- home
- Services and prices
- Neurology
- Restoring speech after a stroke
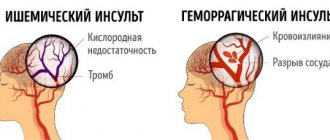
A stroke is an acute disruption of the blood supply to the brain, when cells in the nerve centers die from a lack of oxygen and neural connections are destroyed. Its consequences can be very different: memory loss, partial or complete paralysis, dementia and speech disorders. The latter are classified into several types: light, medium and heavy.
However, the results of a stroke are not irreversible: in most cases, it is possible to return the victim to normal life with the help of a set of rehabilitation measures.
Signs of speech impairment
The fact that the areas of the brain responsible for speech were damaged during a stroke is indicated by the behavior of the victim:
- The patient confuses words and sounds, stumbles, stutters;
- The construction of sentences is disrupted - instead of “I went to the street,” a person can say “I went to the street,” etc.;
- Frequent repetition of the same sounds or words;
- The patient does not understand well what is being said to him, forgets the names of objects;
- Consistent counting skills are impaired;
- Obscene words and expressions appeared.
The last factor often comes as a surprise, since after a stroke even cultured and well-mannered people can begin to swear. Experts say that this is due to the ancient origin of obscene language.
Complications
Neurologists have to deal with numerous complications of the physical and psychological state of a stroke, which include:
- Gross disturbances of mental, cognitive, speech activity;
- Perceptual inhibition;
- Inflammatory phenomena of the bronchopulmonary, genitourinary system due to congestion in an immobilized patient;
- Depressive states with suicidal statements.
These manifestations require the closest attention and active therapy from specialists in various fields.
The Yusupov Hospital has a full range of rehabilitation equipment, including innovative ones, and a staff of highly qualified specialists who are proficient in modern techniques and types of massage and physical therapy. Their efforts, led by the country's best neurologists, are helping people recover from stroke paralysis.
Types of speech disorders
Modern medicine knows two main types of speech disorders after a stroke: aphasia and dysarthria. In the first case, speech is impaired due to the death of neurons and their connections in the brain center that is responsible for speech. Aphasia can be complete or partial. Dysarthria occurs against the background of the fact that the centers in the brain responsible for the functioning of speech muscles have been damaged.
Aphasia
It is the most common cause of speech impairment. There are six variations of aphasia in total:
- Motor
. This form is divided into two more types of aphasia. With afferent aphasia, the patient cannot choose the articulatory posture that is needed in order to pronounce specific sounds. With efferent aphasia, speech is preserved at an instinctive level, but repetition is impaired. Victims have difficulty moving from one position to another. - Dynamic
. In this variant, patients experience problems with active utterance: the inability to correctly formulate a sentence because both external and internal speech are impaired. There are frequent cases of echopraxia - repetition - situations when the patient automatically begins to repeat words, phrases, facial expressions or gestures after the interlocutor. - Sensory
. It is divided into three types: cortical, subcortical and transcortical aphasia. In the first case, the patient lacks both understanding and pronunciation of sounds; in the second, the transmission of impulses from the parts of the brain responsible for the perception of sound information is distorted. In the third case, writing and visual function are impaired, but the patient is capable of perceiving light speech structures. - Sematic
. The victims do not fully understand the complex speech structures that are responsible for spatial relationships. Problems are often observed when completing tasks that contain complex syntactic formulations. Patients forget the names of the simplest household items - dishes, furniture, clothing, electrical appliances, and read slowly. Sometimes acalculia develops, a neuropsychological disease when a person loses the ability to count consistently. - Acoustic-mnestic
. With this aphasia, patients experience difficulties that are associated with the ability to retain information perceived auditorily in memory. During classes with a speech therapist, patients cannot repeat the simplest connections of several words, or understand the meaning of a sentence when it is pronounced at a fast pace or during a conversation with several interlocutors. - Total
. A distinctive feature of this type of aphasia is the complete absence of speech due to damage to a large number of areas of the brain. Total aphasia is subject to hard and long-term correction work from various specialists - from massage therapists to speech therapists.
Dysarthria
A type of speech disorder when a stroke victim has impaired functioning of the organs responsible for articulation (tongue, palate, lips). It is observed much less frequently than aphasia and develops, as a rule, with damage to various brain structures, in particular the cranial nerves involved in the work of speech muscles. Patients experience sluggish and uncertain speech, and difficulty pronouncing individual sounds or words.
Articulatory dyspraxia
Another type of speech impairment is the inability of a person to make consistent movements with the mouth, lips, and tongue - which is divided into two types: kinetic and kinesthetic.
In the first option, difficulties arise when sequentially changing sounds and syllables, skipping them, replacing one syllable or sound with another, and incorrect placement of stresses.
In the second option, disturbances occur in the articulatory structure: the brain experiences difficulty interacting with the muscles responsible for producing sounds.
The formation of motor skills is carried out through adequately coordinated actions. After a stroke, neuronal death can occur in areas of the brain with the premotor, profrontal and motor cortices, which can lead to dyspraxia.
The correction of dyspraxia is carried out by a speech therapist in collaboration with a neurologist and psychologist.
Etiopathogenesis
The main mechanism for the development of paralysis is stroke - damage to the artery with blood escaping beyond the vascular bed. As a result, a hematoma is formed, which gradually grows and compresses the brain tissue. Vital neurons die, loss of function is noted, control of skeletal and smooth muscles decreases, and sensitivity disappears.
This condition is predisposed to:
- Eating disorders – the main role is played by a lack of calcium in the diet, which strengthens the walls of the arteries. In these cases, cardiologists repeat “where it’s thin, that’s where it breaks.” Weakened brain vessels that are prone to damage can cause a stroke;
- Hypertension – the situation is aggravated by increased blood pressure, which can damage weakened blood vessels. In older people, there is a lack of calcium, which can cause artery rupture;
- Compounded heredity - according to recent studies, there is a predisposition to vascular diseases, especially hypertension and strokes. The mechanism has not been fully studied; insufficiency of the neurohumoral mechanism and weakness of the vascular wall are assumed;
- Obesity - this condition is accompanied by a lack of minerals, an increase in blood pressure, which increases the likelihood of developing a stroke with subsequent paralysis;
- Cardiovascular diseases - valve malformations, heart failure, atherosclerosis and thrombosis predispose to cerebral hemorrhage;
- Endocrine diseases - diabetes comes first, leading to hypertension and hemorrhages. Sometimes the causes are hypothyroidism, pathologies of the adrenal cortex;
- Bad habits - nicotine weakens the walls of arteries and increases cholesterol levels in the blood. Natural alcohol in minimal dosages is useful, but an excess of surrogate or drunkenness often ends in stroke and paralysis.
The listed factors can provoke both left and right paralysis. According to statistics, the latter option is observed more often, which increases the patient’s chances of survival due to timely diagnosis.
Ways to restore speech after a stroke
Speech after a stroke is rehabilitated through a set of various measures. This includes taking medications that improve blood circulation and promotes the formation of new neural connections, and physical therapy, massage, speech therapy and articulation exercises, and much more. A plan for speech restoration after a stroke for a particular patient is developed individually based on research and the diagnosis made. Some aspects of rehabilitation therapy require specialist supervision, but not all of them. The patient can perform some exercises to restore speech after a stroke with the help and participation of people close to him, which will make the recovery process more effective.
As soon as the patient's condition has stabilized, the very first exercises begin. The patient is examined by a speech therapist and a neurologist. Special tests help identify existing problems and prescribe further treatment.
There are no guarantees that a person will fully restore speech skills: much depends on how severe the brain damage was, on the body’s ability to regenerate and the interest of the patient and his loved ones in achieving the goal.
It is strictly not recommended to self-medicate and teach the patient to talk on his own. There is a risk of developing complications in the form of echolalia - meaningless repetition of words, verbal embolus, agrammatism, etc. A set of treatment measures is prescribed exclusively by a group of treating specialists.
Speech therapy exercises
Regular sessions with a speech therapist are the key to speech restoration. At first, the specialist works with the patient himself, then relatives can continue training at home.
The basis of a speech therapist’s work is the involvement of certain parts of the brain in the control of speech functions. To do this, he uses different techniques and sets of exercises:
- Phonetic. Through the victim repeating individual sounds, words and phrases after the doctor, the type of speech disorder is determined. The facial muscles of the tongue and lips are under control.
- Semantic. The active thought process is stimulated. A person who has suffered a stroke must complete sentences, series of associations, and talk on various topics.
- Visual. The use of cards with images, book illustrations and other specialized items so that the patient begins to build various connections and associative series. This method is usually used for sensory aphasia.
- Creative. Various types of creative activities are included in the rehabilitation work, in particular those that the patient was interested in. This could be expressive reading of tongue twisters, poetry, acting, music, singing, drawing, etc.
There are several rules for completing tasks:
- Gradually increasing the complexity of the exercises;
- Encouragement of the patient's achievements is mandatory;
- Monitor the patient’s condition and prevent overwork;
- Number of classes – no more than 5-10 per week.
Based on the patient’s progress, the speech therapist should adjust the rehabilitation program from time to time.
Massage
After a stroke, there are often cases of not only speech impairment, but also the appearance of problems with the speech apparatus: in patients, chewing function is impaired, uncontrolled salivation appears, and the corners of the mouth and cheeks sag. There is a need to restore muscle tone and start the process of restoring correct facial expressions. Here a special massage comes to the aid of the patient, which is prescribed by the attending physician depending on the characteristics of the injury in a particular person.
The main objectives of massage within the framework of rehabilitation therapy are:
- Improving blood circulation and activating lymph outflow;
- Normalizing the tone and elasticity of muscle tissue;
- Strengthening the general condition of the body;
- Relieving tension and anxiety in patients.
Massage is prescribed almost immediately after the patient’s condition has stabilized: approximately one to two weeks after the crisis. At first, these are simple stroking of the muscles and gentle rubbing at a moderate rhythm. Then the techniques become more complex, kneading and vibration are used, the intensity and duration of the sessions increases.
The decision to prescribe or refuse massage courses is made by the attending physician. Sometimes a patient may have contraindications to it, an increased risk of developing severe deviations from the norm of body functionality, and other complications.
Articulation exercises
This type of exercise is used to increase control over the muscles involved in speaking.
Speech therapy exercises that develop language:
- Stick it out and hold it in this position for a few seconds;
- Try to reach your nose with your tongue and hold it;
- Pass it from one corner of the mouth to the other several times;
- Move your tongue back and forth across the palate;
- Clatter;
- Lightly bite your tongue after relaxing it;
- Trace your lips first counterclockwise and then clockwise.
Exercises to develop lips:
- Fold them into a tube and pull them out;
- Smile with your mouth closed;
- Raise your lip up, showing the upper row of teeth;
- Roll the air in different directions, inflating first one or the other cheek;
- Blow through your lips, having previously relaxed them;
- Use your fingers to pull them up, down, right, left;
- Alternate between raised and lowered corners of the mouth.
Exercises to restore your voice:
- Alternate pronunciation of vowels;
- Silent articulation of “Y”;
- Pronunciation of vowels one after another with a smooth transition of sound, while reversing stress;
- Repetition of consonant sounds - from voiceless to voiced.
Exercises for facial expressions:
- Working with eyebrows: frowning, being surprised with their help;
- Open very wide and then relax your mouth;
- “Kiss” the air;
- Stick your tongue out to your interlocutor and pull him in different directions;
- Move your jaw.
Depending on the type of disease, the doctor selects an individual set of tasks for each patient.
Breathing exercises
Classes with a speech therapist will be many times more effective if, before starting speech exercises, you perform physical exercises that will improve articulation and function of the facial muscles:
- Pull the letter “U” through the elongated “tube” lips;
- Smile several times so that symmetry is maintained at the corners of the lips;
- If the loss of sensitivity is insignificant, slightly bite the lower and then the upper lip;
- Roll up your tongue;
- Smack expressively;
- Run your tongue over your lips and palate;
- Calmly inflate and deflate your cheeks.
To achieve positive dynamics, exercises must be performed regularly.
Drug therapy
Taking medications in the post-stroke period allows you to prevent the process of cell destruction, normalize blood circulation and start the process of tissue regeneration.
Experts prescribe different types of drugs:
- Blood thinners – medications that reduce blood viscosity and stimulate improved blood circulation;
- Diuretics – relieve swelling, including in the brain;
- Nootropic drugs – stimulate the regeneration of nerve cells;
- Antihypertensive drugs – do not allow blood pressure to reach a critical value, which can cause complications.
Music therapy
In certain situations, when the patient does not speak at all, but can sing, treatment with music helps. All exercises with a speech therapist in such a situation involve singing: the patient sings sounds, words, sentences, repeats the words and motive after his favorite performer.
In addition, music has a positive effect on the human psyche, calming or making him happy. Often patients are in a state of depression or increased anxiety, and here music comes to the aid of specialists, which stabilizes the emotional background.
The positive effect of music on brain recovery after a stroke was studied in scientific workshops. During classes, people with speech impairments had their cerebral cortex activity measured. It has been proven that music stimulates the functioning of the nervous system, promotes the formation of new neural connections, and therefore restores brain properties lost during the disease.
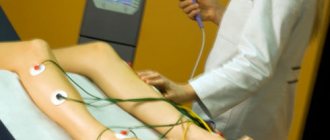
Physiotherapy
A set of therapeutic practices and techniques for stimulating the articulatory apparatus and vocal cords by exposure to electrical impulses, magnetic radiation, light, heat or air, ultrasound, etc.
Some of the main goals of physiotherapy after a stroke are:
- Prevention of complications and new stroke;
- Improving blood circulation and metabolism;
- Preventing the occurrence of blood clots, which can lead to blockage of blood vessels;
- Restoration of muscle tone;
- Relieving pain and swelling;
- Improving the passage of nerve impulses, accelerating the formation of new neurons;
- Normalization of sleep patterns and general well-being of the patient.
Acupuncture
A popular procedure is used to correct motor aphasia and helps restore the tone of the speech apparatus.
The effectiveness of acupuncture has long been proven by science: needles irritate nerve endings in the skin, send signals to the brain and spinal cord, thereby activating the central nervous system and promoting the formation of new neurons. Also, when using this method, muscle activity improves, pain decreases, and the immune system is activated.
Traditional methods
Treatment of stroke with herbs is sometimes practiced by some doctors, prescribing it as an auxiliary therapy. Taking decoctions of viburnum, thyme, St. John's wort, rose hips, and calendula, of course, can help improve blood circulation or increase the body's overall resistance, but it is not a panacea.
We do not recommend starting treatment of relatives who have suffered from a stroke on their own using traditional methods: first consult with your doctor and make sure that the patient is not allergic to this or that drug.
Speech Pathologist Tips and Tricks
Dealing with an emotionally depressed patient is very difficult. Imagine a situation where a person regains consciousness, but he realizes with horror that he is unable to say anything and cannot communicate with others. In this case, “faster” does not mean “better.” The patient should feel the unobtrusive attention of others.
Some tips for relatives:
- Do not treat the patient as an inferior person doomed to disability. Talk to him calmly and carefully. Try to set yourself up for recovery. Pay attention to the smallest positive changes.
- Do not allow indifferent people to approach him. All emotions should be good.
- Play soft music, the patient's favorite radio station.
- Try to interest the patient in a dialogue with you, emphasize the importance of his opinion.
- The hearing load at the patient's location must be controlled. Radio and TV should not be played for long periods of time or loudly. Excessive noise is annoying and tiring.
How long does it take to restore speech after a stroke?
The rehabilitation process usually takes from several months to several years - it all depends on whether the speech centers were severely damaged. Common disturbances in aphasia disappear on average 3-6 months after the crisis.
If the stroke was suffered in a severe form, then the possibility of restoring lost speech skills is about 55%. With moderate severity, it is guaranteed that 75% of the damage can be restored, with mild damage – up to 90%.
The most favorable prognosis is observed in patients who have suffered motor aphasia. In young people, speech is restored almost completely; in older people, minor impairments may remain in the form of unclear pronunciation of individual sounds.
Massage
This method is aimed at preventing bedsores and is used from the first days of paralysis. The right side of the body is warmed up, after which blood circulation and tissue trophism are improved, and mobility in the joints is restored.
To eliminate the effects of paralysis, a standard warm-up includes:
- stroking - from the periphery, along the blood flow;
- rubbing – carried out more intensively, similar to the previous method;
- vibration movements – in the area of soft tissues;
- The procedure ends with stroking.
To prevent new bedsores from arising, it is recommended to massage daily, regularly change the patient’s position and rub the skin with alcohol (if there are no wounds).
Where is the best place to go for rehabilitation?
The very first actions to regain lost skills begin in a hospital setting. The attending physician develops a treatment strategy and prescribes medications that help accelerate the regeneration of brain cells.
Speech restoration after a stroke is carried out both at home and in special rehabilitation centers in Moscow, where qualified speech therapists-aphasiologists, neurologists, psychologists, and massage therapists work with victims.
The patient is first examined and, based on the diagnostic results, a rehabilitation program is prescribed, which allows the person to gradually return to a normal, fulfilling life. Individual consultations are held with the patient’s family and friends and sets of exercises are prescribed, which will need to be continued to be practiced at home.
Consequences of right-sided paralysis
In severe cases, right-sided lesions lead to irreversible complications that develop as a result of massive hemorrhage or violation of treatment rules. We list the most common conditions:
- paralysis of both arms and legs;
- lifelong speech dysfunction;
- disturbance of thinking, memorization, social behavior;
- the appearance of bedsores;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases against the background of reduced physical activity;
- enuresis and fecal continence disorders.
The main task of the doctor is to create conditions that ensure full recovery after a stroke on the right side, which will minimize the development of complications.