Lesions in the white matter of the brain are areas of damage to brain tissue, accompanied by a violation of the mental and neurological functions of higher nervous activity. Focal areas are caused by infection, atrophy, loss of blood supply and trauma. Most often, affected areas are caused by inflammatory diseases. However, areas of change may also be of a dystrophic nature. This is observed mainly as a person ages.
Focal changes in the white matter of the brain can be local, single-focal, or diffuse, that is, the entire white matter is moderately affected. The clinical picture is determined by the localization of organic changes and their degree. A single lesion in the white matter may not affect the dysfunction, but massive damage to neurons causes a disruption in the functioning of nerve centers.
Classification of the disease
In modern medicine, it is customary to distinguish the following types of insufficient blood supply to the brain:
- Binswanger's disease. This type of vascular circulation disorder leads to insufficient blood supply to the white matter of the brain. With this disease, the destruction of neurons occurs, which will soon lead to senile dementia - dementia. The first alarming symptom is severe pressure drops within one day. Then memory begins to deteriorate greatly.
- Pathological processes in the great vessels. Such disorders include narrowing of the lumens, strong bends, and thrombosis of blood vessels, which lead to a lack of circulating blood.
- Consequences of micro-strokes. When small vessels are blocked, there is a clear deterioration in the nutrition of the gray or white matter of the brain. This process cannot happen for a person without consequences. The patient may experience both general signs of the disease and disruptions only in certain body functions.
Symptoms
The set of symptoms depends on the location of the lesions and the depth of damage to the brain tissue. Symptoms:
- Pain syndrome. Characterized by chronic headaches. Unpleasant sensations intensify as the pathological process deepens.
- Rapid fatigue and exhaustion of mental processes. Concentration deteriorates, the volume of operative and long-term memory decreases. It is difficult to master new material.
- Flattening of emotions. Feelings lose their sharpness. Patients are indifferent to the world and lose interest in it. Previous sources of pleasure no longer bring joy and desire to engage in them.
- Sleep disturbance.
- In the frontal lobes, foci of gliosis disrupt the control of the patient’s own behavior. With deep violations, the concept of social norms may be lost. Behavior becomes provocative, unusual and strange.
- Epileptic manifestations. More often these are small convulsive seizures. Individual muscle groups contract involuntarily without threat to life.
White matter gliosis can manifest itself in children as a congenital pathology. The lesions cause dysfunction of the central nervous system: reflex activity is disrupted, vision and hearing deteriorate. Children develop slowly: they get on their feet late and begin to speak.
Pseudoneurosthenic syndrome
Another characteristic sign of changes in blood circulation in the brain are mental disorders of vascular origin. Their symptoms coincide with the classical picture, but changes occur as a result of circulatory disorders.
Accordingly, treating only the mental component will not lead to the desired result: in this case, the disorder is a secondary disease.
- Very often, sleep disturbances occur against the background of a headache and a feeling of heaviness in the back of the head. As a rule, sleep is shallow, short - 3-4 hours, accompanied by natural weakness and a state of “being overwhelmed”. If the cause is poor venous blood flow, then physical activity brings your health back to normal much faster.
- Sensitivity to stimuli - sound, light, sometimes even dim light.
- Tearfulness, irritability, unstable attention. Moreover, the patient is clearly aware of the painfulness of the condition.
- It is difficult to remember new events and record them; chronological orientation is often disrupted: it is difficult to remember the date, day, or date the event.
- The search for small objects - glasses, keys, notepads - is associated with a refusal to perceive certain objects in the field of vision.
- With the further development of diseases of vascular origin, personality changes are possible - a kind of sharpening of the most striking character traits. At the same time, asthenic structures intensify – self-doubt, anxiety, suspiciousness. Gloomy dissatisfaction with others becomes almost constant. Personality changes are noticeably influenced by the nature of the vascular process: arterial hypertension, the location of focal lesions in the brain, and so on.
Unlike true mental disorders, treatment of vascular diseases is carried out mainly by medicinal methods and is quite successful.
Causes
Damaged areas in the white matter are caused by the following diseases and conditions:
- Group of vascular diseases: atherosclerosis, amyloid angiopathy, diabetic microangiopathy, hyperhomocysteinemia.
- Inflammatory diseases: meningitis, encephalitis, multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's disease.
- Infections: Lyme disease, AIDS and HIV, multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
- Poisoning by substances and heavy metals: carbon monoxide, lead, mercury.
- Vitamin deficiency, especially B vitamins.
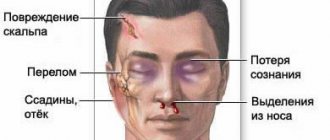
- Traumatic brain injuries: bruise, concussion.
- Acute and chronic radiation sickness.
- Congenital pathologies of the central nervous system.
- Acute cerebrovascular accident: ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, cerebral infarction.
Diseases of vascular origin
Here it should be clarified: vascular genesis is an indication of the origin of the disease, and not the disease itself. When talking about brain diseases of vascular origin, we mean changes associated with circulatory disorders - in venules, arteries, veins, and so on.
These types of violations are divided into several main groups.
- Transient cerebral circulatory disorders are distinguished between general cerebral and focal. The first are characterized by headache, nausea, vomiting; focal ones are responsible for short-term disturbances in motor functions and sensitivity of certain parts of the body. A distinctive feature of this vascular disorder is reversibility . Treatment promises complete restoration of function.
- Blockage of the arteries - narrowing of the working channel in any case leads to deterioration of nutrition, which significantly affects the functionality of the served areas of the brain, and can cause changes of an ischemic nature. Here treatment may even include surgery.
- Rupture of a cerebral aneurysm, cerebral hemorrhage – in fact, a stroke of ischemic or hemorrhagic origin.
What does genesis include?
Focal or organic lesions of the brain substance of vascular origin occur in the following cases:
- Transistor failure in the blood circulation of the brain (TIA) - in this case, focal damage to the brain occurs or the entire brain suffers. In the latter case, the patient is bothered by constant headaches with nausea and vomiting, but with focal damage, the patient loses motor functions for some time, and the sensitivity of certain parts of the body and organs decreases. This disorder is reversible and highly treatable.
- Blockage of the arteries (cerebral atherosclerosis) - in the case of narrowing of the blood vessels, this leads to a deterioration in the nutrition of the brain and this does not have the best effect on the patient’s overall condition. In this case, the disease can lead to ischemic changes in the brain - treatment even involves surgery or surgical intervention.
- A cerebral aneurysm , if it ruptures and there is bleeding in the brain, a hemorrhagic form of genesis develops.
- Ischemic stroke , as an independent phenomenon, is an organic brain disease of vascular origin.
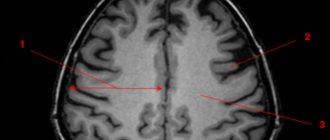
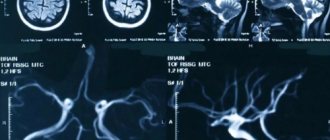
Vascular changes in the brain on MRI
MRI: ischemic zone during stroke (highlighted with a red oval)
If cerebrovascular pathology is suspected, special attention is paid to the condition of the arteries during MRI of the brain. The study always involves the introduction of contrast, and it is called magnetic resonance angiography. In urgent situations in case of vascular accidents, CT is performed, since X-ray diagnostics takes less time and clearly demonstrates the area of damage during hemorrhages, but after stabilization of health, magnetic resonance angiography is quite justified. The study shows atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots and aneurysms (protrusions), their localization, and wall deformation.
With an ischemic stroke, darkened and blurred areas of irregular shape are visible almost immediately on magnetic tomograms, appearing on a computer scan only at the end of the first day. The lesion is often unilateral. The outpouring of blood from a ruptured vessel gives an intense light color, but only in the first hour and a half from the moment of the disaster, and then becomes invisible on MRI, although it is clearly visualized using CT. As a consequence of a stroke, a fluid-filled pseudocyst is formed, and deformation of the nerve tissue appears. MRA is indispensable in the diagnosis of tumor angiogenesis. Increased vascularization of a pathological focus is always suspicious of a malignant neoplasm, which grows and feeds due to increased blood flow. If the vessels do not keep up with the growth of the tumor, areas of ischemia and necrosis appear.
Types of lesions
There are several types of focal GM diseases. The most dangerous are neoplasms. In the early stages, brain tumor symptoms can be confused with migraines and other illnesses. But with growth, the functioning of neurons deteriorates and signal transmission to the brain is disrupted. If the tumor grows, it begins to invade more and more new territories, and the clinical picture begins to increase.
Another type of focal disease is a cyst (a small cavity with liquid contents). For a long time, cavities do not make themselves felt until they begin to grow and increase in size. Despite the fact that they are not prone to growth and increase in size, like neoplasms, they are also considered a foreign body. Cysts can cause compression of blood vessels, which complicates the flow of blood to the brain.
Foci of damage are observed with necrosis. As a result of any previous infections or other diseases, areas of brain cells die without receiving the nutrition they need. Necrosis is dangerous because it entails irreversible changes.
Dangerous focal lesions of the white matter of the brain are intracerebral scars and hemorrhages. Most often they are the result of injuries, falls, blows. These types of foci lead to changes in the composition of the substance.
- Why is a study of the blood vessels of the brain and neck performed?
Any focal brain lesions of vascular origin lead to the destruction of brain cells and can lead to coma.
At-risk groups
Risk groups include people exposed to the following factors:
- Arterial hypertension. They are at increased risk of developing vascular lesions in the white matter.
- Poor nutrition. People who overeat, excessively consume extra carbohydrates. Their metabolism is disrupted, as a result of which fatty plaques are deposited on the inner walls of blood vessels.
- Foci of demyelination in the white matter appear in older people.
- Smoking and alcohol.
- Diabetes.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Genetic predisposition to vascular diseases and tumors.
- Constant hard physical labor.
- Lack of intellectual work.
- Living in conditions of air pollution.