Gender and age
Multiple sclerosis can be diagnosed at almost any age. However, in most cases the disease begins to develop between the ages of 20 and 40. Most often, multiple sclerosis occurs in women of childbearing age (the disease rarely begins before puberty or during menopause). In men, the first symptoms appear between the ages of 15 and 40, and the disease, as a rule, has a more severe form and is less responsive to treatment. About a quarter of patients are men. Most likely, this dependence is influenced by the characteristics of the hormonal system in men and women.
Treatment methods
The main goal of therapy for multiple sclerosis is to prevent further development of the disease, prevent exacerbations and relieve symptoms.
Therapeutic measures involve the use of medications. To combat the consequences, hormonal agents, cytostatics and plasmapheresis are prescribed.
Immunomodulators, beta-interferon, Glatiramer acetate, Natalizumab and some other medications help to exclude the progression of pathology. They are aimed at reducing the risk of relapse, preventing disability and suppressing further spread of plaques.
Various pharmacological groups are used as symptomatic therapy to normalize the functioning of organs and systems, relieve pain, improve motor activity, memory and attention.
If treatment for multiple sclerosis is started in a timely manner, then severe complications can be avoided and the duration of remission can be maximized.
Hereditary factor
MS cannot be called a hereditary disease, but there is a theory according to which genes also play a role in the development of MS. To date, about 20 genes have been identified that determine the structural features of nervous tissue and may be important in the development of MS. This is confirmed by statistics: up to 20% of patients with multiple sclerosis have relatives with multiple sclerosis. However, even in the case of an existing predisposition, multiple sclerosis may not develop if other predisposing factors do not contribute to this.
Viral infections
The influence of infectious agents is one of the fundamental factors in the development of MS, but until now the exact mechanism of influence has not been studied.
There is no evidence to suggest that MS is a direct consequence of any specific disease. At the same time, there is evidence that some infectious agents can serve as a trigger in the development of multiple sclerosis: retroviruses, measles, herpes, rubella, mumps, Epstein-Barr viruses. There is also evidence of the possible influence of staphylococcal infection [6, 7].
Prevalence rate:
Multiple sclerosis
Vera Vyacheslavovna Pshenichnikova, neurologist, candidate of medical sciences, head of the department of neurologists for patients with stroke, talks about what everyone needs to know in order not to miss the first signs of this serious disease.
Multiple sclerosis - what kind of disease?
This is a neurological disease, which is based on an inflammatory process in the central nervous system - in the brain and spinal cord. Most nerve fibers are covered with a sheath - a special substance called myelin. In multiple sclerosis (MS), myelin is destroyed, followed by the formation of connective tissue (hence “sclerosis”). And the term “scattered” means the extent of the lesion.
Inflammation occurs in different parts of the brain at different times and causes a variety of symptoms. At the onset of the disease, sensory disorders and a feeling of weakness may occur. Patients are sometimes observed for several years with diagnoses of osteochondrosis, vegetative dystonia syndrome, and asthenic-depressive syndrome. Subsequently, most patients develop a symptom complex that includes: impaired vision and eye movement; paresthesia, impaired coordination of movements, functions of the genitourinary organs and intestines, more about this below.
What are the reasons for the development of the disease? What are the risk factors?
The cause of the disease is still unknown to us, but the central link is dysregulation in the immune system. The immune system, through a tragic mistake, acting against its own body (autoimmune process) destroys the myelin sheath of nerve fibers in the brain and spinal cord. As a result, various body systems stop receiving signals from the brain and symptoms of the disease appear. There are many reasons that negatively affect the immune system. Therefore, MS is called a multifactorial disease.
Geoepidemiological factors determine the high prevalence of MS among people from Northern Europe; There is a latitude gradient - in zones with higher latitudes (distant from the equator) the incidence is higher. Interestingly, Asians practically do not get MS. Quite popular, especially among American scientists, is the version associated with a violation of the intestinal microbiota. There is a proven connection between vitamin D levels and the prevalence of MS. It is assumed that women who have a significant deficiency of this vitamin during pregnancy have a significantly higher risk of giving birth to a child who subsequently develops MS. Also, in people infected with the Epstein-Barr virus and who have had infectious mononucleosis, the risk of developing MS doubles. Oddly enough, smoking is a risk factor for MS. The incidence of this disease among smokers is higher than among those who have never smoked. But perhaps smoking is a marker of a certain psychotype, and not the cause of the disease.
MS is a disease of the young, although in the last ten years the boundaries have been shifting towards both childhood and the elderly. The peak incidence occurs during the most active period of a person’s life—20–40 years. Typically, the later MS begins, the more severe it is. Women get sick about three times more often than men. The disease is extremely rarely inherited, since MS is not believed to be associated with any specific gene.
When should you be wary?
Exactly how MS manifests depends on the location and extent of damage to the nerve fibers. Symptoms of MS are nonspecific and can lie in the area of neurology, ophthalmology, vertebrology and psychiatry. The disease can be suspected by a combination of the following symptoms:
- Visual disturbances (blurred vision, changes in color perception, double vision) most often occur in one eye, but can affect both eyes.
- Increased fatigue, tiredness. These are one of the most common manifestations of multiple sclerosis, which can occur against the background of physical activity, or can be felt constantly, making it difficult to perform even the lightest work.
- Changes in sensitivity: numbness, burning, tingling, itching, changes in temperature sensitivity in different parts of the body. A variation of this type of disorder is Lhermitte’s syndrome, a sensation of “electric current” passing when the head is tilted.
- Pain in the eye when moving the eyeball.
- Muscle weakness, increased muscle tone of the limbs (increased muscle tension).
- Impaired coordination of movements, expressed in loss of balance, instability when walking, trembling of the limbs.
- Bladder problems: frequent urge to urinate, urinary incontinence, or urinary retention.
- Bowel problems - constipation or fecal incontinence.
- Sexual problems
How not to miss a disease?
It is quite difficult to diagnose the disease in time. First, the symptoms are usually mild and go away quickly. And in our busy life there is no time to do things that do not limit us. And even if the patient reaches the doctor, he receives a diagnosis of depression, asthenia, osteochondrosis. Although in a number of cases, patients themselves ignore the first symptoms: they do not notice that they cannot walk normally, that “the legs become heavy,” “the vision blurs.” We need to listen to ourselves.
SO: if these symptoms appear periodically and spontaneously stop, if they are provoked by physical or emotional stress, occur in a hot climate or after taking a hot bath, you must consult a neurologist and undergo a full neurological examination.
Are there any difficulties in diagnosing the disease?
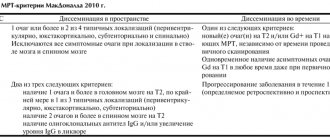
MS is a chameleon disease. It is easy to diagnose when there are visual impairments or movement disorders. But in most cases, diagnosis takes many years. Patients are referred to a specialist after a dozen transient exacerbations and are observed for years by psychiatrists and psychotherapists until the disease progresses to obvious symptoms. Neurological symptoms caused by inflammation and demyelination in the central nervous system, in combination with MRI findings at different periods of time, to the exclusion of all other possible diagnoses, lead to a diagnosis of definite multiple sclerosis. It should be noted that in recent years, due to the availability of MRI, the diagnosis is made earlier.
Where to go for help?
In Moscow, routing is as follows. The patient consults a neurologist and receives a referral to the Interdistrict Multiple Sclerosis Department (IDMS). There are five such branches, each assigned to several districts of Moscow. To speed up the time of getting to a specialist to confirm the diagnosis, it is advisable to do an MRI of the brain and cervical spinal cord in advance.
What treatment approaches are there? What are the forecasts?
Treatment is divided into three main blocks: treatment of exacerbations, treatment that inhibits or changes the course of MS, as well as symptomatic treatment (pelvic dysfunction, spasticity, etc.). In case of exacerbation, immunoglobulin, hormonal drugs, and plasmapheresis sessions are used. Multiple Sclerosis Modifying Drugs (MSMDs) are specific, expensive treatments that are prescribed only at MSDS at the site of attachment. The prognosis of the disease depends on the duration and form of the disease, the response to the treatment, and, of course, adherence to the correct lifestyle (you should avoid prolonged exposure to the sun, visit the bathhouse, sauna). Most people with MS can live a full life with timely and appropriate treatment.
Where do you live?
People living further from the equator are more susceptible to multiple sclerosis.
The culprit is probably vitamin D. Or rather, a lack of it. The body produces vitamin D in response to sunlight. People living in northern latitudes lack sunlight, especially during the winter months. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with many diseases, including multiple sclerosis. However, multiple sclerosis also occurs in southern countries, albeit less frequently. This may be influenced by migration factors.
Smoking
It's no secret that smoking is a bad habit. But few people know that smoking is an established factor in the development of multiple sclerosis. More often the disease is diagnosed in smokers. In addition, the harm from tobacco smoke directly affects the progression of the disease. The reason is that smoking reduces the immune response of T and B lymphocytes, and, as a result, plays an important role in the development of inflammatory diseases. It is no secret that smoking is a bad habit. But few people know that smoking is an established factor in the development of multiple sclerosis. More often the disease is diagnosed in smokers. In addition, the harm from tobacco smoke directly affects the progression of the disease. The reason is that smoking reduces the immune response of T and B lymphocytes and, as a consequence, plays an important role in the development of inflammatory reactions [10, 11].
Psycho-emotional stress and stress
Researchers do not dispute the influence of traumatic situations on the onset of the disease. According to statistics, patients with multiple sclerosis have high rates of anxiety and stress [12].
The psycho-emotional state can affect the physiological parameters of the body. When a person experiences severe stress or is depressed for long enough, the body's immune defenses decrease. Chronic stress, like acute psychological trauma, contributes to the production of a whole complex of neuropeptides - special substances that can significantly disrupt biochemical processes in the body, as well as suppress the activity of cells of the immune system and lead to a state of immunodeficiency. In turn, lymphocytes (immune cells), as the main link in the development of multiple sclerosis, manifest their activity against the background of reduced immunity, stimulating the development of the demyelinating process [12].
Diagnostics
As a result of the constant alternation of exacerbations and remissions, the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis can be difficult and take a long time. To confirm the disease, a set of studies is used, which helps to assess the state of the nervous system and the nature of the spread of the pathological process.
At the first stage, the patient is interviewed, identifying his complaints, general health and the onset of the disease. Additionally, a series of instrumental studies are prescribed to create a clear picture of multiple sclerosis. Among them are used:
- CT and MRI.
- Inspection of potentials.
- Laboratory methods, in particular the study of cerebrospinal fluid and blood.
Based on such data, differential diagnosis is carried out, since the disease, in its symptoms and nature of the course, is similar to many conditions.