Ultrasound diagnostics is one of the safest and most effective ways to detect various diseases of internal organs. This technique is used in various fields of medicine, including assessment of the condition and possible pathologies of blood vessels. In this case, Doppler ultrasound or ultrasound is performed, which is used to examine the neck and head. Early diagnosis allows you to choose gentle and effective treatment methods and prevent the development of complications. First you need to understand what an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the head and neck shows, why this method is effective in diagnosing many diseases.
The Doppler ultrasound effect is based on the ability of ultrasound waves to be reflected from blood cells. As a result, electronic impulses appear that appear on the device screen in the form of images of veins and arteries with blood flow.
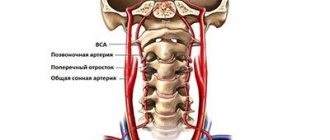
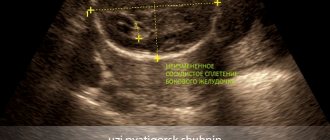
This ultrasound examination allows you to assess the condition of the large arteries that supply the brain, carotid and vertebral arteries, determine the intensity of blood flow, and also identify traces of obstruction.
How is Dopplerography performed?
This examination is carried out in the presence of certain symptoms. Preliminary preparation is necessary so that the results of the ultrasound examination give an accurate picture of the patient’s condition.
There are two types of procedure:
- Transcranial. The sensor is installed on the skull bones in those places where they are thinnest. The procedure gives an accurate picture of the vessels located directly in the brain.
- Extracranial. The technique is used to examine large vessels passing through the neck (carotid arteries, jugular veins, etc.). The sensor is located at each site separately.
Types of ultrasound examination
Doppler ultrasound (CDS - color duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries) is indicated for patients with a wide variety of complaints. The method is used for different organs of the human body:
- Ultrasound Doppler Doppler (CDS) of neck vessels. They scan those arterial and venous branches of vessels that are located outside the cranium and are responsible for normal nutrition of the brain and the outflow of blood from it. The condition of the carotid, subclavian, vertebral arteries, and brachiocephalic trunk is assessed.
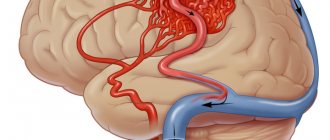
- Ultrasound Doppler Doppler (CDS) of the brain. Provides information about the condition of extracranial blood vessels (located outside the skull), and intracranial vessels (located inside the skull).
- Ultrasound Doppler Doppler (CDS) of the arteries of the lower extremities. During the procedure, it is possible to identify pathologies of the vessels of the extremities and other disorders in the blood flow system.
- Ultrasound Doppler Doppler (CDS) of the veins of the lower extremities. Used to assess the level of patency of deep and superficial veins, determine the functional state of venous valves, and diagnose typically located valves of perforating veins.
- Neurosonography. It is used in children from birth to one year to determine the condition of the brain, possible pathological changes, the size of some of its parts, as well as formations - cysts, hematomas.
The procedure is carried out in real time, the conclusion is immediately issued upon completion.
Indications for the procedure
Doppler sonography is indicated in the following cases:
- Problems with coordination and other symptoms indicating a malnutrition of the brain (the patient is dizzy, has tinnitus, etc.).
- Unstable heart rhythm.
- Hypertonic disease.
- Transient ischemic attacks.
- IOP.
- Previous stroke or heart attack.
- There are suspicions of atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes.
- Fatigue quickly for no apparent reason.
- Cervical osteochondrosis.
This procedure is also indicated if heart surgery is to be performed, if there are pulsating formations in the neck, or if thrombosis is suspected. In children, it is performed in case of serious postural problems and delayed development of the child.
How is it carried out?
Doppler ultrasound is prescribed for suspected vascular pathology. The study is carried out in an office equipped with a modern ultrasound scanner with special sensors. The procedure is completely painless and does not cause discomfort. The doctor applies a special gel to the area of study and uses a sensor to process control points proportional to the projections of the vessel being examined.
The sensor processes the signals and sends them to a computer, which converts them into graphic images and displays them on the monitor. The procedure can last 30-60 minutes, depending on the volume and area of research. The following indicators are assessed:
- wall thickness and diameter of the vessel;
- consistency of vascular valves;
- nature of blood flow;
- resistive and ripple index;
- maximum and minimum speed of blood flow.
15-20 minutes after the ultrasound examination, the patient receives a medical report on a special form. It is also possible to record the result to a flash drive or disk.
Are there any contraindications?
Ultrasound waves are absolutely safe for humans, so there are no special contraindications to this type of ultrasound. The only exception is a violation of the integrity of the skin. The procedure involves contact of sensors with the head or neck, so the examination is postponed until the wound heals.
However, there are a number of special cases that make duplex examination of blood vessels difficult:
- cardiac arrhythmia, which changes the speed of blood circulation through healthy arteries and veins;
- the area under study is hidden under bone tissue;
- slow blood flow in the patient.
These are not contraindications, but in this case changes in the location of the sensors are required. It will be necessary to navigate non-standard conditions, which requires professionalism on the part of the doctor.
In what cases is ultrasound ultrasound prescribed?
The main symptoms signaling a cerebrovascular accident are:
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Deterioration of hearing and memory.
- Frequent attacks of headache.
- Impairment or partial loss of taste.
- Insomnia, difficulty falling asleep.
- Noise, whistling and ringing in the ears.
- Deterioration of visual function, manifested in loss of visual fields.
- Difficulty concentrating.
- Decreased sensitivity and motor activity of the arms and legs.
A doctor may prescribe a procedure in the following cases:
- The patient has diabetes mellitus.
- For arrhythmia, as this increases the risk of cardiac clot rupture and artery blockage.
- The patient has suffered a heart attack or stroke.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
- Before planned heart surgery.
- If the patient is a smoker with many years of experience.
- An area with strong pulsation is visible on the neck (in this case, an ultrasound of the neck is prescribed).
Based on the above symptoms, the doctor can determine the location and name of the vessel in which the patency is impaired. Several pronounced symptoms indicate poor blood flow in a large vessel. In this case, extracranial Doppler ultrasound is prescribed. Violation of only one function will be the reason for conducting transcranial Doppler ultrasound.
Features of ultrasound examination
As a rule, Doppler sonography is planned in advance, but it can be performed urgently. The procedure itself is painless, so patients tolerate it calmly.
The examination is carried out according to the following scheme:
- The patient lies on his back. The head should be relaxed (a flat pillow is placed under it).
- You need to remain calm, breathe evenly and, if possible, not move.
- A special gel is applied to the area under study to prevent the penetration of air between the skin and the sensor.
- The movement of the sensors is controlled by a specialist. As a result, an image of the vessels appears on the monitor screen.
The study lasts no more than 1 hour. During the study, the doctor may ask the patient to do some action: turn his head, squeeze a vein in a certain place, breathe less often, etc.
Dopplerography of extracranial vessels begins with examination of the right lower segment of the carotid artery. The sensor is then moved up the neck. Next, the color mode is activated, which makes it possible to identify a number of pathologies: deformations of the walls of blood vessels, impaired blood flow in certain areas, etc.
USDG BCA
Hello. The neurologist prescribed an ultrasound examination of the BCA. What is this procedure, how is it carried out and is special preparation required? Olga M.
Answered by Nadezhda Ivanovna, ultrasound diagnostics doctor at the MedMix Plus clinic.
Doppler ultrasound of the BCA is an ultrasound examination of the brachiocephalic vessels, that is, in other words, ultrasound of the vessels of the neck. This examination is very important in assessing the condition, anatomy and patency of arteries and veins. Using this ultrasound technology, it is possible to judge the state of the blood supply to the brain, determine the degree of stenosis, thereby enabling the attending physician to determine treatment tactics.
In medical practice, there are several methods for studying the vessels of the neck:
1.USDG (ultrasound Dopplerography ) is a method aimed at assessing the patency of blood vessels and their condition. This method gives a general idea of the vessels. Allows you to identify the internal cause of obstruction, for example, a blood clot or atherosclerotic plaque.
2. Duplex/triplex scanning , which is used by ultrasound diagnostic doctors at our MedMix Plus clinic. On the monitor screen, a specialist sees a vessel in color against a gray background and evaluates its blood flow. This method allows you to assess the cause of the disturbance in the blood supply to the vessels, whether it is external or internal.
Using BCA ultrasound, you can diagnose diseases such as:
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- abnormalities in the structure of blood vessels;
- delamination of the vessel wall;
- arterial aneurysms;
- vasculitis, etc.
Before the symptoms of the disease appear, BCA should be performed when:
- hypertension;
- suffered a stroke;
- lupus;
- diabetes mellitus;
- smoking.
Research is also necessary in the presence of conditions such as:
- dizziness;
- decreased visual function;
- memory impairment;
- headache;
- fainting, etc.
Preparing for the study.
Before performing an ultrasound examination, you need to stop taking foods that can affect vascular tone: tea, coffee, energy drinks, alcohol. You should not visit stuffy or smoky rooms, and you should also stop taking medications that improve memory and attention. It is better to discuss the discontinuation of vascular and cardiac medications with your doctor.
Conducting research.
Doppler ultrasound of the BCA is a standard ultrasound examination procedure. The patient lies on the couch, a cushion is placed under the head. A gel is applied to the neck area, and a specialist conducts a study with a special sensor. The procedure lasts on average 30–35 minutes.
Doppler ultrasound of the brachiocephalic vessels is a painless and accurate ultrasound examination method, which in less than an hour will give an answer about the condition of the neck vessels and the causes of discomfort. Performed routinely, ultrasound of the neck vessels will prevent stroke by 80%. Be healthy!
What can she show?
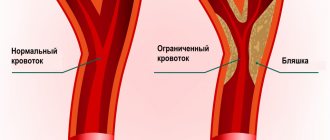
Duplex scanning allows you to determine areas of narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, the direction of blood flow, its speed, as well as the condition of the vascular walls. This study can show the location of cholesterol plaques and the presence of blood clots, which is very important when diagnosing atherosclerosis.
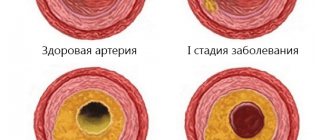
A decrease in the elasticity of the walls of the arteries, as well as their thickening, indicate that the patient has hypertension (high blood pressure). If a change in blood flow is diagnosed, this indicates the presence of obstacles. For example, an aneurysm is a sac-like protrusion of a vessel.
Where can I get Doppler ultrasound of cerebral vessels?
The study is carried out in municipal clinics and public hospitals, specialized clinics, and general medical centers. Depending on the location of the ultrasound, the cost of each type of Doppler ultrasound will be in the range of 500-6000 rubles. The procedure has many advantages, including painlessness and the absence of side effects. Within 20 minutes, a sonologist will be able to determine the presence of anomalies in venous or arterial inflow and assess the degree of development of danger to blood vessels.
However, the procedure will not help determine the cause of compression of the thin arteries, since the capabilities of the device do not allow them to be seen from the outside.
What pathologies can be diagnosed?
Doppler ultrasound has certain limitations in diagnosing diseases. For example, she will not be able to study small veins - for this she needs to perform angiography. But there are a number of pathologies that can be identified:
- Atherosclerosis. By examining the head and neck using ultrasound, it is most often possible to diagnose atherosclerotic disorders. This condition is indicated by echogenicity, the presence of plaques, and thickening of the vascular walls. Moreover, if the lumen of the artery narrows by more than 20%, then the patient is diagnosed with “stenosis.”
- Thrombosis. Thrombosis is characterized by blocking of the arterial lumen by a blood clot. On Doppler ultrasound, inflammation of the vessel wall with a homogeneous formation inside is clearly visible.
- Compression of blood vessels. The examination allows you to see areas where blood flow is impaired due to the impact of swollen tissue on the channels. This allows you to diagnose cervical osteochondrosis and identify problems with blood circulation after injuries.
In addition, these ultrasound examinations can detect a number of other diseases, including vasculitis, post-traumatic dissections of the arterial walls and other pathologies.
Doppler ultrasound is a safe diagnostic method that can be performed in any case if there is a medical need for it. Timely implementation of the procedure allows you to identify the disease at an early stage of its development.
What diseases does it detect?
Doppler ultrasound is a highly informative method used to diagnose various vascular pathologies:
- cerebrovascular accidents;
- phlebeurysm;
- vascular malformations;
- deep vein thrombosis;
- hypoplasia of the vertebral arteries;
- atherosclerosis;
- temporal arteritis;
- postthrombotic syndrome;
- vasculitis;
- aneurysms and other vascular pathologies.
The examination allows you to identify the presence of formations that impede or change blood flow (sclerotic plaques, blood clots), check the homogeneity and rhythm of blood flow, assess the compensatory capabilities of blood flow, identify defects in the structure and flow of blood vessels - narrowing, kinks, tortuosity, aneurysms, compression by scars, vertebrae or spasmodic muscles.
Indications
Ultrasound scanning of blood vessels helps diagnose many brain pathologies.
This technique allows you to study the state of the vascular system in dynamics. Thanks to Doppler ultrasound, it is possible to detect a narrowing of the lumen, a decrease in venous tone, a change in the speed of blood flow, and atherosclerotic lesions. Doppler ultrasound is effective in the following indications:
- dizziness;
- pain in the head area;
- fainting;
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- the occurrence of cramps in the calf area;
- overweight;
- the appearance of fatigue;
- hypertension.
It is worth noting that ultrasound cannot be a substitute for angiography. The latter technique is a popular hardware method. It involves x-ray examination of blood vessels, which is used in radiography, fluoroscopy, and computed tomography.
General characteristics of the examination
To explain what kind of examination this is – Doppler ultrasound – and how it is done, you need to start by deciphering the abbreviation: Doppler ultrasound (you can also hear the name “duplex scanning”). In more detail, Doppler ultrasound is a combined study that combines standard ultrasound and the Doppler effect. Ultrasound allows you to visualize a patient’s specific organ on the screen, determine its size, structure, assess its integrity, and so on. Doppler allows you to assess the condition of the vessels of the examined organs, as well as the quality of blood flow in them.
An ultrasound examination, as practice shows, is informative for both assessing venous and arterial circulation. This procedure is safe, painless, non-invasive.
Preparing for the examination
It doesn’t matter where you decide to undergo an ultrasound examination of the neck vessels, the preparation process is very simple and requires minimal effort from the patient. One of the main conditions for those who take cardiac medications is to notify the doctor about this before diagnosis. He will tell you what to do in this situation. In some cases, patients may have to temporarily delay taking certain medications because it may negatively affect test results. Directly on the day when ultrasound examination of blood vessels is scheduled, smoking, drinking alcohol and drinking black tea and coffee are prohibited.
Before the scan, the patient should remove all jewelry and outer clothing to expose the neck area and the top of the collarbone.
What is the difference between ultrasound and angiography?
Angiography involves studying the corresponding vessels using a contrast agent. Analyze the condition of lymphatic vessels, veins and arteries. During the procedure, modern contrast medications are used, which extremely rarely cause complications.
The following indications are distinguished:
- atherosclerosis;
- aneurysms;
- malformation;
- thrombosis;
- presence of tumors.
Unlike ultrasound, angiography involves a wider list of contraindications. The diagnostic procedure is not performed in case of an allergic reaction to iodine-containing medications.
Angiography is contraindicated in the presence of an acute inflammatory process in the body, cardiac pathologies, severe liver and kidney diseases. Such diagnostics are not performed for thrombophlebitis.
What does triplex ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck show?
Triplex scanning of the vessels of the head and neck allows the doctor to:
— assess the anatomical location of the vessels and their patency;
— determine the presence of stenoses (narrowings), kinks of blood vessels and their significance;
— identify atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots, vascular development abnormalities and their significance;
— assess the condition of the vertebral arteries;
- assess the state of venous blood flow in the vessels of the neck;
— find out the causes of headaches (increased intracranial pressure, vasospasm);
— diagnose the presence of cerebral aneurysms;
— quantitatively assess blood flow in the arteries of the head and neck, calculate total cerebral blood flow;
- see in color areas of vessel narrowing, turbulence in blood flow, areas of lack of blood flow