The most common causes of pain in the temples:
- Constriction of cerebral vessels;
- Disruptions in the cerebral circulatory system;
- Development of infectious diseases;
- Migraine;
- Age-related changes in the body;
- Alcohol or drug intoxication of the body;
- Pinched nerve endings;
- Changes in hormonal levels;
- Inflammation of the walls of the temporal artery;
- Incorrect and unbalanced diet;
- Various pathologies of the temporomandibular joint, etc.
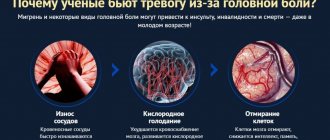
Other consequences that may occur after prolonged pain in the temples include visual and hearing impairment, mental disorders and even stroke. Therefore, it is important to immediately consult a doctor if you experience pain in your temples. The specialist will help determine the original source of the problem and create a course of treatment taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Why does pain occur in the temples?
Physiological reasons
A dull pressing pain in the temples is observed when staying in a stuffy room. If a person cannot go out into the fresh air, the painful sensations increase, sometimes becoming sharp and pulsating. In some people, the symptom is triggered by strong feelings, most often anxiety and fear. May occur against the background of stressful situations. Another possible cause is starvation when trying to quickly lose weight, following strict diets, or eating disorders.
Migraine
The pain is pressing, throbbing, one-sided. The zone of maximum pain is located in the projection of the temple, eye or forehead. Sometimes an aura or prodrome is observed in the form of weakness, impaired ability to concentrate. It is typical for the affected side to change from one attack to another. Migraine symptoms are aggravated by bright light, loud sounds, and any physical activity. Patients try to “lie down” in solitude, silence and darkness.
Cluster headache
Pain occurs during periods of exacerbation, lasting from 2 weeks to 2 months. Appear suddenly, reaching a maximum after 1-3 minutes. The attack lasts from 15 minutes to 1 hour, less often up to 3 hours. Episodes occur at one time, often at night, and can be repeated from one per day to two to four (sometimes eight) during the day. Painful sensations are one-sided, more often on the left.
Localized in the eye, radiating to the temple, ear, cheek and teeth, extremely sharp, unbearable, stabbing or burning. Accompanied by nasal congestion, facial and conjunctival hyperemia. Described by patients as an “eye rupture” or “stabbed in the eye.” Photophobia, nausea and vomiting are observed in 30% of cases. The patient is agitated and rushes about, since physical activity somewhat reduces the intensity of the pain.
Tension headache
The symptom is mild or moderate. The headache is bilateral, non-pulsating, squeezing or squeezing the head with a “hoop”, especially noticeable in the temple area. There is no dependence on physical activity, no nausea or vomiting. The duration of the attack ranges from half an hour to 1 week. Pain increases with strong emotions and decreases with emotional relaxation.
Pain in temples
Primary and symptomatic hypertension
Along with essential hypertension, there are more than 50 diseases that cause high blood pressure. An increase in blood pressure, regardless of etiology, is accompanied by pain in the temples and back of the head. Patients complain of tinnitus, spots before the eyes, shortness of breath, chest pain, restlessness, or a feeling of fear. An external examination may reveal hyperemia of the skin. The symptom is observed in the following pathologies:
- Kidney diseases
: pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, hypoplasia, polycystic disease, amyloidosis, urolithiasis, tumors, diabetic nephropathy, renal tuberculosis. - Endocrine disorders
: pheochromocytoma, Cushing's disease and syndrome, primary aldosteronism. - Pathologies of large vessels
: coarctation of the aorta.
Hydrocephalus
Due to an increase in the amount of fluid in the cerebrospinal fluid system with hydrocephalus, intracranial pressure increases. Along with pain in the temples and throughout the head, intracranial hypertension is manifested by disturbances of consciousness, nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, and sometimes convulsive seizures. The symptom is detected in conditions such as:
- developmental defects: Chiari anomaly, Dandy-Walker syndrome, stenosis of the Sylvian aqueduct;
- intrauterine infections and birth injuries;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- inflammatory processes: encephalitis, meningitis, arachnoiditis;
- vascular pathologies: hemorrhagic stroke, intraventricular hemorrhage;
- neoplasms: colloid cysts, intracerebral ganglioneuromas, germinomas, astrocytomas, etc.
Traumatic brain injury
Headache is a constant symptom of TBI and is observed with injuries of any severity. Accompanied by dizziness, nausea, vomiting, amnesia. Impaired consciousness, paresis, decreased sensitivity, and other manifestations are possible. At first, the pain is usually diffuse. During the recovery period, pain in the temporal areas sometimes prevails.
Temporal arteritis
Caused by autoimmune damage to the temporal artery. Often occurs after viral infections. Horton's disease develops in middle-aged and elderly patients. Accompanied first by aching, then by piercing, burning pain in one or both temples, increasing over 2-3 weeks. The symptom worsens with chewing and talking. Complemented by loss of appetite, sweating, hyperthermia, weight loss, sleep disturbances, myalgia, arthralgia.
Intoxication syndrome
Pain in the temples is one of the possible variants of headache with intoxication syndrome against the background of bacterial and viral infections, local purulent processes. It can be dull, squeezing, aching, pulsating. Increased body temperature, weakness, weakness, dizziness, pain in joints and muscles are observed. Other signs are determined by the cause of intoxication.
Trigeminal neuralgia
Prosopalgia is paroxysmal in nature and is a series of intense, shooting, burning pain impulses that resemble an electric shock and spread from the lateral surface to the center of the face. The duration of the episode is up to two minutes, the attacks are repeated several times. When the nerve is completely involved, the entire half of the face suffers; when the second branch is affected, the pain is localized in the temple area, the outer corner of the eye, the adjacent part of the cheek, and the upper lip.
Damage to the temporomandibular joint
TMJ dysfunction is a problem that can be caused by the following factors:
- Dentofacial pathologies
: trauma, malocclusion, dental defects, poor-quality prosthetics, congenital anomalies. - Muscle overstrain
: bruxism, tonic spasm, overload of masticatory muscles, high speech load. - Psychological factors
: prolonged neuropsychic stress.
Typical symptoms include pain in the temples, eyes, ears, prosopalgia, headaches, difficulty and clicking when opening the mouth. Possible dizziness, sleep disorders, dysphagia, glossalgia, sleep apnea syndrome.
Other reasons
Sometimes hormonal changes become a provoking factor. Girls may experience pain in their temples during the onset of menstruation. Some mature women note the onset of symptoms during menopause. Another possible reason is intoxication. Pain in the temple area is observed in a state of alcoholic intoxication, with an overdose of certain medications, or carbon monoxide poisoning.
Whiskey hangover: which variety is less dangerous?
In order to know which bottle is best to buy in a store, you should ask about the brand and the country where the product was manufactured. Manufacturers of this product offer a huge range of products, which differ in the quality of the raw materials used, the aging period and composition. The most valuable trademarks are considered to be Scottish ones, the quality of which is checked by authorized government bodies at the legislative level. Therefore, buyers know that they are purchasing a legal, certified product, for which they do not mind paying money, but the hangover will practically not make itself felt.
Products from brands from other countries most often contain additional flavorings and harmful additives. The most harmless varieties are those aged for many years due to the fact that most of the fusel oils go into the tree.
Diagnostics
The diagnostic program is compiled by a neurologist. If necessary, a maxillofacial surgeon, infectious disease specialist, and other specialists are involved in the examination. To clarify the pathology, the following procedures may be prescribed:
- Questioning and external inspection
. During the conversation, the doctor finds out the time and circumstances of the onset of the symptom. Asks about the nature and duration of pain, other manifestations, as well as the presence of similar symptoms in blood relatives. Upon examination, increased blood pressure, skin hyperemia, renal edema, signs of endocrine pathology and infectious diseases may be detected. - Neurological examination
. With hydrocephalus, vestibular and cerebellar ataxia and nystagmus are possible. In patients with TBI, general cerebral and focal symptoms are determined. With trigeminal neuralgia, pain in trigger points is detected, with fascicular cephalgia - rhinorrhea, hyperhidrosis, drooping eyelid, conjunctival injection (during an attack). - Neuroimaging
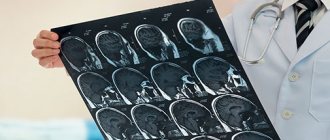
. X-ray, CT, MRI, MRA and ultrasound techniques (duplex, Dopplerography) are informative for hydrocephalus, traumatic injuries, and determining the genesis of compression of the trigeminal nerve. They help to establish the cause of hydrocephalus and assess the severity of vascular damage in patients with arterial hypertension. - Lumbar puncture.
Indicated to clarify the cause of increased intracranial pressure, it is performed as part of an examination for traumatic brain injuries and neuroinfections. The resulting cerebrospinal fluid is sent for microscopic, microbiological, and PCR studies.
In addition, ultrasound of the kidneys and endocrine organs, radiography and computed tomography of the TMJ, laboratory tests to assess the condition of the body, determine the causative agents of common infections and purulent processes can be performed. For migraine, cluster cephalalgia, tension pain, additional studies are not very informative; differential diagnosis, carried out on the basis of clinical signs of the disease, comes to the fore.
Neurologist consultation
Examination methods
Accurate and timely diagnosis is the main condition for recovery from headaches. After examination, the therapist will prescribe additional examination techniques that will help determine the exact cause of the symptoms. Depending on the results of the initial examination and medical history, the following methods may be required:
- blood test to determine inflammatory processes, identify viral and bacterial pathogens of various diseases;
- Dopplerography - examination of blood vessels using ultrasound with the addition of a contrast agent, used to diagnose the arteries of the neck and head;
- MRI, CT are the preferred methods for diseases of the cervical spine and are the most informative in cases of suspected vascular pathologies and neoplasms in the brain;
- electrocardiography is one of the basic methods of examining the heart, which consists of determining the heart rhythm;
- specific blood tests that will determine the level of hormones, vitamins and other substances;
- examination by an ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, neurologist.
The Clinical Brain Institute has modern equipment for diagnosing headaches. If necessary, inpatient monitoring of the patient may be offered to monitor various indicators around the clock.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
The plan of conservative measures is determined by the etiology of the pain syndrome:
- Migraine
. To relieve attacks, simple and combined analgesics are used, and sometimes therapeutic blockades are performed. To prevent new paroxysms, antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and psychotropic drugs are used. - Tension headaches
. Medicinal methods include NSAIDs, antidepressants, muscle relaxants, occipital nerve blocks, non-medicinal methods - massage, manual therapy, acupuncture, biofeedback, relaxation techniques. - Bundle cephalalgia
. Paroxysms are eliminated with the help of triptans; in case of intolerance, oxygen inhalations are prescribed, and local anesthetics are injected into the nasal cavity. Calcium channel blockers are effective for preventive purposes. - Hydrocephalus
. In the case of an acquired variant of the pathology, the causative disease is treated and diuretics are prescribed. - Arterial hypertension
. Etiopathogenetic therapy is carried out. It is recommended to control blood pressure and take antihypertensive drugs. - Temporal arteritis
. The basis of drug therapy is glucocorticoid hormones. If there is no result, they switch to cytostatics. To eliminate symptoms, vasodilators, anticoagulants, and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. - Trigeminal neuralgia
. Anticonvulsants are considered the first line treatment. Additionally, antispasmodics, microcirculation correctors, antihistamines, and therapeutic blockades are used. - TMJ dysfunction
. It may be necessary to eliminate dental pathologies. Soft food is recommended. Pain is reduced with the help of NSAIDs, antidepressants, botulinum therapy, glucocorticosteroid blockades, massage, and physiotherapy.
Varieties of grain strong drink: what you need to know
There are only 3 types of intoxicating drink.
- Malt is made from malted barley. The distillation process is often performed in special cubes, which are shaped like an onion. If such a product is produced in one place, it is usually called “single malt”. Otherwise, raw materials from different harvests or aged in different barrels may be used to produce the final product. There is also malt whiskey, in which there are 2 varieties of the drink.
- In its characteristics and taste, the grain is very similar to vodka, which does not have a specific smell or color. It goes on sale only to become an additional component for producing blended whiskeys.
- Mixed - it contains malt and grain alcohol, to which alcohol (corn, wheat, etc.) is also added. The list of elements can reach 40 items. Such a large number of impurities is taken in order to achieve the desired aroma and taste.
In addition, the intoxicating drink may differ from each other by the grain from which it is produced. Bourbon is a whiskey made from corn.
The effect of alcohol on the nervous system and brain
Ethanol is found in alcoholic beverages in varying quantities. It is what causes the effects that appear after drinking alcohol: slight dizziness, mood changes. However, it poses a danger to the body because it turns into toxic metabolites. It is absorbed into the blood through the mucous membranes of the digestive tract, after which it undergoes a complex transformation path:
- migrates with the bloodstream to the liver, where, under the influence of the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase, it is converted into ethanal (acetaldehyde);
- ethanal reacts with the enzyme aldehyde dehydrogenase, resulting in the formation of acetate;
- acetate, with the participation of liver enzymes, is converted into acetyl-coenzyme-A, which enters the bloodstream and distributes throughout cells and tissues.
Acetyl-coenzyme-A is a dangerous toxin that can build up in the liver, muscles and soft tissues, and also reach the brain. Here it damages nerve cells and destroys neural connections. In the early stages, as well as after a single dose of alcohol, symptoms include headache, dizziness, nausea, and poor attention. However, with regular exposure to ethanol, the consequences will be more severe.
It is important to understand that for the development of alcoholism, it is enough to regularly drink small doses of alcohol. Alcoholic liver disease in men occurs if you take 30 g of ethylene daily - this amount corresponds to 75 g of vodka or 0.6 liters of beer. For women, the toxic dose is 20 g. The liver cannot cope with daily stress, so its inflammation develops - alcoholic hepatitis. The disease can be asymptomatic and detected only in advanced stages, at the first signs of cirrhosis.
Poisoning
When figuring out why the left temple hurts, you should analyze the last few days: how the diet changed, what drugs were taken, what harmful conditions the person was in. Perhaps soreness indicates poisoning. Intoxication often causes pain in the temple on the left and cheekbone on the same side of the head. If you have acute and strong sensations that do not go away for hours, you should consult a doctor.
An additional symptom of acute intoxication is a feeling of fullness in the head. When you touch the sore area, it feels as if a bruise has formed there. The patient feels slightly nauseous and sometimes vomits. The head is dizzy, the person feels weak. In some cases, this indicates influenza and other diseases, sometimes – to poisoning of a different nature.
Features of the pathology
Pain in the left temple is a problem for which you need to consult a neurologist. Such pain syndromes may recur infrequently or be chronic. Moreover, the pain spreads not only in the temporal part of the head, but also radiates to the eye and ear. The presented pathological condition recurs periodically in almost 60% of the population of our planet.
The problem is that not every person with such symptoms seeks medical help, which can lead to the development of diseases that are difficult to treat. In addition, serious complications can result from improper treatment of the disease.
Therefore, if a person has severe acute pain in the left temple area, then he should contact a neurologist and undergo a thorough examination.
A few facts about tape
Surely, every lover of aromatic alcoholic drinks knows that whiskey produced in Scotland is usually called “scotch”. In fact, this type of alcohol is not used in the country. Many tourists who come to the country for the first time may hear that locals, when ordering “scotch,” simply say “whisky” to the bartender. This word implies a national strong drink.
All alcohol produced under this name must meet international quality standards and regularly undergo all levels of testing approved by the English Parliament at the end of the 20th century. The main feature that is taken into account during testing is the absence of additives, impurities (except for coloring with a caramel flavor), and the use of only distilled water.
Control authorities also monitor production lines. The drink must be infused only in oak barrels. The minimum period is three years plus 1 day. At the first stage of production, whiskey must have a strength of no more than 94.8%. After which the strength indicators decrease. The liquid is poured into the prepared bottles at forty degrees. To get real scotch, you must use only malted barley as the main raw material. At the next stages of its processing, the material is converted into wort by adding yeast.
The quality of bourbon was written about in the mid-20th century. The articles said that drinkers might be upset by the fact that the drink was aged less than the stated period. But they will not accept that whiskey contains dyes and additives.
So you've learned why adulterants make hangovers worse, making them longer and more severe. If whiskey has a composition similar in its components to the content of vodka, then it will be able to be absorbed much faster and better. But do not forget that vodka can also be bad if it contains artificial additives.