August 21, 2021
Spastic diplegia is one of the most common forms of cerebral palsy. It occurs in more than 70% of cases of this disease. For the first time in medicine, spastic diplegia was described by the English doctor Little. During his professional career as an obstetrician, he observed how diplegia manifested itself in newborn children. In honor of the doctor, the pathology received another name - Little's disease.
Causes
In modern medicine, it is customary to identify the following causes that provoke spastic diplegia of the lower extremities:
- premature birth - among the causes of prematurity may be Rh conflict between mother and child, fetoplacental insufficiency, premature placental abruption, late toxicosis in the mother, cardiovascular pathologies, diabetes mellitus, previous injuries;
- injuries to the newborn during childbirth - the risk of birth injury increases with prolonged or rapid labor, breech presentation of the fetus, narrow maternal pelvis;
- hypoxia and asphyxia of the newborn - oxygen deficiency during the period of intrauterine stay of the child negatively affects its development, the risk of pathologies increases if the baby does not breathe independently immediately after birth.
The causes of asphyxia in newborns can be pathological childbirth, intrauterine infections of the fetus, ingress of amniotic fluid, and genetic incompatibility of mother and child.
A certain risk of having a child with cerebral palsy exists when the mother drinks alcoholic beverages and abuses smoking during pregnancy. Provoking factors include the work of a pregnant woman in hazardous work and living in unfavorable environmental conditions.
Spastic diplegia is formed due to damage to the precentral gyrus. It gives rise to pyramidal tracts, which in turn are responsible for motor function. One of the most dangerous factors is intrauterine hypoxia, caused by a lack of oxygen supply to the fetus. Since the brain is very sensitive to a lack of oxygen, pathological changes occur immediately after the onset of oxygen starvation.
Much less frequently, diplegia can result from intracranial birth injuries, causing hemorrhages and destruction of brain tissue.
Causes of the disease
Cerebral palsy is a common disease. Its frequency is approximately 2 children per 1000 births, and data may vary depending on the region. The cause of the disorder, like any other cerebral palsy, is pathological changes in the cerebral cortex, subcortical structures, capsules or brain stem. The difference between cerebral palsy and other similar disorders is only in the time of its diagnosis (postnatal period) and the disturbance in the manifestation of reflexes.
Cerebral palsy is the result of abnormal development of brain structures or damage to a healthy brain. The process can occur both during pregnancy and childbirth, and in the early neonatal period. Among the causes of this disease are the following:
- premature birth or birth trauma;
- multiple pregnancy;
- infectious diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy, as well as mercury poisoning;
- traumatic brain injuries in the early neonatal period or in the first few years of life.
Cerebral palsy is not considered a genetic disease, since most of its cases occur in pathologies of pregnancy and childbirth. However, in 2% of cases inheritance is traced to an autosomal recessive type. Up to half of children with a similar diagnosis were born prematurely. The remaining patients were twins in multiple pregnancies, had low birth weight, or were born by instrumental delivery or emergency cesarean section. It is believed that asphyxia (insufficient oxygen supply to the brain) is one of the factors that can trigger cerebral palsy.
Cerebral palsy can also develop in children born at term. Among the causes that cause such pathologies, birth trauma comes first. In the early neonatal period, they can be caused by brain injuries and other types of brain dysfunction. Heavy metal poisoning, jaundice, stroke - all these factors lead to impaired blood circulation in the cerebral cortex, which affects their normal development. In a healthy child, cerebral palsy can be a consequence of drowning or other cases in which temporary cessation of breathing occurs, as well as inflammatory diseases of the brain, including those of infectious origin.
Classification
Depending on the intensity of the manifestation, children with cerebral palsy and spastic diplegia may suffer from the following forms of the disease:
- mild - in the first 6 months of life, children are no different from their healthy peers, later problems appear when walking, but arm movements are not limited, the patient can move independently, mental development is not impaired;
- medium - the patient has diplegia of the lower extremities, movement is possible only with the help of improvised means, minor mental damage is also noted, but social adaptation is not impaired;
- severe - this form of cerebral palsy, spastic diplegia, is noticeable from the first months of the child’s life, pronounced tetraparesis is noted with an emphasis on the lower limbs, motor function is completely impaired, patients are not capable of social adaptation in society.
Children with severe spastic diplegia have a negative prognosis for recovery. This pathology is practically untreatable and can lead to death in adolescence.
Causes and risk factors for the development of spastic diplegia
Since neurologists do not know , they presumably name many reasons. And if at least one of them coincides with your lifestyle or an event in your life during pregnancy, then neurologists are happy: they found the reason, blaming you for this event .
Doctor Nikonov
My opinion: the mother is not to blame, the father is not to blame. Swelling in the muscles is not inherited, and the density of muscle fibers adjacent to each other depends on the information that both the mother and father passed on to the child. This is visible under an electron microscope in a fetus at 6 weeks.
I will list the reasons for the development of spastic diplegia according to neurologists:
- Heredity.
My opinion: there is no data to support this statement, since children with spastic diplegia have all their chromosomes intact.
Neurologists:
- Fetal ischemia or hypoxia. If the blood supply to the brain is disrupted and oxygen starvation, brain damage can occur.
My opinion: there is no evidence either on ultrasound or MRI. This is an assumption, i.e. essay on the topic of oxygen starvation of the brain.
Neurologists:
- Infectious lesions of the brain and musculoskeletal system. When a newborn is infected with an infection, serious diseases can develop, such as meningitis, encephalitis and others, due to which complications are noted, since the body is small and is not able to fight such lesions.
My opinion : not all children develop spastic diplegia after suffering from infectious diseases. This disease develops in those children who have suffered infectious diseases and already have swelling in muscle cells or between muscle fibers.
Neurologists:
- Toxic factor. Alcohol, smoking, taking strong medications, etc. may provoke the development of pathology.
My opinion : it has been proven that the body produces alcohol during meals. For this reason, people feel relaxed after eating. It is impossible to provoke pathology. It either exists (look through an electron microscope) or it doesn’t. The placenta will not allow harmful substances to pass through it - it is a natural filter.
Neurologists:
- Physical impact. Brain damage can occur due to radioactive, x-ray irradiation of a pregnant woman, as well as as a result of electromagnetic irradiation.
My opinion: learned biologists and physicists exclude the possibility of spastic diplegia arising from such physical influences, based on data from studies of children after the atomic explosion in Hiroshima. Neurologists send you for an ultrasound scan themselves.
Neurologists:
- Mechanical reasons. Brain damage can be caused by trauma and damage immediately after birth.
My opinion: A child with the most common form of cerebral palsy, spastic diplegia, could be born with difficulties, since muscle swelling was present in both the mother and the baby, who was born with the pathology. Watch a video on the topic of spastic diplegia:
Symptoms
Spastic diplegia, especially in its mild form, is hardly noticeable in the first months of a child’s life. The newborn baby still has muscle hypertonicity, which he needed during the period of intrauterine development. It gradually weakens, but partially remains until 4-6 months. Hypertonicity, which persists in a child after he reaches six months of age, is one of the signs that makes one suspect spastic diplegia of the lower extremities.
Diplegia in severe form is noticeable from the first days of a baby’s life. Such children are inactive during the period of swaddling and wakefulness, increased muscle tone makes it difficult to bend the limbs.
Other symptoms of spastic diplegia include:
- the characteristic position of the patient’s legs, in which the hips and knees are connected inward, the legs are crossed;
- “dancing” movements when walking, knees rubbing against each other;
- significant delay in motor activity - children begin to walk only at the age of 2-4 years;
- child's tiptoe gait;
- oculomotor disorders, strabismus, decreased visual acuity;
- poor hearing;
- disturbances in the functioning of the speech apparatus, delayed speech development;
- involuntary uncontrolled movements;
- hoarseness of voice.
Diplegia in cerebral palsy is often accompanied by a delay in psychological and speech development. Up to 80% of children diagnosed with spastic diplegia have speaking problems to one degree or another. At the same time, mental retardation is noted in only a quarter of patients with this form of cerebral palsy.
Concept of spastic diplegia
According to the World Health Organization, spastic diplegia is a form of cerebral palsy in which there is a complete disruption of the functioning of the muscles of the limbs.
Doctor Nikonov
In my opinion , spastic diplegia is a form of cerebral palsy in which the functioning of the muscles of the neck, back and buttocks is impaired. The limbs do not move due to the fact that the back muscles do not relax and do not allow the muscles of the limbs to move. Watch a video on the topic:
Neurologists believe that moderate and mild spastic diplegia is caused by damage to both hemispheres of the brain, therefore movements in the upper and lower extremities are impaired.
Doctor Nikonov
My opinion is based on what Professor Sergei Savelyev saw through an electron microscope. Changes in muscles (edema) began in utero before brain development.
Neurologists have a tentative opinion.
Professor Savelyev’s opinion is provable and clearly presented.
Neurologists believe that spastic diplegia is G 80.1. characterized by lower spastic paraparesis, or tetraparesis, which mainly affects the child’s legs. The expression of pathology can vary - from pronounced to mild awkwardness.
Neurologists believe that the cause of the disease in question is increased muscle tone in the arms or legs.
Doctor Nikonov
My opinion: increased muscle tone disappears by six months after the birth of the child. Since increased muscle tone is needed for the fetus to be in the fetal position. At exactly six months, not a single child has increased muscle tone.
Neurologists do not know about muscle swelling , so they answer about increased muscle tone based on assumption, not knowledge.
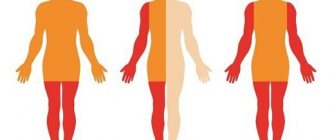
Due to the fact that the muscles of the neck, back and buttocks do not move, the arm is bent at the elbow joint and turned towards the body with a clenched fist. The lower limbs are in a semi-bent position and may cross when walking. Look at the picture below, which shows a typical posture for spastic diplegia:
Recommended video to watch:
The presented video is not educational. The video is the result of the work. Repeating procedure techniques without training from Dr. Nikonov may result in serious injury.
Diagnostics
To determine lower spastic diplagia, a set of diagnostic measures is used. Diagnosis at an early age is often difficult, which creates problems in timely treatment.
Diagnosis is carried out by a pediatric neurologist, and consultations with a pediatrician, ophthalmologist, and otolaryngologist are also prescribed. Pay attention to the history of childbirth, such facts as prematurity, hypoxia during intrauterine development, asphyxia during childbirth.
A neurological examination is of great importance in diagnosis, during which attention is paid to the characteristic signs of disturbances when walking, increased muscle tone, increased tendon reflexes, and impaired skin sensitivity.
Diagnostic measures also include:
- consultation with an ophthalmologist to determine visual acuity and identify oculomotor disorders;
- audiometry by an otolaryngologist, carried out to determine hearing acuity and its possible disorders;
- electroencephalography - performed to assess brain activity;
- neurosonography - necessary to exclude other pathologies with similar symptoms, such as hydrocephalus, cysts, intracranial hematoma;
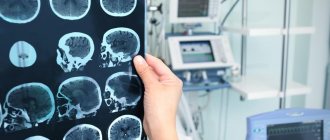
- MRI of the brain - usually performed when it is necessary to clarify previous diagnostic data.
The child’s level of psycho-speech development is assessed. This is done by a child neurologist (at an early age) or a child psychiatrist. If necessary, tests are performed to determine the level of delay in psychological and speech development or to diagnose mental retardation.
Diagnosis of cerebral palsy (cerebral palsy) in the early stages
Doctors at the Clinical Brain Institute argue that the possibility of correcting disorders in cerebral palsy depends on the timely diagnosis of the disease. At the first behavioral disturbances in a child, you should contact your pediatrician and find out whether his development is normal. At home, you can notice the first signs of cerebral palsy, which will then progress. These include:
- at the age of 1 month - lack of reaction to loud sounds, restless sleep;
- 4 months - children do not respond to sound by turning their heads, do not show interest in toys and other objects;
- 7 months - the child cannot sit independently, some patients have difficulty holding their head up;
- 12 months - the child does not begin to pronounce individual words, performs most actions with one hand;
- at any age - squint, convulsions, sudden movements, gait disturbances (lack of support on the full foot).
The most informative method for diagnosing cerebral palsy is MRI. The examination should be carried out when the first symptoms appear, as well as if there is a similar diagnosis in the anamnesis of relatives. The diagnosis must be differentiated from other pathologies that manifest similar symptoms. These include early hereditary ataxia, consequences of traumatic brain injury, phenylketonuria, galactosemia, schizophrenia and other disorders.
Treatment
Treatment of spastic diplegia in cerebral palsy is aimed at rehabilitation of the child, alleviation of symptoms of the disease, psychological and social adaptation. Working with a defectologist, psychologist, and speech therapist is of great importance to acquire self-care skills and adaptation to society.
Conservative therapy
Drug treatment of diplegia involves prescribing the following groups of drugs:
- vascular agents - normalize blood circulation, improve brain function;
- muscle relaxants - relieve muscle spasms;
- nootropics - stimulate mental activity, activate cognitive functions, improve memory;
- botulinum toxin - relieves spastic tension;
- sedatives - to normalize the psycho-emotional background;
- vitamin and mineral complexes - to achieve a general strengthening effect.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures for cerebral palsy are prescribed taking into account the characteristics of the child’s body, rapid fatigue and increased excitability of the nervous system of such patients.
Effective physiotherapeutic procedures include:
- electrical stimulation - the use of pulsed currents to improve blood circulation and normalize muscle tone;
- magnetotherapy and the use of ultrasonic waves - used in the treatment of contractures;
- laser therapy - has a beneficial effect on the walls of blood vessels and muscle fibers;
- balneotherapy - the appointment of pine, hydrogen sulfide, turpentine, oxygen and other types of healing baths;
- thermal procedures - paraffin wrap, mud therapy.
Patients with cerebral palsy are prescribed various types of therapeutic massages. Their goal is to strengthen the muscles, relieve tension and excitability in the muscles, and improve blood circulation.
Acupuncture provides effective results in treatment. Influence on biologically active points on the human body allows you to improve the reflex response of organs and tissues. It is best to start acupuncture sessions before the age of one year.
Biologically active points on a child’s skin are located closer to the surface than on adults, so the time the needle remains on the skin is also shorter. It is recommended to conduct 3-4 courses of acupuncture per year. Each course consists of 10 procedures.
Physiotherapy
Exercise therapy is carried out no earlier than one and a half to two hours before or after physiotherapeutic procedures. Exercises are performed in an active-passive mode with the help of an instructor; it is possible to use special gymnastic equipment - a fitball, balls, sandbags.
Physical therapy exercises help build muscle strength, improve coordination of movements, normalize muscle tone, and improve the emotional state of a small patient.
Swimming has a great effect on the human body. Staying in water has a restorative and sedative effect and activates the central nervous system.
Recently, new rehabilitation methods have gained popularity - dolphin therapy (swimming in a pool with dolphins) and hippotherapy (communication and horse riding). Such activities stimulate emotional, tactile and visual communication, helping the child get a charge of optimism and positive, bright emotions.
Specially trained animals send the child over 100 motor impulses, to which the patient’s brain actively reacts.
At least an hour should pass between massage, exercise therapy or physiotherapy procedures. Procedures are not prescribed if the child has signs of acute respiratory diseases, a feverish state, a tendency to bleed, or the presence of neoplasms in the body.
If the disease is accompanied by increased excitability of the child and sleep disorders, electrosleep therapy is indicated. Electrosleep lasting 30-40 minutes is prescribed, procedures are carried out daily or every other day. This type of physiotherapy is not prescribed if cerebral palsy is complicated by epilepsy or hydrocephalus.
Rehabilitation therapy necessarily includes classes with a psychologist, speech pathologist, and special education teachers in specialized institutions. Play therapy allows you to relieve increased anxiety, fears, neuroses, improve sleep and correct behavior. These types of correctional work are indicated for patients who have delayed mental and speech development.
Treatment methods
Specialists at the Clinical Brain Institute offer individual treatment and adaptation programs for patients with various forms of cerebral palsy. The main goal of the work is maximum socialization of the child, teaching self-service skills, and developing intellectual abilities. Techniques are also used that significantly improve the condition of muscles with hyper- and hypotonicity and prevent significant deformation of skeletal development.
Basic methods of treating cerebral palsy (cerebral palsy)
Treatment methods for cerebral palsy are a set of measures aimed at improving the patient’s quality of life and his socialization. Despite the fact that the disease is chronic and does not end with complete recovery, it is necessary to constantly take measures to improve the child’s quality of life. Doctors may recommend the following treatment methods:
- therapeutic massage is one of the main methods of reducing muscle tone;
- therapeutic exercises (if possible) - special exercises to restore coordination of movements and symmetrical muscle development;
- electroreflexotherapy is a method of stimulating brain neurons, as a result of which the clinical picture of the disease is expected to be smoothed;
- classes with a speech therapist;
- work using animals, including hippotherapy;
- Loading suits - allow you to correct the position of the body and promote the correct development of the spine.
Classes with children must be carried out regularly. During the growth process, it is possible to prevent dangerous complications of cerebral palsy and promote the symmetrical development of skeletal bones and muscle mass. In advanced cases, surgical intervention may be indicated, during which muscle defects and contractures are eliminated, and tendon plasty is performed.
Using assistive devices
Therapy for cerebral palsy includes the use of additional devices. It is important to pay attention to the child’s motor activity and complicate tasks as he develops. During the exercises, it is important to perform them correctly using the right muscle groups. Classes take place with a specialist and at home, and can be carried out using additional equipment:
- walker is a device that is used not only for learning to walk, but also for correcting balance and balance;
- parapodium - a system of orthoses that allows you to move independently even in the absence of muscle tone in the lower extremities;
- verticalizer - a special fixator thanks to which the child can stand independently (this is important, among other things, for the proper development and functioning of internal organs);
- bicycles - models with three wheels, easy to operate, which allow you to move around with reduced function of the lower extremities;
- devices, splints, splints for correcting the position of the limbs.
For maximum socialization of a child, it is important to devote time to physical activity. Modern devices (wheelchairs, bicycles, walkers and parapodiums) allow you to move independently, even with decreased muscle tone. This development allows you to avoid the manifestation of muscle contractures and achieve maximum symmetrical development of muscles and bones. In addition, the room should be equipped with special devices for comfortable movement of the child, handrails, a bathing chair and other auxiliary devices.
Forecast
Cerebral palsy is an incurable disease, so the goal of treatment is to maximize the patient’s adaptation to living in society and improve his overall well-being. Although the overall prognosis for the disease is unfavorable, with proper treatment and additional health procedures, patients with this diagnosis can live to a ripe old age.
With a mild form of the disease, patients can lead a normal life, get education, and work. When choosing a profession, you should definitely take into account the characteristics of your health condition, as well as regularly take courses of preventive treatment and follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
However, only a quarter of patients will be able to move and care for themselves. If a severe degree of the disease is diagnosed, the patient needs constant care and will not be able to lead a full independent life.
Parents of children with cerebral palsy also need psychological help and support. To do this, they can attend special courses and trainings at rehabilitation centers, where they will receive appropriate recommendations for treatment and proper care and will be able to find like-minded people and friends.
Prognosis and prevention
In terms of the motor sphere, spastic diplegia has a more serious prognosis than the hemiplegic form of cerebral palsy. Only a quarter of patients are able to walk independently; half of the patients move with the help of special aids. With severe tetraparesis, movement is only possible in a wheelchair. With mental integrity and minor changes in the muscles of the upper limbs, the social adaptation of patients approaches that of healthy people. In severe cases, patients require constant care. Proper, regular rehabilitation measures and periodic courses of drug treatment improve the prognosis. Measures to prevent the disease include careful management of pregnancy, prevention of intrauterine pathology, adequate choice of delivery method, and correct management of childbirth.
Complications
The negative consequences of the disease are reflected mainly in the condition of the musculoskeletal system. Possible complications include:
- formation of contractures;
- risk of developing joint pathologies - arthrosis;
- muscle atrophy;
- increased risk of injury resulting from poor coordination of movements, unsteady gait, and falls.
Avoiding complications and achieving the most effective rehabilitation of a child is possible only with timely diagnosis and early initiation of treatment.
Clinical signs of spastic diplegia
The incidence of this form of cerebral palsy is 50%.
of the musculoskeletal system include:
Bilateral damage to the extremities of a sick child, legs to a greater extent than arms, earlier formation of deformities and contractures, deformation of joints and spine. Muscle tone in the adductor muscles and hip extensors is greatly increased, the child’s legs are brought close to each other, often crossed. Additionally, symptoms of Babinsky, Rossolimo, etc. may appear. Walking in the case of the formation of contractures and deformities of the feet is difficult or impossible.
Disorders of mental and speech development , pathologies of the sensory organs:
Pseudobulbar syndrome, pathological changes in the cranial nerves, which entails atrophy of the optic discs, hearing impairment and strabismus. There is a delay in speech development. Speech development in children with spastic diplegia is delayed. Speech disorders are manifested by dysarthria and alalia. Hyperkinesis of the articulatory and respiratory muscles makes speech blurry and jerky. Children with this form of the disease have difficulty studying, quickly become exhausted, and are distracted. Memory is reduced.
Other pathologies: Convulsions are possible, but relatively rare.
The decrease in intelligence is moderate or completely absent.
Watch a new film about the Nikonov method:
Prevention
Prevention of the disease should be carried out during the period of pregnancy by the mother. A pregnant woman must register with a specialized medical institution on time to manage her pregnancy.
During the entire period of bearing a child, it is prohibited to smoke or drink alcoholic beverages. Bad habits reduce the supply of oxygen and increase the risk of developing hypoxia in the fetus.
If a woman was taking medications before pregnancy, she should notify her doctor. Not all medications are safe for the development and health of the unborn baby.
Preventive measures also include following the rules of a balanced diet and eliminating negative emotions during pregnancy. Regular visits to the doctor will help prevent intrauterine developmental disorders.
Prevention methods
Complete prevention of cerebral palsy is impossible, especially if the disease is of genetic origin. However, in the process of planning and maintaining pregnancy, as well as during childbirth, it is possible to minimize the likelihood of the disease manifesting itself in a healthy child. Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain can give several recommendations that will allow for maximum prevention of cerebral palsy:
- vaccination of the mother against infectious diseases (measles, rubella), which during pregnancy can cause fetal hypoxia;
- drug treatment for increased risks of premature birth, as well as insufficient blood supply to the fetus;
- consultation with a geneticist, full examination of the mother when planning pregnancy;
- in the first months after birth - preventing head impacts, as well as the mandatory use of car seats for newborns.
At the Clinical Brain Institute you can get detailed advice on the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of cerebral palsy. It is worth understanding that the result of therapy depends not only on the severity of the diagnosis, but also on the timeliness of medical care and the willingness of parents to follow the doctor’s instructions. A huge number of children with a similar diagnosis undergo successful socialization, attend general educational institutions and even develop in the professional sphere.
What do you need to remember?
- spastic diplegia is the most common form of cerebral palsy;
- the disease requires not only the use of drug therapy, but, first of all, a number of health-improving and developmental procedures aimed at adapting the child to society;
- with a mild form of the disease, the child can independently care for himself and lead a normal life, but with regular visits to the doctor;
- Physical therapy exercises play an important role in treatment;
- if indicated, the child is entitled to sanatorium treatment;
- every child with cerebral palsy has the right to rehabilitation with the provision of technical recovery means;
- timely treatment reduces the risk of complications such as contractures, joint pathologies, and muscle atrophy.
Return to list
Treatment of spastic diplegia by neurologists
Neurologists: according to the World Health Organization, curing spastic pathology is impossible.
The goal of treatment by neurologists is to mitigate muscle damage and adapt the child to society. To achieve treatment goals, general physiotherapeutic rehabilitation procedures are used. This could be: regular massage to improve blood circulation in order to reduce muscle tone and prevent contractures.
Doctor Nikonov
My opinion: it is impossible to improve blood circulation. There is either blood circulation or there is not. If blood circulation deteriorates, there will be gangrene. An electron microscope shows the growth of additional arterial capillaries in the muscles where the nuclei have “fell off.” Therapeutic massage is not able to eliminate swelling from muscle cells.
Neurologists prescribe physical therapy, acupuncture, and swimming.
My opinion: for a child with spastic diplegia and his parents, all the recovery methods listed by neurologists are a game of daughter-mother. Until you eliminate the swelling from the muscle tissue, there will be no positive changes. Only exposure using the Nikonov method can eliminate swelling.
Neurologists like to prescribe vojta therapy, a technique for activating reflexes.
My opinion: you can activate reflexes only in those muscles of the child that are without swelling. Only the appearance of improvement is created due to non-swollen muscle groups at the time of application of the technique for a short period of time.
Neurologists prescribe wearing a power system consisting of support elements and elastic adjustable rods.
My opinion: it is impossible to teach a child to walk correctly if the muscles do not move correctly due to swelling.
Drug treatment includes the use of nootropics and homeopathic medicines. Treatment is prescribed in the presence of auxiliary lesions in the form of delayed intellectual and psychological development.
I don't prescribe medications.
Watch a video on the topic of spastic diplegia in children:
It is impossible in the article to describe every particular case of restoration and training of parents to restore their children. Therefore, I am providing you with links to my video channels, where you will find complete information:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCcKEOLTWN3sy9QV5VK2axig
https://www.youtube.com/user/NikonovNikolay
They also suggest watching my video, which shows examples of complete recovery of children:
Me, my patient Bogdan and his happy parents: