This information explains how a lumbar puncture procedure is performed at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK).
A lumbar puncture is a procedure performed to obtain a sample of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Cerebrospinal fluid surrounds your brain and spinal cord. Lumbar puncture (LP) is also called a lumbar puncture.
Your healthcare provider may need to take a sample of your cerebrospinal fluid to check for the following:
- development of infection, such as meningitis;
- bleeding;
- spread of cancer to tissues surrounding the brain or spinal cord.
A healthcare professional may also perform a lumbar puncture to administer certain types of medications directly into the area around the spinal cord. These may be the following medications:
- anesthesia (medicine that blocks pain);
- anti-cancer drugs (such as chemotherapy drugs);
- antibiotics.
to come back to the beginning
Indications and contraindications for lumbar puncture
The procedure in question may be performed to diagnose or treat certain diseases. If you need to obtain accurate diagnostic data, then a lumbar puncture is prescribed if necessary:
- identify or exclude the presence of an infectious agent in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF);
- clarify the indicators of liquor pressure;
- identify the patency of the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord.
In the case of therapeutic measures, a puncture may be necessary to introduce antibacterial agents into the cerebrospinal fluid and get rid of excess cerebrospinal fluid. Indications and contraindications for lumbar puncture are divided into mandatory and conditional. As part of diagnosis and treatment, the procedure is indicated for:
- any infectious diseases of the central nervous system;
- suspected leakage of cerebrospinal fluid;
- malignant tumors localized directly in the structures of the spinal cord;
- hemorrhage into the arachnoid membrane.
Lumbar puncture is also allowed for multiple sclerosis, vascular embolism, systemic diseases, and fever in early childhood. In case of these problems, the appropriateness of the procedure in question is determined by the attending physician.
Cerebrospinal fluid puncture is often performed in premature infants, and this procedure can be decisive in making a diagnosis. Such “complex” newborns may have hydrocephalus without pronounced symptoms, and the diagnostic results from the cerebrospinal fluid will provide answers to doctors’ questions regarding the correct diagnosis.
Contraindications to the procedure in question for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes are:
- cerebral edema, severe and with severe symptoms;
- high intracranial pressure of clarified or unknown etiology;
- diagnosed brain tumors;
- occlusive hydrocephalus;
- problems in the blood coagulation system;
- pregnancy;
- long-term use of anticoagulants.
In some situations, when accurate diagnosis is required, a spinal puncture can be performed despite existing contraindications. For example, the results of a lumbar puncture analysis for meningitis make it possible to determine the type of infectious agent and select effective medications. And if a pathology is diagnosed or suspected in a pregnant woman, then doctors neglect this situation and do everything to save the patient’s life.
What you should pay special attention to
Sometimes, during an IVF cycle, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome may occur, which adversely affects the general condition of the woman. It, like follicle puncture, is also characterized by the presence of pain, and its appearance may coincide in time with the egg retrieval procedure. However, this syndrome also has distinctive features. So, the accompanying symptoms are:
- increased body temperature above 38°C;
- intense abdominal pain, which only slightly subsides after taking painkillers;
- nausea and vomiting;
- difficulty urinating;
- the appearance of repeated loose stools;
- bloating;
- increase in abdominal circumference.
In severe cases, overstimulated ovaries lead to ascites. This is an accumulation of fluid filtered from plasma in the abdominal cavity. As a result, the volume of circulating blood decreases, therefore blood pressure drops and overall well-being suffers greatly.
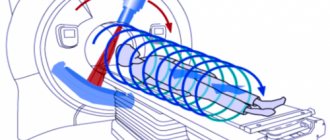
How is a lumbar puncture performed?
Since the procedure in question is quite complex, it is carried out by an experienced doctor and only after preliminary preparation of the patient. Algorithm for preparing for a spinal puncture:
- the skin in the area of the future puncture and insertion of a special needle is treated with medical alcohol and lubricated with iodine;
- then novocaine or lidocaine (painkillers) is injected subcutaneously;
- immediately after the formation of the so-called lemon peel, the administration of these drugs continues intradermally and further into the future puncture.
Many patients wonder whether it hurts to do a spinal tap. Unpleasant (but not painful) sensations are possible only during the period of preparation for the procedure, when the doctor administers painkillers.
After preparation, the procedure itself begins:
- The puncture is made between the spinous processes between the 3rd and 4th vertebrae (in childhood patients - between 4th and 5th). Some patients are terrified of a lumbar puncture because they believe that there is a possibility of spinal cord damage. But the puncture is made where there is simply none! The spinal cord ends between vertebrae 1 and 2, so there is no such threat to health.
- The doctor inserts a special needle with a device that closes its lumen (mandrin) at a slight angle. As soon as the needle enters the subarachnoid space, the specialist feels a certain “failure”. After this, you can remove the mandrin - cerebrospinal fluid will begin to come out of the needle.
- If cerebrospinal fluid does not drain, the patient may be asked to elevate their upper body to increase pressure. If the procedure in question was performed frequently, then the doctor may try to collect cerebrospinal fluid for examination a little higher than the specified location - adhesions may prevent a quick and successful puncture.
- If it is necessary to measure the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid, a special tube is attached to the needle. But an experienced doctor will make such measurements without additional instruments - the output of cerebrospinal fluid at a rate of 60 drops per minute will indicate the norm. But it must be taken into account that the rate of spinal puncture in newborns when measuring pressure will be slightly higher.
Treatment in
The Family Planning Center “For Birth” uses modern methods of assisted reproduction, which are carried out in accordance with international protocols based on evidence-based medicine. Our reproductive doctors, gynecologists and other specialists regularly improve their skills at the best clinics in the field of human reproduction. Modern equipment has been installed, with which you can trace all changes in the endometrium down to the smallest detail. These circumstances are the key to the high effectiveness of the treatment methods used.
Reproductive doctors will help you become parents without risking your health!
Complications and consequences of lumbar puncture
In the first 2-3 hours after the procedure, the patient should be in a horizontal position; some discomfort is possible - for example, a headache after a lumbar puncture, which quickly disappears and does not require the use of painkillers. You should not lift weights or walk a lot in the first 3-4 days.
Possible complications and consequences of lumbar puncture:
- irritation of the meninges;
- persistent pain in the puncture area;
- disc damage and hernia formation;
- bleeding;
- infection of the central nervous system.
More detailed information about the rules of the procedure and the cost of a needle for lumbar puncture can be obtained on the pages of our website Dobrobut.com.
Cost of the procedure
Prices for spinal puncture depend on the level of the clinic, the complexity and nature of the procedure.
In Moscow, the cost of lumbar puncture differs depending on the medical institution:
- Clinic "El. En." — 5400 rubles.
- "PENTA-CLINIC" - 3350 rubles.
- Medical - 2300 rubles.
- Central Clinical Hospital No. 2 of JSC Russian Railways - 1,700 rubles.
- Clinical Hospital No. 119 – 1500 rubles.
- Children's Clinical Hospital named after Semashko - 1450 rubles.
The higher the qualifications of the doctors, the better the equipment of the medical facility and the more complex the procedure, the more you will have to pay for it.
Bone marrow analysis / Bone marrow biopsy
Bone marrow analysis - the collection of bone marrow using a trephine biopsy from the ilium or sternum. Red bone marrow is located in flat bones. The function of bone marrow is the production of new blood cells: red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets. Trepanobiopsy is the procedure for obtaining bone marrow for laboratory testing. The main indications for trepanobiopsy and bone marrow examination are diseases of the blood system and suspicions of them.
Read more about diagnostic studies of the bone marrow and blood system below.
A bone marrow test can be performed on an outpatient basis or in a hospital setting. When the bone marrow analysis is ready, you and your doctor will receive a myelogram - a table with the qualitative and quantitative composition of bone marrow cells. The result of the study allows us to track the process of formation of new blood cells and its disturbances.
What can be checked with trepanobiopsy? Bone marrow analysis is a specialized test used in hematology, oncology and immunology. for diagnosing the causes of anemia and blood cancer (leukemia, etc.). To assess the condition of the bone marrow, the number of cells in it is determined: myelokaryocytes, megakaryocytes, and the percentage of bone marrow elements is calculated. The result of the bone marrow analysis is compared with the results of the general blood test. This study is prescribed and performed only by a doctor strictly for medical reasons.
Possible abnormalities in bone marrow analysis. A decrease in the number of myelokaryocytes is possible with hypoplastic anemia (severe depression or inadequate functioning of the bone marrow), when the human body is exposed to ionizing radiation (radiation) and certain medications (some antibiotics, gold preparations). A large number of myelokaryocytes is most characteristic of leukemia, B12 deficiency anemia, and a condition after large blood loss. A decrease in the content of megakaryocytes and megakaryoblasts is caused by autoimmune processes (systemic lupus erythematosus), leukemia, and radiation sickness. An increase in the number of megakaryocytes and megakaryoblasts usually indicates the presence of myeloproliferative processes and metastases to the bone marrow (for example, in gastric cancer).
Preparation for performing bone marrow trepanobiopsy. We recommend that you refrain from eating 12 hours before the test.
Main indications for bone marrow trepanobiopsy:
- Leukemia and suspicion of it
- Leukopenia (decrease in the number of white blood cells in the blood)
- Lymphogranulomatosis and suspicion of it
- Anemia – decrease in hemoglobin and number of red blood cells in the blood
- Gaucher disease
- Tumor metastases
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of therapy
When to see a doctor
The follicle puncture procedure is rarely accompanied by complications. Therefore, mild pain in the lower abdomen is not regarded as a dangerous condition. However, there are a number of symptoms that should alert you. These include:
- Profuse bleeding from the genital tract, which may indicate serious vascular injury.
- Discharge from the genital tract with an unpleasant odor. This symptom may indicate an infection.
- Increasing abdominal pain that progresses over several hours. May be a sign of intra-abdominal bleeding. The likelihood of this complication is especially high if the pain is combined with dizziness, low blood pressure, pale skin and/or loss of consciousness.
- Pain in the lower abdomen, nausea and vomiting, flatulence, decreased blood pressure. Such signs may indicate the development of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (several follicles simultaneously mature in the gonads, reaching large sizes).
In all these cases, you should immediately contact the clinic where the IVF protocol is performed. The woman needs dynamic monitoring and medical care. In most cases, conservative treatment is sufficient.