Causes of development of impaired coordination of movements
It is important to understand that coordination disorder can manifest itself not only in neurological pathologies and as a side symptom accompanies various diseases. There are many reasons for it:
- cerebrovascular insufficiency, focal cerebral infarctions or strokes;
- brain or spinal cord injuries;
- brain tumors;
- demyelinating diseases (eg, multiple sclerosis);
- congenital malformations of the brain or its vascular system;
- hydrocephalus (both congenital and acquired);
- neuroinfections;
- endocrine disorders;
- various poisonings;
- alcoholism;
- deficiency of vitamin B12 in the body.
How does a lack of coordination of movements manifest itself?
Clinically and due to development, there are the following forms:
Sensitive ataxia. It occurs when the posterior columns and roots of the spinal cord, peripheral nerves, thalamus, and parietal cortex are damaged. It appears like this:
- patients completely lose balance and coordination of movements if they close their eyes;
- Patients with this type of ataxia are characterized by a “stamping” gait - when they step, they strongly bend their legs at the knee and hip joints;
- patients feel as if they are stepping on something soft, while losing the sense of space and direction of movements.
Cerebellar ataxia. This type of coordination disorder develops when the structures of the cerebellum (vermis, peduncles and hemispheres) are damaged and manifests itself as follows:
- the patient leans more towards the affected side when performing the Romberg test and when walking;
- the patient makes uncoordinated and chaotic movements on the side of the lesion;
- with this type of lesion, speech suffers - it becomes inhibited;
- handwriting may also change;
- as with sensitive ataxia, the patient makes all movements under visual control.
Vestibular ataxia. It develops when the brain structures that are responsible for balance are damaged - the brainstem nuclei, labyrinth and vestibular nerve. Vestibular ataxia manifests itself as follows:
- severe dizziness up to nausea and vomiting, which intensifies when the patient turns his head;
- when walking, patients stagger from side to side;
- Such people also develop horizontal nystagmus - involuntary twitching of the eyes from side to side.
Cortical ataxia. It is caused by pathology of the cerebellopontine tract and damage to the frontal lobe and is expressed in the following symptoms:
- instability when walking, especially when turning;
- if the lesion is severe, then patients develop impairments in the ability to stand (astasia) and walk (abasia);
- Cortical ataxia is characterized by mental disorders and sensory organ functions;
- In patients, the grasping reflex may disappear.
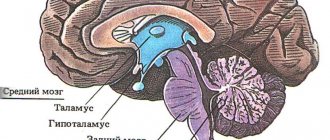
Brain
Medulla
is a direct continuation of the spinal cord
- responsible for breathing, blood circulation, digestion;
- contains reflexes of coughing, sneezing, swallowing, sucking, vomiting, etc.
Cerebellum
responsible for coordination of movements.
Midbrain
- responsible for indicative reactions to light and sound;
- Provides skeletal muscle tone.
Diencephalon
regulates metabolism in the body, coordinates physiological processes, maintains homeostasis (constancy of the chemical composition and temperature of the internal environment) in two ways:
- through the pituitary gland (with the help of neurohormones) controls all other endocrine glands of the body;
- participates in the formation of feelings of hunger, cold, thirst, etc., thus influencing behavior.
Large hemispheres
the forebrain has sulci and gyri (like the cerebellum)
- in the front part of the frontal lobe there is a zone of logical thinking
(it is better developed in humans than in other animals); - in the back of the frontal lobe there is a motor zone of the body
(responsible for voluntary movements); - in the lower part of the frontal lobe, on the border with the parietal and temporal lobe, there is a speech zone
(it is present only in the human brain, other animals do not have it); - in the anterior part of the parietal lobe there is a sensitive area of the body (zone of musculocutaneous sensitivity)
; - the occipital lobe contains the visual area
; this is the central part of the visual analyzer, here the analysis and recognition of visual images takes place; - in the temporal lobe there is a hearing zone
, this is the central part of the auditory analyzer.
You can also read
DETAILED SUMMARY: Brain
ASSIGNMENTS OF PART 2 OF THE USE ON THIS TOPIC
Part 1 tasks
Choose one, the most correct option. In what lobe of the cerebral cortex are the higher centers of the skin analyzer located?
1) frontal 2) temporal 3) occipital 4) parietal
Answer
4
Choose one, the most correct option. Regulation and coordination of physiological processes occurring in internal organs is ensured by
1) diencephalon 2) midbrain 3) spinal cord 4) cerebellum
Answer
1
Choose one, the most correct option. In humans, compared to mammals, there is a strong development of the next lobe of the cerebral cortex
1) frontal 2) parietal 3) occipital 4) temporal
Answer
1
Choose one, the most correct option. In what lobe of the cerebral cortex is the center of skin-muscular feeling in humans located?
1) occipital 2) temporal 3) frontal 4) parietal
Answer
4
Choose one, the most correct option. Regulation and coordination of physiological processes occurring in internal organs is ensured by
1) diencephalon 2) midbrain 3) spinal cord 4) cerebellum
Answer
1
Choose one, the most correct option. The medulla oblongata of the human brain does not regulate
1) respiratory movements 2) intestinal motility 3) heart contractions 4) body balance
Answer
4
Choose one, the most correct option. When cells in the temporal lobe of the cerebral cortex are destroyed, a person
1) gets a distorted idea of the shape of objects 2) does not distinguish between the strength and pitch of sound 3) loses coordination of movements 4) does not distinguish between visual signals
Answer
2
Choose one, the most correct option. The final analysis of the height, strength and nature of sound in a person occurs in
1) inner ear 2) auditory nerve 3) eardrum 4) auditory cortex
Answer
4
Choose one, the most correct option. Voluntary human movements provide
1) cerebellum and diencephalon 2) midbrain and spinal cord 3) medulla oblongata and pons 4) cerebral hemispheres of the forebrain
Answer
4
BRAIN Determine the sequence of locations of the brain sections, starting with those closest to the spinal cord. Write down the corresponding sequence of numbers.
1) cerebral hemispheres 2) medulla oblongata 3) diencephalon 4) midbrain
Answer
2431
MEDLINE - CEREBELLUM - INTERMEDIUM Establish a correspondence between the characteristics and parts of the brain: 1) diencephalon, 2) medulla oblongata, 3) cerebellum. Write numbers 1-3 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) is located directly above the spinal cord B) ensures accuracy and coordination of movements C) contains the center of respiration D) has grooves and convolutions E) includes the hypothalamic-pituitary system E) the centers of hunger, thirst, and satiety are located
Answer
232311
OBLEGATE - MIDDLE - INTERMEDIATE Establish a correspondence between the characteristic and the part of the human brain: 1) middle, 2) intermediate, 3) oblong. Write numbers 1-3 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) contains centers of orientation reflexes B) contains the respiratory center C) is involved in the regulation of body temperature D) is located above the pons E) contains centers of protective reflexes (sneezing, coughing) E) is responsible for the feeling of hunger and satiety
Answer
132132
OBLADUS - INTERMEDIATE Establish a correspondence between the processes and parts of the brain that regulate these processes: 1) intermediate, 2) oblongata. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) regulation of blood glucose levels B) preservation of smooth muscle tone C) control of body temperature D) humoral regulation E) direct regulation of heart rate E) ensuring intestinal motility
Answer
121122
OBLEGNADE - FOREIGN 1. Establish a correspondence between the structural features and functions of the human brain and the section for which they are characteristic: 1) medulla oblongata, 2) forebrain. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the correct order.
A) contains the respiratory center B) the surface is divided into lobes C) perceives and processes information from the senses D) contains (includes) the vasomotor center E) contains the centers of the body’s defense reactions - coughing and sneezing
Answer
12211
2. Establish a correspondence between the function of a part of the human nervous system and the part that performs this function: 1) medulla oblongata, 2) cerebral cortex. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the correct order.
A) regulates the activity of the cardiovascular system B) is responsible for the development of conditioned reflexes C) contains the respiratory center D) analyzes visual and auditory stimuli E) triggers the cough and sneeze reaction E) controls fine finger movements
Answer
121212
INTERMEDIUM - LARGE HEMISPHERES Establish a correspondence between the function of the human forebrain and the section that performs this function: 1) the intermediate brain, 2) the cerebral hemispheres. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) control of complex muscle movements B) analysis of all incoming information C) regulation of body temperature D) ensuring the constancy of the internal environment of the body E) control of mental and speech activity E) regulation of feelings of thirst, hunger and satiety
Answer
221121
1. Select three correctly labeled captions for the picture “Divisions of the Brain.” Write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) diencephalon 2) medulla oblongata 3) midbrain 4) pons 5) cerebral hemisphere 6) cerebellum
Answer
356
2. Choose three correctly labeled captions for the picture depicting the human brain. Write down the numbers under which they are indicated.
1) cerebral hemisphere 2) pons 3) cerebellum 4) hypothalamus 5) medulla oblongata 6) diencephalon
Answer
136
Establish a correspondence between the characteristics and the parts of the brain indicated in the figure by numbers 1 and 2. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) controls salivation B) ensures coordination of movement C) gray matter is located outside, white matter is inside D) the breathing center is located E) controls the balance of the body E) the centers of protective reflexes (vomiting) are located
Answer
122121
Establish a correspondence between the functions and parts of the human brain, indicated in the figure by numbers 1, 2. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) forms neurohormones B) maintains the tone of skeletal muscles C) controls the rotation of the head to a sharp sound D) forms feelings of hunger and satiety E) regulates metabolism
Answer
12211
Establish a correspondence between the characteristics and parts of the human brain, indicated in the figure by numbers 1 and 2. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) contains inhalation and exhalation centers B) is involved in thermoregulation C) is involved in the formation of the feeling of thirst D) controls cardiac activity E) regulates the feeling of hunger and satiety
Answer
12212
Establish a correspondence between the structural features and functions and lobes of the cerebral cortex, indicated in the figure by numbers 1 and 2. Write numbers 1 and 2 in the order corresponding to the letters.
A) is responsible for the perception of light signals B) the auditory sensitivity zone C) is responsible for the perception of sound signals D) if it is damaged, a person goes blind E) the visual zone
Answer
21122
© D.V. Pozdnyakov, 2009-2020
Treatment of ataxia
In treatment, neurologists are greatly assisted by establishing the cause and mechanism of development of the disease. In the treatment of motor coordination disorder, a complex of drug support, physiotherapy and a set of exercises is effective.
Often the main groups of drugs are nootropics, tonics and vitamins. The course of treatment and its volume is determined by the doctor after establishing the cause of the development of ataxia exclusively on an individual basis.
Surgery can also help, for example, removing a tumor or hematoma of the brain, ensuring the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid in case of hydrocephalus, and so on.
Physical rehabilitation increases the chances of maximum recovery and return to normal. It should include sets of exercises with the following components:
- static and dynamic balance;
- prevention of contracture formation;
- general coordination of movements
Prevention of ataxia
The main measures to prevent the disease are timely prevention and treatment of diseases and conditions that cause it.
Development of coordination and vestibular apparatus in a child. Generalization
Good afternoon, dear parents!
“Welcomes you to my blog.
As a manufacturer of educational toys and products for children, our main goal is to help children around the world grow up healthy and happy. Our toys, products for children and play complexes are absolutely safe for children’s health, promote proper physical development and bring real children’s happiness.” This is the first article in a series of materials on the development of such functions of the child’s body as coordination and the vestibular apparatus. From late stages of pregnancy until entering the 1st grade of school. In it we will look at key aspects of developing a sense of coordination, the development of the cerebellum, talk about exercises that help develop coordination and the vestibular system, and also recommend toys that will help your baby develop properly.
Physiological process of cerebellar development
The formation of a child’s physiological coordination mechanism begins in the womb and continues until the human skeleton stops growing, and this is approximately 18-20 years old. In this process, the most important role is played by the development of the cerebellum, which begins to actively grow from about 6 months from birth. At the age of 1 year and 3 months, the active development of the cerebellum begins to gradually weaken. Full development of the child's cerebellum ends at approximately 5 years of age.
The cerebellum is a segment of the human brain located in the occipital region of the skull. The cerebellum consists of two sections - an ancient section or “worm”, and an evolutionarily later, more recent section. The ancient department is responsible for processing signals from the vestibular system, which supports balance and coordination of movements. The new department is responsible for communication with the cerebral hemispheres. Intensive growth of the ancient part of the cerebellum occurs in late pregnancy. Therefore, it is important to avoid premature birth.
The process of development of the cerebellum after birth is directly reflected in the physical skills of the baby. The period of active development can be roughly divided according to external signs into five stages:
- age 5-6 months - the child begins to sit up;
- age 8-9 months - the child crawls;
- age 9-10 months – the child is already standing on his feet;
- age 11-12 months – the child takes his first steps;
- By the age of one and a half years, the child already walks confidently, and sometimes even runs.
It is important to remember that there are cases of individual development of the cerebellum - in such cases, the child may be slightly delayed or, on the contrary, ahead of the usual deadlines. In addition, there are times when a child skips the crawling stage. In general, by the age of one and a half to two years, the child’s cerebellum successfully copes with all basic functions.
The development of the cerebellum at the age of 3 to 6 years moves to a qualitatively new stage; the child already masters all basic motor functions and begins to improve them qualitatively. It is from this age that the child becomes able to perform fundamentally new tasks and the learning process accelerates.
In parallel with the development of the cerebellum, the vestibular apparatus, the basis of human upright walking, also develops in a child aged 6 months and older. The vestibular apparatus is located in the inner ear and consists of two membranous sacs (round and oval), three semicircular canals. The development of this particular organ allows the child to take his first steps in life. Disturbances in the development of the vestibular apparatus lead to developmental delays, a “drunken gait,” and underdevelopment of the cerebellum leads to hyperactivity and other undesirable consequences and syndromes for the child.
Games and exercises to develop children's coordination
All types of exercises and games to develop coordination in a child are active and physical. Games can be divided into two types: static and dynamic. Static games are aimed at developing the ability to maintain a clearly fixed body position, while dynamic games, on the contrary, are aimed at developing the ability to quickly, smoothly, or, conversely, dramatically change one’s position in space.
First of all, let's look at the simplest exercises to develop coordination. These are very simple, but at the same time very effective exercises:
- Easy to maintain balance. Invite your child to walk on a long stick or branch lying on the ground, without touching the ground with the sole. Also, a curb or curb along the sidewalk at the entrance of your house is perfect as a “sports equipment”. Daily use of this simple technique while walking with your child will perfectly develop an even gait, the ability to maintain balance and control the body’s center of gravity in more complex exercises.
- Maintaining balance on a moving surface. The meaning and mechanics of the exercise are the same as in the simple balance exercise with one significant difference - instead of a board or curb, you must use a swinging or moving surface. A lying log or a thick pipe that sways slightly transversely from side to side is ideal. In a more complicated version, a log or pipe can be suspended at a small height and sway not only transversely, but also longitudinally. Perhaps the nearest playground has something similar or a small suspended bridge, which is also perfect for training coordination.
- Exercise with a large ball "Fitball". Exercises with a large ball develop coordination very well. You can lie on your back or stomach on it, let go of your arms and legs, trying not to roll off the ball. You can try to sit on it without touching the floor with your feet. Such exercises have a significant impact on improving coordination and physical dexterity.
- Jumping on a trampoline is an excellent exercise for advanced coordination and vestibular training for both children and teenagers. Rhythmic jumping with smooth acceleration and landing promotes the development of the inner ear and cerebellum. In addition, trampolining trains the central nervous system and strengthens the musculoskeletal system.
- Swings and slides are the key, most important and oldest way to train children's coordination. The first swing for a child begins immediately after birth - this is his rocking crib. Then the rocking stroller. When your child has not yet begun to walk, you can already put him in a special children's swing or ride him down a children's slide. These exercises, instilled from childhood, will protect the child from a fear of heights, accustom him to frequent changes of body position, and lay important foundations for the development of coordination and the vestibular apparatus.
You can purchase swings, slides, as well as full-fledged play complexes in the Pilsan online store, install them on your lawn, in your country house, or even in a playroom in a city apartment, and be sure of the proper development of your children’s coordination and vestibular apparatus.
After the basic exercises, we would like to briefly talk about physical games that develop coordination and the vestibular apparatus. Such games can be divided into two types - static and dynamic.
Static games are intended primarily for training freezing, balancing and keeping the body in balance in a variety of poses. Such games include: “Music of Stops”, “The Sea is Troubled”, “Statues”, “Stunler-Stop”, “Knockout” and others.
Dynamic games, on the contrary, are designed to train the vestibular system in conditions of constant changes in body position. These games are usually collective, for a large number of children. In such games, normal, correct development of the child’s coordination occurs. Dynamic games include: “Mice dance in a circle”, “Sunshine and rain”, “Stream”, “Find yourself a mate” and many others.
We will consider a large number of games for physical development in detail in a separate article.
Toys for developing child coordination
For the full development of coordination, it is necessary to provide the child with toys that contribute to his development. The minimum set of toys for developing coordination includes a rocking chair and a tolokar or any other gurney. The recommended set consists of a whole set of toys and accessories for different ages:
- Walkers and jumpers – suitable for babies aged 6 months to one year. Walkers help you put your feet on the floor faster and speed up the transition from crawling to standing and walking. Jumpers accelerate the development of the vestibular apparatus. Rhythmic smooth vertical movements contribute to the proper development of the cerebellum.
- Rocking chairs and rocking chairs are necessary for children from 1 year of age. As soon as your baby has learned to hold his back straight and sit, feel free to put him on a rocking horse. Daily rhythmic rocking will accelerate the development of the ancient part of the cerebellum and vestibular apparatus.
- Sports equipment - for children from 2 years old. As soon as your baby starts running, feel free to purchase a variety of sports equipment. Supplies for football, basketball, bowling, hoops and any other sports supplies.
- Dry pool – for children from 2 years old. Playing in a dry pool significantly accelerates the development of spatial orientation.
- Tolocars (gurneys) – necessary for children over 2 years old. The first own transport for your baby. Helps develop coordination and musculoskeletal system.
- Velomobiles – for children from 3 years old. A universal pedal children's transport that promotes the comprehensive physical development of the child.
- Swings and play complexes - for children from 3 years old. They promote not only physical but also psychological development, as they are ideal for role-playing games.
A wide range of toys and products for children can completely remove the issue of the full development of coordination and the vestibular system of a child from the moment of birth until entering school.
Frequently asked questions about motor coordination disorders
Which doctors treat motor coordination disorders?
Loss of coordination is treated by a neurologist.
Possible diseases associated with symptoms of incoordination?
Ataxia can develop with focal diseases of the brain, multiple sclerosis, deficiency of vitamins B12 and B1, poisoning with chemicals or alcohol, central nervous system infections, hydrocephalus, hypothyroidism.
What could be the consequences if ataxia is not treated?
If ataxia is not treated, it may lead to injury in the first place, and subsequently to the development of respiratory and heart failure and disability.