Women's frequent mood swings are both a reason for jokes and a cause for concern. And mood swings often indicate disturbances in the functioning of body systems. They bring a lot of inconvenience to a woman’s life: emotional instability does not allow her to cope with stress wisely and does not allow her to make the right impression on loved ones, colleagues, and partners. You should not ignore mood swings - this is fraught with a worsening of these manifestations, and is also dangerous to health. After all, we can talk about a serious hormonal imbalance or the presence of a mental disorder.
Men can also suffer from mood swings - from aggression to apathy, from joy to sadness - but, oddly enough, representatives of the stronger sex are less susceptible to emotional swings.
In this material we talk about how frequent mood swings can manifest themselves, what causes them, how to competently approach diagnostic issues, and how we, doctors at the Marina Ryabus Clinic, help patients cope with this problem. An expert commentary on the material is given by gynecologist Ekaterina Nikolaevna Kozlova.
Kozlova Ekaterina Nikolaevna
★ ★ ★ ★ ★
Gynecologist, oncologist, surgeon
Mood swings in women can be observed at different age periods and, as a rule, in addition to external factors, hormonal levels play a big role. During periods of greatest hormonal changes, such as puberty, postpartum or premenopause, these changes are observed more often. It is important that the woman does not accept this as the norm, but consults a gynecologist who would help her with the selection of corrective therapy. In one case, this may be a behavioral recommendation (sleep and wakefulness, nutrition, physical activity), in another - the prescription of supplementation therapy or hormonal drugs. Quite often, young active women have a bad mood accompanied by a feeling of constant fatigue, despite proper rest. This is an alarming symptom of chronic stress, which leads to “exhaustion” of the adrenal glands and long-term rehabilitation therapy.
Sign up for a consultation
general characteristics
Crying is a psychophysiological reaction that is accompanied by the release of tears, a sharp change in the rhythm of breathing, blood pressure and heartbeat, and involuntary contraction of the superciliary and periocular muscles.
In origin, it is a strong one-time mental experience that occurs in response to intense negative or positive stimuli. From a social point of view, crying is a way of expressing strong emotions. In childhood, physical pain is a common cause of tears. As you get older, this reaction weakens, but can persist in women with increased emotional lability. The term “tearfulness” refers to a character trait or temporary feature of the emotional-volitional sphere. It manifests itself as emotional imbalance, tearfulness: a person cries every day, the tears are caused by random memories, a tense conversation, the unpleasant intonation of the interlocutor, a scene from a movie. Often, tearfulness reduces social activity, interferes with maintaining close relationships, and provokes irritability and misunderstanding on the part of others.
Tearfulness is more common in women and children than in men. This is explained by biological reasons: women have more pronounced hormonal fluctuations (pregnancy, childbirth, menstrual cycle), children have a labile nervous system, so they easily become agitated even to minor stimuli. The cultural factor also influences increased tearfulness in women compared to men. Sensitivity and tearfulness are recognized as feminine traits, while men's tears are seen as a demonstration of weakness.
Complications of depression
If clinical depression is neglected, the following complications may arise:
- Brain tumors;
- Somatic disorders;
- Hormonal disorders;
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Loss of work, study, complete loneliness;
- Suicide.
According to statistics, depression is the most common cause of suicide worldwide. Treatment must be comprehensive and timely.
Causes of tearfulness
Tearfulness is often a symptom of a mental disorder - depression or neurasthenia. In addition, it can be caused by hormonal changes, diseases of the central nervous system, overwork or chronic stress. The causes of tearfulness are varied; tearfulness is often provoked by external events, but has a physiological basis.
Predisposing physiological factors
They say about some people that they are whiny since childhood, about others - on the contrary, that they never cry. Tearfulness most often develops on the basis of a physiological predisposition, which consists of the peculiarities of the functioning of the nervous system and the rate of production of certain hormones. Increased tearfulness is due to the following reasons:
- Instability of the nervous system.
With an unstable type of nervous activity, the processes of excitation and inhibition quickly replace each other, which is externally manifested by frequent mood swings and sudden emotional outbursts. People with this characteristic type of temperament are classified as melancholic or choleric. Tearfulness is characteristic of them from birth. - Hormonal imbalance.
Irritability and tearfulness intensify during periods of hormonal changes in the body in women: during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, menopause, after childbirth. Increased production of some hormones and a lack of others lead to changes in the activity of parts of the brain responsible for the emotional state. - Physical overload.
If the body is unprepared, intense sports or hard physical labor are a source of stress and disrupt the functioning of internal organs and systems. If it is impossible to fully restore strength, tearfulness and irritability increase, and fatigue accumulates. A state of exhaustion gradually develops. - Vitamin deficiency.
The reason for tearfulness due to poor nutrition is a lack of B vitamins. They are responsible for the functioning of the nervous system, the production of hormones, skin condition, and muscle tone. With their deficiency, irritability increases, mood and performance decrease, insomnia develops, and appetite worsens. With prolonged hypovitaminosis, depression, neuroses, hormonal disorders, and Beri-Beri disease develop.
Psychological factors
Psychological causes of tearfulness include personality traits formed during life and external stressful psychotraumatic influences. Depending on this, a distinction is made between people who are tearful in character and those whose excessive tearfulness is explained by the current difficult situation. The most obvious causes of tearfulness are:
- Features of education.
The reason for a child's tearfulness is the attitude of the parents. Sometimes crying becomes a tool to attract the attention of adults and get what they want. If parents do everything to stop the tears - they buy toys, allow them not to go home from a walk, not to wash themselves - the child develops hysterical character traits. Another reason for tearfulness is self-doubt, fears, and a feeling of uselessness. This type of character is called neurasthenic. With insufficient love and support from parents, tearfulness intensifies. - Stress.
Negative experiences caused by a traumatic situation or daily minor troubles can lead to a state of stress. At the initial stages, the body fights and activates physiological and mental reserves. Thanks to this, a person maintains the same performance and emotional balance. Then comes the stage of exhaustion - the body gets tired of fighting, and the adverse effects continue. At the physiological level, this manifests itself as headaches and general malaise; at the psychological level, it manifests itself as tearfulness, irritability, and depression. - Routine.
Not only stress, but also routine in everyday life can lead to nervous exhaustion. In situations of monotonous work with repetitive stereotypical actions and an impoverished external environment, performance decreases. Monotony is accompanied by the experience of boredom, apathy and dissatisfaction with life, and tearfulness. Women are especially susceptible to emotional disturbances. Their tearfulness increases in the absence of friendly communication and variety of leisure activities.
Mental disorders
Tearfulness and increased tearfulness develop in some mental disorders. All of them are accompanied by a decrease in the body’s adaptive abilities, fatigue, depression, and instability of emotions. Patients cry often, do not always have an external reason for crying, and do not control their condition. Tearfulness can be a symptom of the following disorders:
- Depression.
With depressive disorders, patients are almost constantly in a state of low mood, sadness, and sadness. They have no interest in what is happening, so it is difficult to distract them and cheer them up. Tears and crying appear easily, often without external reasons. - Astheno-neurotic syndrome.
Neurasthenia occurs when a combination of psychotraumatic effects and intense physical or mental stress. Chronic lack of sleep and emotional burnout can be a provoking factor. Manifested by irritability, easy fatigue, and tearfulness. - PTSD.
Sometimes, unexplained tearfulness is a symptom of post-traumatic stress disorder. Sudden tears are triggered by memories of scary scenes and traumatic events from the past. Images pop up in the head involuntarily, in dreams and in reality, when the surrounding environment is somewhat reminiscent of an old situation (the same smell, sound, phrase). - Generalized anxiety disorder.
The causes of tearfulness in patients with an anxiety disorder are constant worry, fear, obsessive thoughts, and sleep disorders. With a long course of this pathology, panic attacks occur with vegetative crises (dizziness, breathing problems, palpitations). Tearfulness becomes even more noticeable, especially in women. - Childhood fears.
A characteristic feature of childhood is the ease of developing fears. They are formed under the influence of external situational influences and provoke the development of neurotic reactions, including crying. The cause of fear in infants and young children is the care of the mother. The more often the mother is absent, the more whiny the child becomes. Similarly, tearfulness in kindergarten develops with fear of strangers.
Somatic diseases
Frequent causes of tearfulness are physical illnesses. Frequent crying may indicate a change in brain function or severe hormonal imbalance. A more obvious connection cannot be ruled out: people cry when they experience pain and worry about the irreversible deterioration of their health and appearance. There are several somatic causes of tearfulness:
- Decreased quality of life.
Serious illnesses are characterized by limited mobility, deterioration of well-being, and changes in the patient’s appearance. Often patients are forced to give up their usual physical activity and communication, perform professional duties, and eat their favorite foods. This condition may be accompanied by reactive depression - crying, feelings of hopelessness, depression, uselessness. - Pain syndrome.
The feeling of frequent or constant pain is the cause of tearfulness in somatic patients, especially children. Physical suffering is manifested by a decrease in the patient’s activity, fixation on sensations coming from the body, depression and irritability. - Organic brain damage.
The cause of tearfulness is damage to nerve cells in the parts of the brain responsible for the formation of emotions and behavior. An example of such a disorder is “weakness”, tearfulness of the elderly with Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, atherosclerosis, and multiple sclerosis. Similar emotional disorders are possible with brain tumors, neuroinfections, and after traumatic brain injuries. - Endocrine diseases.
Emotions are affected by endocrine pathologies such as hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus, and Addison's disease. A lack or excess of certain hormones causes sudden bursts of irritability, anger, and crying. As a rule, patients notice them, but cannot explain the cause.
Stages of development of depression
The disease occurs in several stages and is accompanied by characteristic physical and psychological symptoms. To help a person, you need to start treatment as early as possible.
Primary depression
The mood gradually worsens, but somatic disorders “pop up” first. The person experiences weakness, dizziness, sadness and drowsiness. Interest in work, study or hobbies gradually disappears.
Terminal stage
A person’s appetite disappears or increases, and weight changes. Concentration is impaired, general weakness increases, and insomnia or drowsiness is noted. Persistent depression of mood occurs, and suicidal thoughts haunt.
Last stage
The last stage can occur in two ways. In the first, a person simply lies motionless, neglecting not only important matters, but also natural needs. In the second case, aggression occurs, the patient commits auto-aggressive acts and suicidal actions.
Survey
Determining the causes of tearfulness is carried out by specialists from various fields - psychiatrists, neurologists, endocrinologists. Primary diagnosis is carried out using clinical methods, including interviewing the patient and his relatives, as well as observing behavior. In most cases, patients are able to critically evaluate their experiences, so they independently report to the doctor about frequent crying, emotional sensitivity, mood swings and other symptoms. A conversation with relatives helps to clarify the duration of the symptom and its causes. To establish the etiology of tearfulness, the following is used:
- Study of the emotional sphere of personality.
Comprehensive psychodiagnostic testing allows us to determine the presence of depression, leading character traits and personality traits that are the basis of tearfulness. Various questionnaires (MMMPI, Cattell questionnaire) and projective techniques (color choice test, drawing of a person) are used. - Laboratory studies of hormones.
If a conversation with the patient does not reveal the psychological causes of tearfulness, but there are signs of an endocrine disease, a blood test is performed to determine the content of hormones. The concentration of hormones of the adrenal glands, thyroid, pancreas, parathyroid and/or gonads is examined. - Instrumental studies of the brain.
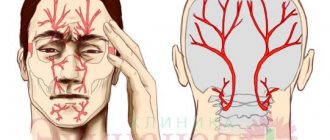
If the patient complains of emotional disturbances and there are signs of organic damage to the central nervous system, a neurological examination, CT and MRI of the brain, ultrasound of cerebral vessels and other diagnostic procedures are performed. The results make it possible to determine pathological changes in cerebral structures and tissues.
Types of Mood Swings
Globally, mood swings are usually divided into:
- cyclothymic – affective disorders associated with a sharp transition from high mood to apathy;
- depressive – chronic mood disorders associated with illness, medication, hormonal levels, etc.;
- biopolar - constant changes in mood, from a depressive state to inspiration on the verge of euphoria.
Cyclothymic disorders include two types of disorders - hypothymic and hyperthymic manifestations. In the first case, we are talking about situations of apathy, depression, uncertainty, and dissatisfaction. In the second - about cases of increased activity, severe excitability, little sleep, etc. The essence of cyclothymic disorders is the inevitable cyclical transition from one state to another.
Depressive states are temporary, caused by external causes associated with hormonal changes and injuries. Depression can develop while taking medications. The hallmarks of depressive mood swings are feelings of depression, emptiness, lack of self-confidence and reluctance to do anything. In other words, the patient loses his taste for life.
Bipolar disorders are conditions in which a person abruptly moves from a period of activity and creativity to a period of apathy and reluctance to do anything.
The types of mood disorders listed above are typical for both women and men. In this material we will pay attention to representatives of the fair sex.
MIGUNOVA ANASTASIA ANDREEVNA
Cosmetologist
Initial consultation: RUB 4,500
Make an appointment with a doctor Instagram
VYATKINA IRINA SERGEEVNA
Gynecologist-endocrinologist
Initial consultation: RUB 8,500
Make an appointment with a doctor Instagram
KALININA EKATERINA ALEXANDROVNA
Cosmetologist
Initial consultation: RUB 4,500
Make an appointment with a doctor Instagram
KOZLOVA EKATERINA NIKOLAEVNA
Gynecologist-endocrinologist, oncologist
Initial consultation: RUB 5,000
Make an appointment with a doctor Instagram
Treatment
The main therapy should be aimed at eliminating the cause of tearfulness - reducing the intensity of stress, normalizing the woman’s hormonal levels, changing the parenting style. If it is impossible to influence the etiological factor or influencing the cause requires long-term, labor-intensive treatment, symptomatic remedies are used. Thanks to them, tearfulness decreases, the patient becomes more balanced and socially active, and the effectiveness of basic therapy increases. Symptomatic help for tearfulness includes breathing exercises, psychotherapy, medication, and changes in activity patterns.
Yoga is a great way to find peace of mind
Breathing exercises
At the physiological level, crying is manifested by a complex of reactions of the respiratory, cardiovascular and nervous systems. A person is able to control his breathing voluntarily. To stop the beginning attack of crying, it is necessary to eliminate the feeling of spasm in the throat and holding your breath. The easiest way to do this is with breathing exercises, which include slow and deep breathing, deep breaths through the nose with noisy exhalation through the mouth, fast and intense breathing. The most effective method is selected by the patient individually by trial. In women, the diaphragmatic breathing technique gives good results.
Behavioral psychotherapy
Behavioral techniques are aimed at switching attention, changing external activity that supports crying. The simplest exercises are running, purposeful activity, provoking another emotion (anger or joy). While running, a sequence of movements is established, muscles contract rhythmically, breathing intensifies - all these processes prevent crying.
Specially created purposefulness of actions switches attention from sad and sad thoughts to solving the problem. Distraction options: searching for keys in a bag, making a shopping list. It can be difficult to provoke anger or joy on your own, but with training this skill is developed. It is necessary to remember a funny or angry situation and the people who participated in it, and reproduce the images in your thoughts in as much detail as possible.
Transactional analysis
Psychotherapy using the method of transactional analysis is a more complex way of dealing with tearfulness. According to this direction, a person’s personality is represented by three states - Adult, Parent and Child. Tearfulness is most characteristic of the latter, since crying stores the conscious and subconscious experience of childhood. During psychotherapy sessions, the patient is taught to remain in the position of an Adult, analyze situations and make decisions, without allowing emotions to determine behavior. At the same time, attention shifts from experiences of the past and future to the state of “here and now.”
Drug therapy
Medications can be used to combat tearfulness. Their selection is carried out by a psychiatrist or psychotherapist, depending on the combination of symptoms. If tearfulness manifests itself along with anxiety and increased irritability, anxiolytics, sedatives, and herbal sedatives are prescribed. For nervous exhaustion and signs of depression, antidepressants and tranquilizers are used, and for sleep disorders, sleeping pills are used.
Normalization of the daily routine
The basic cause of tearfulness is the instability of the processes of inhibition and excitation in the nervous system, therefore, to maintain emotional balance, it is necessary to adhere to the correct regime. The most important things are adequate sleep of at least 8 hours at night, regular exposure to fresh air, and alternation of mental and physical labor. Patients are advised to make a plan for the day and week, be sure to include walks, hobbies and sports that bring pleasure.
Consequences of depression
Depression has social and physiological consequences. This means that high-quality treatment is necessary: otherwise, a person’s life can turn into a complete nightmare, or even end in one moment.
Diseases
Because of this disorder, not only the psychological, but also the physical state of a person deteriorates. There are:
- Migraine;
- Arthritis;
- Alcohol or drug addiction;
- Sexual dysfunctions;
- Diabetes;
- Diseases of the nervous and cardiovascular system;
- Depression in a pregnant woman leads to organic changes in the fetal brain.
General state
Due to depression, a person may enter into conflicts with loved ones, isolate himself from everyone, and ultimately be left alone. Problems with performance lead to lack of success in school and in the workplace, exclusion from education, and dismissal from work.
The worst consequence of depression is suicidal behavior. According to statistics, patients with depressive disorder are at the highest risk of suicide. In this case, a person can both prepare for suicide and commit it impulsively, during an attack of despair. To prevent such a terrible outcome, you need to contact a specialist in a timely manner; It is recommended to undergo therapy in a hospital.
Watery eyes and contact lenses
Sometimes, when using lenses that have expired, incorrect selection, or poor quality care for them, tearing may occur. It is explained:
- microtraumas that appear on the conjunctiva due to deformed lenses;
- infection;
- an allergic reaction to the components of soft contact lens care products, or to the components of the blister solution (even for daily contact lenses);
- constant eye strain due to incorrectly selected diopters;
- irritation from low-quality lenses or lens care compositions.
Ophthalmologists will help you avoid these unpleasant situations: obtain a Bausch&Lomb® certificate for vision diagnostics, which is carried out under optical conditions, and the selection of free contact lenses.
The doctor will tell you how to wear contact lenses, how to properly clean them, when you need to replace the lenses with new ones, and, of course, what to do if your eyes water when using them.