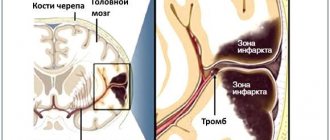
A stroke, formerly called apoplexy or cerebral stroke, is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation. Blood does not enter the brain cells, they stop receiving oxygen and begin to die.
During a stroke, a person's abilities that are controlled by the affected area of the brain, including, for example, memory and muscle control, are lost.
A stroke can happen to anyone, anywhere, at any time, which is why it is important to be educated about the signs of a stroke and know what to do.
Causes of stroke at the age of 25-30 years
- Blood diseases, disturbances in its composition - increased levels of protein in the blood, a tendency to clog capillaries, a large number of microthrombi in the vessel bed.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system - hypertension, pathological vascular diseases of an organic nature.
- Diabetes.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Infectious diseases - meningitis, encephalitis, herpetic lesions and other infections that affect the biochemical composition of the blood.
- Benign and malignant tumors. An enlarged tumor can cause cerebrovascular accidents by mechanically squeezing the walls of blood vessels. A tumor inside the wall of a blood vessel has the same mechanism of action.
- Drug abuse. Some medications, taken independently without the supervision of a doctor, can cause blood and heart diseases, which in turn can lead to a stroke. This same risk group includes women taking contraceptive and hormonal medications.
- Wrong lifestyle. Smoking, alcoholic drinks, sedentary and sedentary lifestyle, constant stress, lack of healthy eating habits.
Precursors of stroke in women
Stroke occurs more often in women than in men.
Signs of an impending stroke in women:
- limbs move worse or do not move, weakness in the arm and leg on one side;
- weakness, drowsiness, increasing headache, which leads to nausea, lethargy;
- decreased sensation in a limb or one side of the body;
- impaired speech perception and ability to speak;
- loss of balance, ability to navigate in space.
Prevention
Regardless of age, it is important to monitor your blood pressure levels. If there are deviations from the norm, you should contact a specialist. The doctor will prescribe the necessary treatment and give recommendations regarding physical activity, nutrition and rest. Sometimes, during an examination, a young person may be diagnosed with atrial fibrillation or irregular heartbeats. This disease leads to blood stagnation, which in turn can result in a stroke. Any problems with blood circulation require consulting a doctor. Only timely assistance will save you from much more serious problems in the future.
Quitting smoking, controlling alcohol consumption, deciding to exercise, a properly selected diet, and autogenic training are the best prevention of ischemic stroke that a young person can do on his own.
Stroke is a real and serious threat to life. Therefore, from a young age it is necessary to pay attention to prevention, and also consult a doctor if warning signs appear.
Life is under attack
L.A. Kalashnikova Doctor of Medical Sciences, State Research Institute of Neurology, Russian Academy of Medical Sciences
Who would argue that a stroke is very serious? Not so long ago, this diagnosis was strongly associated with old age. Today, this disease leads the sad list of “rejuvenated” diseases. The blow is increasingly hitting young and full of energy people. Moreover, he treats them with his characteristic cruelty and deceit. What are the causes of early stroke, is it possible to predict its occurrence and how to protect against it? These questions are answered by a neuropathologist at the Institute of Neurology of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Doctor of Medical Sciences Lyudmila Andreevna Kalashnikova .
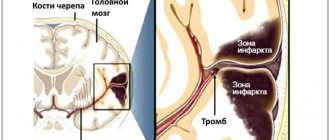
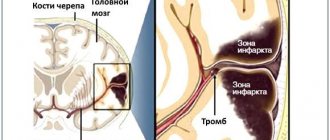
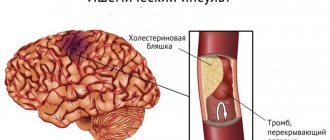
— Lyudmila Andreevna, how does a stroke at a young age differ from a stroke in older people? — There are two types of strokes. The first of them is hemorrhagic, or hemorrhage; as a rule, it develops against the background of high blood pressure due to a rupture of a vessel wall that has lost its elasticity or a congenital anomaly (aneurysm). In this case, the wall of the vessel ruptures and blood flows from its lumen into the brain tissue, which leads to its serious damage. This type of stroke most often develops in middle-aged and elderly people suffering from arterial hypertension. The second type of stroke - ischemic - is associated with deterioration of blood supply to the brain. Its cause may be a blockage of a brain vessel or a narrowing of its lumen, which leads to necrosis (cell death) of a certain area of the brain. Previously, it was believed that ischemic stroke occurs, as a rule, only in older people. Doctors believed that its main cause was atherosclerosis, in which cholesterol plaques developing in the wall of the vessel narrow its lumen and interfere with blood circulation. But in recent years, especially after the introduction of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, it has become obvious that ischemic strokes very often occur in fairly young people. According to the World Health Organization criteria, these are people under 45 years of age. Moreover, the causes of ischemic stroke are completely different.
- And what is this difference? — If in older people, as I already said, the cause of ischemic stroke is atherosclerosis, as well as hypertension, then in young people only 10-20% of all cases are associated with this disease. A stroke in young people causes a violation of the coagulation properties of the blood, increasing its “thickness” and clotting. In this case, blockage of the vessel occurs not due to cholesterol plaques, but due to thrombosis. When small-caliber arteries are affected, this leads to relatively mild strokes, but sometimes to widespread, repeated ones. When large arteries, such as the middle cerebral artery and the internal carotid artery in the neck, become blocked, the consequences can be very serious. The whole world is actively studying coagulation disorders and their treatment today. Moreover, in a number of situations our research is in no way inferior to Western research.
- And what are our discoveries? — As with any other disease, in order to successfully treat the disease it is necessary to understand its causes. Today it has already been proven that one of the most common causes of “thickening” of the blood is problems in the human immune system associated with the production of special antibodies (they are called antibodies to phospholipids) that interfere with the blood coagulation system. Brain thrombosis can develop in a variety of veins and arteries, including brain vessels - it is not known in which place the blood clot will “shoot”. In this case, correct diagnosis is very important. Even before special immunological studies are carried out, it can sometimes be suspected that this is the reason that led to an ischemic stroke. And here it is important to remember that often such strokes are combined with other serious systemic manifestations.
- For example? “For example, today it is known that women are more susceptible to ischemic stroke. In general, they have immune disorders more often. The first manifestation of a hypercoagulable state in women caused by antibodies to phospholipids is usually not thrombosis of the brain, but thrombosis of completely different areas. This may be thrombosis of the placental artery, then the disease begins with miscarriage, spontaneous abortion or intrauterine fetal death. Sometimes, also often during pregnancy, thrombosis of the leg veins can develop. And some time after childbirth, and sometimes right during pregnancy, a stroke occurs.
Since we are talking about women, I would like to say one more very important thing. Sometimes an increase in blood clotting can be caused by taking contraceptives. Moreover, nowadays patients take them not only to prevent pregnancy, but also to treat various hormonal disorders. The hormone estrogen contained in these drugs increases blood clotting, which can provoke thrombosis and cause a stroke.
— Is an immunological problem the only cause of stroke? - Unfortunately no. Very close to this pathology is the so-called Sneddon syndrome - a disease named after the English dermatologist Sneddon, who first described it. It is characterized by the appearance of branched bluish vascular spots (livedo) on the skin, giving it a “marbled” appearance. We believe that its causes are also related to blood clotting disorders, which are a consequence of the production of antibodies to phospholipids. True, not all such patients have these antibodies. Apparently, more subtle research is needed.
To date, our Institute has examined more than a hundred patients with this disease, and we have extensive experience in its treatment. In other countries it is much less. After our foreign publications, the work of Russian scientists became known throughout the world. In addition, there are other bleeding disorders that we are actively studying together with hematologists.
— Diagnosis is diagnostic, but what about treatment? — Treatment is aimed at reducing blood clotting using special medications. If this is not done, these people often develop repeated disorders - which can result in very severe widespread brain damage, which can lead to memory loss, impaired movement, coordination, or repeated strokes, which can be fatal. Today we have patients who have been receiving this treatment for 15-16 years and are in a relatively stable condition. Previously, when we did not know the causes of this disease, most often the ending was death. Therefore, when a young person has a stroke, a detailed examination is necessary. The success of treatment is largely related to the ability to study the properties of blood clotting. Large institutions have them today.
— Are the causes of these immune disorders congenital or acquired? - Acquired. We have long noticed, and many scientific works have been devoted to this, that infection plays a big role in their appearance. As a rule, these are repeated sore throats, pneumonia or frequent bronchitis. But they are only a kind of trigger mechanism when there is an innate predisposition to the development of disorders, a genetic defect of the immune system.
— Could a stroke be associated with trauma? - This also happens. Severe trauma, and in some cases general concussion received from a car accident, fall, etc., can lead to the development of a hematoma in the wall of the vessel. Because of this, the lumen of the vessel supplying the brain narrows, and, as a result, a stroke occurs. The time and rate of stroke development depends on how quickly the hematoma grows. In some cases, its symptoms appear quite quickly, within a few hours after the injury, and in others - after a few days. Over time, a hematoma, like an ordinary bruise, can resolve, and the lumen of the vessel is restored. Then repeated examination of the vessels no longer reveals it. In this case, its timely implementation is very important - in the acute period. Moreover, if earlier it was invasive angiography (with the introduction of a contrast agent into the vessels), now there is magnetic resonance angiography, which is painless and safe for the patient. In addition, there are other lesions of the vascular wall. But these are very rare cases that are of interest mainly to scientists.
— Is there a connection between stroke and heart disease? - Yes. This type of stroke is called cardioembolic. It accounts for about a third of all cases. It can occur with damage to the endocardium, heart valves, or disturbances in its rhythms. As a result, small blood clots form, which travel through the bloodstream to the brain and lead to ischemic stroke. But this all happens again with increased blood clotting.
— Does a stroke often lead to disability? — The causes of ischemic stroke at a young age are very different, and the further condition depends on how large the lesion has formed in the brain. If the stroke is extensive and has led to serious motor and speech disorders, such a person cannot work. If an ischemic stroke is associated with damage to the arteries, then its symptoms come and go. The person restores all his functions and outwardly appears completely healthy, he does not have any visible defect. Here it is very important to identify the existing pathology that led to the stroke and prevent it from developing again. When it comes to changes in blood composition, a person must constantly take anticoagulants and small doses of aspirin (a medicine that reduces blood clotting) - be treated constantly, as for diabetes or hypertension.
— Although a stroke strikes us, as a rule, unexpectedly and not by chance, it is called a stroke, what can be done to prevent it or mitigate the consequences? — Since the overwhelming majority of strokes at a young age are associated with increased blood clotting, factors that aggravate it should be avoided: taking medications containing estrogen (including contraceptives), smoking, large doses of alcohol and fatty foods. Women should also be wary of a disease such as migraine. We have noticed that when they suffer from migraines, they often have a tendency to “thicken” their blood, and taking contraceptives can aggravate this condition. This is most often observed in a special form of migraine, which was previously called associated, and now called migraine with aura. The onset of a headache attack in this case is preceded by a number of neurological symptoms. These are, as a rule, visual disturbances in the form of flickering, luminous stripes. Such a prolonged migraine attack can sometimes be complicated by a so-called migraine infarction.
If there are signs of atherosclerosis at an early age, it is mainly associated with a hereditary predisposition to lipid metabolism disorders, it is also necessary to conduct a timely examination. Diagnosis of atherosclerosis is quite simple - we scan the arteries of the head and identify sclerotic plaques. The diet is selected accordingly. And if necessary, cholesterol-lowering medications are prescribed.
For any neurological disorders, do not hesitate to visit a doctor. You should always pay attention to any weakness in an arm or leg, numbness, or unexpected double vision that is not directly related to injury or visual impairment. You should be alert to unexpected speech disorders when a person cannot formulate a thought, finds it difficult to say something, or begins to poorly understand what is being said. All these symptoms indicate that a certain brain structure is suffering. Even if these symptoms come and go, they must be taken very, very seriously.
If you have experienced a stroke with a good recovery, and you do not have atherosclerosis or hypertension, you should definitely conduct more in-depth research and try to find out its causes. Unfortunately, in city hospitals today there are no such opportunities, since the problem requires good technical equipment, but they are available in specialized institutes.
And finally, no matter how trite it sounds, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle. After all, the risk factors here are exactly the same as for other vascular diseases: unfavorable heredity, a tendency to increase blood pressure, abnormal lipid metabolism - aggravated by frequent stress, poor diet, alcohol abuse and smoking.
The conversation was conducted by Svetlana Troitskaya
© Magazine “Egoist”, 2003, No. 6
The relationship between brain regions and the clinical picture of stroke
If the right lobe is affected, this is expressed by paralysis of the left limbs or loss of sensitivity in them.
The patient has a pronounced depressive state and a decrease in the desire for recovery. If the hippocampus area is affected, then the patient cannot grasp objects with his hand, loses the ability to navigate in space, cannot remember what happened yesterday, but memories of a longer period are preserved.
The hippocampus is responsible for emotions, short-term and long-term, spatial memory necessary for orientation in space.
If the left lobe is affected, then paralysis, decreased or loss of sensitivity in the right half of the body is characteristic, the patient does not perceive speech and speaks inarticulately.
If the cerebellum is affected, there is a lack of coordination, the patient feels nausea and dizziness. When the stem structures are damaged, the patient may experience double vision, the act of swallowing is disrupted, and involuntary movements occur.