A weak nervous system is an indicator of the innate etiology of the strength of nervous processes, which is used to indicate the performance and stability of nervous structures. It reflects the ability of neurons to tolerate, without entering a state of inhibition, either quite intense or long-lasting, albeit weaker, excitation. People with a strong system are able to withstand and endure even intense stimuli, while those with a weak system, on the contrary, react poorly and withstand stimuli. The latter are characterized by indifference and impatience.
Signs
A comprehensive understanding of one’s own person and the environment provides a definition of the stability of the nervous system.
It is believed that people with weak systems are more susceptible to stressors. Moreover, in accordance with the modern position of specialists, the number of such persons is constantly increasing with each subsequent generation.
A certain “reserve” of strength, which the nervous system is rich in, is laid down at birth. The described indicator characterizes the performance and stability of all nervous structures of the body.
Those with a weak nervous system are unable to endure the effects of intense stimuli. They have difficulty retaining information that comes to them. That is why people with “weak nerves” are ready to share it with those around them.
The considered characteristic of the totality of nervous structures is responsible for the laziness of people. Moreover, such people, even existing in poverty, will not make any efforts to change the situation and improve their situation.
A person with a weak nervous system, in addition to the above symptoms, is also characterized by indecision. He is constantly tormented by doubts. Sensitive individuals doubt themselves and those around them, even people who want to help. They constantly make excuses in order to disguise their own mistakes. Often this is expressed in envy, especially towards people more successful than them.
A sign of a weak nervous system in a person is causeless anxiety, often leading to a nervous outburst.
At the same time, in representatives of a weak type of nervous system, conditioned reflexes are developed more quickly than in other types, which allows them to assimilate material more easily and grasp information faster. This is due to the significant dynamism of the excitation process. Persons with “weak nerves” learn better when logically formulated and united by a common idea.
TYPES OF NERVOUS SYSTEM
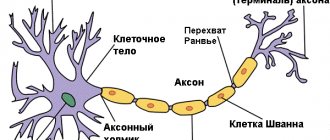
TYPES OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM (types of higher nervous activity), complex basic. congenital and acquired individual properties of the nervous system of animals and humans, determining differences in behavior and attitude to the same environmental influences. The concept of T.n. With. introduced by I. P. Pavlov (1927). He identified three main ones. properties of nervous processes (excitation and inhibition): strength, balance of the processes of excitation and inhibition and their mobility (speed of transition from one state to another). There are 4 main types. The strong unbalanced type is characterized by the rapid development of positive (excitatory) conditioned reflexes (CR), while inhibitory RC are formed with great difficulty; In animals of this type, vegetative functions after their disruption are restored for a long time and unevenly. A strong, balanced inert type is characterized by the slow formation of positive and inhibitory UR, which means that after consolidation into a certain stereotype, the UR is retained. sustainability; reactions of adaptation and restoration of vegetative processes proceed slowly. In a strong, balanced, mobile type, positive and inhibitory URs are quickly formed and easily transformed when the stimulus changes; Animals of this type are characterized by easy adaptability of vegetative functions to changes in the environment, their rapid and complete restoration after eliminating the factors that caused the disturbance. The weak type is characterized by weak excitatory and inhibitory processes, URs are produced with great difficulty, and those formed are easily inhibited; vegetative processes are sluggish, easily disrupted, difficult and incompletely restored. People, as a rule, have various combinations of properties of various so-called. With. Neuroses and psychosomatic diseases more often occur in representatives with a predominance of a strongly unbalanced or weak type of nervous system.
In humans, in addition to common T. n. s., I.P. Pavlov highlighted special. types characterizing the interaction of the first and second signaling systems and the relationship between them: the mental type, with a predominance of the second signaling system over the first (a special development of the ability for abstract, abstract thinking is observed); artistic type, with a predominance of the first signaling system (a pronounced tendency towards figurative and emotional thinking; among people of this type there are many artists, writers, musicians, actors); medium type, when both signaling systems are represented in equal proportions. Most people are of the average type. They are characterized by a harmonious combination of figurative-emotional and verbal-logical. thinking. With the introduction of new research methods, the structure of technical sciences is being clarified. With.; new properties of the nervous system are described, e.g. lability and dynamism, characterizing the speed of nervous processes. Significant differences have been established. properties of the nervous system in different sensory organs (the phenomenon of partiality).
In children
Most children in everyday life, activities, and studies are active, lively, cheerful, resilient, and energetic. But there are other children who are characterized by passivity, isolation, and inability to withstand prolonged or intense stress. As a rule, they are distinguished by sensitivity and pronounced impressionability. The listed features in the behavioral pattern of children, first of all, are explained precisely by the type of nervous system.
A weak type of nervous system is characterized by high excitability and increased sensitivity in comparison with a strong type of nervous activity.
A weak nervous system in children is characterized by the following symptoms:
– excessive impressionability;
– mood swings, gloomy-depressed state after failures;
– inability to engage in several types of activities simultaneously;
– decreased ability to work;
– lack of confidence;
– rapid fatigue during prolonged activity;
– low concentration.
Often, such students have difficulty absorbing information in a classroom lesson, filling in the gaps with scrupulous, conscientious homework.
Those with the described type of nervous structures quickly get fed up, tend to get carried away easily, and also quickly cool down to their newfound hobby. They cannot stand criticism; during tests, exams, or a final assessment of the quality of the material learned, their answers do not correspond to their knowledge (they know more than they answer). They may suddenly cry or scream.
Children with the type of nervous system under consideration cannot tolerate public forms of disapproval, censure, and condemnation; they sadly experience bad grades.
The process of watching movies or reading books for such little ones is quite emotional. The content captivates the kids so much that you can often see tears in their eyes. Even after time has passed after reading a novel or watching a film, memories of the plot that attracted them cause inexplicable feelings in the soul of the offspring.
Increased anxiety and nervousness in them can also be triggered by finding themselves in unfamiliar conditions or in an unusual environment, if they have to decide something on their own or take some action. Even if it is necessary to do some small thing, the tension will be visible on their face.
However, the characteristics of a weak nervous system are not limited to negative manifestations alone.
Children with the described type of nervous structures are calm, diligent, careful, quiet, obedient. They function thoughtfully and effectively in familiar tasks, obtaining satisfaction. Such kids have the ability for comprehensive, in-depth analysis and careful comprehension of educational material. They also easily absorb systematic information.
Types of nervous system
Types of nervous system
Both everyday experience and scientific data show that individual individuals that form any species of living beings, along with the general characteristics characteristic of all individuals of this species, have a number of traits characteristic of these particular individuals. This conclusion fully applies to the functions of the cerebral hemispheres, and it is the various individual characteristics of the activity of the cerebral hemispheres that most of all determine the individual characteristics of all functions of the body. Currently, the physiology of the cerebral hemispheres has precise techniques that have made it possible to establish the basic functional characteristics of the properties of the cerebral cortex and to create on this basis a doctrine of the main types of the nervous system. Functional features of the cerebral cortex
Strength of nervous processes
The functional properties of the cerebral cortex are characterized, firstly, by a feature called the strength of nervous processes.
The concept of force follows from the concept of performance and refers to both excitation and inhibitory processes. As is already known, a strong stimulus gives a strong effect only if the intensity of the stimulus does not go beyond a certain limit. When this limit is exceeded, the excitation process is replaced by an inhibitory process, as a result of which the magnitude of the reflex response to such a super-strong stimulus falls (excessive inhibition). Thus, it is possible to measure the limit of performance of cortical nerve cells in relation to their development of the excitation process. Experience shows that there are strong types of the nervous system, characterized by a high limit of working capacity, and weak types, with a low limit of working capacity of the nervous system. Balance of nervous processes
In addition, the activity of the cerebral hemispheres is characterized by a sign of balance.
This term is understood as the ratio, the balance between the strength of the irritative and the strength of the inhibitory processes. Both of these processes can be developed equally, and then we speak of a balanced nervous system. But sometimes one process is more pronounced than the other, and then they speak of an unbalanced type. Mobility of nervous processes
The third important feature characterizing the work of the cerebral hemispheres is the mobility of cortical processes. Since both in ordinary life situations and in experimental conditions there are often cases when a rapid change from one process occurring in some functional cortical focus to another process is required (for example, a change from an irritable process to an inhibitory one or vice versa), it is very important so that the main cortical processes are sufficiently mobile, when one nervous process is easily and quickly replaced by another, its opposite. On this basis, the types of the nervous system can be divided into mobile and sedentary, stagnant, in which this change occurs slowly and with difficulty.
Classification of nervous system types depending on the quality of reactions
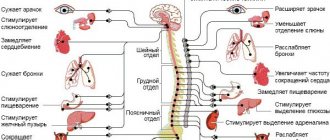
As a result of studying a huge number of individual facts based on the use of special techniques, it was possible to establish the presence of the following four main types of the nervous system. I. Sanguine type, or living type. This is, so to speak, the ideal type that stands at the center of the classification. It is distinguished by the good development of all the main functional characteristics of cortical cells: a strong excitation process and a strong inhibitory process, approximately the same strength of both processes, that is, balance, as well as good mobility, that is, the speed and ease of changing one nervous process to another. II. Melancholic type, or weak type. The most characteristic feature of people of this type is the low efficiency of the cortical elements, which causes them to often have extreme inhibition (unconditioned). In this type, both the excitation process and the inhibitory process are weak, but inhibition processes still predominate in the cortical dynamics. People belonging to this type display traits of timidity and cowardice in their behavior; there are many variations of this type. III. Choleric type, or unrestrained type. People of this type have great strength in both nervous processes, but in them the excitation process sharply prevails over the relatively weaker inhibitory one. Hence the characteristic feature of this type is imbalance. There are also various variations of this type. IV. Phlegmatic type, or calm type. A characteristic feature of this type is low mobility, that is, stagnation of cortical processes. Possessing sometimes great strength and balance of the nervous system, people of this type with difficulty and slowly replace one process with another. It must be borne in mind that the above classification is, like any classification, only a convenient scheme. In fact, in addition to the above types, there are many individuals belonging to various intermediate types. Attributing a given person to one type or another is further complicated by the following circumstance. The fact is that the characteristics of each person’s nervous system are the result of a complex interaction of traits, both inherited and acquired as a result of various interactions with the environment that occur during individual development. Experience shows that inherited traits can undergo significant changes due to the fact that the cerebral hemispheres have great plasticity. The reason for this discrepancy lies in the conditions of education received in the early period of life. A powerful influence on the characteristic features of the nervous system is also found in long-term environmental conditions. Through careful training based on knowledge of the laws of cortical activity, a weak type of human nervous system can be significantly improved, making it stronger. Thus, inherited traits are not something fatal and inevitable - they can be changed. The concept of the type of nervous system is not limited to those physiological properties that directly characterize the functions of the cerebral cortex. Typical features are reflected in other body systems. Thus, from a physiological point of view, a type is a certain variation of the entire organism as a whole. It has been established that in representatives of different types of the nervous system, changes and disturbances in the activity of internal organs, the emergence of pathological processes occur with unequal ease and differ in well-known features.
In adults
The variation in nervous activity under consideration is characterized by the inability to tolerate super-intense stimuli: it can either switch off immediately (inhibition dominates the process of excitation), or it is “carried away” without brakes, which is accompanied by unexpected consequences (inhibition does not have time to cope with excitation).
Signs of a weak nervous system in adults are represented by the following manifestations.
People with the described variation in nervous activity are characterized by rapid fatigue. They need extra breaks to rest. Against the background of interference and in the presence of distractions, they experience a sharp decline in productivity.
They are also characterized by an inability to distribute attention between several simultaneous actions. They have difficulty coping with stressors. In conditions of intense functioning, their effectiveness declines, anxiety and uncertainty appear.
A weak nervous system is characterized by significant resistance to monotonous work, therefore representatives of the described type of functioning of the nervous structure tend to achieve better results in their usual daily activities. They work effectively according to instructions. They have the ability to systematize and plan work, and scrupulously control the activities performed.
The variant of the nervous structure under consideration is characterized by the presence of the potential to show reactions to signals of insignificant strength and to recognize similar stimuli. As a rule, it is sensitivity that determines the ability to notice nuances of shades, subtleties of sounds, notes of smells, as well as features of statements and halftones of interpersonal relationships.
In addition to the above, owners of a weak nervous system are characterized by stable indifference, which is expressed in the perception of any “blows” of fate without complaints, statements, or protests.
This type also affects the laziness of their owners. Moreover, it is found not only on the psychological level, but also has physical manifestations. Examples of this are subjects who exist outside of poverty, but at the same time, without making a single effort to change anything in order to improve their own existence and status in society.
A weak nervous system is also characterized by pronounced caution. In order to realize what they have planned or to carry out their plans, such individuals always wait for the right time, which often develops into a habit. This leads to the transformation of excessive caution and the desire to always play it safe into pessimism. Constantly thinking about the possibility of failure, which can lead to the collapse of life plans, gives rise to nervousness, indigestion, slow blood circulation and many other psychosomatic ailments.