associated with slow closure of ion channels, familial infantile myasthenia. - Hereditary paroxysmal myoplegia:
hyper-, hypo- and normokalemic, Andersen-Tawil syndrome. - Infections:
botulism, tick-borne encephalitis. - Endocrine pathology:
hyper- and hypothyroidism, Conn's syndrome, Addison's disease. - Myopathies:
inflammatory (acute myositis, polymyositis, dermatomyositis), metabolic (including storage diseases), mitochondrial. - Muscular dystrophies:
progressive (Duchenne, Becker, Emery-Dreyfus), non-progressive (myotubular myopathy). - Diseases of the musculoskeletal system:
arthrosis, tendonitis, injuries. - Vascular pathology:
obliterating endarteritis, varicose veins of the lower extremities, Takayasu's disease. - Poisoning:
organophosphorus compounds, carbon monoxide, cyanides, aromatic hydrocarbons (toluene, benzene), plants (hemlock), nicotine, cocaine. - Taking medications:
D-penicillamine, antibiotics, antitumor drugs, statins, cortisone, colchicine, chloroquine.
Weakness in the muscles of the whole body is provoked by various systemic diseases and intoxications. It is noted in acute and chronic infections, autoimmune pathology, and malignant tumors. Low motor activity in older people, with immobilization, prolonged bed rest are common causes of widespread limb weakness.
Causes of facial muscle weakness
The facial muscles are innervated by the facial nerve (VII pair). Any pathology that disrupts the conduction of impulses along motor fibers - from the corticonuclear pathway to the peripheral part - can cause muscle weakness. It is also worth considering the direct damage to the muscles themselves. The list of probable pathologies includes the following conditions:
- Neuritis of the facial nerve (Bell's palsy).
- Facioscapulohumeral myodystrophy of Landouzy-Dejerine.
- Degenerative diseases:
progressive bulbar palsy, syringobulbia. - Tumors:
base of the skull (Garcin's syndrome), cerebellopontine angle, temporal bone and middle ear. - Hemorrhages and infarctions of the pons area.
- Congenital anomalies:
Chiari malformation, Klippel-Feil syndrome. - Infections:
herpetic ganglionitis of the geniculate ganglion (Ramsay-Hunt syndrome), polioencephalitis, Lyme disease, syphilis. - Meningitis:
bacterial, tuberculous, fungal. - Systemic pathology:
sarcoidosis, periarteritis nodosa, Behcet's disease. - Consequence of injuries, facial surgery, installation of a cochlear implant.
- The effect of chemotherapy drugs.
The facial nerve is often damaged by inflammatory processes in the ear and parotid salivary glands. Compression or rupture of its fibers is observed in TBI with a fracture of the base of the skull. The risk of facial nerve paresis increases in older people, with a long history of smoking, and the presence of concomitant pathologies (diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension).
Causes of paresis
The upper or first neuron of the motor pathway begins in the motor cortex of the precentral gyrus, goes as part of the pyramidal tract through the internal capsule and trunk, ending in the anterior horns of the spinal cord. There, the impulse is transmitted to the second motor neuron, the axons of which make up the roots and peripheral nerves. Damage to these structures at any length is accompanied by paresis, which is typical for various pathologies of the nervous system:
- Strokes:
hemorrhagic, ischemic, subarachnoid hemorrhage. - Tumors and traumatic brain injuries.
- Demyelinating diseases:
leukodystrophies, multiple sclerosis, Devic's opticomyelitis. - Motor neuron diseases:
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, spinocerebellar and bulbospinal atrophy. - Cerebral palsy.
- Neurodegenerative processes:
Wilson-Konovalov's disease, Shtrumpel's disease, Refsum's disease. - Myelopathy:
compression, spinal cord ischemia, transverse myelitis. - Damage to peripheral nerves:
polyneuropathies (metabolic, toxic, hereditary), tunnel syndromes, plexopathies. - Acute polyradiculoneuritis:
diphtheria, Guillain-Barré syndrome, ascending Landry's palsy. - Infections:
polio, meningococcal meningoencephalitis, rabies. - Vertebrogenic pathology:
intervertebral hernia, osteochondrosis, scoliosis. - Intoxication:
nerve poisons, salts of heavy metals (thallium, lead, arsenic).
Disturbances in spinal conduction are often caused by spinal cord injuries, which entail compression, ischemic damage, and swelling of the nervous tissue. There are also direct wounds - gunshots, bone fragments from fractures. Typically, the cervical spine is susceptible to such damage; the thoracic and lumbar spine are affected much less frequently. In case of concussion of brain tissue, the changes are transient in nature, in other cases they are more persistent.
Metastatic tumors (lung, breast or prostate cancer) are a common cause of compression of the spinal cord; lymphoma, multiple myeloma, and epidural hematomas are less common. If weakness appears in the arms or legs, tuberculous spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis with subluxation of the atlantoaxial joint, and spinal vascular malformations are excluded.
Signs of a stroke
To diagnose cerebral blood supply disorders, it is necessary to use stroke recognition techniques:
- When trying to smile, you need to pay attention to the corners of the mouth - in case of a stroke, it can be directed downwards, the smile looks crooked and asymmetrical;
- When trying to speak, it may be difficult to pronounce even the simplest words and sentences;
- When trying to raise both arms, asymmetry is observed;
- The protruding tongue falls to the side.
If at least one of the symptoms is positive, you must immediately call an ambulance. Under no circumstances should you give him water, feed him, lift him, or take him by handy transport to the nearest hospital, as this can cause harm.
Help in the acute period
Which doctors are needed in the treatment of stroke depends on the period of the disease, but in any case, they must be experienced, highly qualified specialists who know how to properly provide assistance in this situation.
When diagnosing an ischemic stroke in a patient, the doctor’s goal is to restore blood supply with subsequent rehabilitation. This may require blood thinning medications or mechanical removal of the clot using a catheter. To remove atherosclerotic plaques, endarterectomy is performed, and to increase the diameter of blood vessels, plastic surgery with stenting is performed.
How long to stay in hospital if you have a stroke
Poor blood circulation in the brain, in other words, stroke, treatment involves three stages:
- prehospital;
- stay in the intensive care unit;
- treatment in a general ward.
The length of stay of a patient in a hospital, according to treatment standards, is 21 days, provided the patient has no violations of vital functions, and 30 days in case of serious violations. When the length of a patient’s stay in a hospital is insufficient, a medical examination is carried out followed by the development of an individual course of rehabilitation.
All patients diagnosed with stroke are subject to hospitalization. The length of stay in intensive care depends on a number of factors, including:
- depression of vital functions;
- degree of damage to brain tissue. With a major stroke, patients stay in intensive care longer;
- the need for constant monitoring if there is a high risk of recurrent stroke;
- severity of the clinical picture;
- level of depression of consciousness and others.
Basic and differentiated therapy
Treatment of a patient in the intensive care unit involves basic and differentiated therapy.
Basic treatment is aimed at:
- fight against cerebral edema;
- restoration of normal functioning of the respiratory system;
- patient nutrition;
- maintaining hemodynamics at an acceptable level.
Differentiated therapy involves:
- normalization of arterial and intracranial pressure, elimination of cerebral edema after hemorrhagic stroke. In the first two days, a decision is made regarding the need for surgery. Neurosurgeons at the Yusupov Hospital daily perform surgical interventions to eliminate the consequences of stroke and save the lives of hundreds of patients. All manipulations are carried out using modern medical equipment using effective proven techniques;
- accelerating metabolic processes, improving blood circulation and increasing the resistance of brain tissue to hypoxia when diagnosed with ischemic stroke. The length of stay in intensive care directly depends on the timely and adequate course of treatment.
In most cases, young people recover much faster than older patients.
It is possible to transfer a victim from the intensive care unit to a general ward after meeting a number of criteria:
- the patient can breathe independently, without the support of devices;
- the patient is able to call a nurse or doctor for help;
- there is a stable level of heart rate and blood pressure;
- the possibility of bleeding is excluded.
Only after the patient's condition has stabilized can the doctor transfer the patient to the ward. In a hospital setting, various rehabilitation procedures are prescribed to quickly restore lost functions.
In the neurology department of the Yusupov Hospital, patients are not only developed an individual course of rehabilitation therapy, but also given psychological support.
If necessary, psychologists work with loved ones and relatives of the patient to teach them the basics of caring for a person who has suffered a stroke.
Treatment
Therapy after a stroke helps restore normal blood flow to the damaged area of the brain and reduce the risk of developing vascular problems and having another stroke. The patient may be prescribed a complex of medications and folk remedies.
Drug therapy
If the right side of the body is paralyzed after a stroke, the doctor first prescribes medications.
- Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents (for example, Warfarin and Curantil) - prevent the formation of blood clots, making it more fluid, which improves blood flow even through the narrowest sections of blood vessels. These drugs help improve the condition of patients with atherosclerosis, blood clots, or narrowed blood vessels.
- Agnioprotectors (“Alprostan”, “Parmidin”) - normalize the functioning of the walls of blood vessels, reducing the risk of reducing the lumen in the arteries.
- Antispasmodic drugs (such as Vincamine and Papaverine) help relax the vascular walls, which increases blood flow.
- Diuretics (“Veroshpiron”, “Hypothiazide”) - help remove excess fluid from the body, reducing the risk of developing cerebral edema and exacerbation of hypertension.
- Nootropics (“Actovegin”, “Piracetam”) - increase brain performance. Nootropics are prescribed throughout recovery and for some time after full recovery.
Drug therapy is selected individually, based on the diagnosis and the general health of the patient. In case of serious disorders, the patient is given all types of medications and his blood pressure is monitored.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine provides additional assistance in recovery and is prescribed along with basic medications. In case of serious health problems, consultation with a specialist is necessary to draw up a specific treatment and preventive program.
Let's consider the most effective folk remedies.
- Taking a bath with the medicinal plant oregano. First you need to boil water along with the herb in the proportion of a liter per spoon and then pour it into the bath. For an average bath, 5 or 6 liters of decoction is enough.
- Honey and propolis are thoroughly mixed in a vessel with a ratio of 100 to 1, after which they are left to infuse for three days. The finished product is taken a couple of drops twice a day.
Folk remedies help improve blood flow and supply brain tissue with essential nutrients, as well as improve the functioning of the immune system.
Recovery period
The rehabilitation period is aimed at restoring lost functions and improving the quality of life of patients who have suffered a stroke. The doctor develops a rehabilitation program individually for each patient, taking into account the scale of the vascular accident, age, comorbid pathology, etc.
In case of strokes, doctors assign a special role to the prevention of recurrent strokes, which includes proper nutrition, giving up bad habits, eliminating excess weight, and regular monitoring by a doctor.
Is full recovery possible after a stroke?
The patient’s relatives play a significant role in the rehabilitation of a patient after a stroke. It depends on their attention, care, patience and correct actions whether the patient’s lost functions can return.
The recovery process after a stroke is a difficult period, both for the patient himself and for his loved ones. The rehabilitation time depends, first of all, on the degree of damage to brain tissue. Patients may have impaired coordination of movements, mobility of limbs, speech, memory, hearing, and vision.
The patient’s persistence and positive attitude can speed up the recovery time of lost functions.
An experienced team of doctors will speed up the rehabilitation process thanks to a well-designed individual treatment program.
Levels of recovery after stroke
After hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes, there are three levels of recovery:
- the first is the highest. We are talking about the complete restoration of lost functions to their original state. This option is possible in the absence of complete death of nerve cells in a region of the brain;
- the second level is compensation. The early stage of recovery, usually in the first six months after a stroke. Lost functions are compensated by the involvement of new structures and functional restructuring.
- The third level involves readaptation, that is, adaptation to the emerging defect. The patient’s relatives and friends play a significant role in this process. They are the ones who help the patient learn to live with the emerging defect.
Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital, if necessary, work with the patient’s relatives, teaching them the specifics of care, as well as providing them with psychological support.
Etiopathogenesis
If the patient is paralyzed, then a stroke (hemorrhage) has occurred. Violation of the integrity of the arterial wall leads to the formation of a hematoma. As blood accumulates outside the vessel, it begins to put pressure on neighboring brain structures. Under these conditions, nerve cells responsible for key brain functions, such as muscle control, die, causing entire parts of the body to go numb.
A stroke with paralysis of the right side can be caused by the following factors:
- Wrong diet. It is very important to monitor the amount of calcium in the foods you eat, as it is a key element in maintaining the health of arterial walls. A lack of calcium leads to weakening of blood vessels and increases the risk of their damage. In this case, even small blood congestions can provoke hemorrhage.
- High blood pressure. Excessive blood pressure on the walls of the arteries can lead to their damage in the weakest places. As a rule, people at high risk are older people who experience deterioration in the elasticity of the vascular walls due to natural aging and low calcium levels.
- Hereditary predisposition. Recently, it was found that patients with a family history of stroke are likely to have a heart attack or stroke at some point in their lives. These are mainly patients with hypertension. While the specific inherited cause of the disease has not yet been established, it may be weak blood vessels and problems with neurohumoral regulation.
- Excess weight. Fat people tend to have low levels of minerals in the blood and high blood pressure - leading causes of stroke, which can paralyze the body.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system. Impaired blood flow and rupture of a vessel in the brain can provoke pathologies such as heart defects, heart failure, the formation of atherosclerotic plaques and blood clots.
- Endocrine diseases. The most common cause of stroke among this group of pathologies is diabetes. People with this condition often suffer from high blood pressure. Also at risk are patients with low levels of thyroid hormones and problems in the adrenal cortex.
- Alcohol and tobacco abuse. Nicotine reduces the strength of arterial walls and increases cholesterol levels in the blood. High-quality alcoholic drinks in small quantities can even be beneficial, but frequent and excessive consumption of alcohol easily provokes hemorrhage with subsequent paralysis.
The causes of paralysis of both the right and left parts of the body are indicated above. Statistics show that bad habits are the most common factor in paralysis, in which it is much more likely to help the patient survive if diagnosed in time.
Prognosis for recovery after stroke
Favorable factors for recovery after a stroke include:
- timely early start of rehabilitation therapy;
- spontaneous early recovery of lost functions.
Among the unfavorable factors of recovery after a stroke are:
- advanced age of the patient;
- large area of brain tissue damage;
- poor blood circulation around the affected brain tissue;
- damage to cells in functionally important areas of the brain.
Basics of Stroke Recovery
In the process of rehabilitation, the positive attitude of the patient himself and his desire to return to independent life are important. Psychological support and assistance from the patient’s relatives plays a huge role. You can make an appointment with a neurologist by phone.
Memory recovery after stroke
Treatment of patients after a stroke takes place in the neurological department. Memory restoration depends on many factors: the size of the area of brain damage, the location of the damage, and the timeliness of medical care. The faster blood circulation in the brain is restored, the greater the chance of memory recovery after a stroke.
Memory restoration after a stroke is possible with the participation of several specialists - a neurophysiologist, psychologist, neuropsychologist, neuropsychiatrist. Help for a patient after a stroke is provided at the rehabilitation clinic of the Yusupov Hospital. In the hospital, the patient is treated according to an individual recovery program; many specialists take part in the development of such a program. When developing the program, the patient’s health condition, the severity of brain damage, and memory impairment are taken into account.
In some cases, it takes several years to restore memory and speech; during recovery, the doctor prescribes medication, a special diet, various trainings - color therapy, rhythm therapy, music therapy and others. Memory restoration at home is not always successful due to the lack of a training program and knowledge in the field of rehabilitation of patients after a stroke.
You can make an appointment with a neurologist at the Yusupov Hospital by phone. Consultation with a specialist, full patient care, rehabilitation using innovative equipment, massages and exercises will help the patient regain full memory.
Restoring a hand after a stroke
A positive attitude and support from family have an impact on rapid recovery from illness. Partial paralysis of the arm is a common occurrence after a stroke and is characterized by stiffness of movement and limited motor ability of the arm. Functional paresis (partial paralysis) refers to neurological syndromes, caused by disruption of the nervous system, damage to the nervous system pathway due to damage to the cerebral cortex after a stroke. Paralysis of the arm is the complete absence of voluntary movements of the limb.
Recovery from a stroke may involve the hand or the entire limb. With partial paralysis, the ability to move the arm or hand freely is impaired; the person cannot fully care for himself or perform basic actions. To restore motor ability, the patient must perform daily exercises for finger motor skills and limb motor skills.
The rehabilitation process of restoring motor activity of the limbs requires patience from the patient and a lot of work - this will allow you to return to a full life after a stroke. You can make an appointment with a neurologist by phone. The rehabilitation doctor will develop individual exercises for the patient, the patient will be under constant medical supervision and receive qualified assistance from specialists.
Types of paralysis on the right side
According to the nature and localization of vascular accidents, the types and subtypes of paralysis are classified:
- Central paralysis. It develops when the areas of the brain and spinal cord responsible for the function of movement and the state of the neuromuscular complex are damaged. Characterized by specific spastic reactions. With the central form of paralysis, all muscles are affected, which are in constant tension, and when calm they show clonus - rhythmic twitching, mainly in the area of the knees and feet. In many areas, diagnostic reflexes are absent or weakened.
- Peripheral paralysis. With this type of stroke, a decrease or absence of neurological reflexes develops. The tone in the muscles is not determined, they atrophy, decrease in mass, patients lose the ability to move, self-care and generally do any activity. The main task is to restore the conduction pathways of impulses from the brain and spinal cord to the neuromuscular system. By the nature of the pathological symptoms and the areas of their location, it is possible to determine which segments of the central nervous system are out of order.
Factors influencing the speed and quality of rehabilitation
There are many factors that influence the speed of recovery after a stroke, so predicting the duration of rehabilitation and likely results is quite difficult.
How long rehabilitation after a stroke will last depends on the individual parameters for each person, as well as on other factors:
- volume of damage: an extensive stroke significantly worsens the severity of the patient’s condition, and also causes many neurological complications that adversely affect the timing of recovery and its quality;
- patient’s age: the older the victim, the longer the recovery;
- localization of damage: circulatory disorders of deep structures are difficult to treat;
- type of stroke: hemorrhagic strokes are less common, but occur in a more aggressive form, and also have a high mortality rate, although the prognosis for rehabilitation is more favorable than for ischemic stroke;
- caused by disorders: the presence of multiple cerebral symptoms, comatose states, severe paralysis and sensory disturbances give an unfavorable prognosis for recovery;
- timeliness of therapy: the most positive results of therapy can be achieved by starting treatment measures in the first 4 hours after the onset of the first symptoms; seeking help at a later time worsens the prognosis;
- compliance with medical recommendations: after the patient is discharged from the medical institution, the patient is given recommendations that can improve the quality of life, prevent the formation of relapse and negative complications.
The severity of the lesion has the greatest impact on the likelihood of restoration of lost functions and the timing of rehabilitation. With extensive strokes, violations of the most important functions are observed, even if the prescribed rehabilitation program is followed, the prognosis is rather disappointing. The greatest difficulties arise with the complete return of speech and motor functions. Close relatives who will devote a lot of time to special activities with the patient can positively influence the situation.
Stroke Prevention
Prevention of heart attack and stroke in women and men are links in one chain of measures that prevent disability and death in people suffering from cardiovascular diseases.
Cardiologists and neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital use modern diagnostic methods to examine patients, allowing them to identify risk factors for vascular diseases and take measures aimed at preventing diseases. Medicines for the prevention of stroke and heart attack allow you to control the course of the disease, reduce the incidence of acute cardiovascular crises, and the likelihood of complications.
Chance of full recovery after stroke
The rehabilitation period is individual; for some, a few months are enough; for others, it will take years to achieve a positive result. The earlier restoration procedures are started, the more favorable the prognosis. At the same time, the patient’s attitude and focus on results is important; The greater a person’s desire to return to a full life, the more effective the classes and exercises.
At the Yusupov Hospital, a well-coordinated team of professionals (neurologists, rehabilitation specialists, therapists, cardiologists, speech therapists, psychologists) takes part in the rehabilitation of patients after a stroke. Doctors create an individual program for each patient, aimed at the best possible result, observing the following principles:
- early start of restorative procedures;
- systematicity and duration of events;
- complexity of procedures;
- multidisciplinarity of classes;
- compliance of procedures with the patient’s condition;
- active interaction between doctors and the patient and his family.
You can make an appointment with the doctors at the Yusupov Hospital and find out how much rehabilitation after a stroke costs by calling.