Varieties
Sensitivity disorders are divided into two groups - increased or decreased.
Reduced ones include analgesia, hypoesthesia, and termanesthesia. With analgesia, a person does not feel pain; it can occur in many diseases and injuries of the nervous system. Hypoesthesia is manifested by a decrease in tactile sensitivity; the patient does not respond to skin punctures or insects crawling on the body. Thermaneesthesia is characterized by a violation of the perception of temperature conditions (warm and cold influences).
Increased sensitivity distinguishes terms such as hyperalgesia, hyperesthesia and hyperpathia. Hyperalgesia is a pathologically increased perception of pain; sharp or increased perception of stimuli is called hyperpathy. In this condition, the unpleasant sensations continue for quite a long time, the patient cannot determine the exact location and the sensations of irritation continue longer than contact with the irritant occurs. Hyperesthesia is an increased perception of stimuli, but at the same time the patient is able to sense the correct location of the stimulus and what type of impact.
Disorders in which the patient perceives a single effect as multiple are called polyesthesia. Allocheiria is a condition in which the patient feels irritation not at the site of its impact, but in the same areas on the opposite side of the body. With dysesthesia, there is a perverted perception of stimuli, that is, their confusion. When exposed to pain, the patient may feel warmth; when exposed to low temperatures, a tingling sensation. Paresthesia is a spontaneously occurring and short-term sensation of numbness, burning and a feeling of “crawling sensations”.
Pain along the nerves
Many diseases of the nervous system are accompanied by pain along the nerves. Neuralgia is often confused with musculotendinous pain in fibromyalgia. We have modern diagnostic equipment to determine the cause of pain along the nerves and experienced specialists to treat not only the pain, but also the symptoms. In particular, we perform electroneuromyography and ultrasound of the nerves.
Pain along the nerves (neuralgia) is most often caused by:
- pinched nerves,
- mono- and polyneuropathy,
- inflammation of the nerve trunks - polyneuritis.
The pain first appears at typical points where the nerves pass through narrow channels in the area of large joints near the tendons. Pain can only be felt when pressing on the points or appear spontaneously. In more severe cases, pain may occur along the nerves along the arms and legs.
Regardless of the cause of the pain along the nerve, we will find the cause, relieve you of the pain and prevent its further occurrence.
Typical places where pain appears along the nerves:
Occipital nerve; Trigeminal nerve
Brachial plexus and arm nerves; Intercostal nerves; Lumbosacral nerve plexus and leg nerves;
The source of pain along the nerve is usually easy to determine based on electroneuromyography and examination by a neurologist.
Types of hypersensitivity
If sensitivity is increased on one or more teeth, it is called limited. If for everyone - generalized.
Table 1. Types of hyperesthesia
| № | View | Reaction |
| 1. | Light | for cold, hot |
| 2. | Average | as with 1st degree plus for sour, sweet, salty |
| 3. | Expressed | as in grade 2 plus mechanical irritants (when brushing teeth, eating) |
Basic points of proper hygiene
Use a synthetic, medium-hard or soft brush. Change it every three months.
The toothpaste should be suitable for very sensitive teeth. Typically, such products contain hydroxyapatite, strontium chloride, fluorides, potassium nitrate, or a combination of calcium carbonate and arginine.
Take enough paste. For children under 3 years old - the size of a grain of rice, from 3 to 14 years old - the size of a pea, for adults you need to squeeze out about one centimeter.
Brush your teeth for 2 minutes: 30 seconds on each surface, top and bottom. Monitor time using an hourglass or mobile phone timer. Electric toothbrushes emit a short beep every 30 seconds and a long beep every 2 minutes from the start of brushing.
How and why do signs of anxiety appear?
Anxiety is a normal state that triggers a self-preservation mechanism. Clinicians highlight not only psychological disturbances during stress, but also real physical sensations. Psychological symptoms of increased anxiety:
- frequent worries, premonitions, insecurity;
- sleep disturbance, decreased activity;
- unreasonable fear for loved ones, feelings of fear, mental heaviness;
- fear of a new environment;
- difficulty communicating with others;
- decreased performance, impaired concentration of thoughts - the entire field of thoughts is occupied by anxiety (patients constantly experience stress, are afraid to do unnecessary actions);
- inadequate self-criticism, tearfulness.
Other changes occur before arousal occurs. Physically, the disease is manifested by sweating, redness of the face and neck, increased breathing, pulse, heartbeat, a lump in the throat, bloating and loose stools. Outwardly, the person looks tense, nervous, clenches his fists, fiddles with buttons, clothes, his own fingers, and bites his nails.
What diseases can be hidden behind?
Diagnosis of the condition in children and adults is the field of activity of psychoneurologists, clinical psychologists, and psychiatrists. The final diagnosis is made on the basis of a physical examination, interview, tests, assessment of the anxiety scale, study of life and clinical history.
An increase in the level of stress and anxiety should be differentiated from depressive states, maladjustment reactions, the initial stages of schizophrenia, as well as from other psychiatric diseases caused by the development of phobias, obsessive thoughts and conditions.
Tooth sensitivity: causes
- Demineralization of enamel. It becomes more loose due to the leaching of calcium, phosphorus, and other trace elements.
- Thinning of enamel. As a result of increased abrasion due to malocclusion and the occurrence of wedge-shaped defects.
- Untreated caries or violation of the marginal seal of the filling.
- Exposure of roots as a result of injury, metabolic-dystrophic process or inflammation of the gums.
- Changes in the pH of saliva due to the consumption of certain drinks, foods, and medications. A pH of less than 5.5 is considered dangerous.
- Some diseases accompanied by gastroesophageal reflux and endocrine disorders.
- Vitamin deficiency, exposure to radiation, work in hazardous industries, living in a region with an unfavorable environmental situation.
- Smoking.
More often than not, several reasons are discovered at once. The enamel becomes thinner, loses strength, and cannot protect dentin from irritants. The result is pain.
Elimination of tooth sensitivity
Using ultrasound, the doctor removes soft and hard deposits from the teeth. After removing plaque, teeth become more sensitive for a short time, so remineralization or deep fluoridation is immediately carried out. During remineralization, the enamel is treated with active compounds of calcium and phosphates. Deep fluoridation – coating with sodium fluoride. Both procedures significantly strengthen the enamel's resistance to irritants.
The doctor uses agents that reduce the movement of fluid in the dentinal tubules. It “seals” them using desensitizers or reduces their volume through remineralization. Protecting exposed dentin reduces the force of transmission of the irritant impulse from the enamel to the nerve.
Cleaning sequence
- Using sweeping movements, clean the outer and then the inner surfaces of the bottom row. Move from molars to incisors. Then do the same on the top row. Hold the brush at a 45-degree angle and do not use a sawing motion. This leads to damage to the enamel.
- Brush chewing surfaces with small circular movements.
- Close your jaws and walk along your gums in a circular motion.
- Brush your tongue using a leisurely four to five strokes from root to tip.
- Treat the interdental spaces with dental floss.
- Rinse your mouth.
It is more effective to clean with an electric brush or irrigator. The quality of hygiene increases 3–4 times. Hyperesthesia can be dealt with faster.
Is it possible to strengthen sensitive teeth at home?
Yes. If you can’t get to the dentist, you can try to help yourself. There are several remedies that can solve the problem of hyperesthesia at home.
Table 3. Popular products for home use
| № | Name | Mechanism of action | Age category |
| 1. | ROCS Medical Minerals, GC Tooth Mousse | Remineralizing gels | Adults and children |
| 2. | Colgate Duraphat 2800 ppm | Fluoridating paste | 10–15 years |
| 3. | Colgate Duraphat 5000 ppm | From 16 years old | |
| 4. | ELMEX junior | Fluoridating paste | 6–12 years |
| 5. | ELMEX | From 13 years old | |
| 6. | LACALUT Extra Sensitive | Paste that reduces tooth sensitivity | For adults |
| 7. | Colgate Sensitive Pro-Relief | ||
| 8. | PRESIDENT Sensitive | ||
| 9. | LACALUT Sensitive, 300 ml | Rinse for sensitive enamel | From 15 years old |
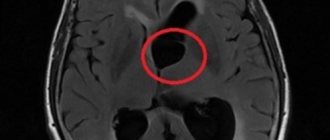
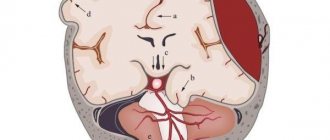
Dizziness
These symptoms occur when organs that provide balance suffer (inner ear, cochleovestibular nerve, brain stem, cerebellum) and are often accompanied by nausea and vomiting. The appearance of dizziness and unsteadiness indicates the inability of the nervous system to correctly navigate in space and maintain the body’s center of gravity within the area of support. Hence the risk of falling.
Damage to the inner ear and cochleovestibular (auditory and vestibular) nerve or vestibular ataxia is accompanied by severe dizziness with a feeling of spinning, nausea and vomiting. This kind of dizziness is called systemic. Typically, dizziness increases after changing body position (standing or lying down), turning or tilting the head. The inner ear and cochleovestibular nerve often suffer from neuroinfections and inflammatory processes in the throat and paranasal sinuses. It is also possible to experience hearing loss similar to sensorineural hearing loss.
Damage to the cerebellum (cerebellar ataxia) , in addition to systemic dizziness, is often manifested by intention tremor , i.e. trembling of the arms and legs when trying to make an accurate movement, when approaching the target (for example, when hitting a lock with a key). Usually we have to deal with damage to the cerebellum in multiple sclerosis, chronic alcohol intoxication and cerebrovascular accident. In the case of vascular disorders, the picture may be complemented by transient or permanent visual impairment due to the commonality of the cerebellar circulatory system and the visual cortex.
Balance imbalance due to sensitivity disorder (sensitive ataxia) occurs due to a deficiency of information signals coming from sensory receptors of muscles and joints. In this case, the brain is not provided with complete data about the spatial position of various parts of the body, hence the disorder of balance and coordination of movements. Sensitive ataxia is a typical symptom of polyneuropathy. A characteristic sign is unsteadiness to the point of falling with the eyes closed or in the dark, when it is difficult to use vision for spatial coordination.
Frontal ataxia (gait ataxia) occurs when the anterior parts of the cerebral hemispheres are damaged and is manifested by a loss of walking skill in the absence of systemic dizziness and with preserved strength in the legs. This is possible with neuroinfections, multiple sclerosis, circulatory disorders, tumors, alcoholism and other diseases.
The basis of treatment for dizziness and balance disorders is the correct identification of the cause and its elimination. Therefore, treatment in our clinic will begin with clarifying the cause of what is happening . In most cases, dizziness and unsteadiness can be significantly reduced or eliminated altogether.
A little anatomy
A tooth consists of a crown and root part, connected by a neck. The coronal part is covered with enamel, the root part is covered with cement. Beneath the enamel and cement there is dentin, a hard tissue. Inside there is soft tissue - the pulp; blood vessels and nerves pass through it.
Dentin is not sensitive, but consists of many tubules in which fluid circulates. The irritant causes fluid movement, which is detected by the nerve endings of the pulp. A person feels their reaction as pain.
Sensitivity of teeth. Stages of treatment
- Eliminate the cause of hyperesthesia: get rid of plaque, deposits, stones, caries, wedge-shaped defects.
- Carry out professional oral hygiene.
- Strengthen the enamel with calcium and fluoride.
- Teach the patient how to use a toothbrush and floss correctly.
- Choose suitable dental care products: toothpaste, mouthwash.
Table 2. Tooth sensitivity: causes and how to treat
| № | Cause | What to do |
| 1. | Soft coating. | Careful hygiene with home remedies. |
| 2. | Hard coating. | Professional hygiene in dentistry. |
| 3. | Caries in the white spot stage. | Deep fluoridation, remineralization. |
| 4. | Caries, pulpitis, periodontitis. | Dental treatment. |
| 5. | Exposure of the cervical part, wedge-shaped defect. | |
| 6. | Malocclusion. | Orthodontic therapy. |
Skin rashes due to nerve damage (shingles)
Skin rashes with nerve damage are most often associated with viral aggression. The appearance of skin rashes indicates a decrease in the body's immune defense. Our task is to relieve you of skin rashes and improve the functioning of the immune system so as to stop the viral attack. Read more about the treatment of herpes zoster
Skin rashes with herpetic lesions of peripheral nerves (herpes zoster) appear on the skin in the area of the nerve affected by the virus.
Symptoms of herpes zoster:
- severe pain that gets worse when touching the skin,
- bubbles giving way to crusts,
- redness,
- severe itching is possible.
What is increased anxiety?
Increased anxiety is a person’s high sensitivity to anxiety and stressful life situations. The condition is more often registered in children of preschool and high school age, as well as in women with psycho-emotional instability, concomitant neurological diseases, and mental childhood trauma.
A slight increase in a person’s stress level is considered as an individual personality trait, as a feature. If stress becomes intrusive and worsens the quality of life of the patient or others, then they speak of mental pathology. The prevalence of the disease among other affective disorders is 33%, 25% occurs in childhood.
Mental changes. Nervous exhaustion. Asthenia. Depression. Psychosis
Depression and asthenia are frequent companions and a supporting factor in many chronic diseases. They are caused not just by a decrease in mood, but also by a biochemical imbalance of the central nervous system, incl. disorganization of the serotonin systems of the brain. A kind of vicious circle “illness-depression-illness” is formed. In most cases, a good treatment result is based on working with this vicious circle, i.e. on the treatment of the underlying disease and restoration of regulatory processes in the nervous system, incl. and serotonin regulation.
Under the influence of antidepressant treatment, immunity indicators and blood biochemistry, blood pressure, ECG, EEG change for the better, and sleep improves. The restoration of lost movement functions occurs faster, and spasticity also decreases.
Reasons for mental changes
There are several main reasons for depression in diseases of the nervous system:
- Immune and infectious aggression against the nervous system;
- Prolonged stress caused by illness;
- Long-term unpleasant symptoms (pain, weakness, etc.);
- Unpleasant medical procedures;
- Cerebrovascular accident;
- Forced change in lifestyle;
- Side effects of certain medications (for example, interferons).
Symptoms of mental changes
Personality change. The development of personality changes can be found in almost any brain disease. It is characterized by a sharpening (strengthening) of some personal characteristics to the detriment of others or the appearance of pathological personality traits. Thus, pathological aggressiveness, greed, suspicion, negativism and depression, euphoria, a pathological tendency to flat jokes, hypo- or hypersexuality, neglect of hygiene, excessive religiosity, etc. may appear. The ability to adequately assess one’s own actions decreases, hence conflicts with other people and troubles with the law. With a long course of the disorder, especially in the absence of treatment, a decrease in intelligence is possible.
Psychosis. In the long-term period of traumatic, infectious and intoxication diseases that cause the death of brain cells, periodic organic psychoses may develop. Often psychoses occur at regular intervals (sometimes they have a clear seasonality).
Possible symptoms:
- Twilight stupefaction with excitement;
- Hallucinations;
- Rave;
- Insomnia;
- Autonomic disorders (changes in blood pressure, body temperature, menstrual cycle, etc.).
Treatment of personality disorders
We recommend seeking help if you experience symptoms of a personality disorder. In our clinic, treatment is carried out in several directions at once:
- Preventing the death of brain matter. In addition to treating the underlying disease, nootropic drugs, antioxidants, and polypeptide drugs are used.
- Relief of depression and agitation, sleep disorders. Here, mainly nootropics with a calming effect, antidepressants and antipsychotics are used, in the correct combination that preserves normal vital functions.
- Working with a psychotherapist to understand and correct social and personal problems.