Stroke is an acute disease that is accompanied by the death of brain cells due to acute cerebrovascular accident. It manifests itself with general cerebral and local symptoms. The development of a stroke is possible in two scenarios: either after 24 hours from the onset of the disease, its symptoms persist, or death occurs.
Diagnostic examination for developing stroke includes:
- clarification of complaints and history of the disease;
- neurological examination;
- blood tests (determining the level of enzymes and blood glucose, the state of the coagulation and anticoagulation systems).
- Dopplerography - study of blood flow in the vessels of the neck and brain;
- computed tomography helps distinguish between ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes;
- Magnetic resonance imaging is more informative in cases of developing stroke;
- magnetic resonance angiography and computed tomography angiography are non-invasive methods for assessing the carotid and cerebral arteries;
- an electrocardiogram allows you to assess the condition of the heart muscle;
- Echocardiography (EchoCG) is a research method with which doctors at the Yusupov Hospital identify blood clots in the cavities of the heart, which allows them to assess the risk of developing a recurrent stroke.
Make an appointment
What is a stroke, its types
A stroke is a disorder of cerebral circulation leading to brain damage.
The pathology is widespread. In the Russian Federation alone, there are 3 cases of stroke per 1000 inhabitants. In the post-mortem extract, it is listed as the cause of death in 23.5% of people.
Even if patients do not die after suffering a vascular accident, more than 80% of them remain disabled. Often neurological disorders are so severe that the patient is unable to care for himself. Stroke is the third leading cause of death.
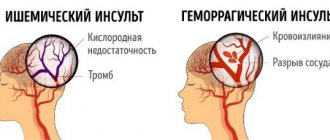
There are 2 types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic. The mechanism of their development and the features of treatment have nothing to do with each other. There is also a special type of hemorrhagic vascular damage - subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Ischemic
Ischemic stroke is a cerebral circulatory disorder accompanied by an acute onset. Pathology develops due to disruption or complete cessation of blood supply to the brain. This leads to softening of its tissues and infarction of the affected area. It is cerebral vascular ischemia that is one of the main causes of death worldwide. Such a stroke occurs 6 times more often than hemorrhagic lesions.
It can be of 2 types:
- Thrombotic . Develops due to blockage of blood vessels in the brain by a blood clot.
- Embolic . Occurs when blood vessels located far from the brain become blocked. The most common source of embolism is the heart muscle (cardioembolic stroke).
In 80% of cases, the pathological focus is localized in the middle cerebral artery. Other vessels account for the remaining 20%.
Reasons that can provoke ischemic damage to cerebral arteries and veins:
- Myocardial infarction.
- High or low blood pressure.
- Atrial fibrillation.
- Diabetes.
- Lipid metabolism disorders.
Risk factors include: old age, hereditary predisposition to vascular accidents, as well as lifestyle features.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke do not increase as quickly as symptoms of hemorrhagic brain damage.
Its manifestations:
- Drowsiness, dazedness.
- Brief fainting.
- Headache, dizziness.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Pain in the eyes that gets worse with movement.
- Cramps.
- Sweating, hot flashes, dry mouth.
Depending on which part of the brain is affected, the neurological manifestations of ischemia differ. The lower and upper extremities are affected to a greater or lesser extent, paresis of the tongue and face is observed, and visual and/or auditory function deteriorates.
Hemorrhagic
Hemorrhagic stroke is bleeding into the cranial cavity. The most common cause of blood vessel rupture is high blood pressure.
Other provoking factors include:
- Aneurysm.
- Malformation of cerebral vessels.
- Vasculitis.
- Systemic connective tissue diseases.
- Taking certain medications.
- Amyloid angiopathy.
The onset of the pathology is acute; most often the manifestation occurs against the background of high blood pressure. A person experiences severe headaches, dizziness, accompanied by vomiting or nausea. This state is quickly replaced by stupor, loss of consciousness, and even the development of coma. Convulsions are possible.
Neurological symptoms manifest themselves in the form of memory loss, deterioration of sensitivity and speech function. One side of the body, which is on the opposite side of the lesion, loses the ability to function normally. This applies not only to the muscles of the torso, but also to the face.
A stroke with blood escaping into the ventricles of the brain is difficult to endure. The victim develops symptoms of meningitis and has seizures. He quickly loses consciousness.
The next 3 weeks after a stroke are considered the most difficult. At this time, cerebral edema progresses. It is he who is the main cause of death of patients. Starting from the fourth week, in surviving people, the symptoms of the lesion begin to reverse. From this time on, the severity of brain damage can be assessed. They are used to determine what degree of disability to assign to the victim.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is understood as a condition that develops as a result of a breakthrough of blood vessels into the subarachnoid space of the brain. This pathology is a type of hemorrhagic stroke.
The subarachnoid space contains cerebrospinal fluid, the volume of which increases due to blood flow. The patient's intracranial pressure increases and meningitis of aseptic nature develops. The situation is aggravated by the reaction of cerebral vessels. They spasm, which leads to ischemia of the affected areas. The patient develops an ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack.
The following reasons lead to hemorrhage into the subarachnoid space::
- Traumatic brain injuries with damage to the integrity of blood vessels.
- Aneurysm rupture.
- Dissection of the carotid or vertebral artery.
- Myxoma of the heart.
- A brain tumor.
- Amyloidosis.
- Diseases associated with blood clotting disorders.
- Uncontrolled use of anticoagulants.
The pathology manifests itself as a severe headache. Possible loss of consciousness. In parallel, symptoms of meningitis develop, with neck stiffness, vomiting, and photophobia. A distinctive sign is an increase in body temperature. In severe cases, there is a disorder of respiratory function and cardiac activity. With prolonged fainting and coma, one may suspect that blood has entered the ventricles of the brain. This occurs during its massive outpouring and threatens with serious consequences.
Acute stage of the disease
Rehabilitation in the acute period takes place in a medical institution under the guidance of doctors. It is advisable to begin rehabilitation treatment as soon as the patient’s condition stabilizes, optimally 3-4 days after the stroke. The main tasks at this stage are: restoration of simple motor and speech functions, prevention of complications and relapses, assessment of the degree of damage to the body and development of a rehabilitation program.
To restore the motor system, passive gymnastics, massage and treatment by changing body position are used, when the patient’s limbs are placed in various positions to prevent the development of muscle hypertonicity. The return of lost speech skills begins with simple articulation exercises, gymnastics of the tongue, cheeks, and lips. Speech is more actively restored 3-6 months after a stroke, but full recovery requires 2-3 years of work with the patient.
An important condition that accelerates rehabilitation in the acute period is the use of medications and physiotherapeutic pain-relieving procedures - magnetic, electro- and laser therapy.
Signs and symptoms of stroke
A stroke manifests unexpectedly for a person, although sometimes it is preceded by certain symptoms. If you interpret them correctly, you can avoid a terrible vascular catastrophe.
Warning signs of an impending stroke include:
- Prolonged headaches. They do not have a clear localization. It is not possible to cope with them with the help of analgesics.
- Dizziness. It occurs at rest and can intensify when performing any actions.
- Ringing in the ears.
- Sudden attack of atrial fibrillation.
- Difficulty swallowing food.
- Memory impairment.
- Numbness of arms and legs.
- Loss of coordination.
- Insomnia.
- Increased fatigue.
- Decreased overall performance.
- Rapid heartbeat and constant thirst.
The listed signs may have varying intensities. You should not ignore them; you should consult a doctor.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke increase slowly. With hemorrhagic brain damage, the clinical picture unfolds rapidly.
You can suspect a brain catastrophe based on the following symptoms::
- General cerebral symptoms . The patient experiences unbearable headaches. Nausea ends with vomiting. Consciousness is impaired, and both stupefaction and coma may occur.
- Focal symptoms . They directly depend on where exactly the lesion is localized. The patient may have decreased or completely lost muscle strength on one side of the body. Half of the face is paralyzed, causing it to become distorted. The corner of the mouth lowers, the nasolabial fold smoothes out. On the same side, the sensitivity of the arms and legs decreases. The victim’s speech deteriorates and he has difficulty oriented in space.
- Epileptiform symptoms . Sometimes a stroke provokes an epileptic attack. The patient loses consciousness, has convulsions, and foam appears at the mouth. The pupil does not react to the light beam; on the side of the lesion it is dilated. The eyes move right and left.
- Other symptoms . The patient's breathing quickens and the depth of inspiration decreases. A significant decrease in blood pressure and increased heart rate are possible. Often a stroke is accompanied by uncontrolled urination and defecation.
When the first signs of a stroke appear, you should not hesitate to call an ambulance.
ICD-10
I63 Cerebral infarction
- Causes
- Pathogenesis
- Classification
- Symptoms of ischemic stroke Brain infarction in the MCA basin
- Cerebral infarction in the ACA basin
- Cerebral infarction in the PCA basin
- Cerebral infarction in the vertebrobasilar region
- Differential diagnosis
- Therapy in the acute period
Diagnostic methods
It is important to quickly distinguish a stroke from other diseases that can lead to the development of similar symptoms. It is almost impossible to do this on your own, as well as to determine the type of vascular accident.
The main difference between an ischemic stroke is a gradual increase in symptoms that do not lead to loss of consciousness. With hemorrhagic hemorrhage, the patient passes out quickly. However, stroke does not always have a classic course. The disease may begin and progress atypically.
Diagnosis begins with examination of the patient. The doctor collects anamnesis and determines the presence of chronic diseases. Most often, you can get information not from the victim himself, but from his relatives. The doctor performs an ECG, determines the heart rate, takes a blood test, and measures blood pressure.
It is possible to make the correct diagnosis and obtain maximum information about the patient’s condition thanks to instrumental diagnostic methods. The best option is a CT scan of the brain. Performing an MRI is difficult because the procedure takes a long time. It takes about an hour. It is impossible to spend this amount of time diagnosing an acute stroke.
Computed tomography allows you to clarify the type of pathology, where it is concentrated, to understand how badly the brain is damaged, whether the ventricles are affected, etc. The main problem is that it is not always possible to perform a CT scan in the shortest possible time. In this case, doctors have to focus on the symptoms of the disease.
To determine the source of the stroke, the method of diffusion-weighted tomography (DWI) is used. The information will be received within a few minutes.
Other examination methods include:
- Lumbar puncture.
- Cerebral angiography.
- Magnetic resonance angiography. It is performed without the introduction of a contrast agent.
- Doppler ultrasound.
Once the diagnosis is made, the doctor will immediately begin treatment.
FAQ
How is a stroke different from a heart attack?
Cerebral infarction is one of the types of stroke and it is ischemic in nature, i.e. accompanied by a cessation of blood flow to the brain. A characteristic feature is the gradual development of the clinical picture and the predominance of focal symptoms: disturbances in speech, vision, gait, movements up to paralysis, sensitivity.
Can a stroke and heart attack happen at the same time?
If we consider only the brain, mixed stroke occurs, when the causes of stroke include both hemorrhage and ischemia. They can occur simultaneously when a vessel ruptures in one area and blood flow stops in another. Also, ischemia can develop at the site of subarachnoid hemorrhage after some time.
If we consider a heart attack as a heart disease, then these conditions can also be diagnosed simultaneously. Moreover, a stroke can develop as a result of a heart attack: the functioning of the heart suffers, and insufficient blood flows to the brain. This is how we get a stroke.
Does a stroke only occur in the brain?
Stroke (Latin insultus “swoop, attack, blow”) is an acute disruption of the blood supply to the brain due to ischemia (infarction) or hemorrhage. If ischemia occurs in other organs, it is also called a heart attack. For example, myocardial infarction, intestinal, kidney, etc. It is characterized by severe pain, dysfunction of the affected organ and other symptoms.
Does stroke occur with normal or low blood pressure?
Arterial hypertension is one of the main, but not the only causes of stroke. Thrombosis, atherosclerosis, and diabetes mellitus, in which blood pressure is normal or even reduced, are also risk factors. In addition, with low pressure, the brain is not sufficiently supplied with oxygen, which is a prerequisite for the development of ischemic stroke.
Do children have strokes?
Stroke is also diagnosed in children. It can develop even in the perinatal period. Causes: abnormalities in the coagulation system, pathologies of the cardiovascular system, including vascular malformations, bad habits of the mother during pregnancy, oxygen starvation during childbirth, trauma.
In the perinatal period and up to one year, the disease is accompanied by anxiety, frequent crying, loss of appetite, impaired reflexes in the newborn period, strabismus, and convulsions. The diagnosis is made based on an examination by a pediatric neurologist, ultrasound of the brain, and tomography results. At older ages, symptoms are similar to those of stroke in adults.
The child's body is more flexible and responds more quickly to therapy. The main thing is to diagnose a stroke in time and begin treatment.
Can a stroke go away on its own?
There is such a condition - transient stroke. It is accompanied by a short-term circulatory disorder, but no irreversible changes in brain tissue occur. The external manifestations of such a stroke are the same as a normal one, but less pronounced: headache, dizziness, darkening of the eyes, changes in sensitivity in various parts of the body. And they pass within 24 hours. However, the condition requires qualified treatment and rehabilitation, elimination of risk factors, because in the future there is a possibility of a secondary stroke.
At what pressure can a stroke occur?
A stroke can develop at any pressure. Arterial hypertension causes hemorrhagic stroke, hypotension causes ischemic stroke.
Do pine cones help prevent stroke?
Pine cones lower blood pressure, so they should not be consumed if you have hypotension. The effect is due to the tannins contained in the buds. The composition also contains vitamins C and P - they strengthen the walls of blood vessels and improve blood circulation.
The advisability of using products based on herbal raw materials is decided by the attending physician after a detailed examination. In general, pine cones for stroke can only be used as a complementary method.
Who is at risk
There are people who need to be especially wary of developing a stroke, as they are at risk.
Among them:
- Persons with hypertension.
- Patients with diabetes.
- Men and women over 65 years of age.
- People with abdominal obesity.
- Persons with a hereditary predisposition to vascular pathologies.
- Patients who have previously had a stroke or heart attack.
- Patients with diagnosed atherosclerosis.
- Women over 35 years of age taking oral contraceptives.
- Smokers.
- People suffering from heart rhythm disturbances.
- People with high cholesterol levels.
Most often, patients with the listed diagnoses are registered at the dispensary. Special mention should be made of people living in a state of chronic stress. Emotional stress negatively affects all systems of the body and can cause a stroke.
Causes
Since ischemic stroke is not considered as a separate disease, it is impossible to determine a single etiological factor for it. However, there are risk factors associated with an increased incidence of ischemic stroke, which can be divided into two groups:
1. Modifiable.
- myocardial infarction
- arterial hypertension
- atrial fibrillation
- diabetes
- dyslipoproteinemia
- asymptomatic lesions of the carotid arteries.
2. Unmodifiable.
- hereditary predisposition
- age
In addition, there are risk factors associated with lifestyle: low level of physical activity, acute stress or prolonged psycho-emotional stress, excess body weight, smoking.
How to provide first aid for a stroke
There is a clear algorithm for providing first aid to a person suffering from a stroke :
- Call a medical team . To do this, you need to dial 103 from a landline phone. If you happen to have a smartphone at hand, then the call is made to the single number 112. The doctor must immediately be informed that the person is unwell and there is a suspicion of a stroke.
- The victim must be laid on a flat surface so that his head is higher than his body. They take off his glasses and remove his lenses. If possible, you need to help him get removable dentures.
- If there is no consciousness, then you need to open the patient’s mouth slightly and turn his head to the side . This is done to prevent aspiration of vomit. It is imperative to listen to the patient’s breathing.
- For better access to fresh air, it is recommended to open a window or vent..
- Before the arrival of the medical team, it is necessary to prepare documents, if any..
Doctors need to be informed about the person’s illnesses, as well as what medications he is taking. It is prohibited to give the victim any medications. Medication correction should be carried out by emergency physicians. You should not try to give water or food to a person. This may make the situation worse.
If the patient falls and has an epileptic attack, there is no need to unclench his teeth or try to hold him. It is necessary to protect the victim from injury. To do this, place a soft object, such as a pillow, under his head. If a stroke with an epileptic attack happened on the street, then you can use a jacket or other suitable thing. Foam flowing from the mouth is wiped away with a cloth. The head should be elevated at all times.
There is no need to try to bring a person to his senses with ammonia. Until the end of the attack, it should not be moved from place to place.
If breathing stops, resuscitation measures must be started immediately. To do this, perform a heart massage and breathe mouth to mouth or mouth to nose.
Where to go for help?
It is impossible to provide complete rehabilitation after a stroke in the home environment. Therefore, the most reasonable option for the family of an elderly person who has suffered an attack would be to enter into an agreement with a specialized institution, where he can receive help from highly qualified specialists and undergo a comprehensive rehabilitation program developed taking into account his diagnosis and characteristics of the body.
The Trust boarding house network has been providing care and rehabilitation to stroke victims for the past 5 years. The staff consists of highly qualified doctors and nurses with medical education. The boarding houses have all the conditions for a comfortable stay and full recovery after a stroke:
- Individual rehabilitation programs aimed at adaptation after a stroke and prevention of a recurrent attack.
- Regular medical examination of the patient.
- A full range of rehabilitation procedures: exercise therapy classes, exercises for the rehabilitation of speech and cognitive functions.
- Drug therapy.
- Social and psychological assistance, warm and attentive attitude towards each ward.
- Cozy rooms equipped with functional beds, wheelchairs, orthopedic mattresses.
- Prevention of bedsores and daily hygiene.
- Specialized 6 meals a day, rich in vitamins and microelements.
- Organization of leisure and communication.
By entrusting us with the care of your loved ones, you create decent conditions for life and restoration of their health, thereby reducing the recovery time after a stroke. To find out more details about our programs, leave a request on the website, and we will call you back at a time convenient for you.
Treatment and rehabilitation
The patient receives treatment in a hospital. All patients with suspected stroke are hospitalized on an emergency basis. The optimal period for providing medical care is the first 3 hours after a brain accident has occurred. The person is placed in the intensive care unit of a neurological hospital. After the acute period has been overcome, he is transferred to the early rehabilitation unit.
Until the diagnosis is established, basic therapy is carried out. The patient’s blood pressure is adjusted, the heart rate is normalized, and the required blood pH level is maintained. To reduce cerebral edema, diuretics and corticosteroids are prescribed. Craniotomy is possible to reduce the degree of compression. If necessary, the patient is connected to an artificial respiration apparatus.
Be sure to direct efforts to eliminate the symptoms of stroke and alleviate the patient’s condition. He is prescribed medications to lower body temperature, anticonvulsants, and antiemetics. Medicines that have a neuroprotective effect are used.
Pathogenetic therapy is based on the type of stroke. In case of ischemic brain damage, it is necessary to restore nutrition to the affected area as quickly as possible. To do this, the patient is prescribed drugs that resolve blood clots. It is possible to remove them mechanically. When thrombolysis fails, the patient is prescribed Acetylsalicylic acid and vasoactive drugs.
In case of a stroke, it is extremely important to provide timely treatment to the damaged areas of the brain. A course of use of the drug accelerates the process of recovery of brain cells after a stroke, even in cases of impaired blood circulation or hypoxia. This allows for rapid restoration of memory, thinking, speech, swallowing reflex and restoration of other functions of daily activities. Gliatilin has a positive effect on the transmission of nerve impulses, protects brain cells from repeated damage, which prevents the risk of recurrent stroke.
The drug is well tolerated by patients; it is contraindicated for use by pregnant, lactating women and people with hypersensitivity to choline alfoscerate.
Courses will need to be taken regularly. You definitely need to do physical therapy, undergo physical therapy, and visit a massage therapist. After a stroke, many patients have to restore motor skills over a long period of time and learn to care for themselves independently.
Relatives and friends should provide support to the patient and not leave him alone with the problem. Psychologists are involved in the work. Sessions with a speech therapist are often required.
Late and remote periods
At a later stage, the body’s potential for rehabilitation after a stroke gradually decreases, but the patient must continue to study and train self-care skills. This period already passes at home, so responsibility for the health and mental state of the patient falls entirely on his loved ones.
You can change your usual exercise therapy complex by adding new exercises and classes with simple exercise equipment, for example, an expander. It is recommended to talk with the patient as often as possible, ask questions, thereby encouraging him to be vocal.
A year after the stroke, the exercises no longer have a pronounced effect, so in the long-term recovery period, the main attention should be paid to consolidating skills and periodic visits to the doctor for follow-up examinations.
Conditions for successful rehabilitation after a stroke
A stroke is a difficult ordeal, especially for older people, who can suffer from it with unpredictable consequences. How long it will take to recover - even doctors cannot answer this question for sure. But in order to shorten the rehabilitation period after a stroke, the patient must provide a number of conditions:
- rehabilitation should take place under the strict guidance of a qualified doctor according to an individually developed program;
- the rehabilitation process must be continuous and comprehensive. This means that it is necessary to work on restoring all body functions simultaneously and sequentially;
- in the home environment, it is necessary to create all the conditions for the successful rehabilitation of the patient: equip the sleeping place with an anti-decubitus mattress, allocate a place for doing therapeutic exercises and purchase the necessary exercise equipment, as well as additional equipment - walkers, wheelchairs, canes, special personal hygiene products;
- provide a balanced diet throughout the entire period of rehabilitation;
- take care to create a favorable home atmosphere, sensitive and caring attitude towards the sick person.
Possible consequences, complications
The main danger of a stroke is death. If a person survives, the disease will still make itself felt with certain complications.
Early consequences include:
- Brain swelling.
- Coma.
- Pneumonia.
- Paralysis. It can be partial or complete. Most often, one half of the body is affected.
- Repeated stroke.
- Bedsores.
- Mental disorders. They can manifest themselves in moodiness, irritability, aggression, and anxiety. Sometimes dementia develops.
- Sleep disorders.
- Myocardial infarction, gastric ulcer. These disorders develop against the background of increased levels of stress hormones.
After an ischemic stroke, death occurs in 15-25% of cases. Hemorrhagic damage to the blood vessels of the brain leads to the death of 50-60% of patients. The cause of death is precisely severe complications, for example, pneumonia or acute heart failure. The first 3 months after a stroke are considered the most dangerous.
Arms recover worse in patients than legs. A person's future health is determined by the severity of brain damage, the speed of medical care, his age and the presence of chronic diseases.
Long-term consequences include:
- Formation of blood clots in various parts of the body.
- Depression.
- Speech problems.
- Memory loss.
- Deterioration of intellectual abilities.
After a stroke, you have to deal with the consequences for many months. Sometimes a person never manages to fully recover. For rehabilitation to be as successful as possible, you must strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions.
Stroke is a serious pathology because it affects the brain. Therefore, even the slightest suspicion of a developing vascular accident is a reason to urgently seek medical help.
Rehabilitation after stroke in the early recovery period
The early recovery stage is crucial for the patient and should ideally take place in a sanatorium or rehabilitation center. When deciding to leave the victim at home, you should remember that successful recovery after a stroke is impossible without the active participation of specialized specialists who will have to be invited to the home.
The first three months after the onset of the disease are especially productive and favorable for rehabilitation. At this stage, they move from the simplest exercises to more complex ones - they teach a person to roll over, rise, sit down, and stand up independently. Next, elements of active physical therapy are gradually introduced, physiotherapy, massage, speech work are continued, and complexes are performed to restore vision and eye movements, cognitive functions (memory, thinking, attention).
A common consequence of a stroke is complete or partial loss of vision, dysfunction of the eyelid, presbyopia, when a person cannot distinguish small print or small objects at close range. All these disorders require qualified assistance from an ophthalmologist, who will prescribe either medication or surgical treatment. In mild cases, they can do with therapeutic exercises for the eyes.
To restore attention, memory, and intellectual abilities, there are many exercises: memorization tasks, memorizing poetry, solving riddles, rebuses, putting together puzzles, chess, checkers. However, for complete rehabilitation of cognitive functions, psychological and correctional classes are necessary individually or in groups. Additional stimulation is provided by medications that should be prescribed by a doctor.
Diagnostic methods
It is important to quickly distinguish a stroke from other diseases that can lead to the development of similar symptoms. It is almost impossible to do this on your own, as well as to determine the type of vascular accident.
The main difference between an ischemic stroke is a gradual increase in symptoms that do not lead to loss of consciousness. With hemorrhagic hemorrhage, the patient passes out quickly. However, stroke does not always have a classic course. The disease may begin and progress atypically.
Diagnosis begins with examination of the patient. The doctor collects anamnesis and determines the presence of chronic diseases. Most often, you can get information not from the victim himself, but from his relatives. The doctor performs an ECG, determines the heart rate, takes a blood test, and measures blood pressure.
It is possible to make the correct diagnosis and obtain maximum information about the patient’s condition thanks to instrumental diagnostic methods. The best option is a CT scan of the brain. Performing an MRI is difficult because the procedure takes a long time. It takes about an hour. It is impossible to spend this amount of time diagnosing an acute stroke.
Computed tomography allows you to clarify the type of pathology, where it is concentrated, to understand how badly the brain is damaged, whether the ventricles are affected, etc. The main problem is that it is not always possible to perform a CT scan in the shortest possible time. In this case, doctors have to focus on the symptoms of the disease.
To determine the source of the stroke, the method of diffusion-weighted tomography (DWI) is used. The information will be received within a few minutes.
Other examination methods include:
- Lumbar puncture.
- Cerebral angiography.
- Magnetic resonance angiography. It is performed without the introduction of a contrast agent.
- Doppler ultrasound.
Once the diagnosis is made, the doctor will immediately begin treatment.
Who is at risk
There are people who need to be especially wary of developing a stroke, as they are at risk.
Among them:
- Persons with hypertension.
- Patients with diabetes.
- Men and women over 65 years of age.
- People with abdominal obesity.
- Persons with a hereditary predisposition to vascular pathologies.
- Patients who have previously had a stroke or heart attack.
- Patients with diagnosed atherosclerosis.
- Women over 35 years of age taking oral contraceptives.
- Smokers.
- People suffering from heart rhythm disturbances.
- People with high cholesterol levels.
Most often, patients with the listed diagnoses are registered at the dispensary. Special mention should be made of people living in a state of chronic stress. Emotional stress negatively affects all systems of the body and can cause a stroke.
Classification
Ischemic stroke can be a consequence of one or another disease of the cardiovascular system. There are several pathogenetic variants of ischemic stroke. The TOAST (Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment) classification, which is most widely used, distinguishes the following types of ischemic stroke:
- cardioembolic - ischemic stroke caused by arrhythmia, valvular heart disease, myocardial infarction;
- atherothrombotic - ischemic stroke that occurred due to atherosclerosis of the large arteries, which resulted in arterio-arterial embolism;
- lacunar - ischemic stroke caused by occlusion of small arteries;
- ischemic stroke associated with other, more rare causes: blood hypercoagulation, arterial wall dissection, non-atherosclerotic vasculopathies;
- ischemic stroke of unknown origin - a stroke with an unknown cause or with the presence of two or more possible causes, when it is not possible to establish an accurate diagnosis.
In addition, a minor stroke is distinguished when the existing symptoms regress during the first three weeks of the disease.
There are also several periods of ischemic stroke:
- The most acute period is the first 3 days. Of these, the first three hours were defined as a “therapeutic window”, when it is possible to use thrombolytic drugs for systemic administration. In case of regression of symptoms during the first day, a transient ischemic attack is diagnosed;
- acute period - up to 4 weeks;
- early recovery period - up to six months;
- late recovery period - up to 2 years;
- period of residual effects - after 2 years.
How to provide first aid for a stroke
There is a clear algorithm for providing first aid to a person suffering from a stroke :
- Call a medical team . To do this, you need to dial 103 from a landline phone. If you happen to have a smartphone at hand, then the call is made to the single number 112. The doctor must immediately be informed that the person is unwell and there is a suspicion of a stroke.
- The victim must be laid on a flat surface so that his head is higher than his body. They take off his glasses and remove his lenses. If possible, you need to help him get removable dentures.
- If there is no consciousness, then you need to open the patient’s mouth slightly and turn his head to the side . This is done to prevent aspiration of vomit. It is imperative to listen to the patient’s breathing.
- For better access to fresh air, it is recommended to open a window or vent..
- Before the arrival of the medical team, it is necessary to prepare documents, if any..
Doctors need to be informed about the person’s illnesses, as well as what medications he is taking. It is prohibited to give the victim any medications. Medication correction should be carried out by emergency physicians. You should not try to give water or food to a person. This may make the situation worse.
If the patient falls and has an epileptic attack, there is no need to unclench his teeth or try to hold him. It is necessary to protect the victim from injury. To do this, place a soft object, such as a pillow, under his head. If a stroke with an epileptic attack happened on the street, then you can use a jacket or other suitable thing. Foam flowing from the mouth is wiped away with a cloth. The head should be elevated at all times.
There is no need to try to bring a person to his senses with ammonia. Until the end of the attack, it should not be moved from place to place.
If breathing stops, resuscitation measures must be started immediately. To do this, perform a heart massage and breathe mouth to mouth or mouth to nose.
Treatment and rehabilitation
The patient receives treatment in a hospital. All patients with suspected stroke are hospitalized on an emergency basis. The optimal period for providing medical care is the first 3 hours after a brain accident has occurred. The person is placed in the intensive care unit of a neurological hospital. After the acute period has been overcome, he is transferred to the early rehabilitation unit.
Until the diagnosis is established, basic therapy is carried out. The patient’s blood pressure is adjusted, the heart rate is normalized, and the required blood pH level is maintained. To reduce cerebral edema, diuretics and corticosteroids are prescribed. Craniotomy is possible to reduce the degree of compression. If necessary, the patient is connected to an artificial respiration apparatus.
Be sure to direct efforts to eliminate the symptoms of stroke and alleviate the patient’s condition. He is prescribed medications to lower body temperature, anticonvulsants, and antiemetics. Medicines that have a neuroprotective effect are used.
Pathogenetic therapy is based on the type of stroke. In case of ischemic brain damage, it is necessary to restore nutrition to the affected area as quickly as possible. To do this, the patient is prescribed drugs that resolve blood clots. It is possible to remove them mechanically. When thrombolysis fails, the patient is prescribed Acetylsalicylic acid and vasoactive drugs.
If a patient develops a hemorrhagic stroke, it is important to stop the bleeding. To do this, the patient is prescribed drugs that thicken the blood, for example, Vikasol. It is possible to perform an operation to remove the resulting hematoma. It is aspirated using special equipment, or through open access by performing craniotomy.
Relatives and friends should provide support to the patient and not leave him alone with the problem. Psychologists are involved in the work. Sessions with a speech therapist are often required.
Pathogenesis
A certain sequence of molecular biochemical changes in the brain substance, caused by acute focal cerebral ischemia, can lead to tissue damage, resulting in cell death (cerebral infarction). The nature of the changes depends on the level of decrease in cerebral blood flow, the duration of this decrease and the sensitivity of the brain substance to ischemia. The degree of reversibility of tissue changes at each stage of the pathological process is determined by the level of decrease in cerebral blood flow and its duration in combination with factors that determine the sensitivity of the brain to hypoxic damage.
The term “infarction core” refers to a zone of irreversible damage, and the term “ischemic penumbra” (penumbra) refers to a zone of reversible ischemic damage. The duration of the penumbra's existence is the most important point, since over time, reversible changes become irreversible. The oligemic zone is a zone in which a balance is maintained between tissue needs and the processes that provide these needs, despite the decrease in cerebral blood flow. It is capable of existing for an indefinitely long time without passing into the core of the infarction, therefore it is not classified as a penumbra.